Forces on Charged Particles
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
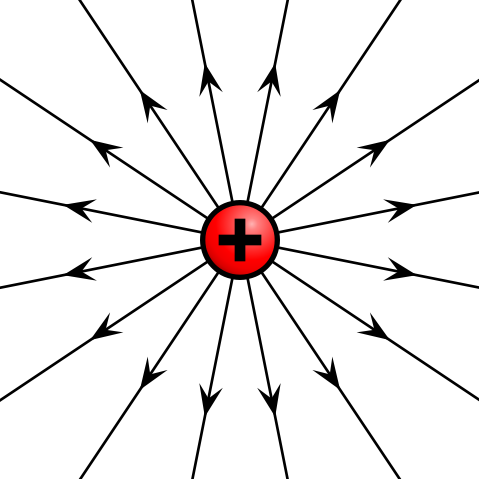
What force does this positive test have?
Outwards
2
New cards
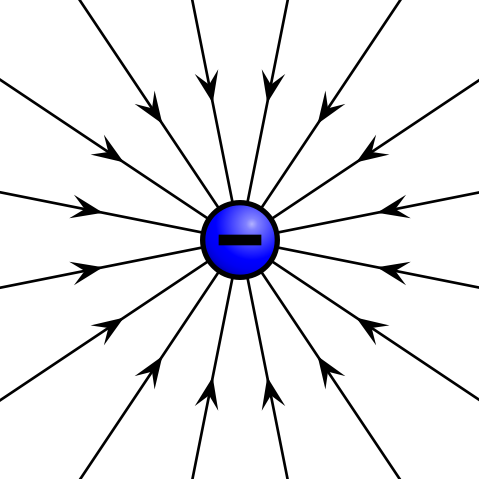
What force does thisn positive test have?
Inwards
3
New cards
What happens to the strength of the fields as we move away from the charge?
Decreases
4
New cards
What do charged particles experience in an electric field?
A force
5
New cards
How can we tell the strength of the force in an electric field?
How close the field lines
6
New cards
Name 3 examples of everyday applications with electric fields?
Photocopying, pollution control, and paint spraying
7
New cards
Where do electric fields exist?
Around charged particles and between charged parallel plates.
8
New cards
What is voltage (potential difference) in terms of work done and charge?
For every 1J of work done in moving 1C of charge between 2 points, the potential difference is 1V
9
New cards
What does a moving charge produce?
Magnetic field
10
New cards
What will the energy appear as, if the charge moves in the direction of the electric force?
Kinetic energy
11
New cards
What will the energy appear as, if a positive charge is moved against the direction of the electric force?
Electric potential energy
12
New cards
What happens when a positive charge is released from a plate?
The electric potential energy converts into kinetic energy
13
New cards
What affects the direction of the magnetic field?
The direction of current flow
14
New cards
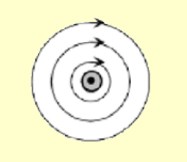
What does this **dot** represent?
Current coming **out** of the page
15
New cards
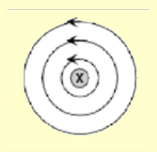
What does this **cross** represent?
Current going into the page
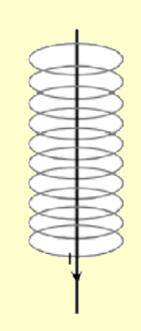
16
New cards
What are particle accelerators designed to do?
Speed up and increase energy of a beam of particles by producing electric fields that accelerate the particles.
17
New cards
What do beams of charged particles experience?
A deflection by both electric and magnetic fields
18
New cards
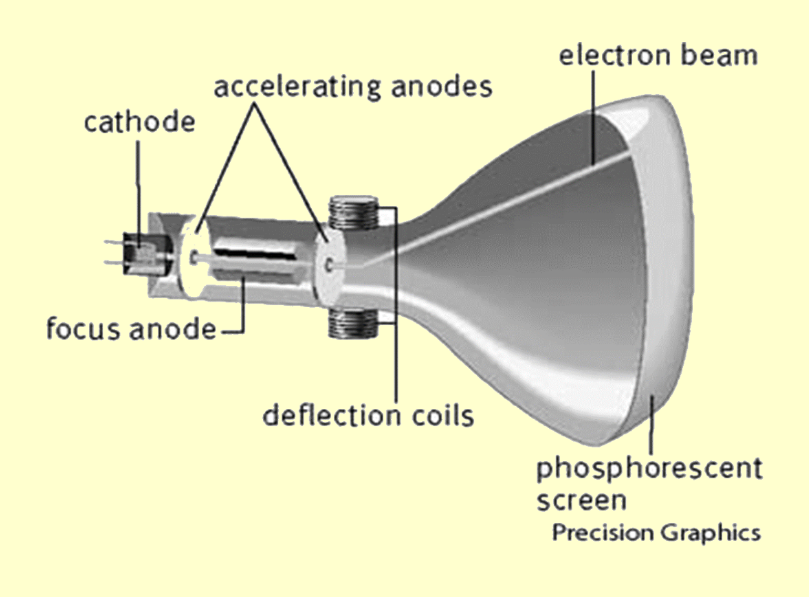
Where does the repelling of elecrtons from the negative electrode occur?
The cathode
19
New cards
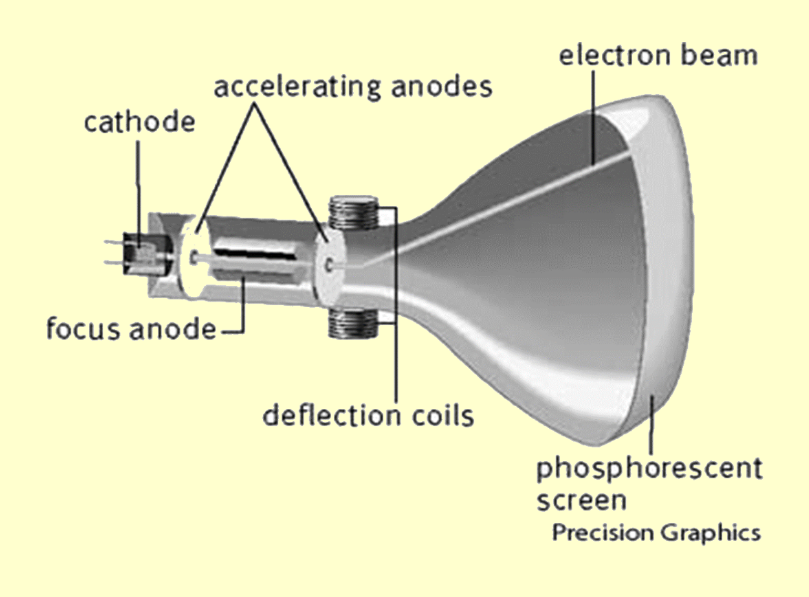
Where does the attractions of elecrtons towards the positive electrode occur?
The anode
20
New cards
Why is the voltage across electrodes usually a few thousand volts?
So it gives the electron enough energy to make a small glow on the fluorescent screen
21
New cards
How do electrons keep moving in a linear accelerator?
They must always move from a negative electrode to a positive electrode
22
New cards
What do the series of elecrtodes do in an linear accelerator?
They keep electrons moving rather than using large voltages
23
New cards
What are the 3 types of particle accelerators?
Linear accelerator, Cyclotron and Synchrotron
24
New cards
Why are alternating supplies sometimes used in a linear accelerator?
So particle always accelerates in the same direction