unit 3: developmental psychology (gorski)
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
im adding to it okay…
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
chromosomes
made of protein and a single molecule of DNA that serve to carry the genomic information from cell to cell.
DNA
a molecule that contains the genetic code that is unique to every individual; protein containing genetic information
Genes
a segment of DNA that contains instructions for making proteins or other molecules in the body
nature
biological factors that influence a person's development and personality
nurture
environmental factors that influence a person's development and personality
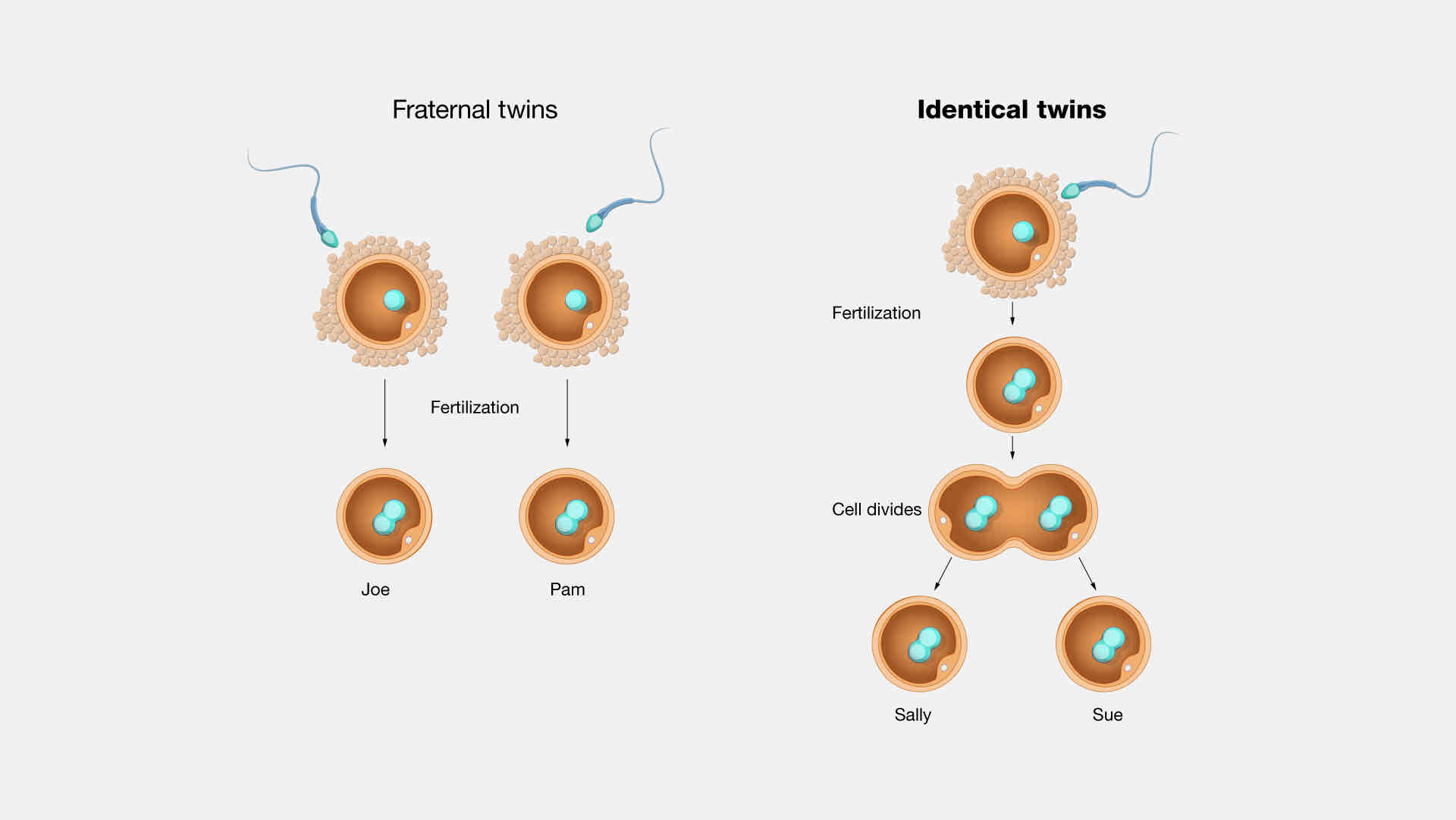
fraternal twins
twins that develop from two separate eggs fertilized by two different sperm
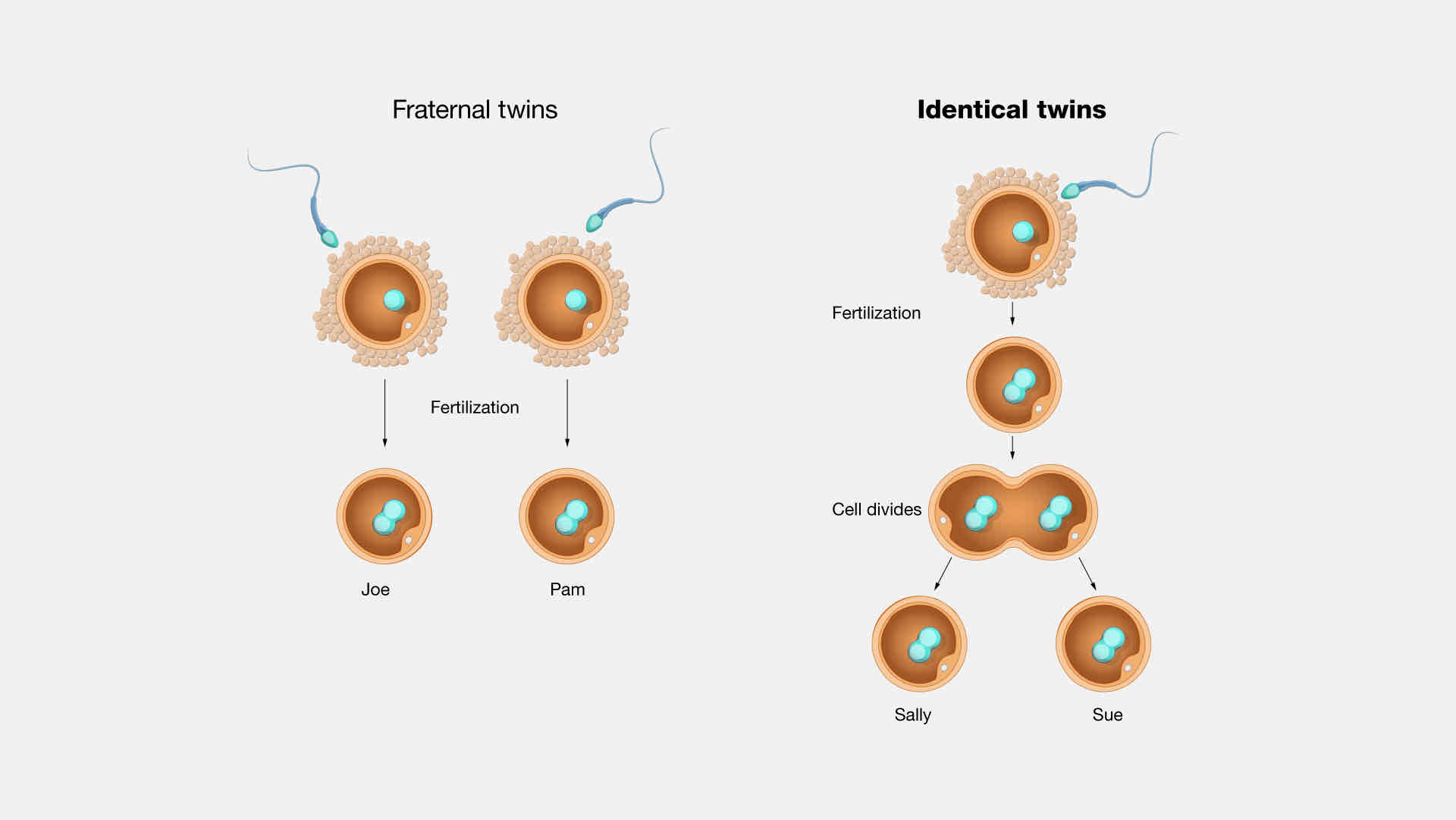
identical twins
twins that develop from two separate eggs fertilized by one sperm; same DNA
predisposition
a person's likelihood of developing a mental or physical disorder or disease
maturation
development of a person's mental, physical, and emotional characteristics from birth to death
rooting reflex
when babies face or mouth is touched head will turn towards it; helps find food
moro reflex
baby hears a loud noise or movement and the arms are thrown up
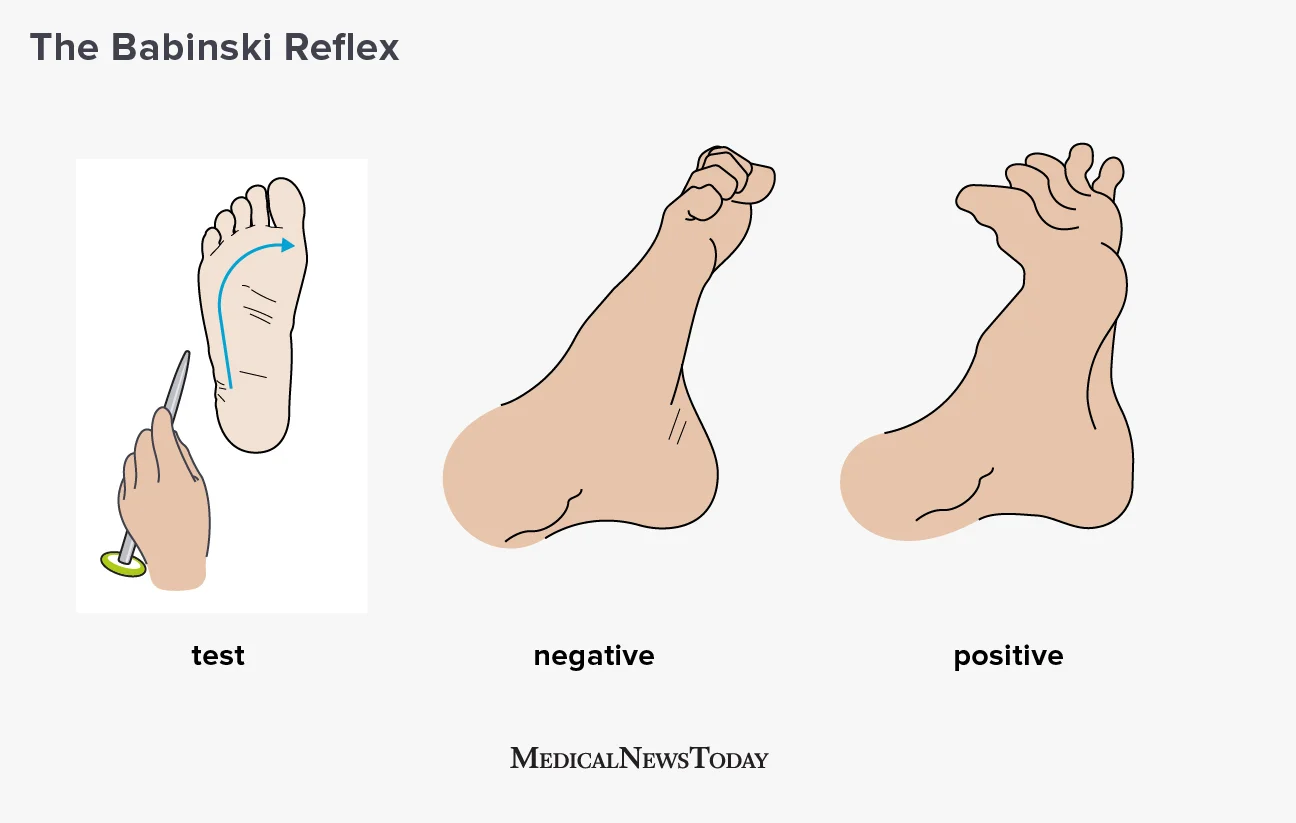
babinsky reflex
bottom of baby’s foot is touched and big toe flexes while other toes fan out
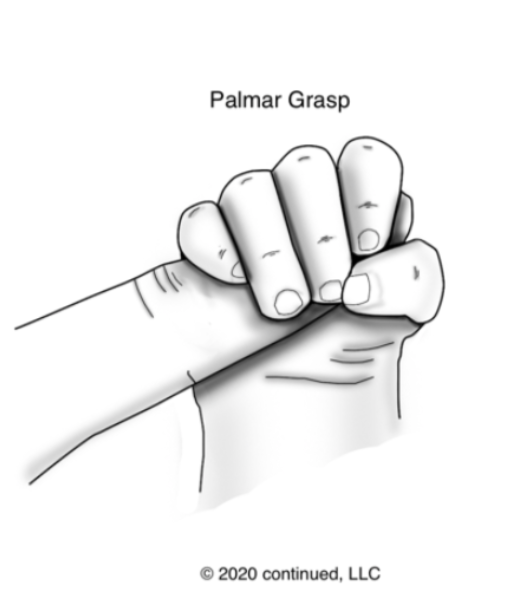
palmar grasp
place a finger in baby’s palm and it closes its fingers around it
tonic reflex
the baby’s head is turned towards its side and leg and arm extends while opposite side flexes
stepping reflex
baby’s is upright touching surface and begins to “walk”
neuroplasticity
brains ability to create neural connections; the brain's ability to adapt and change its structure and function in response to internal or external stimuli
critical period
the first 3 years of a child’s life specific time during development when the brain is most sensitive to environmental influences or stimuli
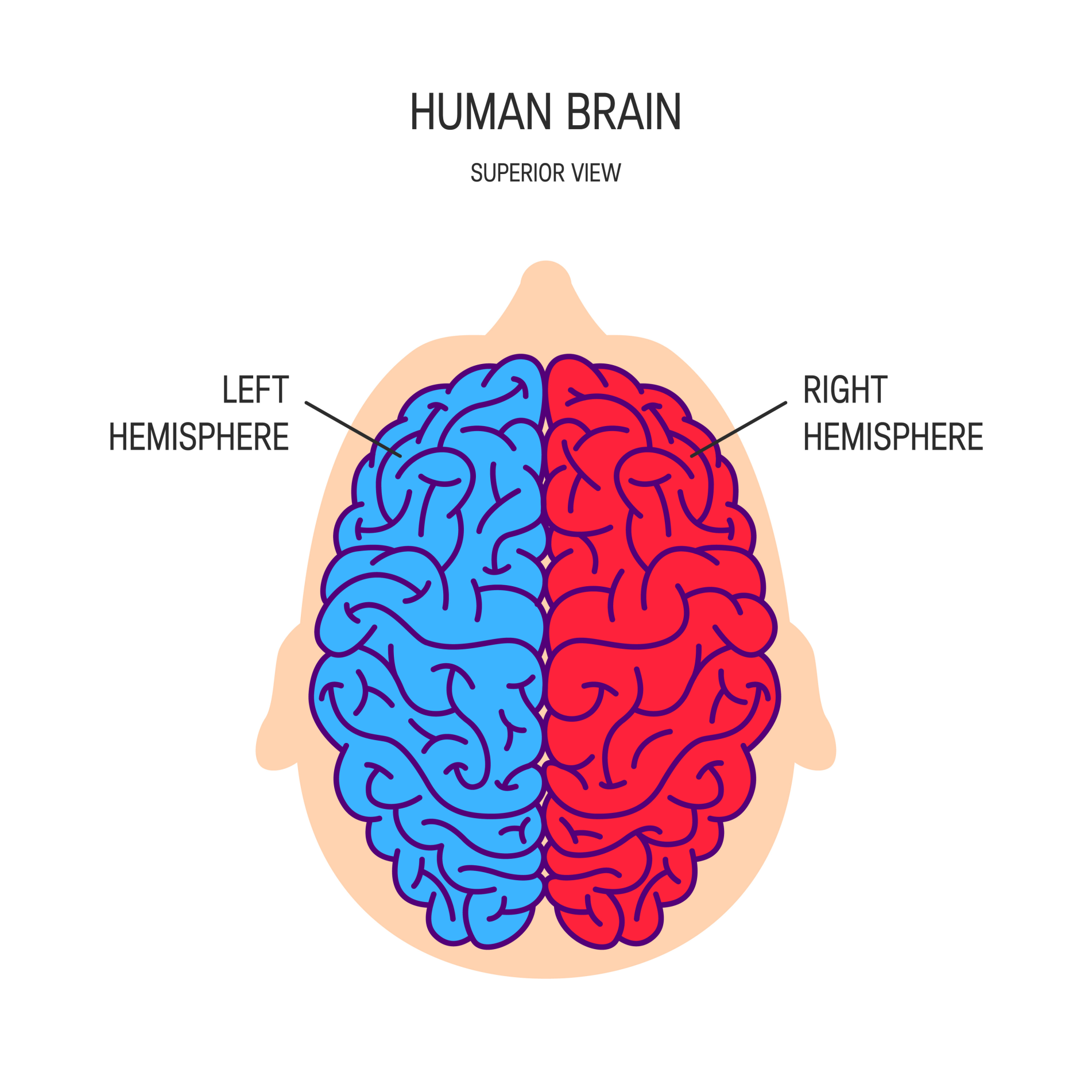
hemispherectomy
one half of the brain, either the left or right side
Rosenzwieg Rat Study
This study showed the effects of different environments on the brain. Rosenzweig found that rats living in the EC developed a heavier and thicker brain cortex.
teratogen
something that can induce or increase birth defects in a developing child; smoking
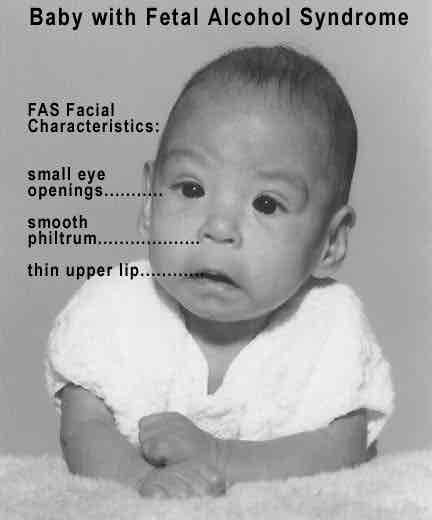
fetal alcohol syndrome
drinking affects baby’s central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
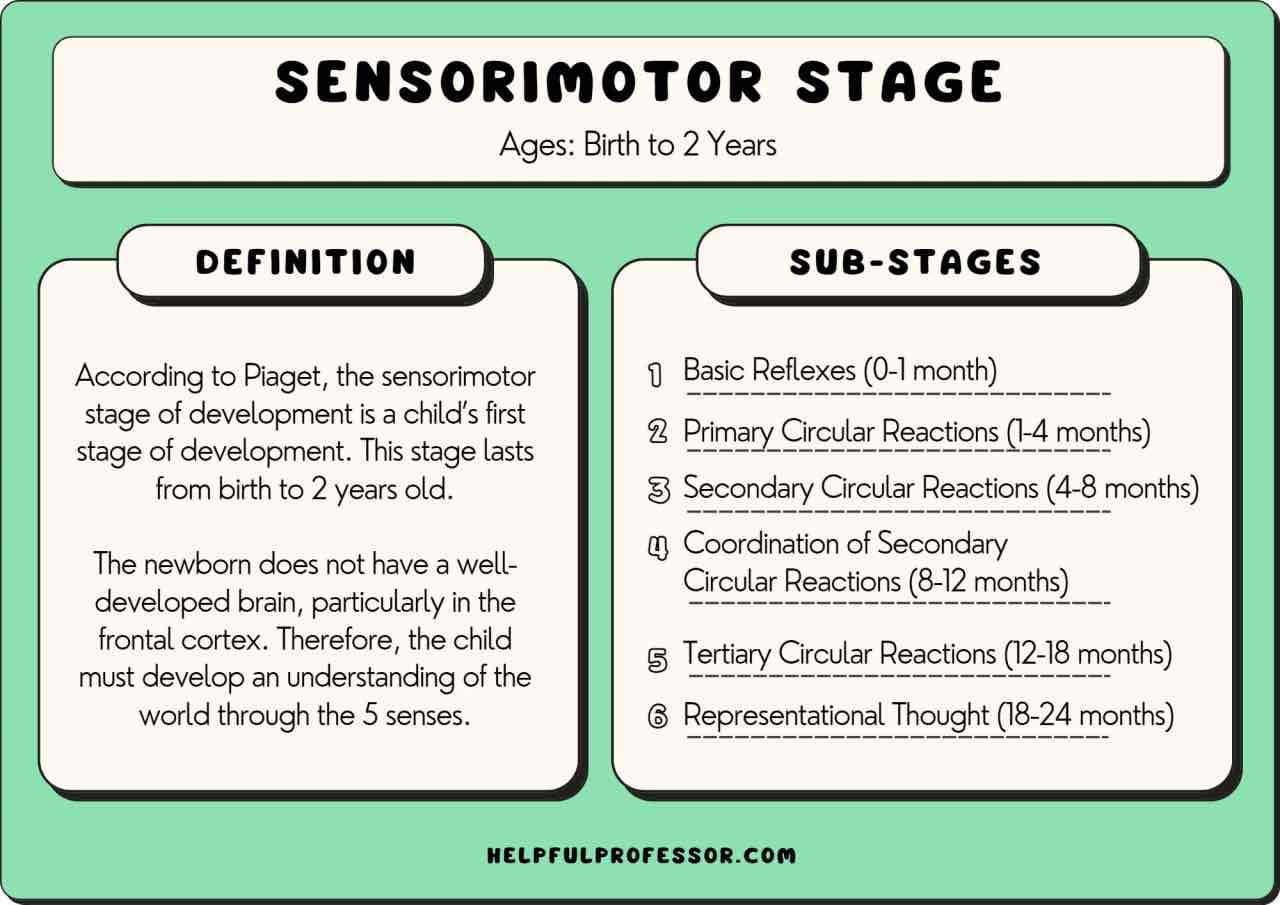
sensorimotor (piaget)
experiencing the worlds through senses and actions; object permanence and stranger anxiety
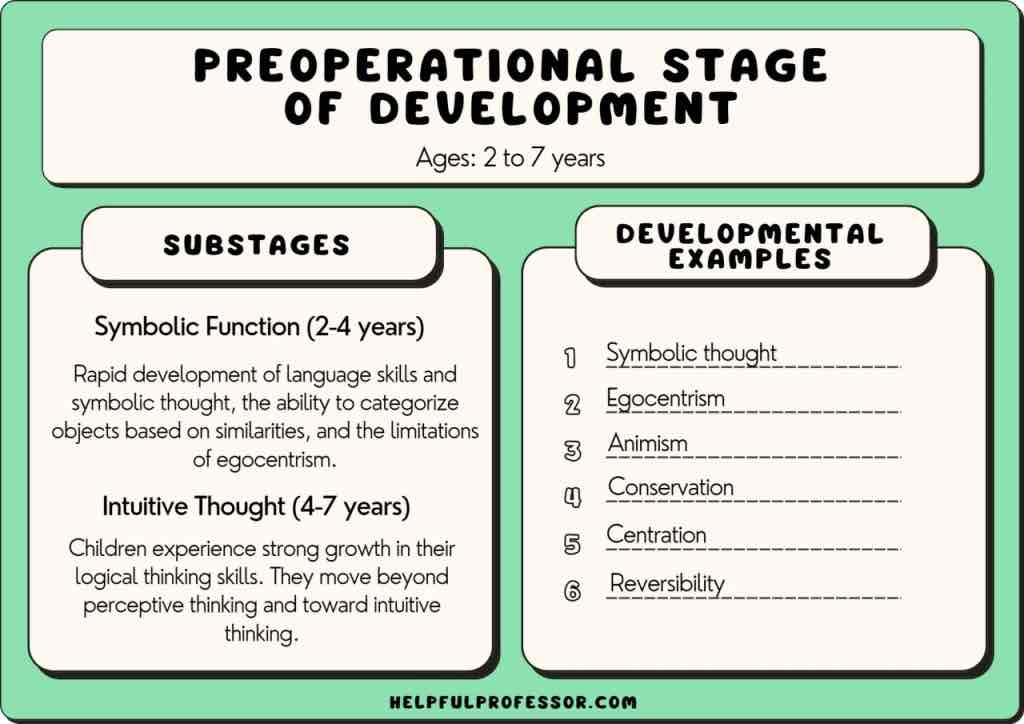
preoperational (piaget)
representing things with words and images but lacking logical reasoning; pretend play, egocentrism, language development
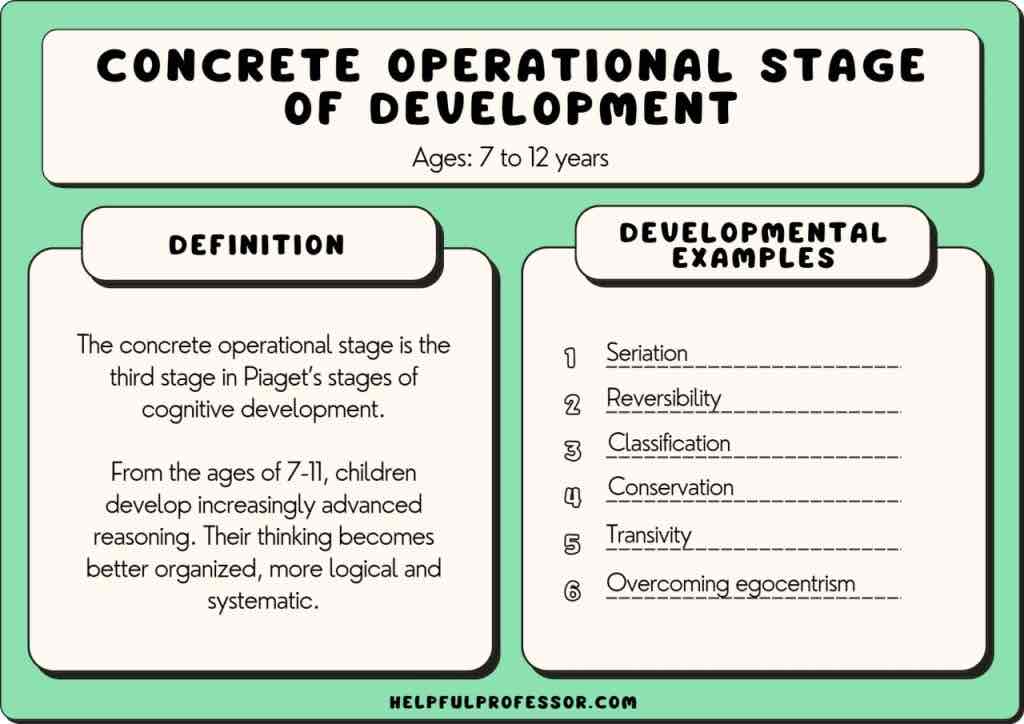
concrete operational (piaget)
thinking logically about concrete events and grasping concrete analogies and performing arithmetic al operations; conservation and mathematical transformations
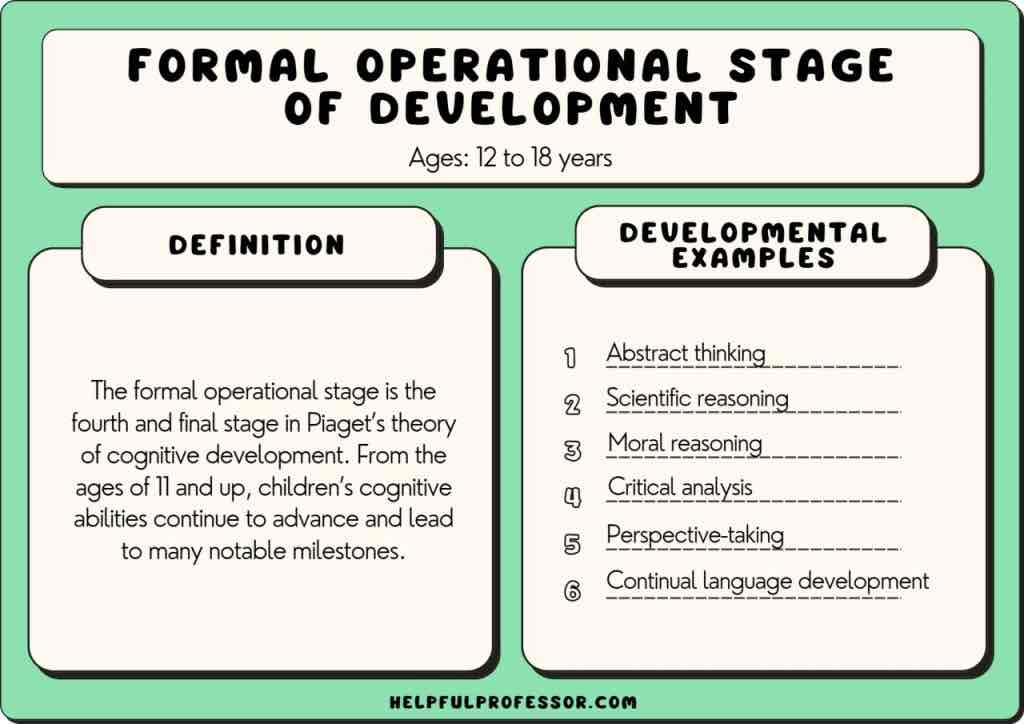
formal operational (piaget)
abstract reasoning; abstract logic, potential for moral reasoning
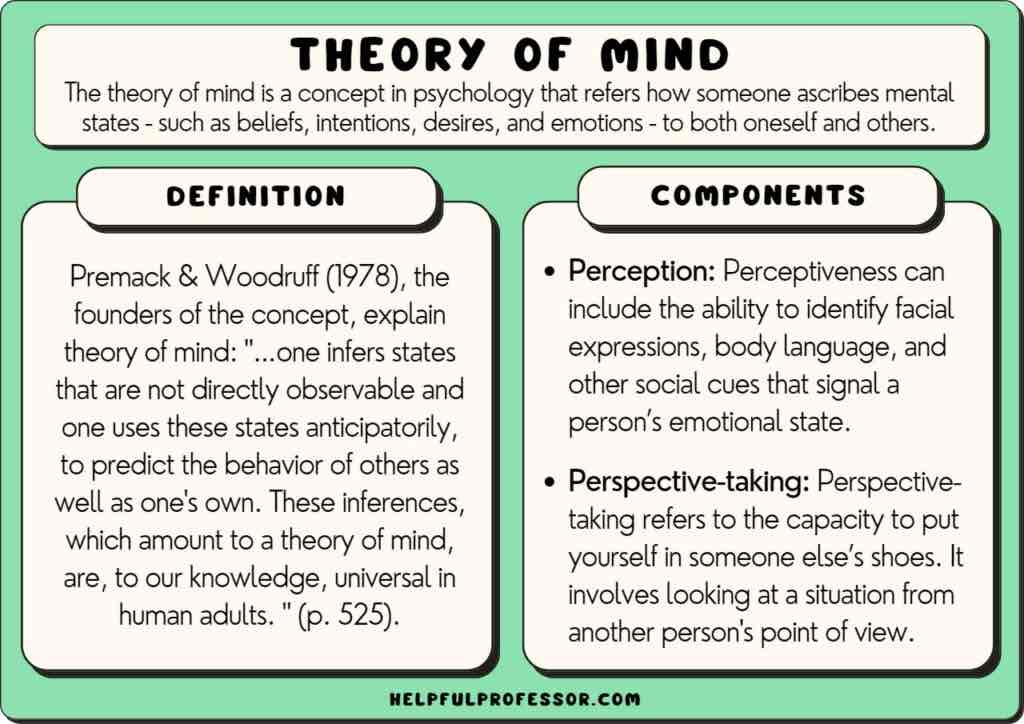
theory of mind
ability to understand different perspectives
assimilation
understanding new information through existing schemas
accommodation
changing schemas to reflect new information
schema
a way of organizing information
scaffolding (vygotsky)
learning happens best in a social environment; psychological technique that involves providing support to help a learner achieve a goal or complete a task that they would not be able to do on their own
zone of proximal development (vygotsky)
what you can do with the help of others
what you can do on your own

phoneme
small distinctive sound units.
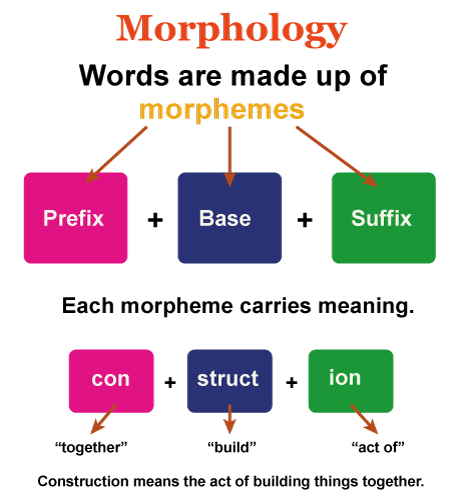
morpheme
smallest unit of meaning; created by combining phonemes
language stages
Cooing
Babbling
One-word Stage
Telegraphic
Cooing
when babies begin to make vocalizations, usually between 6 weeks and 4 months old
Babbling
baby makes consonant-vowel or vowel-consonant sounds
One word stage
a phase of language development where children use single words to convey meaning
telegraphic stage
a stage of language acquisition in children when they begin to speak in short sentences that resemble the style of writing in telegrams
grammar semantics
the study of how grammatical devices convey meaning
pragmatic semantics
The study of the intended meaning of an utterance, or the deeper, inferred meaning of a word or phrase.
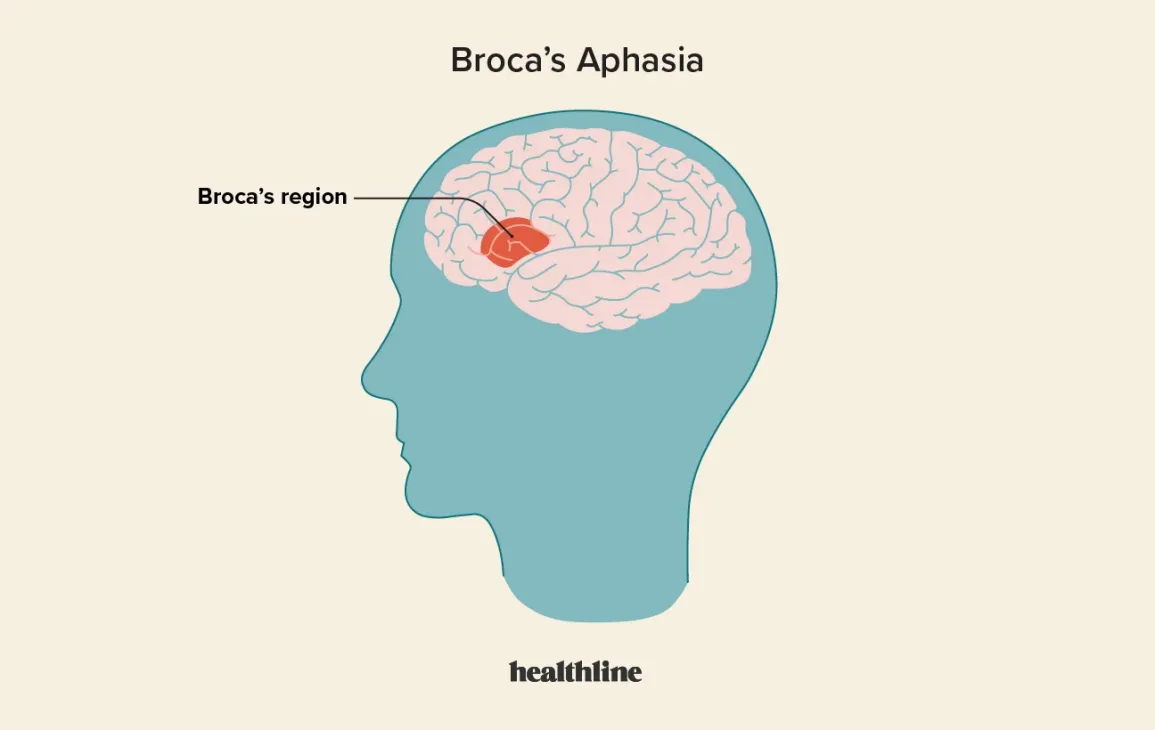
Broca’s aphasia
a language disorder that affects how people speak, but not their understanding of words
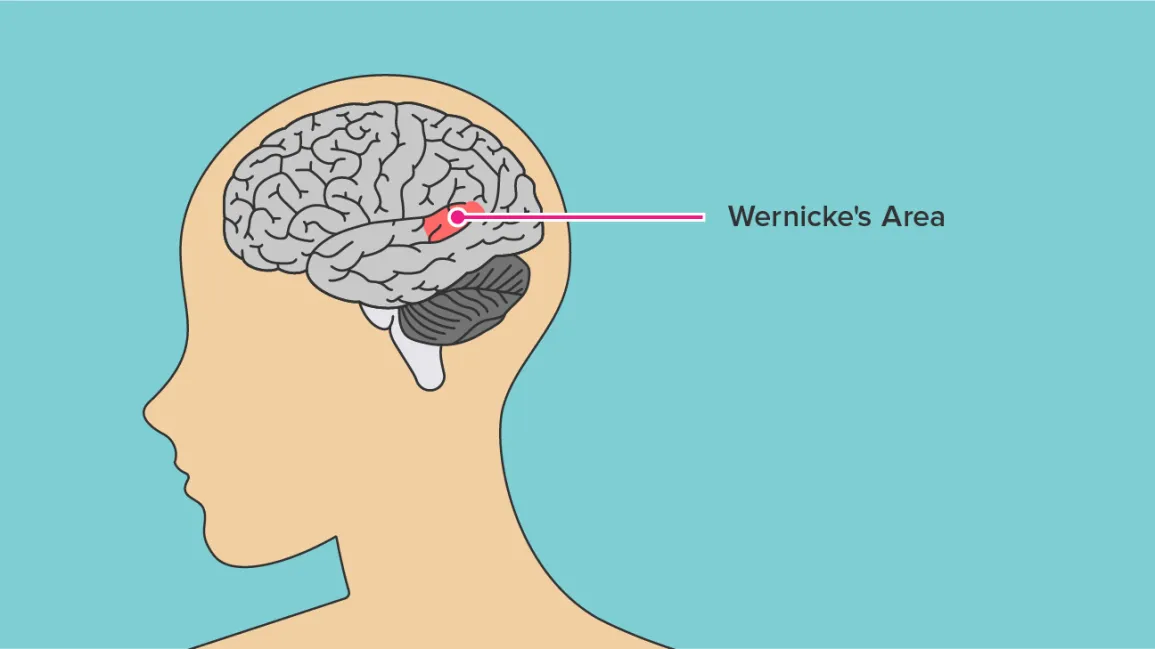
wernicke’s aphasia
a language disorder that makes it difficult to understand and produce meaningful speech
secure attachment
a healthy attachment style that develops when a child feels safe and protected by their caregiver, and can consistently rely on them to meet their needs
insecure attachment
a relational pattern that can make it difficult to trust others and maintain healthy relationships; characterized by a lack of trust and a lack of a secure base
Harrows Monkeys
The Harlow attachment theory demonstrated the importance of social contact with the mother and peers for the proper social development of infant monkeys, and the developmental impairment that results from social isolation.
Ainsworth Strange Situation
a psychological experiment that tests the attachment of infants to their primary caregiver
ERikson
ericsson’s psychological stages
eriksons self concept
informed assent
a process that involves obtaining permission from a person who is not legally able to give informed consent to participate in a medical procedure or research study; children
enthocentrism
the tendency to view one's own culture as the standard and to judge other cultures based on that standard, often perceiving them as inferior or "other"
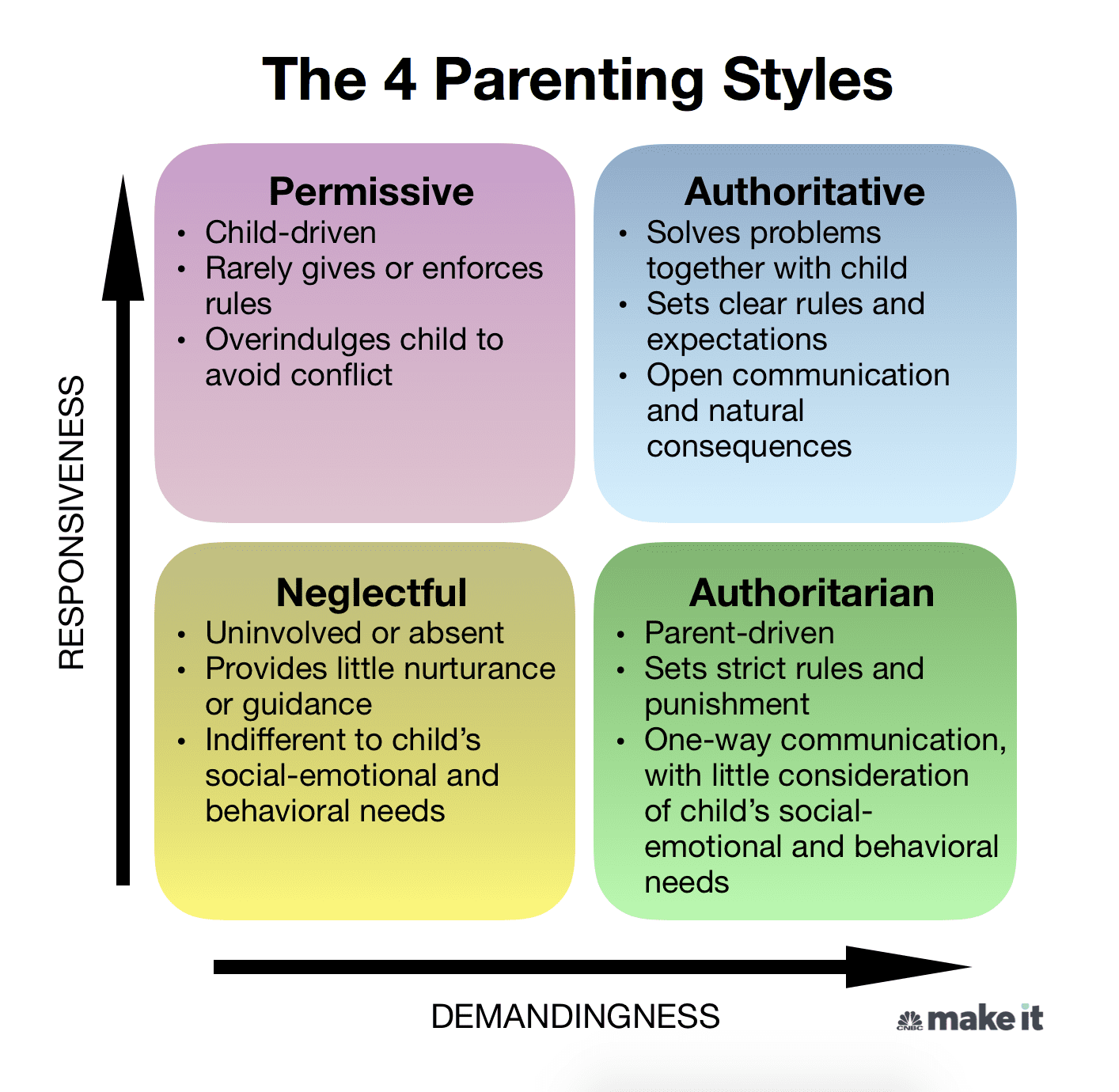
permissive parent
high responsiveness and low demands, where parents are warm and nurturing but avoid setting firm rules or enforcing boundaries, often acting more as friends than authority figures
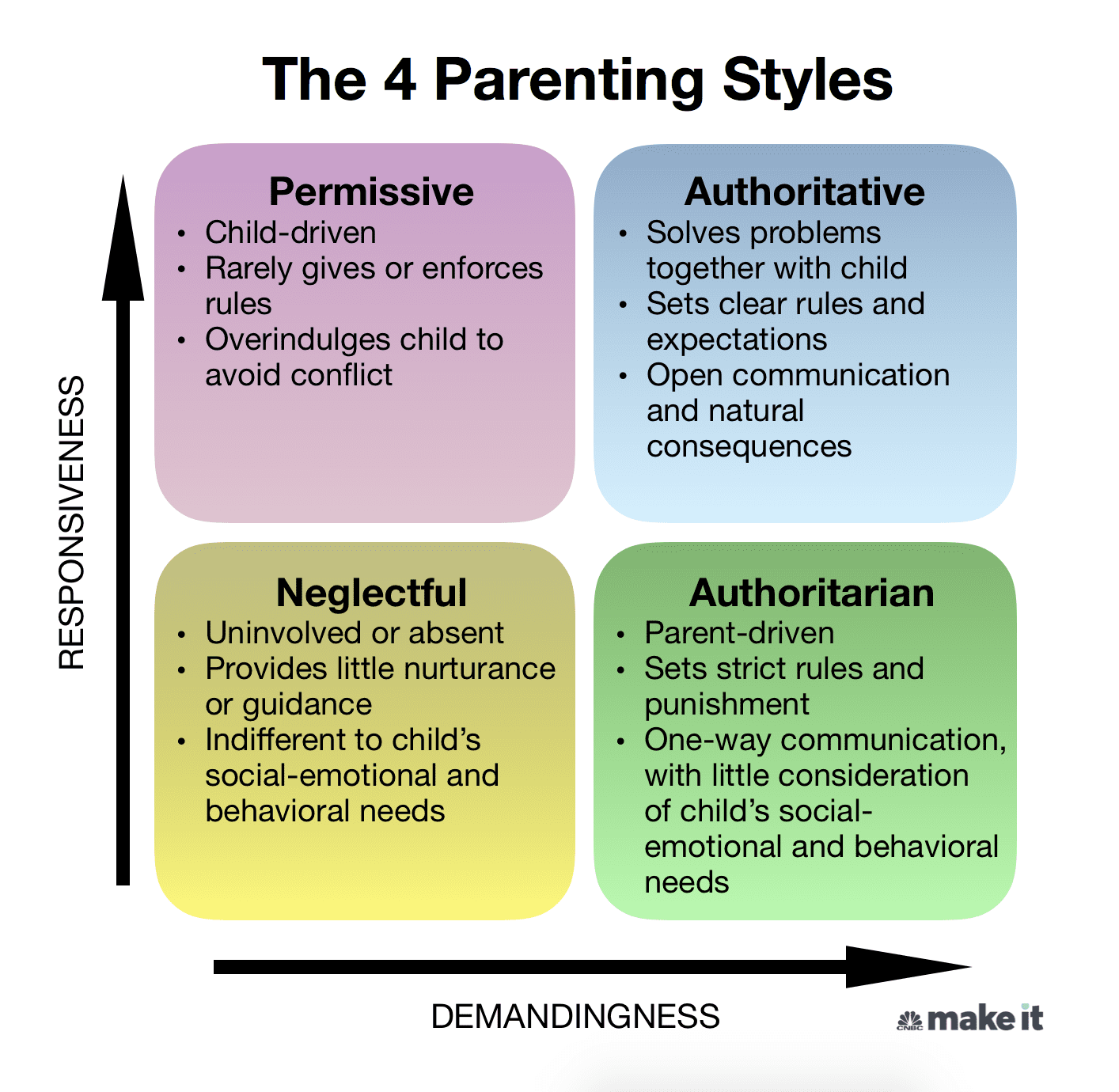
authoritative parent
balances warmth, responsiveness, and clear expectations, fostering independence and self-regulation in children while maintaining a nurturing and supportive environment.
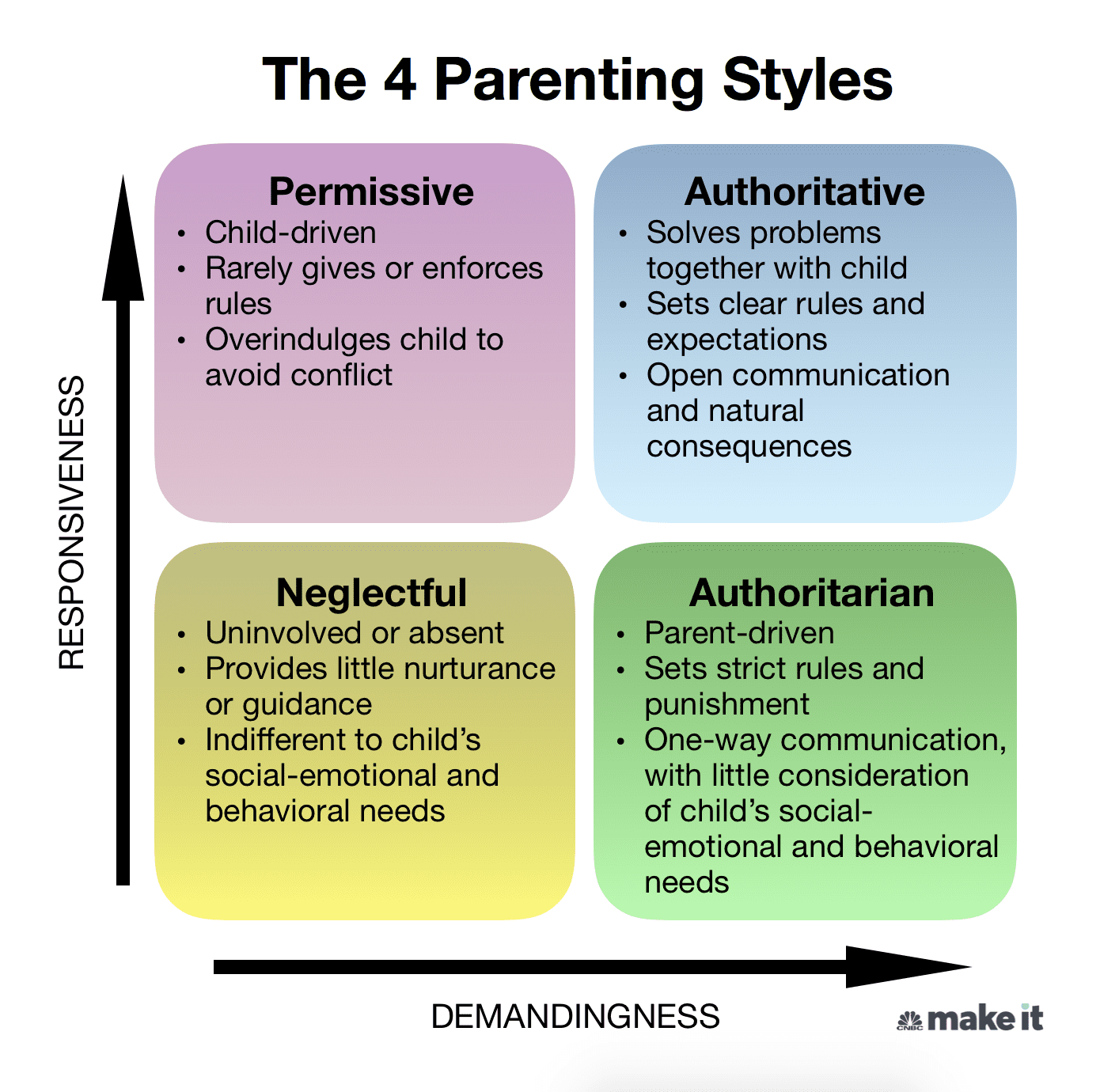
authoritarian parent
a strict style characterized by high demands, low responsiveness, and a focus on obedience and control, with little room for negotiation or discussion
adolescence
the transitional stage from childhood to adulthood that occurs between ages 13 and 19.
puberty
a complex process of physical, hormonal, and emotional changes that marks the transition from childhood to adulthood, enabling sexual maturity and reproductio
sex
what you were assigned to at birth
gender
refers to the roles, behaviors, expressions, and identities of people
mearche
the onset of menstruation
spermarche
the first ejaculation
primary sex characteristics
the biological traits directly involved in reproduction, such as the gonads (ovaries and testes) and external genitalia
secondary sex characteristics
physical traits that develop during puberty, are related to sex but not directly involved in reproduction; pubic hair
display rules
culturally specific norms that dictate how and when individuals are expected to express emotions in social situation
gender identity
culturally specific norms that dictate how and when individuals are expected to express emotions in social situation
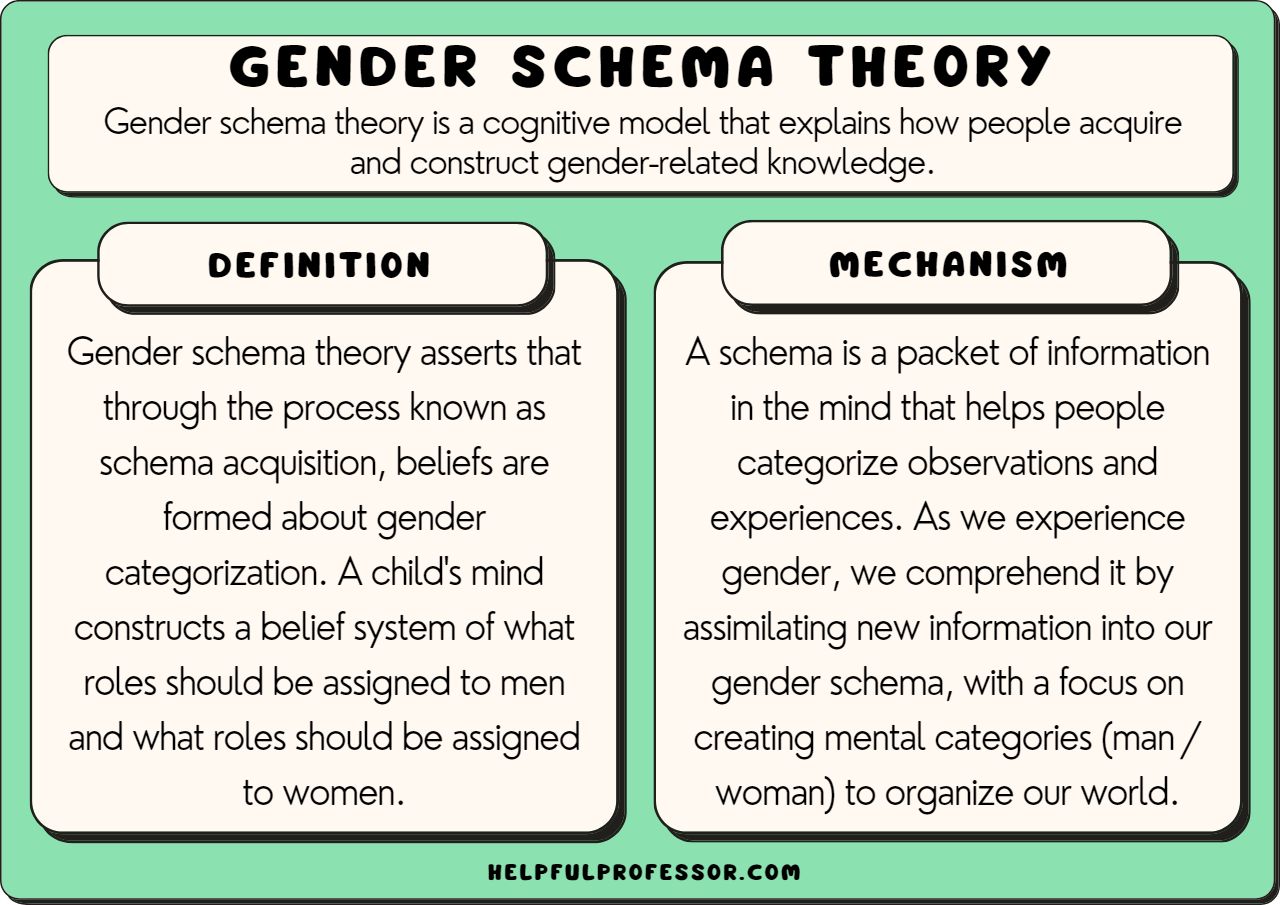
gender schema
a mental framework or organized set of beliefs and expectations about gender roles and traits that influence how individuals perceive and interpret the world, and how they behave.
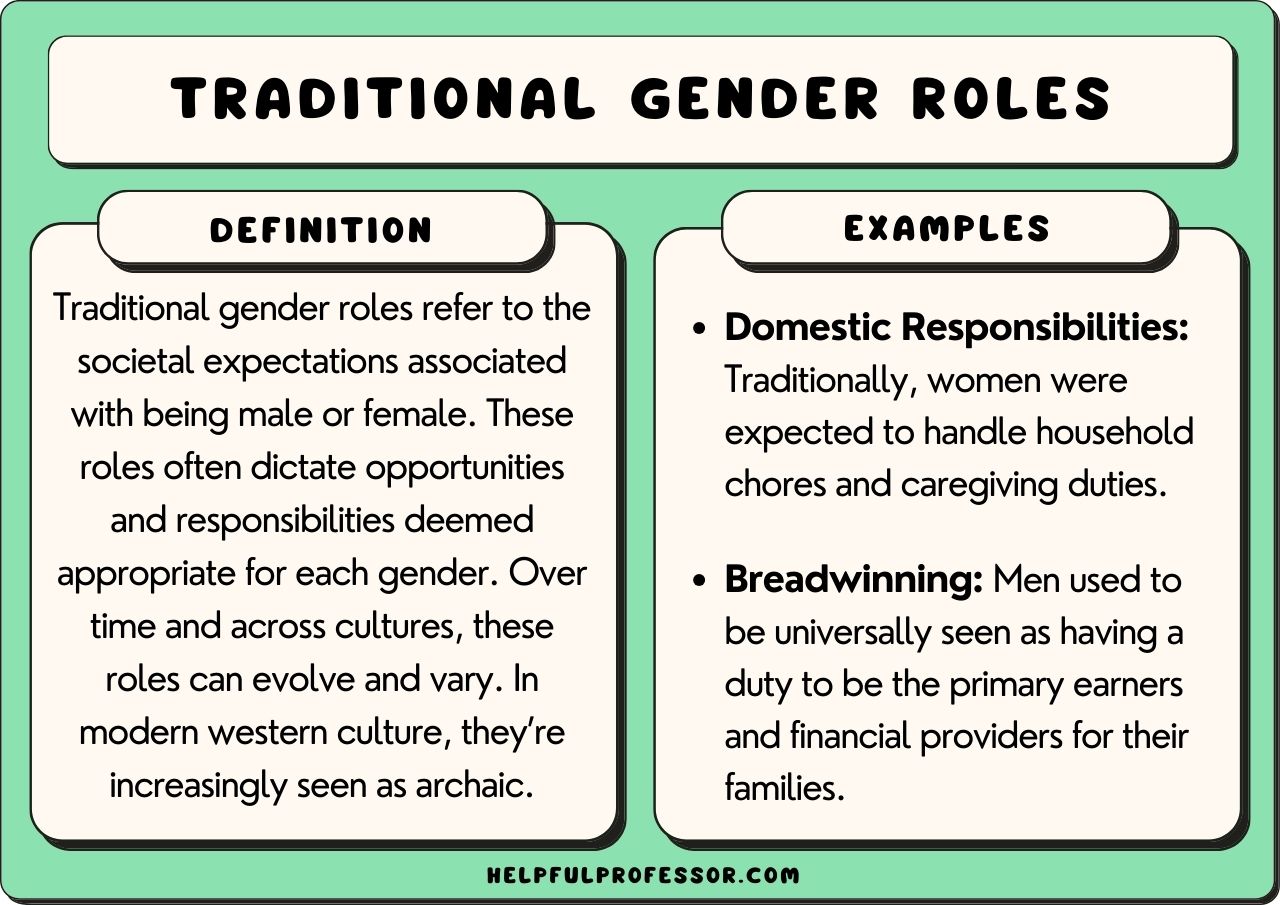
gender roles/norms
the socially and culturally constructed expectations and behaviors associated with being male or female, shaping how individuals are expected to act, think, and interact in societ