topic 4 - atomic structure
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
state the size and radius of an atom
very small
with a radius of 1 x 10-10
state the basic structue of an atom
a positively-charged nucleus
composed of both protons and neutrons
surrounded by negatively-charged electrons
state the size of the radius of a nucleus in comparison to the size of the atom
1:10,000
state where most of the mass in an atom is concentrated
nucleus
state how the electrons in an atom are arranged
at different distances from the nucleus
in shells
based on energy levels
with electrons closest to the nucleus having the lowest energy levels
state how the absorption of electromagnetic radiation affects the electronic configuration of electrons in an atom
electrons move further away from the nucleus
electrons gain energy
state how the emission of electromagnetic radiation affects the electronic configuration of electrons in an atom
electrons move closer to the nucleus
electrons lose energy
state the number of electrons in an atom in comparison to the number of protons
number of electrons is equal to the number of protons
state the electrical charge of an atom
atoms have no electrical charge
state whether or not the number of protons changes between atoms of the same element
the number of protons remains the SAME
state what the name for the number of protons in an atom is
atomic number
state what the name for the number of protons and neutrons in an atom is
mass number
state whether or not the number of neutrons changes between atoms of the same element
the number of neutrons can CHANGE
state the name of atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons
isotopes of the same element
state what happens if an atom loses outer electrons
it will become a positive ion (cation)
state what can cause the scientific model to change
new experimental evidence
state what atoms were thought to be before the discovery of electrons
tiny spheres
that cannot be divided
state which model the discovery of the electron created
plum pudding model
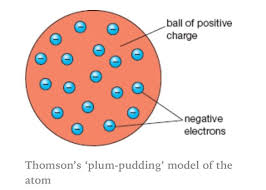
state what the plum pudding model suggested
the atom is a ball
of positive charge
with negative electrons embedded in it
state what the results from the alpha particle scattering experiment led to
the conclusion that the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus
and that the nucleus was charged
explain how Niels Bohr adapted the nuclear model
Bohr suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus
at specific distances
state the name of particles with a positive charge
protons
state what the work of James Chadwick provided
evidence to show the existence of neutrons within the nucleus
state what the scattering experiment was
the scattering experiment was when a beam of alpha particles was directed through a gold foil
carried out by Ernest Rutherford, Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden
explain what the new evidence from the scattering experiment was
when the beam of alpha particles was directed through the gold foil
researchers were expecting the particles to travel through the foil
and the beam to slightly change direction
however they discovered that most of the alpha particles passed through the foil
some of the alpha particles changed direction but continued through the foil
and a few of the alpha particles bounced off the foil
explain why the new evidence from the scattering experiment led to a change in the atomic model
the bouncing back of some of the alpha particles could not be explained by the plum pudding model
so a new model had to be created
explain the differences between the plum pudding model and the nuclear model
the plum pudding model is a positive sphere with negative charges embedded in it
there are no empty spaces
in the nuclear model, there is a central positive nucleus
with mostly empty space
and lots of negative charge varying distance from the nucleus
state what nuclear equations are used to represent
radioactive decay
state the representation of a beta particle in a nuclear equation
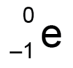
state the representation of an alpha particle in a nuclear equation
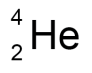
state what an alpha particle consists of
2 protons
2 neutrons
state the charge of an alpha particle
+2
state the charge of a beta particle
-1
state when a beta particle is produced
when a neutron changes into a proton and electron
state what a beta particle is
a fast-moving electron
state how an atom becomes more stable
by giving out radiation
state what the process of atom giving out radiation is
radioactive decay
state what activity is
the rate at which
a source
of unstable nuclei decays
state what activity is measured in
becquerel (Bq)
state what count rate is
the number of decays
recorded each second
by a detector (e.g. Geiger-Muller tube)
state what nuclear radiation may be emitted as
an alpha particle
a beta particle
a gamma ray
a neutron
state how many protons and neutrons an alpha particle is made of
2 protons
2 neutrons
charge on alpha particle
+2
charge on beta particle
-1
charge on gamma particle
0
state when and where a beta particle is ejected
from the nucleus
as a neutron turns into a proton
state what a gamma ray is
electromagnetic radiation
from the nucleus
state whether alpha particles can penetrate through paper
no
state whether beta particles can penetrate through paper
yes
state whether gamma rays can penetrate through paper
yes
state whether alpha particles can penetrate through aluminium
no
state whether beta particles can penetrate through aluminium
stopped by a few mm of aluminium
state whether gamma rays can penetrate through aluminium
yes
state whether alpha particles can penetrate through lead
no
state whether beta particles can penetrate through lead
no
state whether gamma rays can penetrate through lead
no
state the ionising power of alpha particles
high
state ionising power of beta particles
low
state ionising power of gamma rays
very low
state the range of alpha particles in air
3-5cm
state range of beta particles in air
1m
state range of gamma rays in air
1km +
alpha particle symbol

beta particle symbol

what can the emission of radiation cause
change in mass
or change in charge of nucleus
what changes does alpha decay cause
decrease in mass
AND decrease in charge of nucleus
what changes does beta decay cause
no change in mass
charge of nucleus INCREASES
what changes does the emission of gamma rays cause
NOTHING
what is the pattern of radioactive decay
random
definition of half-life radioactive isotope
time it takes
for the number of nuclei of a sample
of radioactive isotopes
to halve
explain how half-life is linked to the random nature of radioactive decay
half life allows us to predict the decay of a sample over time
despite the unpredictability of individual decay events
state how to calculate half life
measure radioactive activity of sample
plot on graph
determine time taken for activity to drop to half (e.g. initial activity = 8, plot at 4 bc. is half of 8)
time taken is the half life
state how to calculate net decline in radioactive emission
(1/2)number of half lives = fraction
convert fraction to ratio (e.g. ¼ = 1:4)
definition of radioactive contamination
unwanted presence of materials
containing radioactive atoms
on other materials
what causes hazard of radioactive contamination
decay of the contaminating atoms
what affects the level of hazard caused by radioactive contamination
type of radiation emitted
definition of irradiation
process of exposing an object to nuclear radiation
does an irradiated object become radioactive?
no
compare hazards of contamination and irradiation
irradiation doesn’t cause the object to become radioactive whereas contamination does
risk depends on type of radiation emitted for both irradiation and contamination
state precaution to prevent irradiation
lead clothing
absorbs most of the radioactive radiation
state precaution to prevent contamination
radiation suit
prevents radioactive atoms from entering a person
effects of radiation on humans
can cause genetic mutations in cells
causing cancer
state who discovered radiation and when
Marie Curie
discovered radium element
in 1898
calling the behaviour of radium radioactivity
explain how Marie Curie’s findings helped protect people
Curie argued that radium could not be used in products until its properties were better understood
causing the 1927 findings that radiation exposure increased the risk of cancer
explain the importance of studies on the effects of radiation on humans being published and shared
so that findings can be checked by peer review
for accuracy
state what sources background radiation is produced from
natural sources
man-made sources
state natural sources of background radiation
rocks - emit radon gas
cosmic rays
food
state man-made sources of background radiation
nuclear weapons/accidents
exposure from medical testing
what is background radiation/radiation dose affected by
occupation
location
state what radiation dose is measured in
Sv (sieverts)
do radioactive isotopes have similar half-life values?
no, there’s a VERY wide range of half-life values
explain why hazards associated with radioactive material differ according to half-life
half life dictates the time scale of the risk
shorter half life isotopes emit intense radiation for a short time
longer half life isotopes emit radiation over an extended period
medical uses of nuclear radiation
exploration of internal organs
control or destruction of unwanted tissue
describe use of nuclear radiation for exploration of internal organs
gamma emitters used as tracers
injecting radioactive material into the body
to track the movement of substances around the body (e.g. blood)
to create an internal image of the body (can detect tumours)
explain why gamma rays are used in the exploration of internal organs
highly penetrating
so rays are able to pass through the body
and be detected outside the body
low ionising power
minimises harm caused to the patient
describe use of nuclear radiation for control and destruction of unwanted tissues in external radiotherapy
uses small gamma rays
directed at cancerous tumours
machine producing gamma rays rotates
to target tumour at different angles
minimising exposure of healthy tissues to gamma ray
minimises damage to healthy cells
explain why gamma rays are used the control and destruction of unwanted tissues
low ionising power
minimises harm caused to the patient
describe use of nuclear radiation for control and destruction of unwanted tissues in internal radiotherapy
small pellets of radioactive material (emitting gamma rays)
are inserted into a tumour
to expose the tumour to radiation directly
definition of nuclear fission
splitting of large, unstable nucleus
into two smaller daughter nuclei
probability of spontaneous fission
rare