Medialab Hematology
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Bone marrow beggings producing cells in the ________ month of fetal life
Fourth to fifth (4-5m)
Liver: 1 month
Spleen: 2 month
Which of the following cellular components not develop solely in Bone Marrow
Lymphocytes
Is a myeloid, erythroid and megakaryocyte stages
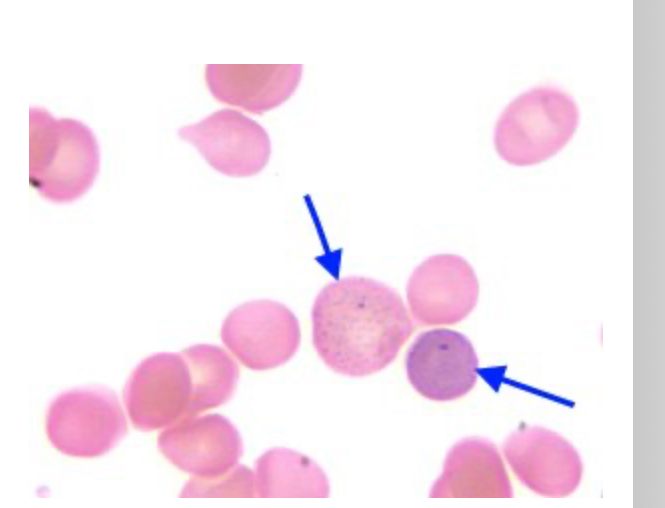
This abnormalities are associated with
Increased red blood cells production
We see: spherocytes and basophilic stippling
All following are granulocytes EXCEPT
Mott cell
Mast cell
Neutrophilic band
Basophil
Almost appear granulated but are containing Russell’s bodies (accumulation of immunoglobulins in the cytoplasm)
Potent platelet inhibitors of platelet aggregation is produced by endothelial cells
Prostacyclin
Prevents formation of platelet plug in primary hemostasis
Platelet function
Clotting
Plug formation
Release serotonin
Repair of injured tissues
Thrombopoiesis, from least mature to most mature
Stem cell
Magakaryoblast
Promegakaryocyte
Megakaryocyte
Thrombocyte
Important proteins regulators of iron metabolism EXCEPT
Hemosiderin
Is an iron-rinch brown pigment NOT protein
Hepcidin, Transferrin receptor, Ferroportin are important proteins
Negative regulator of intestinal iron absorption
Hepcidin
Is the “master iron regulating protein”
In which developmental stage do red blood cells begin forming hemoglobin in amounts large enough to be visualized on a Wright-stained bone marrow aspirate smear?
Polychromatic normoblast
Hemoglobin synthesis is detectable in the basophilic normoblast, but the formation of large amounts of hemoglobin begins in the polychromatic (polychromatophilic) normoblast.
The following polypeptide chains are found in normal adult hemoglobin A:
Alpha y beta
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the bone marrow compartments?
The two main compartments of the bone marrow are the vascular sinuses and hematopoietic cords
Bone marrow biopsy in adults
Iliac crest (posterior)
Bone marrow celullarity formula
100 - age = cellularity of BM
El range es ± 10 de la edad
Effusion fluids are classified as transudates or exudates. According to Light's criteria, all of the following applies to an exudate EXCEPT?
Pleural fluid lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) <2/3 the normal upper limit for serum
To be classified as an exudate, the pleural effusion must meet one of the following criteria:
Pleural fluid/serum LDH > 2/3 the upper limit for serum
Pleural fluid/serum protein ratio >0.5
Pleural fluid/serum LDH ratio >0.6
Serum-ascites albumin gradient (SAGG) <1.1 g/dL
In adults hematopoiesis occurs:
Proximal end of long bones
Most common nucleated cell in Bone Marrow
Metamyelocyte 6-17%
Alder Reilly anomaly
Large, darkly staining cytoplasmic granules composed of partially digested mucopolysaccharides
Phenotypes indicatives of a natural killer (NK)
CD2+, CD3-, CD11b+, CD16+
CD20
B cell marker
CD41, CD42
Megakaryocytic cell markers
The tibia not have active hematopieitic in the bone marrow in ADULTS
Only on children
Mature B cell expression marker
CD19
Life spam of red blood cell
120 days
3-4 months
Blood composed of
45% formed elements
55% plasma
A patient has the following hematology test results. Classify the anemia present by choosing one of the options below.
Hgb = 8.1 g/dL
Hct = 31%
RBC = 4.0 x 1012/L
Microcytic, hypochromic
MCV= 31/ 4.0 × 10=77.5 (microcytic 80-100 normal)
MCH = 8.1/4.0 × 10= 20.25pg (decreased)
The bone marrow in alpha thalassemia usually demostrates
Hyperplasia
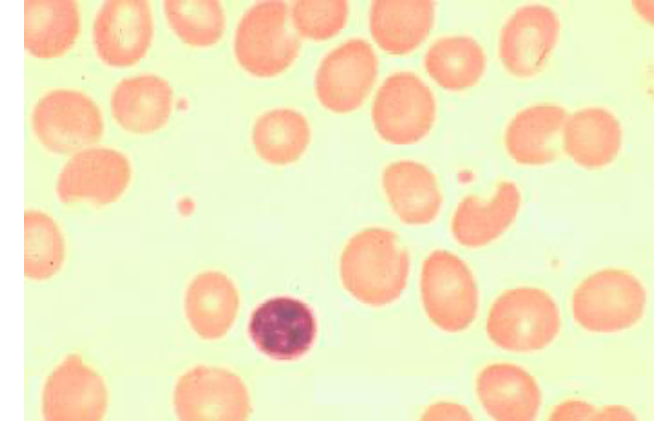
Which MCV confirm this image
110 fL
For which of these conditions or procedures there may be an increased number of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow, but a decreased number of circulating platelets?
Folic acid deficiency
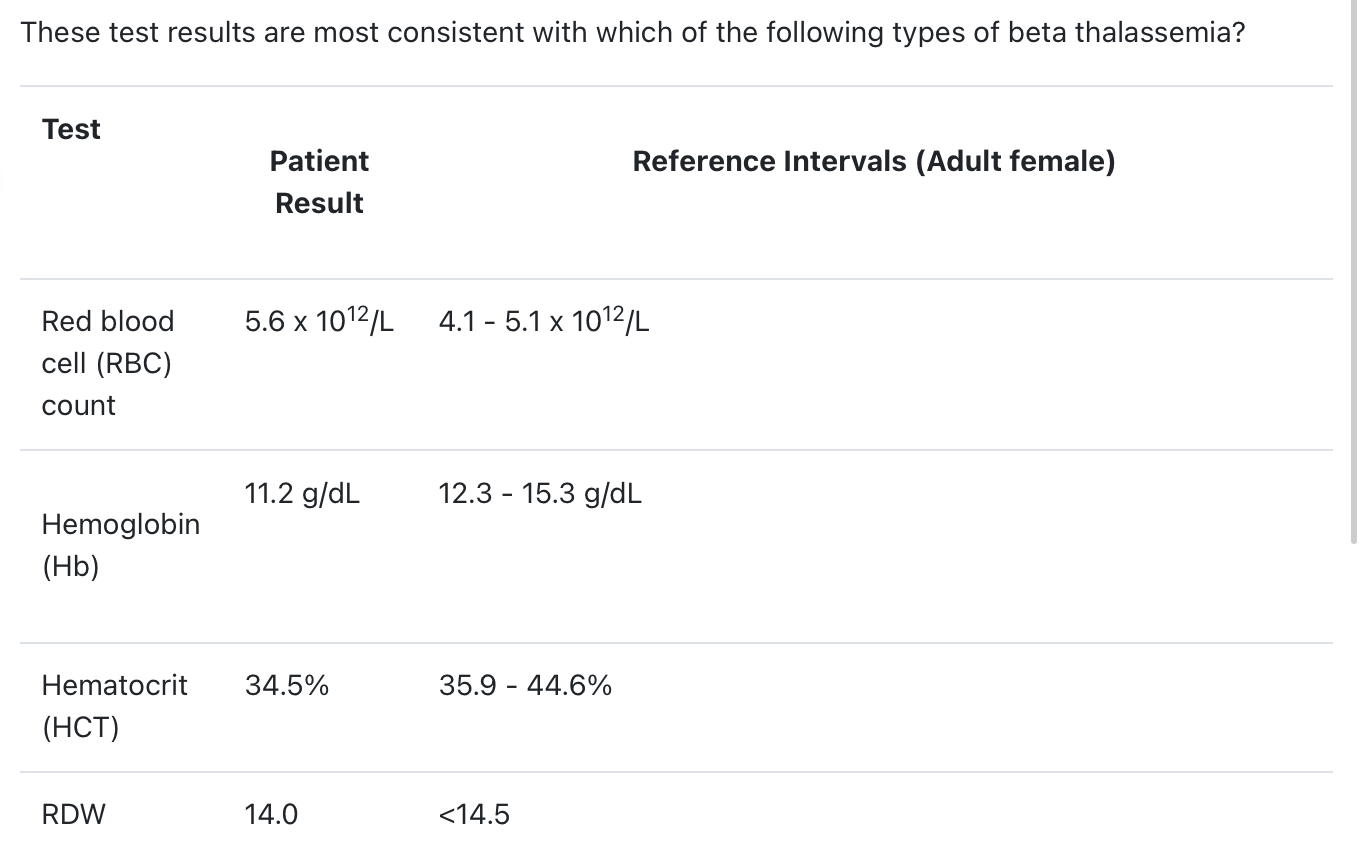
Beta thalassemia minor
Which of the following combination of globin chains comprise Hemoglobin H?
Four beta chains
Beta thalassemia chromosome
11
Alpha thalassemia chromosome
16
Which group of conditions increases the risk of HbS polymerization?
Acid pH
Dehydration
2-3 DPG increased
Which of the following laboratory test results indicates that a sickle cell patient may be in aplastic crisis?
Decreased retic count
A patient is admitted to the emergency room with lethargy and pallor.
The CBC results are as follows:
RBC = 4.1 x 1012/L
Hemoglobin = 7.9 g/dL
Hematocrit = 29%
How would classify this anemia?
Microcytic hypochromic
Calculating MCV, MCH, MCHC
Causes of hemolytic anemia
Plasmodium infection
Thermal injury
Brown recluse spider bite
An alpha thalassemia patient is diagnosed as having three of their four genes deleted which code for alpha hemoglobin chains. Which one of the following types of hemoglobin is abnormal and would be found in such a patient?
HbH
What is a correct characteristic of Alpha Thalassemia?
Decreased or absent alpha chain production results in excess gamma chain production during and shortly after birth, followed by excess beta chains later.
Which hemoglobin increase in delta-beta thalassemia major
HbF 100%
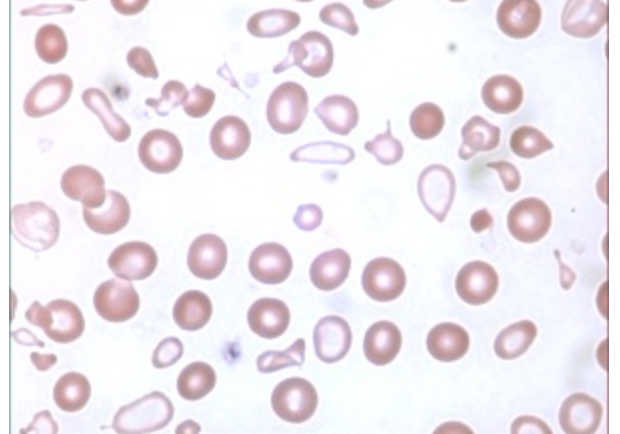
A patient is admitted to the emergency room with severe lethargy, glossitis, and muscle dysfunction. After the physician orders a complete blood count with differential, the hematology technologist observes cells matching the image to the right.
Which condition is most consistent with the clinical and laboratory findings?
Iron deficiency anemia
Anemia of chronic inflammation, also known as anemia of chronic disease, can be caused by all of the following mechanisms EXCEPT:
Decreased ferritin
(Are normal or increased)
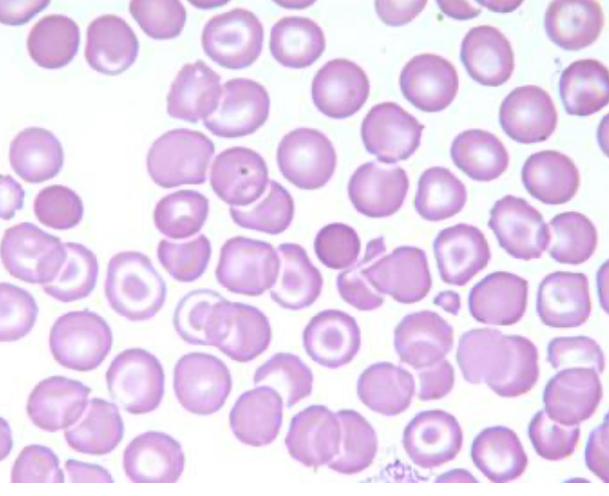
A peripheral smear with red blood cells photographed in a typical field was submitted for review. All of the following conditions are most likely associated with the red blood cell population found here, EXCEPT:
Hereditary Hematomachrosis (HH)
Associated with: Srvere liver disease,Hemoglobinopathy, Beta thalassemia
Which of the following hemoglobins is replaced by hemoglobin H (HbH) after birth in individuals with HbH disease?
Bart’s