A Level Physics: Mechanics and Materials
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/177
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:34 PM on 1/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
1
New cards
What is a scalar quantity?
Something with only magnitude
2
New cards
What is a vector quantity?
Something with magnitude and direction
3
New cards
Give 6 examples of scalar quantities.
Mass, temperature, time, distance, speed and energy
4
New cards
Give 5 examples of vector quantities.
Displacement, velocity, force, acceleration and momentum
5
New cards
When resolving, the horizontal component is always ...
... xcosθ
6
New cards
When resolving, the vertical component is always ...
... xsinθ
7
New cards
A body in equilibrium can be ...
... at rest or moving with a constant velocity
8
New cards
If a closed loop triangle can be drawn with 3 coplanar forces, what does it say about the body?
That it is in equilibrium
9
New cards
Why can the vertical component here be ignored?
P has no vertical component so the other forces must cancel the vertical component out because the body is in equilibrium
10
New cards
What is a moment?
The product of the force and the perpendicular distance from the point to the line of action of the force
11
New cards
M \=
F x d
12
New cards
What is the principle of moments?
For the body to be in equilibrium, the sum of the clockwise moments about any point equals the sum of the anticlockwise moments
13
New cards
What is a couple?
A pair of forces of equal size which act parallel to each other, but in opposite directions
14
New cards
How do you calculate the moment of a couple?
The magnitude of one force x the perpendicular distance between the lines of action of the forces
15
New cards
What are the units for a moment?
Nm
16
New cards
What is inertia?
An object's resistance to a change in velocity
17
New cards
What is weight?
The force experienced by a mass due to a gravitational field
18
New cards
w \=
m x g
19
New cards
What are the units for gravity?
Nkg^-1
20
New cards
What is the centre of mass of an object?
The point through which a single force on the body has no turning effect and where its whole weight can be considered to act through
21
New cards
How can you fin the centre of mass via experiment?
1. Hang an object freely from a point 2. Draw a vertical line downwards from the point of suspension, using a plumb bob 3. Hang the object from another point and repeat 4. Where these two lines cross is the centre of mass
22
New cards
An object will topple over if a vertical line drawn downwards from its centre of mass ...
... falls outside its base area, due to a resultant moment providing a turning force
23
New cards
An object will be more stable if it has ...
... a low centre of mass and wide base area
24
New cards
What is displacement?
How far an object has travelled from its starting point in a given direction
25
New cards
What is velocity?
The rate of change of an object's displacement
26
New cards
What is acceleration?
THe rate of change of an object's velocity
27
New cards
velocity \=
s/t
28
New cards
acceleration \=
v/t
29
New cards
What is the name of the speed of an object at a given point in time?
Instantaneous speed
30
New cards
How do you find the average speed or velocity?
Divide the total displacement by the total time
31
New cards
For a displacement-time graph, how would an accelerating object be shown?
Curved
32
New cards
If the object is accelerating at a uniform rate, the rate of change of the gradient will be ...
... constant
33
New cards

What kind of acceleration does the displacement-time graph show?
Big acceleration
34
New cards

What kind of acceleration does the displacement-time graph show?
Small acceleration
35
New cards

What kind of acceleration does the displacement-time graph show?
Deceleration
36
New cards
How can you tell if the velocity is constant on a displacement-time graph?
The graph is a straight line
37
New cards
What is the gradient of a displacement-time graph?
The velocity
38
New cards
What does it mean if, in a velocity-time graph, the graph becomes negative?
The object is travelling in the opposite direction
39
New cards
What is the gradient of a velocity-time graph?
The acceleration
40
New cards

What kind of acceleration does the velocity-time graph show?
Large acceleration
41
New cards

What kind of acceleration does the velocity-time graph show?
Decreasing accleration
42
New cards

What kind of acceleration does the velocity-time graph show?
Increasing acceleration
43
New cards

What kind of acceleration does the velocity-time graph show?
Small acceleration
44
New cards
What is the are under a velocity-time graph?
The displacement
45
New cards

The velocity-time graph shows a ball being dropped and bouncing twice. What is happening here?
Ball hits the floor
46
New cards

The velocity-time graph shows a ball being dropped and bouncing twice. What is happening here?
Ball rebounds
47
New cards

The velocity-time graph shows a ball being dropped and bouncing twice. What is happening here?
Top of bounce
48
New cards
What is the area under an acceleration-time graph?
The change in velocity
49
New cards
On an acceleration-time graph, if a \= 0, what does it mean?
The object is moving at constant velocity
50
New cards
On an acceleration-time graph, if the acceleration becomes negative, what does it mean?
The object is decelerating
51
New cards
Give 3 advantages of using a data-logger to track motion compared to traditional methods like a stopwatch.
1. Data is more accurate as you don't have to account for human reaction times 2. Automatic systems have a much higher sampling rate than humans 3. You can see data displayed in real time
52
New cards
u +at \=
v
53
New cards
(u+v)/2 x t \=
s
54
New cards
ut + at^2/2 \=
s
55
New cards
u^2 + 2as \=
v^2
56
New cards
What is free fall?
The motion of an object undergoing an acceleration of 'g'
57
New cards
What is the only force acting on an object in free fall?
It's weight
58
New cards
All objects in free fall ...
... accelerate at the same rate
59
New cards
Describe a method to calcutlate g.
1. Set up a vertical electric circuit with a switch, timer, electromagnet and trapdoor and attach a ball bearing to the electromagnet 2. Measure the h from the ball bearing to the trapdoor 3. Flick the switch to start the timer and disconnect the electromagnet 4. The ball will fall and knock the trapdoor down, breaking the circuit which stops the timer- record this time 5. Repeat 3 times and find an average, then repeat at different h 6. Plot a graph of h against t^2 to find 1/2g as the gradient
60
New cards
In an experiment to calculate g, why is it best to use a small and heavy ball bearing?
Air resistance will be so small, it can be ignored
61
New cards
In an experiment to calculate g, why is it best to have a computer automatically release and time the ball bearing's fall?
There will be a smaller uncertainty than with human reaction time
62
New cards
In an experiment to calculate g, where will the largest source of error come from?
Measuring h as the ruler will have an uncertainty of +/- 1 mm which is much larger than any error from switch delay or air resistance
63
New cards
How would you find g on a displacement-time graph?
By finding the change in gradient between two points because a \= v / t
64
New cards
Which parts of SUVAT can be predicted if an object is falling?
u \= 0 a \= -9.81
65
New cards
Which parts of SUVAT can be predicted if an object is thrown upwards?
u is not 0 a \= -9.81
66
New cards
Which parts of SUVAT can be predicted if an object is thrown downwards?
u is not 0 a \= -9.81
67
New cards
Which parts of SUVAT can be predicted if an object is thrown horizontally?
Vertical u \= 0 a \= -9.81 Horizontal a \= 0 u \= constant
68
New cards
Which parts of SUVAT can be predicted if an object is projected at an angle?
Vertical a \= -9.81 Half way through v \= 0
69
New cards
What is Newton's 1st law?
The velocity of an object will not change unless a resultant force acts on it
70
New cards
What is Newton's 2st law in words?
Acceleration is proportional to force
71
New cards
What is Newton's 2nd law as an equation?
F \= ma
72
New cards
What is the resultant force?
The vector sum of all the forces
73
New cards
In which direction is acceleration always measured in?
The same as the resultant force
74
New cards
Prove that all objects fall at the same rate, regardless of mass using Newton's 2nd Law.
F \= ma. Ignoring air resistance, weight is the only force acting on the object so W \= F \= mg \= ma. The two masses cancel out so g \= a and g is a constant for a uniform gravitational field
75
New cards
What is Newton's 3rd law?
When two objects interact, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other
76
New cards
In Newton's 3rd law, the two forces must be equal, opposite and ...
... the same type, like both gravitational or electrical
77
New cards
What are the two main types of friction?
Dry friction and fluid friction
78
New cards
What does the force of fluid friction depend on?
The viscosity of the fluid
79
New cards
As speed increases, fluid friction ...
... also increases
80
New cards
The larger the area pushing against the fluid ...
... the greater the resistance force
81
New cards
Frictional forces always act ...
... in the opposite direction to the motion of the object
82
New cards
Frictional forces can never ...
... speed things up or start something moving
83
New cards
Frictional forces convert kinetic energy into ...
... heat and sound
84
New cards
What is lift?
An upwards force on an object moving through a fluid
85
New cards
Lift happens when ...
... the shape of an object causes the fluid flowing over it to change direction
86
New cards
In which direction does lift act?
Perpendicular to the direction the fluid flows in
87
New cards
What is the terminal speed?
When the friction force equals the driving force
88
New cards
What conditions are required to reach terminal speed?
A driving force that stays the same and a frictional or drag force that increases with speed
89
New cards
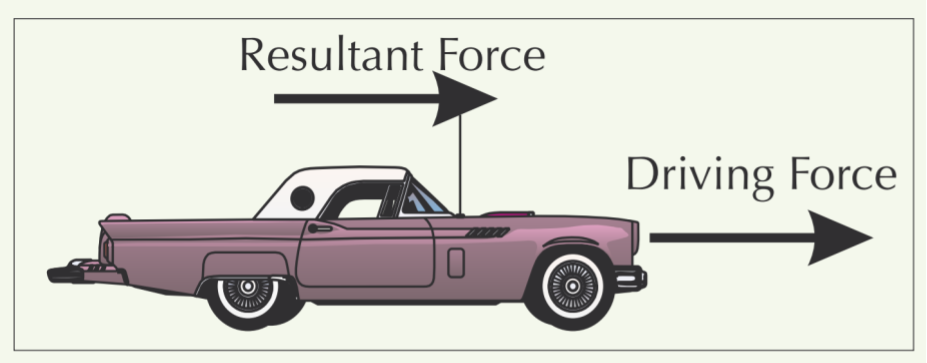
Describe this picture which shows the first stage of reaching terminal speed.
The car accelerates from rest using a constant driving force
90
New cards
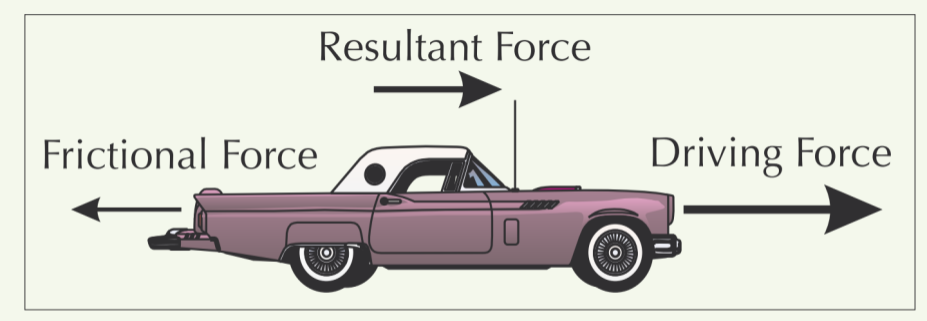
Describe this picture which shows the second stage of reaching terminal speed.
As speed increases, frictional forces increase, reducing the resultant force on the car and hence reducing acceleration
91
New cards
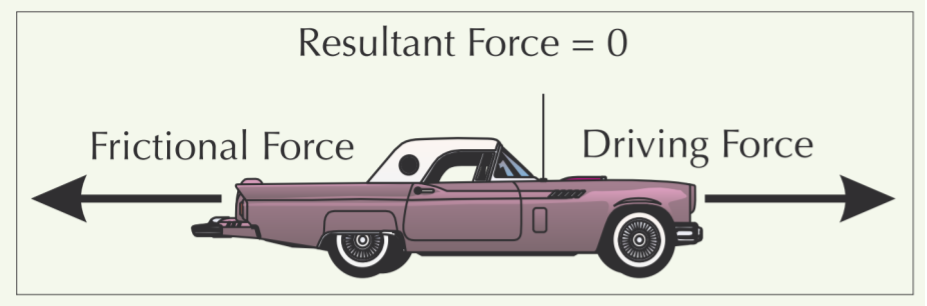
Describe this picture which shows the third stage of reaching terminal speed.
The frictional forces are now equal to the driving force and there is no resultant force and no acceleration, so the car carries on at constant speed
92
New cards
Give two ways you can increase a vehicle's maximum speed
Increasing the driving force by increasing the engines size and reducing the frictional force by making the body more streamlined
93
New cards
Describe a skydiver's fall before they open their parachute.
The skydiver's weight will initially be greater than the air resistance, but will soon speed up so the air resistance and weight are the same. The skydiver has now reached terminal speed
94
New cards
Describe a skydiver's fall after they open their parachute.
The parachute increases the air resistance so it is bigger than the skydiver's weight, slowing them down. Eventually the air resistance and weight will equal again, reaching a lower terminal speed
95
New cards
Momentum \=
mass x velocity
96
New cards
What units is momentum measured in?
kg ms^-1
97
New cards
Assuming no external forces act, momentum is ...
... always conserved
98
New cards
What is an elastic collision?
A collision where momentum and kinetic energy are conserved
99
New cards
What is an inelastic collision?
A collision where momentum is conserved, but kinetic energy isn't
100
New cards
The rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to ...
... the resultant force