Protein synthesis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
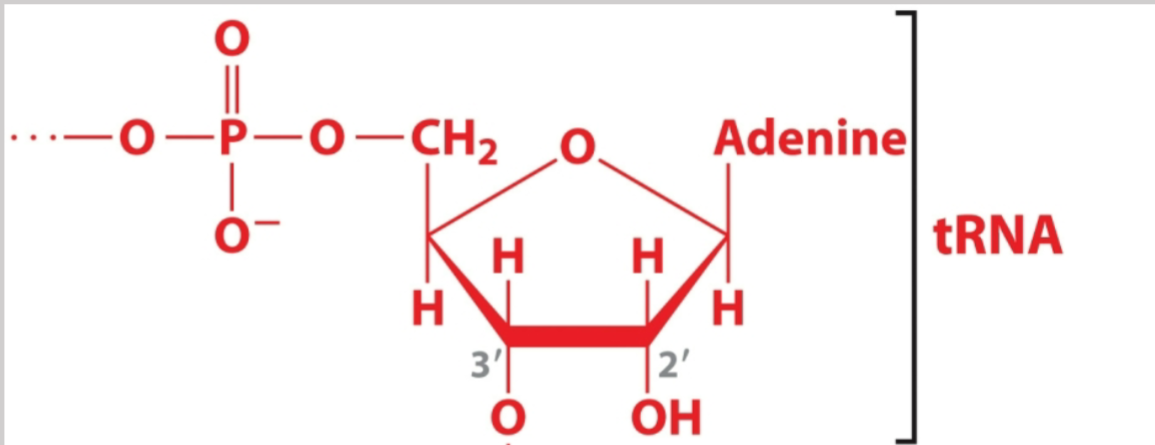
Transfer RNAs
tRNAs bind amino acids and take them to ribosomes to build
polypeptides
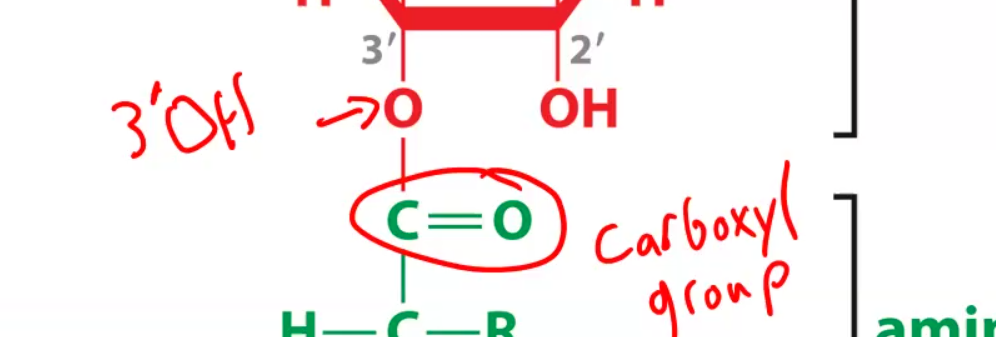
Aminoacyl tRNA Synthetase
covalently links amino acid to the
tRNA via a hydrogen bond between the OH and carboxyl group
Picture of tRNA
picture of amino acid
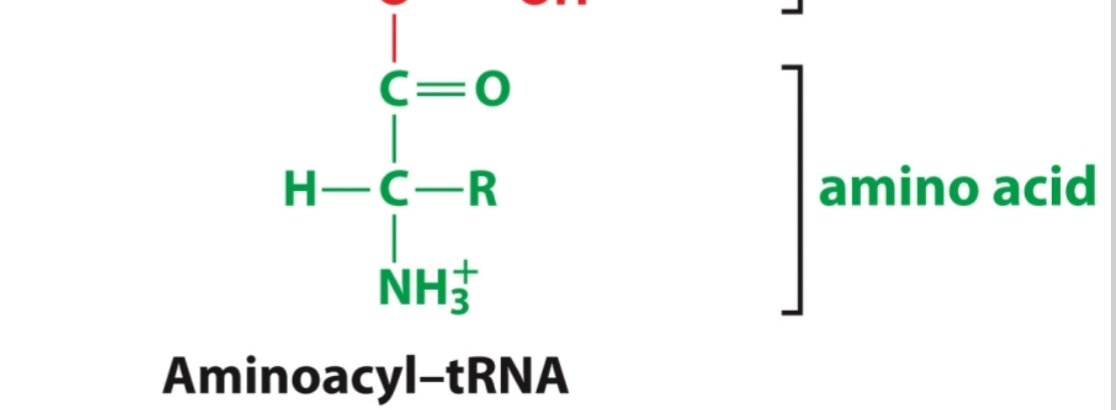
Aminoacylation
tRNA charging. Before translation can proceed, tRNA molecules must
be chemically linked to their respective amino acids
Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases
Enzymes that catalyze aminoacylation
• 20 different synthetases, one for each amino acid
• Highly specific; recognize only one amino acid
• Can recognize multiple tRNAs but only ones for
its amino acid
Wobble Hypothesis
Most tRNAs can bind multiple codons – the first two bases must be
specific bases but the anticodon can “wobble” on the third base.
Reading frame
Three ways in which the
sequence can be read in groups of three.
Each different way of reading encodes a
different amino acid sequence. TATA box dictates where to start the reading frame
Nonoverlapping
A single nucleotide may
not be included in more than one codon. Once three is has been read, it moves on to the next three
The universality of the code
near universal, with some exceptions
What are the 3 steps to translation
initiation, elongation, and termination
What are the characteristics of RNA code
Reading frame, nonoverlapping, and the universality of the code
What is the differnece between Eukaryote and prokaryote translation
Euk has tail and cap bind proteins and is scanned while in a circle to find the AUG or start codon
What are the prokaryotic translation factors
IF 2, EF-TU, EF-G, and RF 1
What are the eukaryotic translation factors
eIF 2, eEF1, eEF2, and eRF 1
What does IF2 or eIF2 do
delivers initiator tRNA to the P site of the ribosome
What does EF-Tu or eEF1do
delivers aminoacyl-tRNA to A site of ribosome during elongation
What does EF-G or eEF2 do
binds to A site to promote translocation following peptide bond formation
What does RF1 or eRF1 do
binds to A site at a stop codon and induces peptide transfer to water