Unit 3 Flashcards
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/85
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
1
New cards
production is
converting inputs into outputs
2
New cards
firms must make ---- to earn profit
products (output)
3
New cards
inputs are the ---- used to make outputs
resources
4
New cards
input resources are also called
factors
5
New cards
total physical product is
the total output or quantity produced
6
New cards
marginal product is
the additional output generated by additional inputs (workers)
7
New cards
marginal product formula
change in total product divided by change in input
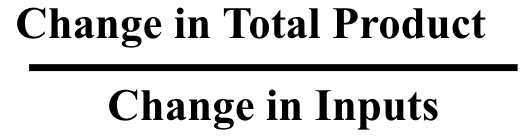
8
New cards
average product
total product divided by units of labor

9
New cards
fixed resources
resources that don’t change with the quantity produced
10
New cards
variable resources
resources that do change with the quantity produced
11
New cards
law of diminishing marginal returns
as variable resources are added to fixed resources, the additional output produced per additional worker will decrease
12
New cards
three stages of return
1. increasing marginal returns
2. decreasing marginal returns
3. negative marginal returns
13
New cards
increasing marginal returns
marginal product is rising and total product is increasing at an increasing rate due to specialization
14
New cards
decreasing marginal returns
marginal product is falling and total product is increasing at a decreasing rate because of fixed resources (each worker adds less and less)
15
New cards
negative marginal returns
marginal product is negative and total product is decreasing because workers get in each others way
16
New cards
short run
at least one resource is fixed, production capacity is fixed
17
New cards
long run
all resources are variable, no fixed resources, production capacity is changeable
18
New cards
total costs
total fixed cost, total variable cost, total cost
19
New cards
per unit costs
average fixed costs, average variable costs, average total costs, marginal cost
20
New cards
fixed cost
cost for fixed resources that don’t change with the amount produced
21
New cards
average fixed cost (AFC) formula
fixed cost divided by quantity

22
New cards
variable cost
cost for variable resources that do change as more or less is produced
23
New cards
average variable cost (AVC) formula
variable cost divided by quantity

24
New cards
total cost
sum of fixed and variable costs
25
New cards
average total cost formula
total costs divided by quantity

26
New cards
marginal cost
additional cost of an additional output
27
New cards
marginal cost formula
change in total costs divided by change in quantity
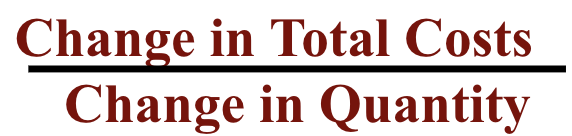
28
New cards
ATC and AVC curves will
get closer but never touch
29
New cards
marginal product curve reasoning
more workers are hired → marginal product increases → law of diminishing marginal returns → marginal product decreases
\
MP and MC are mirror images
\
MP and MC are mirror images
30
New cards
marginal cost curve reasoning
marginal cost of units produced decreases as marginal product increases, eventually increases due to diminishing marginal returns
\
MP and MC are mirror images
\
MP and MC are mirror images
31
New cards
ATC shape reasoning
when MC is below average, it pulls ATC down and when MC is above average, it pulls ATC up, and this creates bowl curve
32
New cards
MC intersects the ATC at
the ATC’s lowest point
33
New cards
returns to scale
1. increasing
2. constant
3. decreasing
34
New cards
increasing returns to scale
when doubling input, output more than doubles
35
New cards
constant returns to scale
when doubling input, output doubles
36
New cards
decreasing returns to scale
when doubling input, output less than doubles
37
New cards
long run ATC curve is made up of
all the different short run ATC curves
38
New cards
why do economies of scale occur
firms that produce more can better use mass production techniques and specialization
39
New cards
LRATC - economies of scale
mass production techniques are used so LRATC falls
40
New cards
LRATC - constant returns to scale
LRATC is as low as it can get
41
New cards
LRATC - diseconomies of scale
LRATC increases as firm gets too big and difficult to manage
42
New cards
LRATC graph
downward slope → economies
constant slope → constant
upward slope → diseconomies
constant slope → constant
upward slope → diseconomies
43
New cards
diminishing marginal returns don’t apply in the long run because
there are no fixed resources
44
New cards
total revenue formula
price x quantity
45
New cards
profit formula
total revenue - total cost
46
New cards
explicit costs
payments made by firms for using the resources of others, AKA out of pocket costs
47
New cards
implicit costs
opportunity costs that firms pay for using their own resources
48
New cards
accounting profit
total revenue - accounting costs
49
New cards
economic profit
total revenue - economic costs
50
New cards
profit maximizing rule
MR = MC
51
New cards
shut down rule
firms should continue to produce as long as price is above AVC
* if price is below AVC, minimize loss by shutting down bc loss is bigger than fixed coss
* shut down if P < AVC
* if price is below AVC, minimize loss by shutting down bc loss is bigger than fixed coss
* shut down if P < AVC
52
New cards
marginal cost and supply
price increases → quantity increases
price decreases → quantity decreases
\
MC increase → supply decrease
MC decrease → supply increase
price decreases → quantity decreases
\
MC increase → supply decrease
MC decrease → supply increase
53
New cards
MC above AVC is a ---- supply cirve
short run
54
New cards
barriers to entry
factors that prevent new firms from entering a given market
\
low barriers → more competition → less profit per firm
high barriers → less competition → more profit per firm
\
low barriers → more competition → less profit per firm
high barriers → less competition → more profit per firm
55
New cards
normal profit
* no economic profit
* in an efficient competitive market, firms with identical products make a normal profit
* in an efficient competitive market, firms with identical products make a normal profit
56
New cards
four market structures
1. perfect competition
2. monopolistic competition
3. oligopoly
4. monopoly
57
New cards
imperfect competition markets
* monopolistic competition
* oligopoly
* monopoly
* oligopoly
* monopoly
58
New cards
perfect competition characteristics
* many small firms
* identical products (perfect substitutes)
* low barriers
* seller has no need to advertise
* price takers → no control over price
* identical products (perfect substitutes)
* low barriers
* seller has no need to advertise
* price takers → no control over price
59
New cards
types of barriers to entry
* economies of scale
* only one electric company because they can make electricity at lowest cost
* natural monopoly
* superior technology
* geography/ownership of raw materials
* government created barriers
* patents
* only one electric company because they can make electricity at lowest cost
* natural monopoly
* superior technology
* geography/ownership of raw materials
* government created barriers
* patents
60
New cards
monopoly characteristics
* one large firm
* unique product (no close substitutes)
* high barriers
* monopolies are price makers
* unique product (no close substitutes)
* high barriers
* monopolies are price makers
61
New cards
oligopoly characteristics
* a few (less than 10) large producers
* identical or differentiated products
* high barriers to entry
* price maker
* mutual interdependence
* firms worry about decisions of competitors and use strategy
* identical or differentiated products
* high barriers to entry
* price maker
* mutual interdependence
* firms worry about decisions of competitors and use strategy
62
New cards
monopolistic competition characteristics
* relatively large number of sellers
* differentiated products
* some control over prices
* low barriers
* non-price competition (advertising)
* differentiated products
* some control over prices
* low barriers
* non-price competition (advertising)
63
New cards
why perfectly competitive firms are price takers
charge above market price → nobody will buy
charge below market price → not necessary because demand stays the same
* price is the same at all quantities demanded
* demand curve is perfectly elastic
charge below market price → not necessary because demand stays the same
* price is the same at all quantities demanded
* demand curve is perfectly elastic
64
New cards
price taker means
price is set by the industry
65
New cards
for perfect competition, MR =
MR = D = AR = P
66
New cards
for perfect competition, the demand curve is
industry → downward sloping line
firm → horizontal line
firm → horizontal line
67
New cards
perfect competition firm profit
MC = MR intersection down to ATC
68
New cards
69
New cards
characteristics of MR = MC
* applies to all markets
* only applies of P > AVC
* can be restated as P = MC for perfectly competitive firms
* only applies of P > AVC
* can be restated as P = MC for perfectly competitive firms
70
New cards
per unit tax is an example of a ---- increase
variable cost
* causes supply to decrease
* causes supply to decrease
71
New cards
subsidy is an example of a ---- decrease
variable cost
* causes supply to increase
* causes supply to increase
72
New cards
if fixed cost increase, quantity will
remain the same because MC/supply doesn’t change
73
New cards
per unit tax ---- affect the quantity produced
will
74
New cards
lump sum tax ---- affect the quantity produced
will not
75
New cards
change in fixed cost changes
ATC and AFC but not MC
76
New cards
change in variable cost changes
ATC, AVC, and MC
77
New cards
perfect competition in the long run
profit → firms enter
loss → firms leave
* all firms break even (make no economic profit)
* no economic profit = normal profit
* extremely efficient
loss → firms leave
* all firms break even (make no economic profit)
* no economic profit = normal profit
* extremely efficient
78
New cards
no economic profit is the same as ---- accounting profit
positive
79
New cards
change in number of firms impacts market supply by
firms leave → price increases → quantity decreases
80
New cards
constant cost industry
entry of new firms into the market does not increase the costs for firms already in the market
81
New cards
in a constant cost industry, supply curve is
horizontal
82
New cards
in an increasing cost industry, the supply curve is
upward sloping
83
New cards
productively efficiency
producing at the lowest possible cost (P = min ATC)
84
New cards
allocative efficiency
producing at the amount most desired by society (P = MC)
85
New cards
long run perfectly competitive firm efficiency
allocative and productive
86
New cards
short run perfectly competitive firm efficiency
allocative but not productive