WWI
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
World War I technologies, people, & battles. + a bit about the Russian Revolution
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Total war
channeling of a nation's entire resources in a war effort
conscription
“the draft,” which required all young men to be ready for military or other service
Contraband
during wartime, military supplies and raw materials needed to make military supplies that may legally be confiscated by any belligerent
Lusitania
British liner torpedoed by a German submarine in May 1915
atrocity
horrible act committed against innocent people
fourteen points
list of terms for resolving WW1 and future wars outlined by American President Woodrow Wilson in January 1918
self-determination
right of people to choose their own form of government
armistice
agreement to end fighting in a war
pandemic
spread of a disease across a large area, country, continent, or the entire world
reparation
payment for war damage or damage by the losing side of the war; making amends for a wrong by paying money or helping those that have been wronged
radical
someone who has extreme beliefs
collective security
system in which a group of nations acts as one to preserve the peace of all
mandate
after World War 1, an order administered by a Western powe; an official order or commission to do something
entente
nonbinding agreement to follow common policies
militarism
glorification of the military
Alsace and Lorraine
region of northern Europe on the border between France and Germany which was ceded to Germany after the Franco-Prussian War
ultimatum
final set of demands
mobilize
prepare military forces for war; to make mobile
neutrality
supporting neither side in a war or conflict
Proletariat
working class
soviet
council of workers and soldiers set up by Russian revolutionaries in 1917;
V.I. Lenin
A Russian communist revolutionary who led the Bolsheviks to victory in the Russian October Revolution; served as the premier of the Soviet Union from 1922 until his death in 1924; adapted the ideas of Karl Marx to create a type of communism known as Marxism-Leninism
Marxism
the political and economic theories of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, later developed by their followers to form the basis for the theory and practice of communism
Communism
a political theory derived from Karl Marx, advocating class war and leading to a society in which all property is publicly owned and each person works and is paid according to their abilities and needs
Bolsheviks
a member of the majority faction of the Russian Social Democratic Party, which was renamed the Communist Party after seizing power in the October Revolution of 1917; color was red
Bloody Sunday (Russia)
A group of workers led by the priest Georgy Apollonovich Gapon marched (peacefully) to the winter palace with a petition signed by many people to make demands of their Tsar and request change. They refused to leave until the Tsar received the petition even though he was out of town. Soldiers at the palace then openly fired upon the protesters
Dumas
a series of representative councils formed by Tsar Nicholas II in response to riots after Bloody Sunday; dismissed by him after only 75 days because the Tsar wanted full power and authority
Cheka
Founded by Lenin in 1917; Soviet secret police organization; Used to suppress opposition; Carried out mass executions; Played a key role in Red Terror; Renamed multiple times; like a Russian version of the Secret Service except way more violent
Commissar
communist party official assigned to the army to teach party principles and ensure party loyalty during the Russian Revolution
stalemate
deadlock in which neither side can defeat the other
the Bolshevik revolution
Vladimir Lenin led the Bolshevik party with the goal of Overthrowing the Provisional Government in Russia (the Tsar) to establish a socialist government and end the rule of the bourgeoisie
zeppelin
large gas-filled balloon; not really used anymore because of the Hindenburg disaster
U-Boat
German submarine
Convoy
a group of merchant ships protected by warships
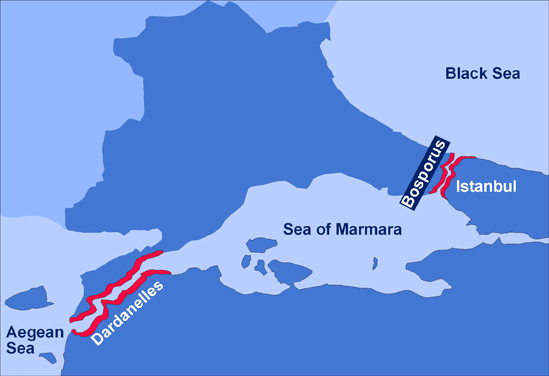
Dardanelles strait
vital strait connecting the black sea in the Mediterranean Sea in present-day Turkey
T.E. Lawrence
Thomas Edward Lawrence (1888-1935), also known as Lawrence of Arabia, was a British archaeologist, writer, and expert on Arabia who helped lead an Arab rebellion and guerilla war against the Ottoman Turks during WW1. In 1926, he published a memoir of his activities in those years, The Seven Pillars of Wisdom.
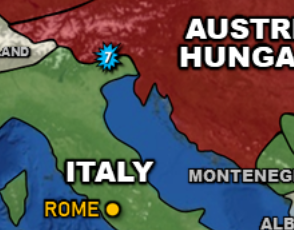
Battle won on October 24, 1917 by Central Powers against Italian forces
Battle of Caporetto
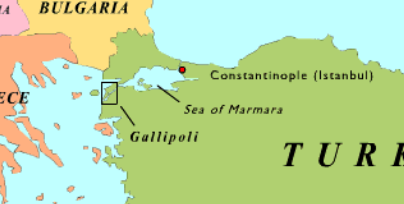
1915-1916 battle on a peninsula in Turkey in which the Allied forces attempted to secure a sea route to Russia and knock the Ottoman Empire out of the war
Battle of Gallipoli
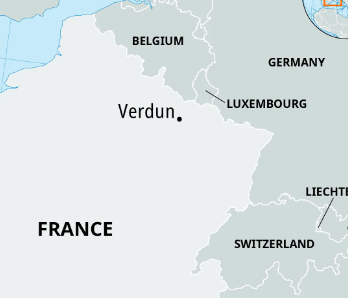
battle in France between Franks and Germans from February to December in 1916; longest battle in WWI; Germans wanted to “bleed France white” and break their morale by capturing a symbolic city; France won
Battle of Verdun
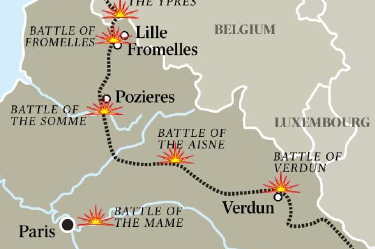
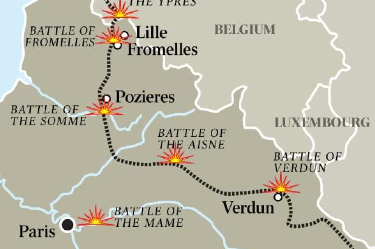
Battle between British and French against Germans; one of the largest battles of WWI; In France; July 1 to November 18, 1916; Allied forces tried to relieve pressure on French forces and break through German lines
Battle of Somme
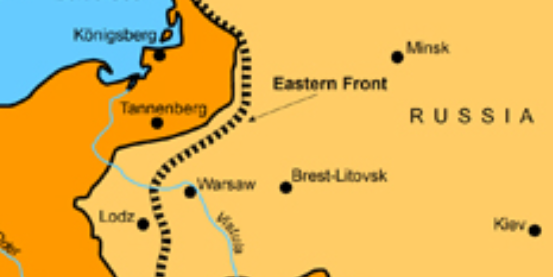
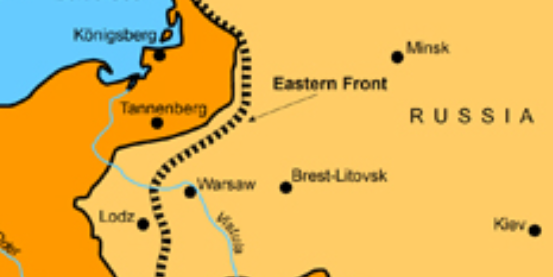
Germans v. Russians in present day Poland from August 26-30, 1914; German forces successfully defeated the Russian army, a significant victory for the Central Powers
Battle of Tannenberg
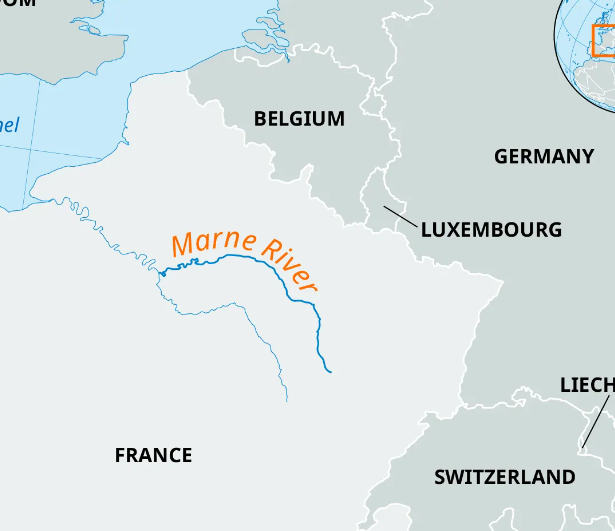
French & British vs. Germans near Paris, France from September 6-12, 1914; allies successfully halted German advance toward Paris, a turning point in the war
Battle of Marne
Alfred Nobel
inventor of dynamite and an explosive device called a blasting cap, which inaugurated the modern use of high explosives
Gavrilo Princip
assassinated archduke Ferdinand
Francis Ferdinand
Archduke of Austria-Hungary who got assassinated
Kaiser Wilhelm II
Last German Emperor and King of Prussia, ruled both the German Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia (not Russia) before abdicating
Colonel T.E. Lawrence (“Lawrence of Arabia”)
Led Arab revolts against Turkish rule in the Arabian Peninsula

Georges Clemenceau
French statesman and dictator; played a key role in negotiating the Treaty of Versailles (1841-1929); Prime minister of France; very anti-German & desired to defeat German army at all costs; known as “The Tiger”

David Lloyd George
He was the British representative at the Paris Peace Conference in 1919; pushed for a revenge-based treaty at Versailles and signed the treaty, hampering the 14 points; Minister for Munitions (ammo.)

Woodrow Wilson
28th president; ‘a dreamer’; known for drafting the 14 points which were ideas for the rebuilding of the postwar world that other countries largely wrote off at the time
Schlieffen Plan
plan devised by Germany to attack France on the Western front before attacking Russia because they thought it would take longer for Russian troops to mobilize; backfired bc Russia mobilized faster than expected and German forces were divided between the Eastern and Western fronts
The fourteen Points
a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end WWI; Issued by Woodrow Wilson, largely ignored by other countries
The Allies
alliance originated from the triple entente; France, the United Kingdom, Russia, the United States, Italy, and Japan; won the war
Central Powers
Stemmed from the triple alliance; Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
a peace treaty signed between the new Bolshevik government of Soviet Russia and the Central Powers that ended Russia’s participation in WWI; signed at Brest-Litovsk after two months of negotiations and was forced on the Bolshevik government by the threat of further advances by German and Austrian forces
League of Nations
An organization of nations formed after World War I to promote cooperation and peace
EXACT start and end dates of WWI
July 28, 1914 - November 11, 11:11:11, 1918 (four years from start to end
Examples of new technology & its impact during WWI
Gas masks, machine guns, barbed wire, zeppelins, tanks, armed airplanes, mines; led to trench warfare and higher death counts; caused mass destruction; the reason that the war was called ‘a new kind of war’
Result of sinking of the Lusitania
May 1915 Lusitania sunk by German U-boats, killing 128 Americans. The Germans had warned the Americans that any ship bearing the flag of Britain or its allies would be sunk, but people assumed that the germans would let citizens on board get into lifeboats before sinking and ignored the warning. The Lusitania took a direct hit from a German U-boat submarine and sank within 20 minutes. This triggered an anti-German sentiment in America, stunning and outraging Americans, though they were not ready for war. President Woodrow Wilson wanted to remain neutral while previous president Theodore Roosevelt wanted retaliation. Germany defended its aggression, claiming that Lusitania had carried supplies for their enemies and was therefore fair game. British propaganda snowballed against the Germans as a result of this, and anti-German riots broke out in London + more people enlisted.
Zimmerman Note
1917 Britian intercepts note from Arthur Zimmerman to ambassador in mexico attempting to convince Mexico to attack the U.S. The obvious threats to the United States contained in the telegram inflamed American public opinion against Germany and was the final straw which convinced U.S. Congress to declare war against Germany
United States involvement in the war
Joined toward the end after we got fed up with Germany destroying ships sailing to Britain and killing the American citizens inside. Sent troops and supplies to the Allies, helped with supply of troops after Russia pulled out of the war
Why the Balkans were called the “powder keg” of Europe
Because of all of the different ethnic conflicts in the region. One little spark leads to huge conflicts
Why the Black Hand wanted to assassinate Archduke Francis Ferdinand
The goal of the Black Hand was to unite all ethnic Serbs under an expanded, greater Serbia. They wanted to assassinate Archduke Francis Ferdinand to liberate Serbia from Austria-Hungarian rule
How nationalism, imperialism, and militarism push Europe toward war (give examples for each term)
Nationalism caused citizens to want their country and its belief to win the war so they joined the army or medical services to help. Imperialism brought the war to parts of Africa and Australia bc of territories owned by the Central Powers and the Allies. Militarism caused other countries to build up their militaries due to fear of other countries’ militaries, leading to war.
Trench warfare and how it caused a stalemate on the Western Front
Trench warfare led to a stalemate in WW1 due to the defensive advantage it provided. Trenches made it difficult for either side to make significant advances, leading to a deadlock. This, combined with heavy artillery and machine gun defense, made line-breaking attacks futile.
How total war affected ordinary citizens
governments rationed food, raised taxes, and ordinary people could get drafted, women began to work in place of the men at war, placed restrictions on places like pubs to prevent people from speaking or rallying against the government, governments were strict about expression of dissent among citizens & limited free speech, motor cars and horses were taken from workers like milkmen to be used in service for the war
Propaganda
All governments controlled public opinion through special censorship boards; Newspapers and journalists simplified and glorified the war/its battles; horror stories were told among children about Germans killing babies and committing other atrocities; Used to control how people thought, what they did, and what they felt that they could do; led to hostility toward foreigners (ex.: British people attacking shops known to be run by Germans); Exaggerated events like the sinking of the Lusitania bc people believed almost anything that they read; Caused a ‘spy mania’ where people were more afraid of spies than they needed to be
Treaty of Versailles
Signed on June 28, 1919 at the palace of Versailles; treaty was one of several that officially ended the five years of conflict that was WWI; outlined the terms of peace between Germany and the Allies, led by the United States, France, and the United Kingdom; “war guilt” clause forced Germany and other Central Powers to take all the blame for WWI; meant that those countries lost territories (in Africa specifically), reduced military forces, and had to pay reparations to the Allied Power; Some historians think that the Treaty of Versailles contributed to German economic and political instability that allowed for the formation of the Nazis a year later; Other historians say that the treaty was actually very restrained because the Allied forces did not occupy the Central Powers after the war; Took Germany several decades to pay off their reparations; Treaty was more lenient than the armistice treaty (Treaty of Brest-Litovsk)
reason that WWI was considered a global conflict since most fighting occurred in Europe
Japan joined the Allies, then China, Brazil, and America joined in response to their citizens and ships falling victim to German U-boat attacks. This tied in Asia, South America, and North America. The fighting countries in Europe had colonies and land in Africa, bringing their conflicts to that continent and causing fighting between African regions belonging to countries on different sides of the war. Colonies like Samoa in Australia were also dragged into the war, meaning that every continent was involved except Antarctica