IB HL Physics - Thermodynamics Definitions
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Internal Energy
The total energy contained within a system due to the motion of its particles, including kinetic and intermolecular potential energy of the molecules. Unit: Joules.
Heat Transfer
Energy transferred as heat in a system due to a change in temperature. Notated as Q. Unit: Joules.
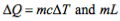
Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of a substance by one degree Kelvin/Celsius. Notated as L. Unit: J kg⁻1 K⁻1.
Specific Latent Heat of Fusion
The energy release when one kilogram of solid goes through a phase change to become liquid. There is no change in temperature during the phase change. Unit: J kg⁻1.
Specific Latent Heat of Vaporization
The energy absorbed when one kilogram of liquid goes through a phase change to become gas. Notated as L. There is no change in temperature during the phase change. Unit: J kg⁻1.
Avogadro’s Constant
The number of particles in one mole of a substance, approximately equal to 6.022 x 10²³. Notated as N_A.
Boltzmann’s Constant
A physical constant that relates the average kinetic energy of particles in a gas with the temperature of the gas, approximately equal to 1.38 x 10⁻²³ JK⁻1. Notated as k_B.
Gas Constant
A constant that appears in the ideal gas law, relating pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles of a gas, approximately equal to 8.31 JK⁻1. Notated as R.