Exam #1 OB/Maternal
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
Pain that comes with changing positions while pregnant
Round Ligament Pain
The most favorable type of pelvis for natural birth vs pelvis structure for c section birth
Favorable type- Gynecoid
Least favorable type- Platypelliod
"0 position, head is engaged” means what
Babies head is inline with ischial spine
How many female reproductive cycles are there
-Endometrial Cycle
-Hypothalamic-pituitary Cycle
-Menstral/Ovarian Cycle
What are the four stages of the endometrial cycle
1) Menstrual
2) Proliferative
3) Secretory
4) Ischemic
Menstrual Phase
1-6 days
Estrogen Low
Endometrium Shed
Proliferative Phase
7-14 days
Estrogen Peaks
Ovulation occurs → Cervical mucous is clear, thin, watery-like → favorable to sperm
Prior to ovulation → Temp down // After ovulation → Temp increase
Secretory Phase
15-26 days
Estrogen drops
Progesterone Increases
Ischemic Phase
27-28 days
Estrogen + Progesterone decreases
Endometrium becomes pale and deteriorates
Ovarian Cycle is composed of what two phases
1) Follicular Phase
2) Luteal Phase
What splits the follicular phase and luteal phase (ovarian cycle)
Ovulation due to mature follicule rupturing due to LH surge
What are the secondary symptoms of ovulation
-Spinbarkheit → Change of the cervical mucus
-Mittleschmerz→ Pain on one side while ovulation occurs
-Temp Changes
Ovarian cycle phase that oocyte grows inside the maturing follicle
This phase varies in length
Follicular Phase
The luteal cycle phase begins when the ovum leaves the follicle
LH helps develop the corpus lumen
-This phase is fixed in length
Luteal Phase
Hypothalamic-Pituitary Cycle is composed of what two hormones that peak at ovulation
A.FSH.F→ Anterior → FSH → Follicular Phase
P.LH.L → Posterior → LH → Luteral
Primary vs Secondary Amenorrhea
Primary → “Never had a period” → No menses by age 15 with secondary sex characteristics or No menses by age 13 without secondary sex characteristics
Secondary → “Do not have a period anymore.”
Endometrial tissue going outside of the uterus attaching itself to other body parts
Endometriosis (lots of scar tissue, diagnosis is scoping that can cause infertility)
High androgens, & high insulin resistance, with facial hair syndrome
PCOS
Factors Affecting Female Fertility
-Anovulation (no ovulation)
-Tube scaring
-Age over 40
-Genetic
-Lifestyle, or heart-shaped uterus
-Fibroids
Factors Affecting Male Fertility
Hormonal disorders affecting sperm production
Testicular factors → Sperm transport
Genetic factors → Klinefelter syndrome
Age
Lifestyle or environment
Non-medical Management of infertility
Healthy BMI, Exercise, abstain from alch, cigs, drugs, use lube, and decrease scrotal temp (no laptops on lap)
Medical management for infertility
Clomiphene citrate & Letrozole (PCOS treatment)
Metformin → Support ovulation (PCOS)
Stabilize chronic medical conditions & treat infections
What are the benefits of planned pregnancies
Avoid tetragoenic substances
Best timing to get pregnant
2 days before and the day of ovulation are the peak
How long does a sperm live after intercouse
3-5 days
Corrtius Interruptus is called
Withdrawl method (one of the least effective)
Standard Day Method Model
-Red dot is the first day of the menstrual cycle
-Brown = non-fertile = abstain from sex on days 8 to 19
-White = fertile = Have sex
A model that analyzed urinary metabolites of LH and estrogen to predict ovulation
Marquette Model
When should a diaphragm, cervical cap, or contraceptive sponge be placed and then taken out before and after sex
Before → 3 hrs
After → No more than 24 hrs
Estrogen-Progestin Contraceptives (Common Coc)
Suppresses FSH & LH, which affects the endometrial lining and thickens the cervical mucus
Do not give to patients with DVT or heart problems
Progestrine-Only Contraceptive
Inhibits ovulation, thickens & decreases cervical mucus, thins out the endometrium
Only use it for 2 years because it can cause osteoporosis
Must take at same time everyday
Emergency Contraption “Plan B”
Does not kill an already established pregnancy
What is the number one thing causing maternal mortality in the US vs MO
US → Mental health
MO → Cadiovascular
Care that should occur any time a HCP sees a person with female reproductive organs of childbearing age is called
Preconception Care
Prenatal Visit Interview
-Happens around 8 weeks
-Get all the history
-Occupation or social history
-Mental health screening
Presumptive vs Probable vs Positive signs of pregnancy
Presumptive → Subjective info pt tells you
Probable → Object sign from our assignment (Chadwick → Cervix is blue) & preg test
Positive → Ultrasound
G stands for what
Number of pregnancies
P stands for what
Number of deliveries OVER 20 weeks
TPAL stans for
Term → deliverers
Preterm → deliveries and (stillbirth after 20 weeks )
Abortion → miscarriage (before 20 weeks)
Living

Answer this GPTAL Question #1
Gravida→4
Para → 1
T→ 1
P→ 0
A→ 2
L → 1

Answer this GPTAL Question #2
Gravida → 3
Para → 2 (twins count as one delivery)
T→1
P→1 (twins count as one preterm)
A→ 0
L→ 3 (twins count individually)
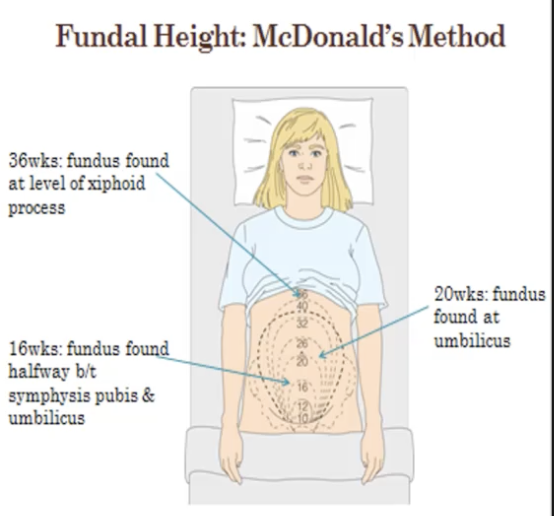
McDonald’s Method is
Measuring from the pubic symphysis to the top of the fundus
Correlates with gestational age + or - 2cm
What is another word for fetal movement
Quickening
1st trimester lab screening
“All the blood tests”
-CBC → Look for anemia
-Blood type & RH factor (neg mom needs Rohgam)
-Urinalysis
-RPR → Screen for syphilis
-Hep B
-HIV
2nd Trimester lab screening
“Screen for that Diabetes”
-1 hr GTT → Above 130-140 mg/dl is fail → Go onto 3 hr test
3rd Trimester lab
“Repeat a few tests.”
-GBS
-Anemia test (H&H)
-STI test
Some personal hygiene tips for pregnant people
-Avoid Hot Tub
-Wear loose clothing
Why do you avoid laying supine during preganancy
Aorta Vena Cava or Supine Hypotensive Syndrome → Diminishes the blood supply & pressure in mother.
Braxton Hicks Contractions
-Non-laboring contractions
-Do not come regularly
-Stop when walking around
-Usually are weak and feel on one side
What are some assessments and screenings that occur on the fetus in the 1st trimester
-Transvaginal Ultrasound
-Doppler FHT
-Chronic Villus Sampling → High risk for infection!!
What are some assessments and screenings that occur on the fetus in the 2nd trimester
-Fetal Anatomy Survey Ultrasound → Is it a boy or a girl? Plus, are the major organs all intact
-Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein → Elevated levels can indicate neural tube defects
-Amniocentesis → Diagnostic test
-Quad Screening Test
What is an Amniocentesis
-Diagnostic test to look for and confirm any abnormalities
-Make sure mother has an empty bladder
-Rhogam is administered
-Can be risky
What are some assessments and screenings that occur on the fetus in the 3rd trimester
-Fetal Movement tests → After 24 weeks
-Non-Stress Test
-Biophysical Profile (BPP) → Ordered if the non-stress test comes up non-reactive
-Contraction Stress Test
Non-Stress Test need to know criteria
Reactive
-Normal baseline
-Moderate variability
-Two or more accelerations in 20 mins
-Absence of decelerations
Non-Reactive
-Absence of acceleration in 40 mins
-Abnormal everything else listed above
Biophysical Profile (BPP) looks for what 5 criteria
Shows baby oxygenation
1) Fetal breathing
2) Fetal movement
3) Fetal tone
4) Amniotic fluid index (AFI)
5) Non-stress test
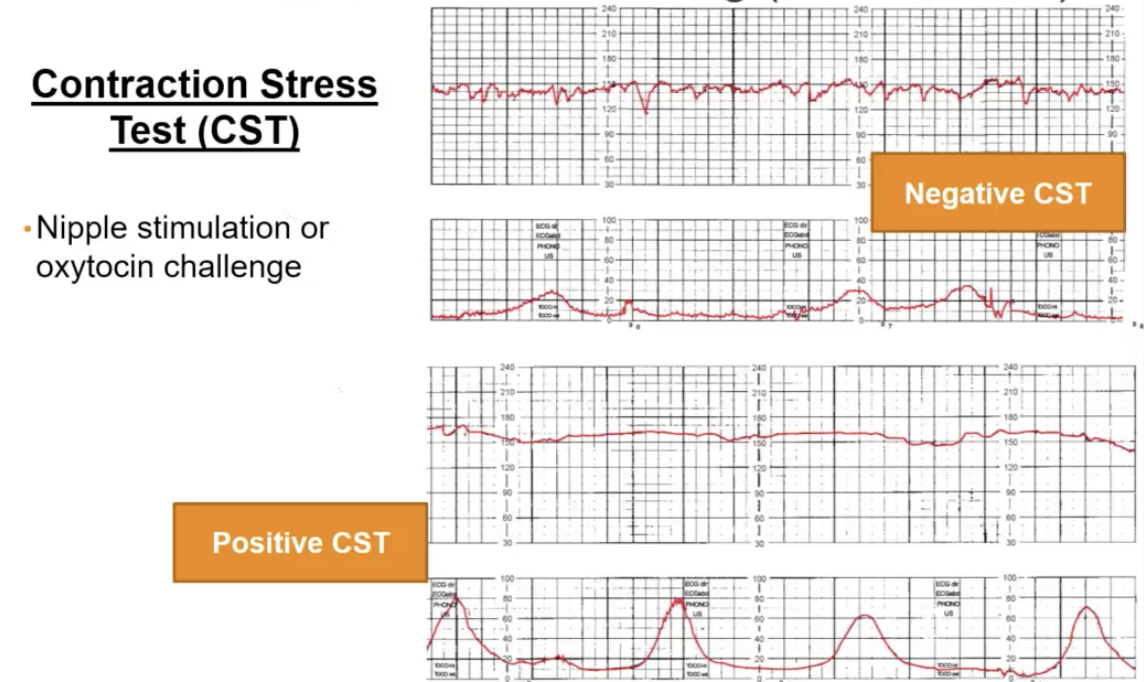
Contraction Stress Test criteria
Ordered to see if the baby can have contractions and be delivered vaginally
Negative = Good ; Positive = Bad
Abortion that is pregnancy loss prior to 20 weeks pregnancy
Spontaneous Abortion
#1 Cause of bleeding in the 1st and 2nd trimesters
What is the most common cause of Spontaneous Abortion
Chromosomal Abnormalties
What are the types of abortion
-Threatened abortion
-Inevitable abortion
-Incomplete abortion
-Complete abortion
-Missed abortion
Clinical Manifestations of spotting/bleeding or cramping or back aches
-Cervix is closed
-Placenta remains attached to uterine wall
-May result in pregnancy loss or not
Threatened Abortion
Clinical Manifestation of increased cramping with mild to moderate bleeding
-Cervix dilates
-Placenta is separated from the uterine wall
Inevetable Abortion
Clinical Manifestation is increased cramping with severe vaginal bleeding that won’t stop
-Cervix is dilated
-Placenta is separated from the wall
-Fetal tissue is passed but some contents are still in uterus
-Need intervention to stop bleeding
Incomplete Abortion
(Complete is when all the stuff does come out)
The fetus is dead in the uterus, but has not been passed
-Cervix is closed
-Usually happens in the first trimester
-No more nausea and vomiting all of a sudden, mother feels really good
Missed Abortion
Partial detachment from the chorionic membrane to the uterine wall where blood accumulates between the placenta and the uterine wall during pregnancy is called what
Subchorionic Hematoma → Resolve spontaneously or leads to miscarriage
Implementation of a fertilized ovum outside the endometrial lining of the uterus, usually in the ampulla of the fallopian tube (12 weeks it would be ruptured)
Ectopic Pregnancy
Risk factors for Ectopic Pregnancy
-Tubal damage
-Endometriosis
-Increase in progesterone
-Hx of ectopic pregnancy
-Infertility
-Smoking
Clinical Manifestations of Ectopic Pregnancy
-Missed menses
-Abdominal Pain on one side
-Referred shoulder pain
-Low hCG levels
-Rigid tender abdomen
-Spotting
Lab & Diagnostic testing of Ectopic Testing
-Low hCG levels
-Increased WBC
-Ultrasound
What medication is giving to eliminate the Ectopic pregnancy
Methotrexate (can only do this if you catch it early so preach early pregnancy confirmation)
Pathological proliferation of trophoblastic cells that become fluid-filled vesicles
(Bengign neoplast or “empty egg”) is called what
Molar Pregnancy (Gestational Trophoblastic Disease)
Race at risk for Molar Pregnancy
Asian women
Complete vs Partial Molar Pregnancy
Complete → Empty egg gets fertilized by sperm → all 46 paternal chromosomes → Higher increase of choriocarcinoma
Partial → One Egg is fertilized by 2 sperm → 69 chromosomes → fetal parts may be present.
Clinical Manifestations of Molar Pregnancy
Hyperemesis, brown “prune juice” blood, uterine enlargment, and elevated hCG level
Treatment for Molar Pregnancy
-D & C surgery to remove it
-No pregnancy for 1 year
-Use that contraception
-Monitor hCG levels
Bleeding during the second half of pregnancy contains what two major conditions
Abruptions vs Previa
What happens to the placenta during an Abruption
Placenta separates from uterine wall
Placental Abruption Risk Factors
-Hypertension/preeclampsia (vasoconstriction)
-Trauma
-Cocaine use (vasoconstriction)
-Smoking (vasoconstriction)
Abruption Clinical Manifestations
-Painful
-Dark red bleeding on the inside
-Hard, rigid abdomen
Type of abruption where there is no bleeding
Central Abruption
Type of abruption where there is no bleeding and more than 50% of the placenta is removed
Complete Abruption
Complete Abruption interventions
Need have a preterm delivery immediately
Why do we give steroids to pregnant mothers
To mature the lungs of the baby becasue they are going to have a preterm delivery and they want those organs matured STAT.
Improper placental tissue that can cover the cervix
“Placenta Firtst”
Placenta Previa
Total vs Partial Previa
Total → placenta covers all of the cervix
Partial → Placenta covers part of cervix
Both require C section
Marginal vs Low Lying
Marginal→ Little piece covers the cervix
Low-lying → Placental is touching the cervix on the low end of uterus
Previa Clinical Manifestations
-Painless
-Bright red bleeding
-Non-tender, soft, and relaxed
Previa Nursing Management
-No vaginal exams unless with a speculum
-Avoid sexual intercourse
What is Vesa Previa
Umbilical Cord and blood vessels under the babi’s head → Emergency C Section
Cervical Insufficiency Treatment
IM Progesterone & Cercal Ceclage (have to loose one baby before going that)
The softening and compressibility of the cervix within the early weeks of pregnancy is called what sign
Godell’s sign
Anatomical Fundal Height Landmarks for 12 wks, 20 wks, 36 wks, 37-40 wks & (24 hr postpartum)
12 weeks → Pubic Symphysis
20 weeks → Umbilicus
36 weeks → Xiphoid process
37-40 weeks → Regression of fundal height due to the baby dropping into the pelvis, aka “lightening.”
24 hr Postpartum → Umbilicus
The softening of the lower uterine isthmus refers to what sign?
Hegar’s sign
What happens to the ovaries during pregancy?
Ovulation ceases
Vagina changes due to pregnancy
-Increase in thickness and acidity of secretions
-Leukorrhea →Thick, white, vaginal discharge due to an increase in estrogen
-Favors yeast
Breast pregnancy changes
-Increase size & tenderness (prominent in 1st trimester)
-Striae
-Areolae darken, and nipples are pronounced
-Colostrum
Blood volume increases by how much during pregnancy
50%
Blood pressure during pregnancy
Blood pressure decreases → Lowest at the 2nd trimester
Cardiac output & Heart rate during pregnancy
Both increase
Why do clients have physiological anemia of pregnancy
-Plasma volume increases faster than RBC
-Leads to Hemodilution
-Decrease in H&H
Does WBC increase or decrease during pregnancy
WBC Increases