Act Geometry notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Last updated 5:34 AM on 10/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
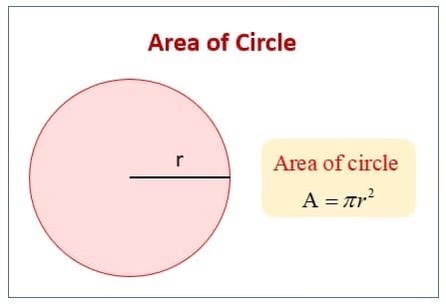
the formula for the area of a circle
*r is the radius*
2
New cards
the radius of circle
is half of the dimeter
3
New cards
to simplify a rotation in
rewrite it in fraction form
4
New cards
what does the pythagorean theorem state?
a2+b2=c2, where a and b are the lengths of the legs at a right triangle with a hypotenuse of length c.
5
New cards
the length of a line segment is?
the sum of the lengths of its parts
6
New cards
the formula for the circumference of a circle
c=2 3.14r where r is the length of the radius. the diameter of a circle is twice the length of the radius.
7
New cards
when given the circumference of c, it is:
efficient to calculate the length of the diameter d with the formula c=3.14d
8
New cards
the circumference of a circle is:
equal to 3.14 times the length of the diameter.
9
New cards
the diameter of a circle is:
a segment that passes through the center and has end points on the circle.
10
New cards
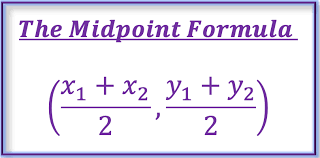
the midpoint formula
(xm,ym) = coordinates of the midpoint.
(x1, y1,) = coordinates of the first point.
(x2, y2) = coordinates of the second point.
(x1, y1,) = coordinates of the first point.
(x2, y2) = coordinates of the second point.
11
New cards
when parallel lines are intersected by another line (called a transversal) the pairs of alternate interior angles are called?
congruent
12
New cards
the measures of the interior angles sum up to?
180
13
New cards
additional notes.
the tangent ratio is only defined for an acute angle of a right triangle. so it may be necessary to first draw the missing side to complete a right
14
New cards
additional notes.
the tangent of an acute angle is a right triangle is equal to the ratio of a the length of the leg opposite the angle to the length of the leg adjacent to the angle.
15
New cards
when parallel lines are cut by transversal, the following pairs of angles are formed:
congruent corresponding angles.
congruent alternate interior angles.
supplementary consecutive interior angles.
congruent alternate interior angles.
supplementary consecutive interior angles.
16
New cards
additional notes.
the diagonal of a rectangle divides the rectangle into two congruent right triangles.
17
New cards
additional notes.
use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of a diagonal of a rectangle.
18
New cards
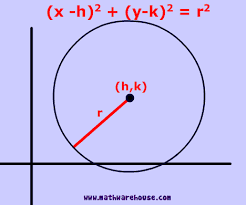
the equation of a circle in standard form:
(h, k) is the center and r is the radius
19
New cards
Sine =
Opposite/Hypotenuse
20
New cards
Cosine
Adjacent/Hypotenuse
21
New cards
Tangent
Opposite/Adjecent
22
New cards
Isosceles Triangle
an ***isosceles triangle*** is a triangle that has two sides of equal length.
23
New cards
Equilateral Triangle
an ***equilateral triangle*** is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length.
24
New cards
Right Angled Triangle
Right triangles are triangles in which one of the interior angles is 90 degrees, a right angle.
25
New cards
Rhombus
__parallelogram__ with opposite equal acute angles
26
New cards
Quadrilateral
1. a four-sided figure.
27
New cards
Trapezoid
a __quadrilateral__ with only one pair of parallel sides.
28
New cards
Parellelogram
a parallelogram is a simple quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides.
29
New cards
Pentagon
five sides and five angles
30
New cards
The formula for an area of a triangle
1/2**Base*Height*
31
New cards
Area of a Rectangle
Length\*Width
32
New cards
Length x Width x Height
Length x Width x Height = Volume of Cuboid
33
New cards
The formula for the volume of a sphere
4/3*pi*radius 3
34
New cards
Area of a trapezoid
1/2\**(Base1+base2)*Height*
35
New cards
if you have coordinates that are Vertical and Horizontal
Horizontal and vertical shifts are independent (ie, do not affect each other), so it is possible to calculate the result of both translations in a single step.
36
New cards
Area of a triangle
= 1/2 x base x height
37
New cards
angles of a triangle add up to?
180
38
New cards
area of a rectangle
A=length*width
39
New cards
Volume of a cylinder
V = πr2h