Lecture 15 | Environmental Economics
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Case Studies, Key Concepts & Terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What was the 1st step in regulating CO2 (2009)?
EPA declared as pollutant
CO2 can be regulated under the Clean Air Act. Why has it not been regulated?
expensive & complicated
What are the 3 models for regulating CO2?
toll road, permit, cap & trade
Toll Road Model
tax on emitters, more emitted, more paid
What are 3 pros of the Toll Road Model?
encourage low emissions, gov revenue, easy to determine payment
What are 4 cons of the Toll Road Model?
consumers pay, measuring emissions tricky, new taxes not popular, companies overseas
Permit Model
regulatory emission limits, fine those who exceed
The ___ Model is how we regulate most pollutants
permit
What are 3 pros of the Permit Model?
framework exists, limits adaptive/tweaked, innovation
What are 4 cons of the Permit Model?
no enforcement, sue & hold in court, expensive monitoring, companies overseas
Cap & Trade Capitalistic Model
sets limit, sell or buy credits if under/over
Under the Cap & Trade Model: if you’re ____ the limit, you can buy credits from others to avoid a fine. If you’re ___ the limit, you can sell credits to others.
over, under
What are 5 pros to the Cap & Trade Model?
market driven, carrot & stick, businesses profit, no motivation overseas, has reduced acid rain
What has the Cap & Trade Model worked for in the past?
reducing SO2 emissions
Describe the Carrot & Stick Analogy
get hit with stick = penalty, eat carrot = reward
What are 4 cons to the Cap & Trade Model?
consumers pay, bureaucracy, strict enforcement, gaming system
Regulating CO2 comes with a ____ for any of the 3 models
cost
Why should we reduce CO2 emissions now instead of later?
cost of switching rises the longer we depend on fossil fuels
Environmental Economics
control pollutions, promote sustainability in capitalistic & democratic society
How is environmental economics tailored for both a capitalistic and democratic society?
provide incentives, people must want it
Environmental economics is not just about money, but _____
persuasion
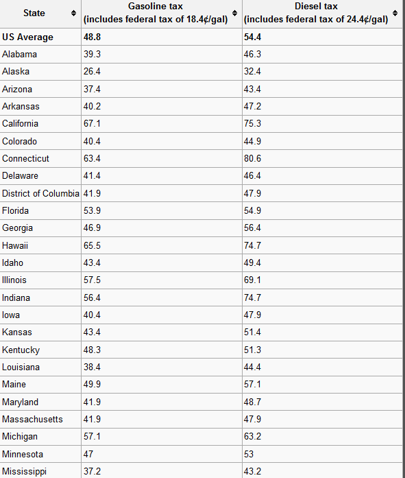
What 2 reasons does the gas tax exist for?
raise gov money, discourage driving
How does environmental economics use tools?
encourage people/business to behave how we want
How does a gas tax change behaviors?
less driving = less pollution, congestion, wear & tear
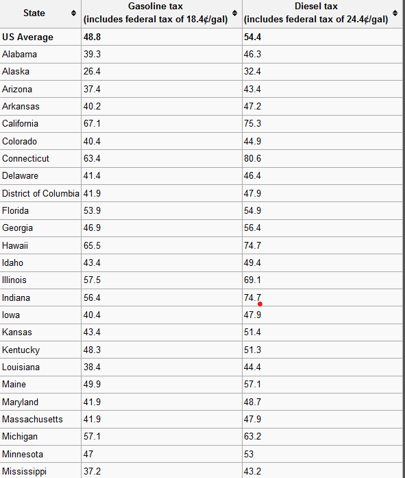
Why does California have a much higher gas tax than Georgia?
more drivers
Policy Instruments
tools to change behaviors
List 4 examples of policy instruments:
laws, regulations, taxes, subsidies
Why do we want to change people/businesses’ behaviors? What can these reasons be?
want to protect something, tangible or intangible

Tangible Factor & Examples
can see & touch, house, wetland, stream

Intangible Factors & Examples
not physical, has value, sunset, clean water, fun
Explain why clean water is considered intangible:
sense of safety
We want to protect tangible & intangible factors because they have _____. Therefore, we want to ____ behaviors that remove/reduce this. Damage steals from _______
value, discourage, all of us
What 3 behaviors should be discouraged?
businesses polluting, people damaging property, disrespecting Precautionary Principle
What is an example of a response to disrespecting the Precautionary Principle?
criminal penalties
Both ____/____ and ____/____ should be used to change behaviors
stick/punishments, carrot/encouragement
List some examples of giving the “carrot” and “stick”
gas prince increase, tax incentives for electric; new taxes on CO2, sell unused credits; flunking exam from not showing up, easy grade for showing up

Consider the example of river pollution in class. Why are environmental economics decisions so complex?
balancing rights & costs
In what way can valuing environmental damage be easy?
damage calculates monetary value
In what ways can valuing environmental damage be difficult?
damage to experience/enjoyment, putting cost on intangible, hard to come up with #

Provide some policy instruments to deal with the following scenarios:
Waste in your yard
Hazardous retention ponds
Sunbathing nude
Stream pollution that kills deer
Fertilizer in pond/algal blooms
Amazon Deforestation
fines, permits/limits, laws, fines, subsidies for monitoring, tax incentives/cap & trade
Commons Resource
openly available, benefits us all

List 5 Common Benefits the Environment Provides:
clean air/water, food, raw resources, recreation, pollution processing
Why is a private company harming the environment such a major cause for concern?
no benefits, services worth 3-33 trillion
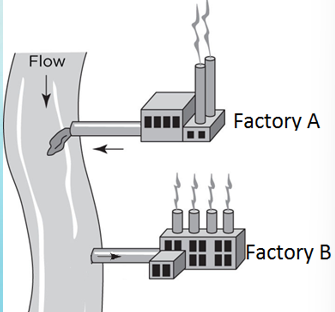
Factory A & B both depend on this river to produce the same product. If A pollutes the river upstream of B, what are the potential consequences on Factory B?
spend money to clean, has to charge customers more, driven out of business
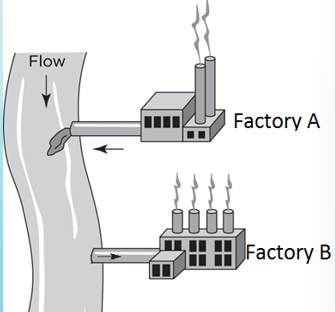
What is an important interaction between private entities?
interfering with access to same benefit
What are two competing factors of recreation?
common good to enjoy, too much traffic = damage
How do we reduce the threat of recreation on the environment? In what ways does this help the environment?
admission fees, repair damage & discourage visitors
What 4 reasons cause people to damage the environment?
SIBR: think short term, individual profit instead of group loss, no belief that benefits will end, resources grow slowly
Explain what is meant by people think short term:
don’t give up benefits today to prevent losses in 100 years
Explain what is meant by individual profit is valued more than aggregate loss:
more concerned about personal benefit than costs of the group
Which reason that people harm the environment does Tragedy of the Commons fall under?
individual profit over aggregate loss
Explain what is meant by no one really believes environmental benefits will end:
nimby, no one thinks their impact is large
Explain why environmental resources growing slowly causes people to harm the environment:
have to get it before someone else does