Axial Musculature
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
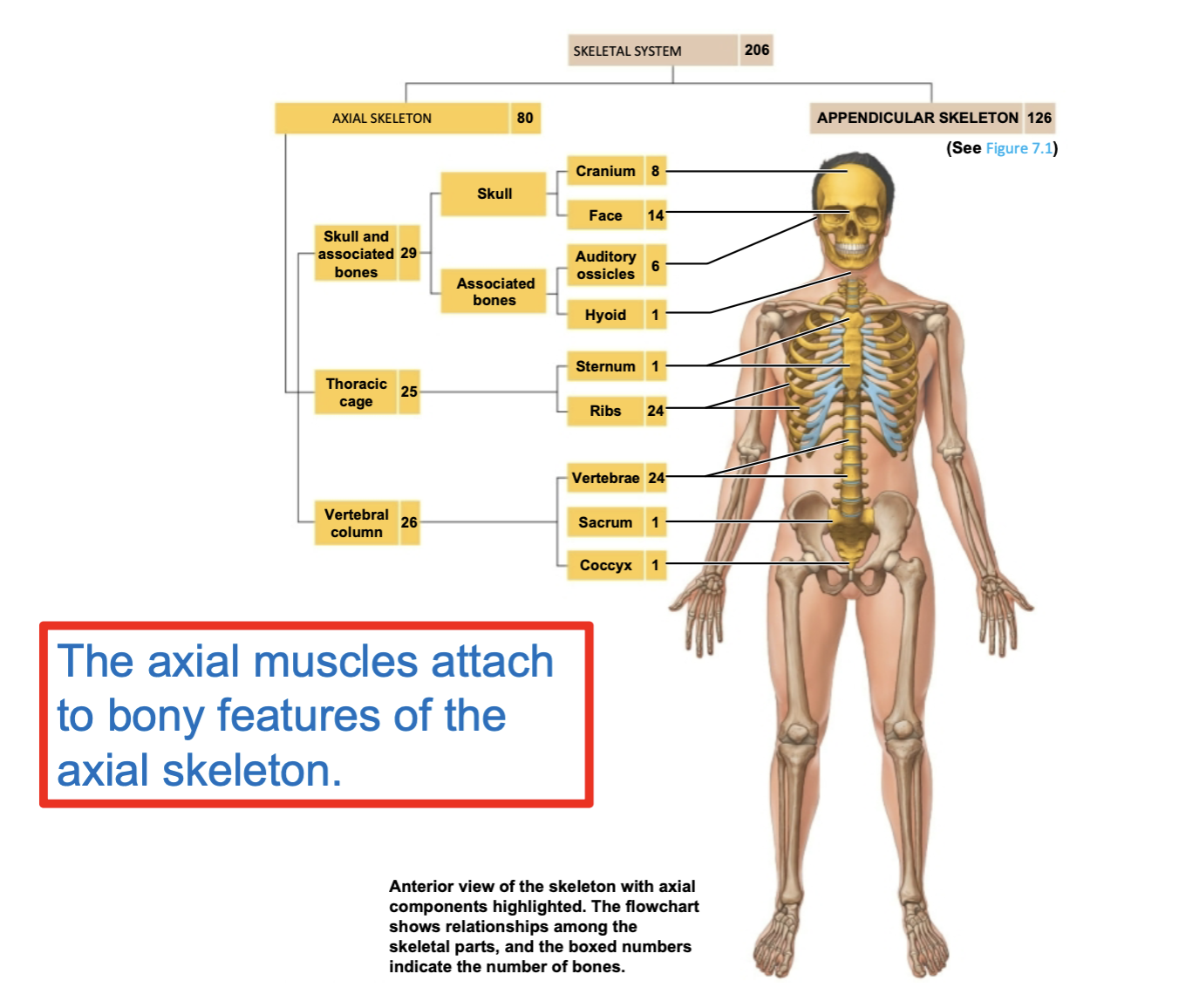
Axial skeleton includes:
bones of the skull
sternum
ribs
vertebrae
sacrum and coccyx
and other associated bones of this part of human skeleton
Axial musculature
muscles that position the head and vertebral column
muscles that move the rib cage
Axial muscles subdivided into:
appendicular musculature
Axial musculature (muscles that stabilize or move appendicular skeleton)
Axial muscles can be placed into 4 groups based on location or function:
muscles of head and neck
muscles of vertebral column
muscles of rib cage and lateral walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities (thoracic and abdominal wall muscles)
muscles of the pelvic floor
Muscles of head and neck
muscles of facial expression — move skin of face
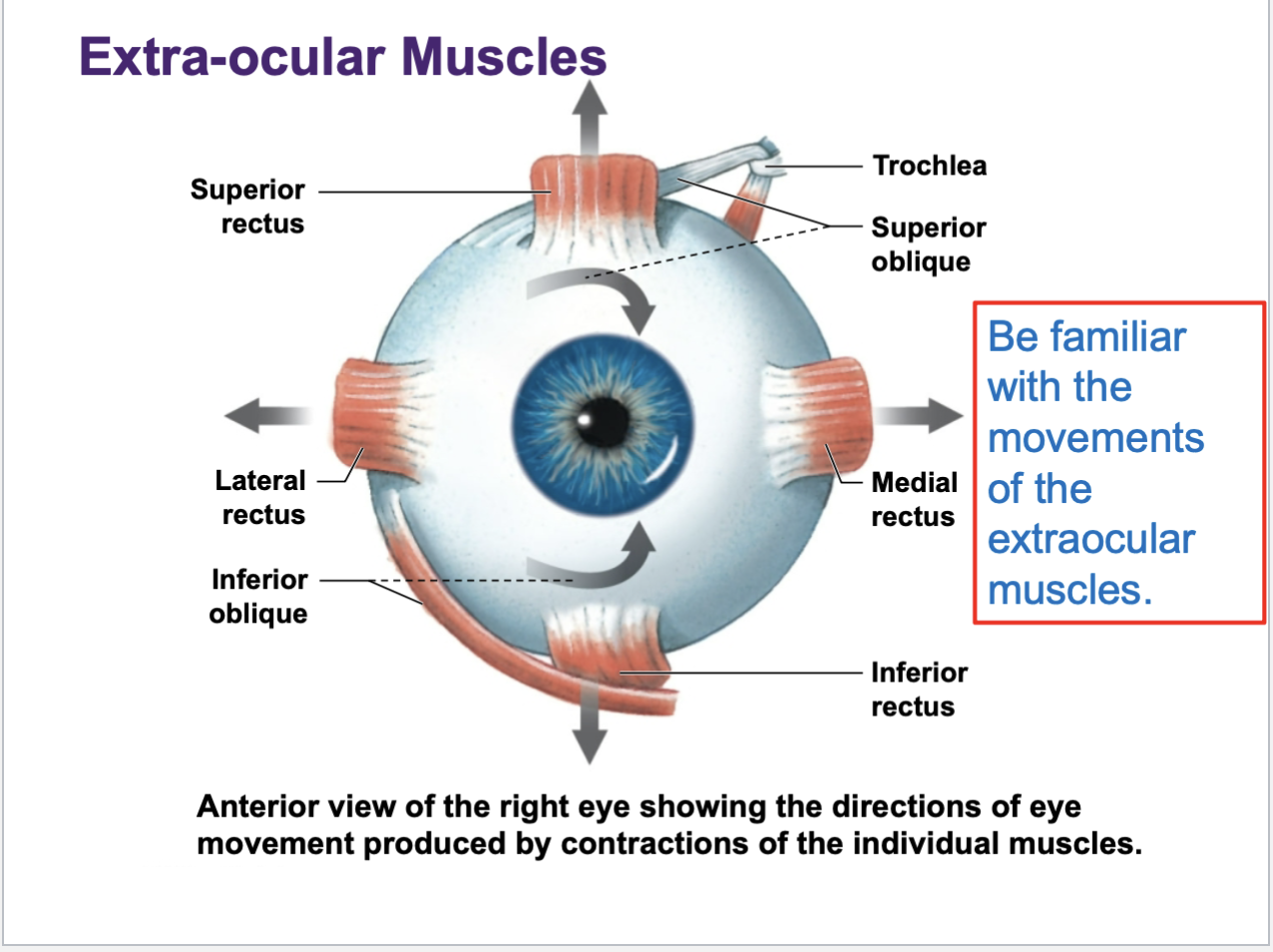
extra-ocular muscles — move the eyeball
muscles of mastication — chewing muscles
muscles of the tongue
muscles of pharynx — throat wall
anterior muscles of the neck
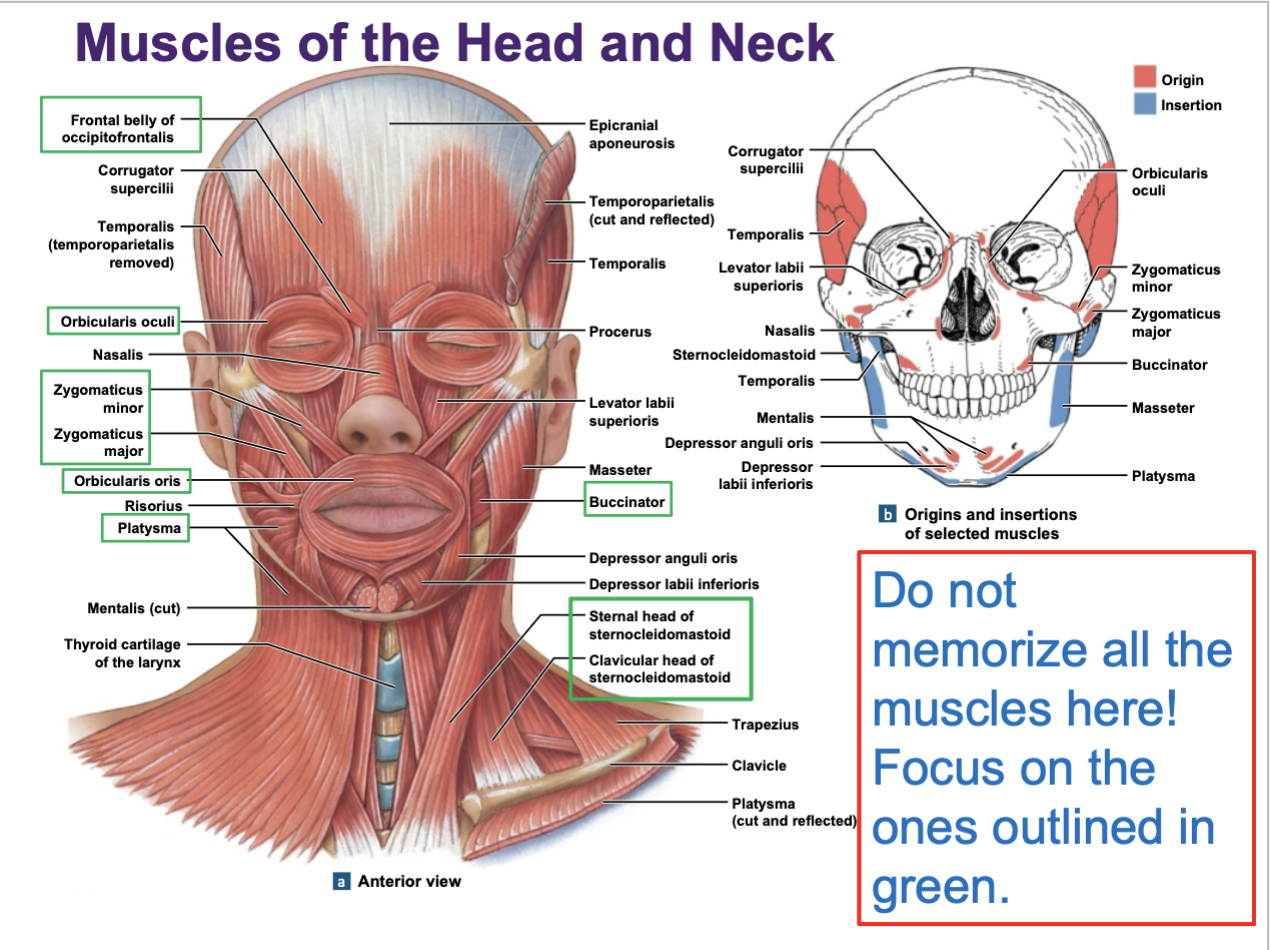
What cranial nerve innervates these expressive muscles?
Facial nerve (CN VII)
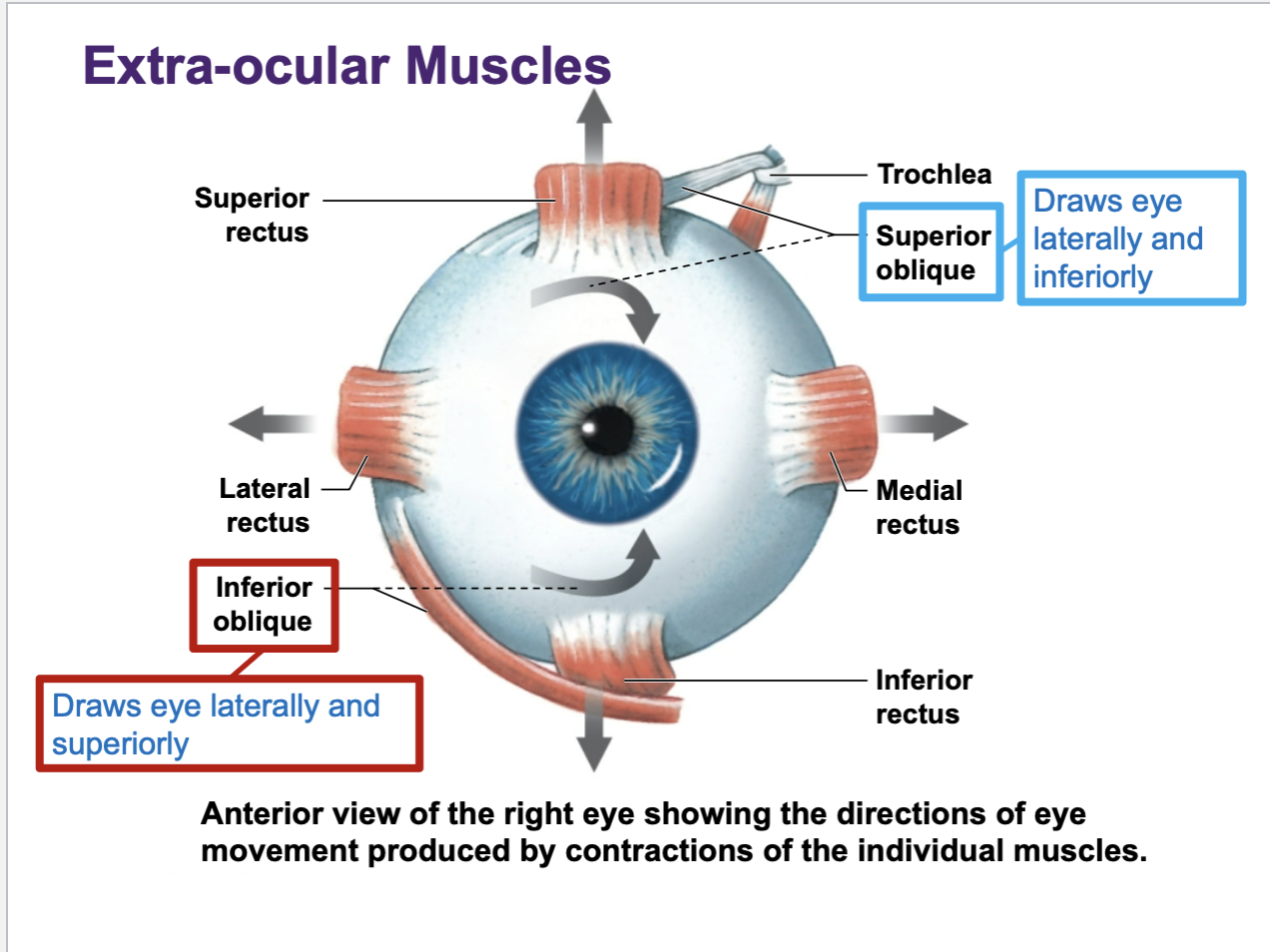
Superior oblique
draws eye laterally and inferiorly
Inferior oblique
draws eye laterally and superiorly
Facial expression focus on these: occipitofrontalis, orbicular oculi, orbicularis oris, zygomaticus major/minor, platysma
Important neck muscles to know is
sternocleidomastoid
Buccinator muscle
located in the cheeks (the walls of the mouth). It helps to circulate food around the mouth as we chew.
It can help generate suction as we drink through a straw. It keeps the cheeks tight so that we do not bite down on the inside wall of the mouth when we chew. This muscle distends out when you see someone playing the trumpet. The name ‘buccinator’ translates as trumpeter.
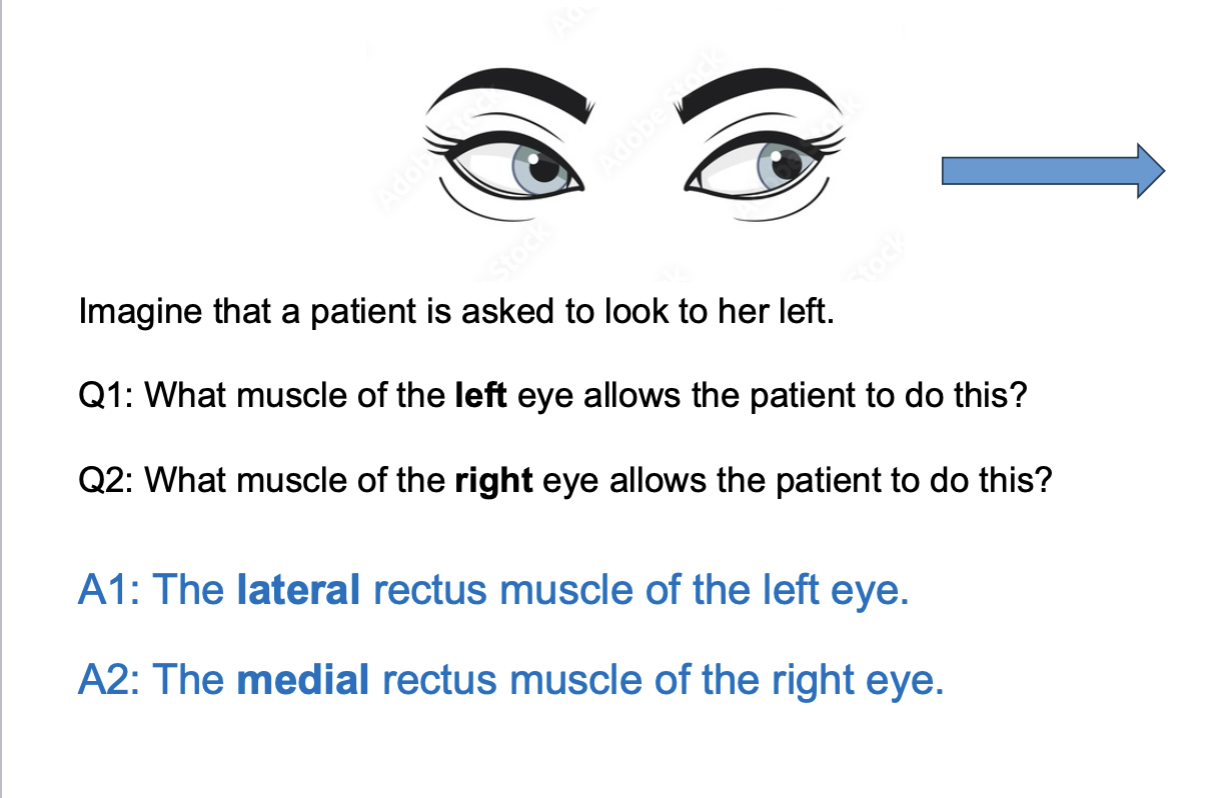
Muscles that physically move the eyeball around are known as the …
extraocular muscle
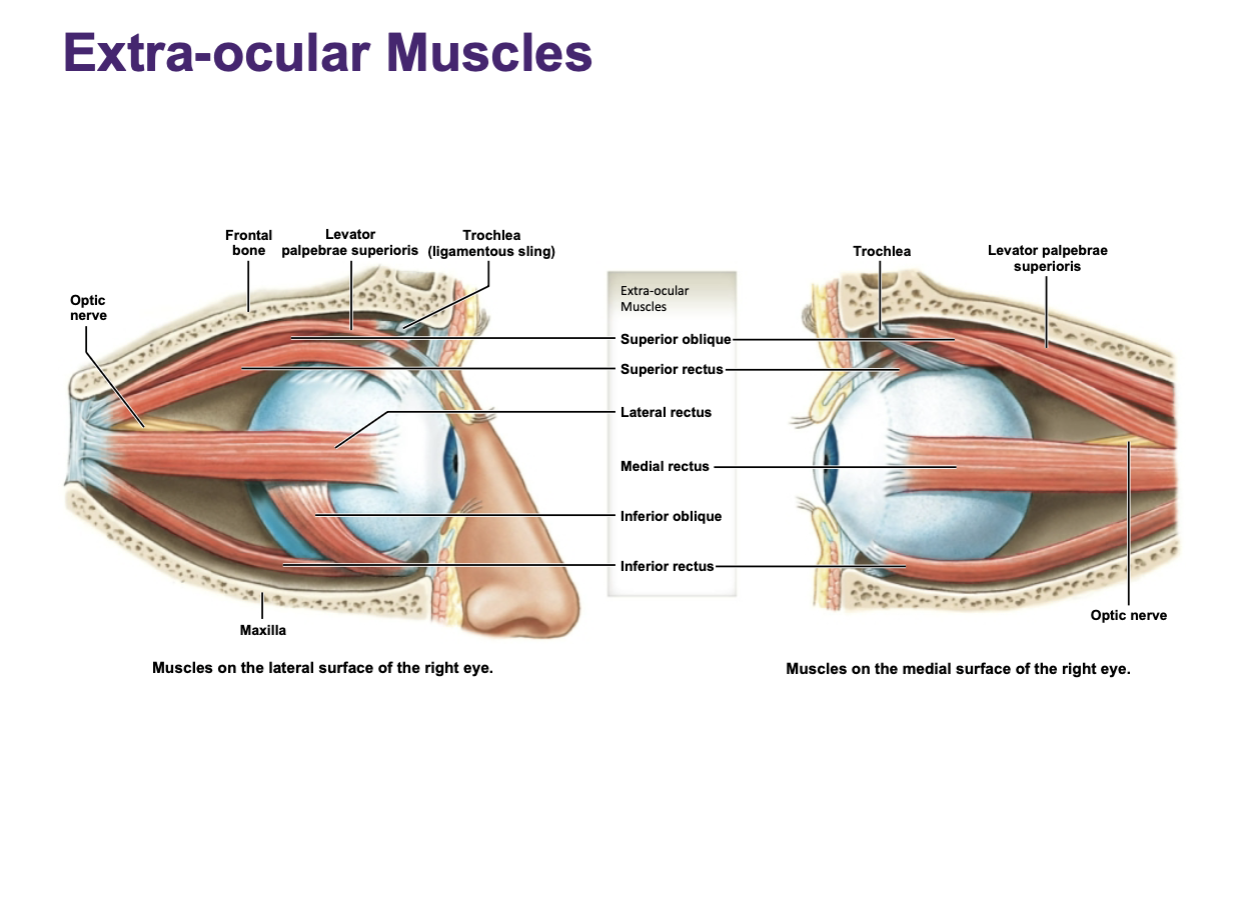
Mastication
chewing
Main chewing muscles:
masseter
temporalis
pterygiods
for the most part, these muscles are working to elevate the mandible so that the biting surfaces of the teeth are brought closer together to crush food
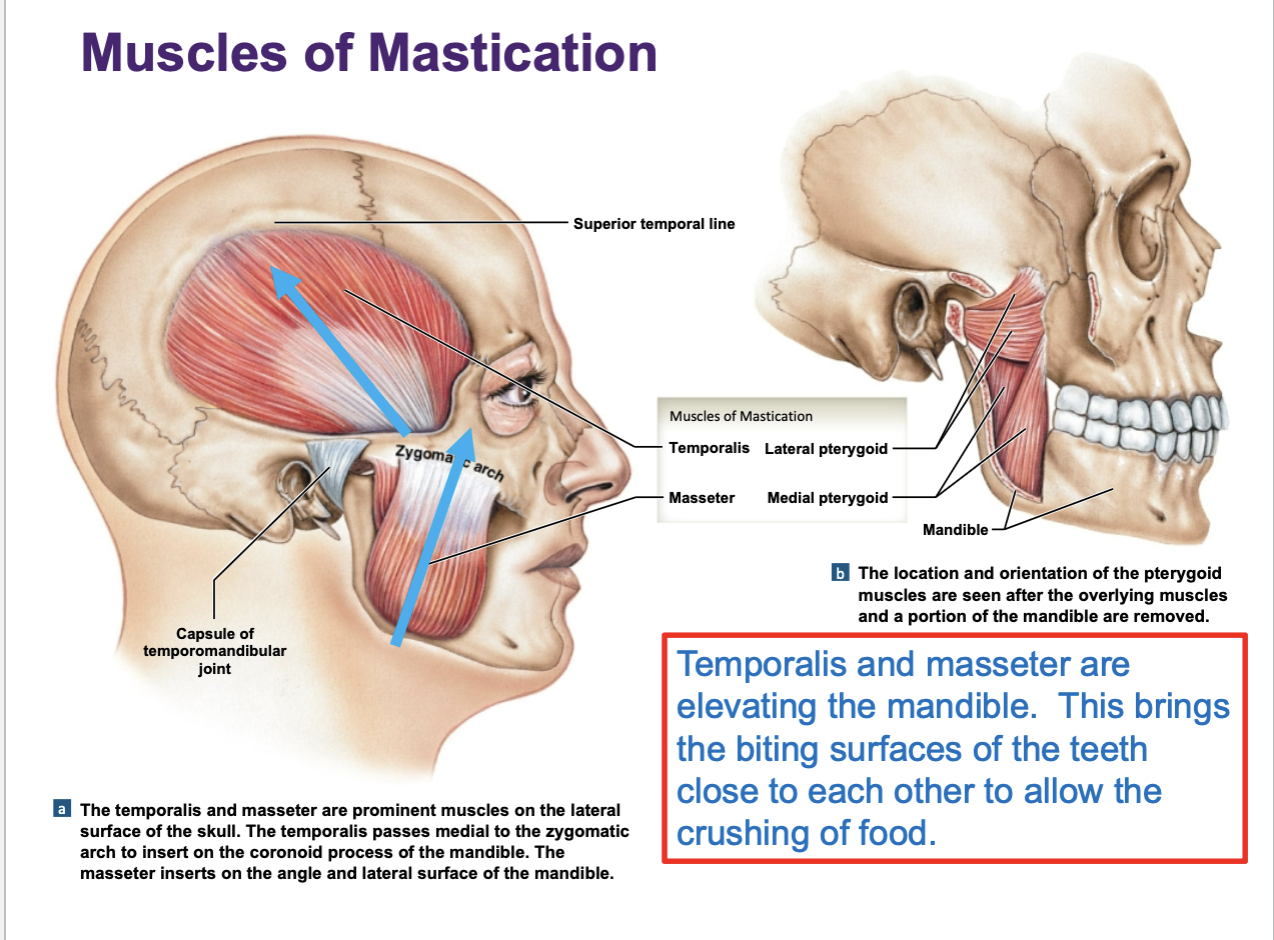
muscles of tongue will have a …
“-glossus” in their names
they help w mechanical breakdown of food along w swallowing
muscles in the throat wall usually have …
“-pharyngeus” in their names
they work to move food from mouth into the esophagus
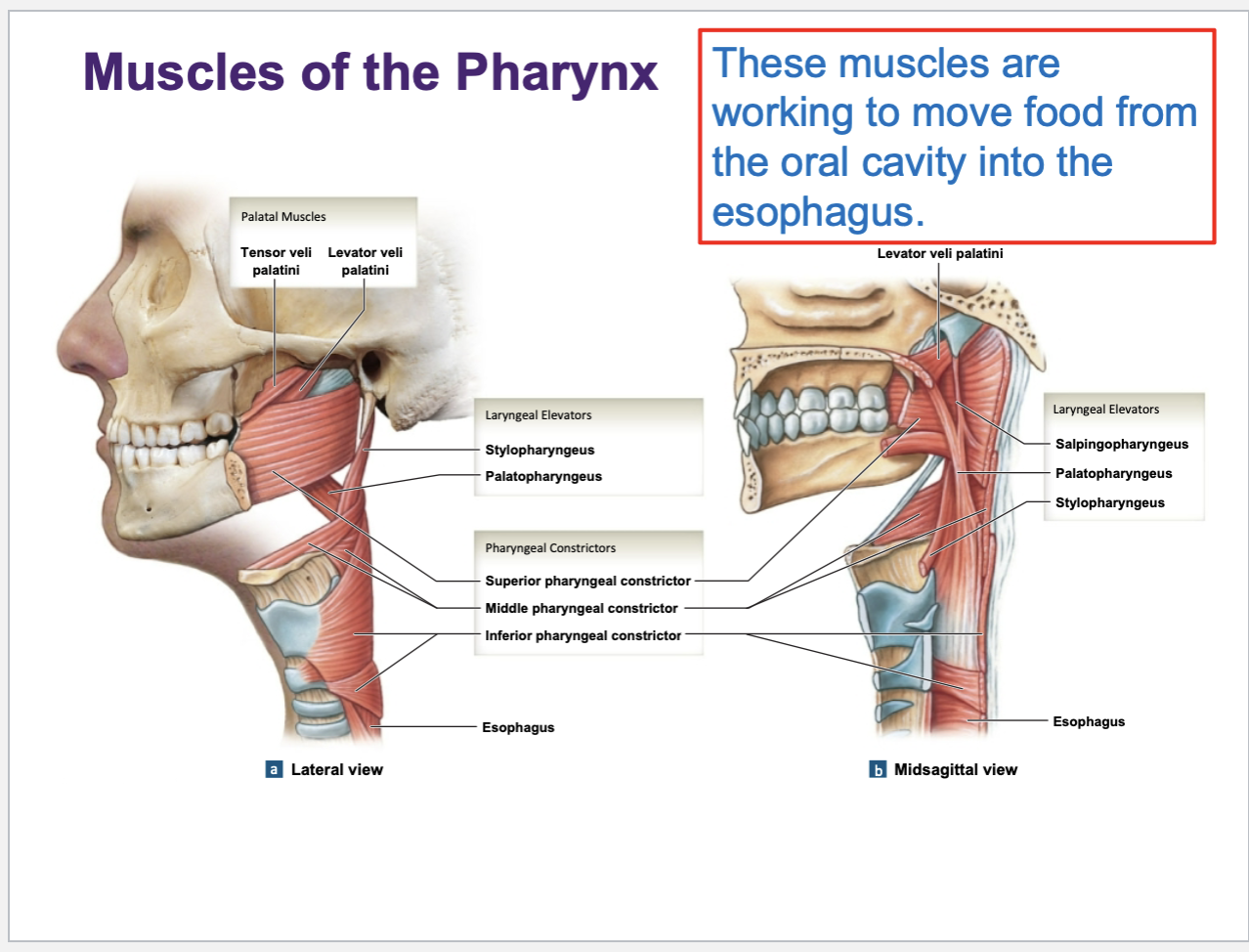
Muscles operating on the skull and spinal column:
These muscles are found in pairs: (one on the left and one on the right)
Bilateral contraction: muscle is contracting on both sides of the body at same time
unilateral contraction: muscle is actively contracting on one side of the body
ipsilateral: body moves toward the SAME side on which contraction takes place
Contralateral: body moves toward the OPPOSITE side on which contraction takes place
Bilateral and unilateral actions of the sternocleidomastoid muscle in the neck…
Uni - ipsilateral lat flexion; contralateral lat rotation
Bi - flexion/extension of neck (depends on position/context); forced breathing
Name main suprahyoid muscles: DMS
Digastric: elevates the hyoid bone and helps depress the mandible during swallowing and chewing.
Mylohyoid: forms the floor of the mouth and elevates the hyoid and tongue during swallowing.
Stylohyoid: elevates and retracts the hyoid bone, elongating the floor of the mouth during swallowing.
Their main functions (they elevate and fixate the hyoid bone and larynx in the neck)
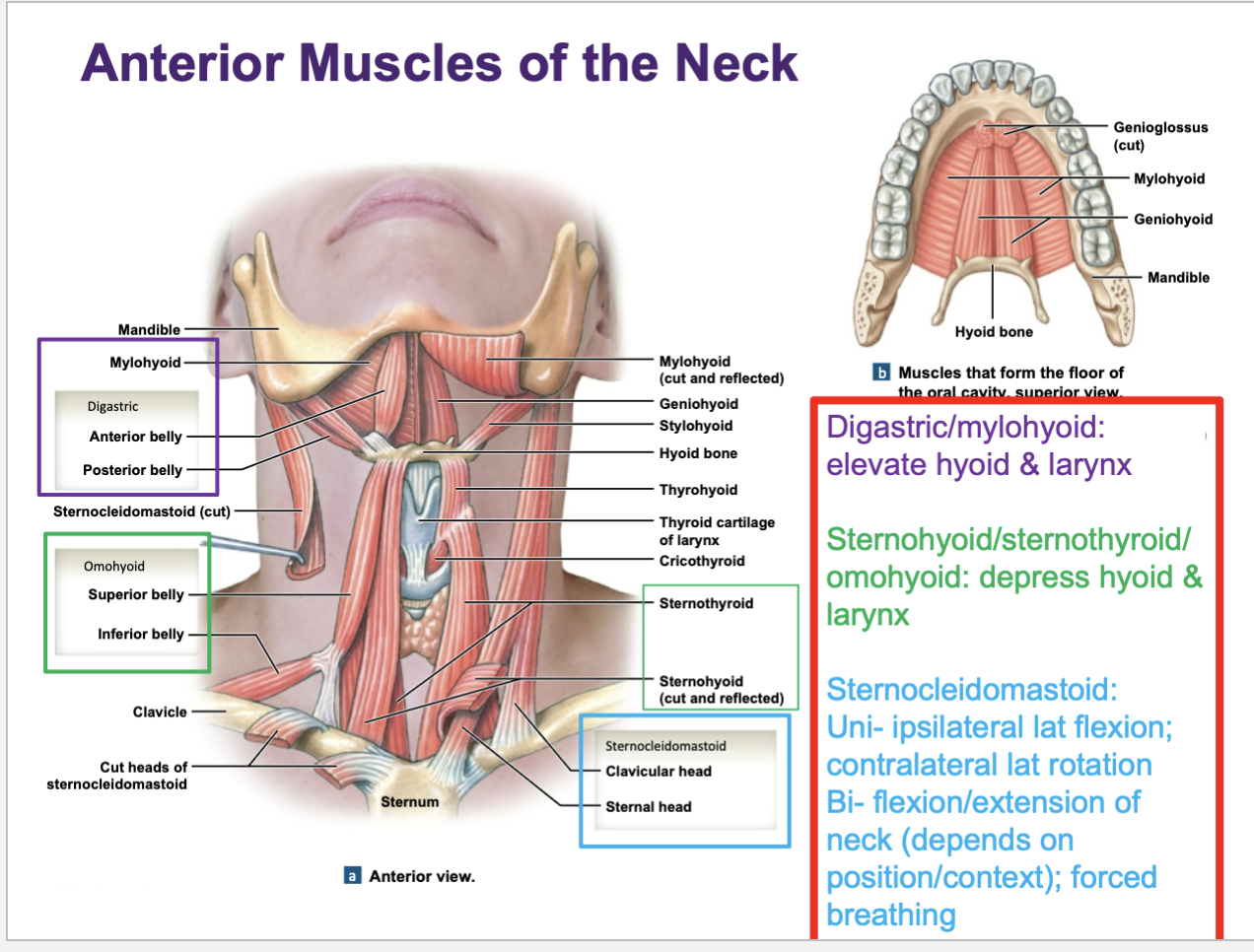
Name main infrahyoid muscles: SOTS
Sternohyoid: depresses the hyoid bone after it has been elevated during swallowing.
Omohyoid: depresses, retracts, and stabilizes the hyoid bone.
Sternothyroid: depresses the thyroid cartilage (larynx) during swallowing.
Thyrohyoid: depresses the hyoid bone and elevates the larynx.
Erector spinae muscles of the back
powerful group of muscles consisting of 3 vertical columns of muscle running up and down the length of the back.
From lateral to medial: iliocostalis ; longissimus ; spinalis
Iliocostalis column
has segments that are attaching to portions of the ribcage
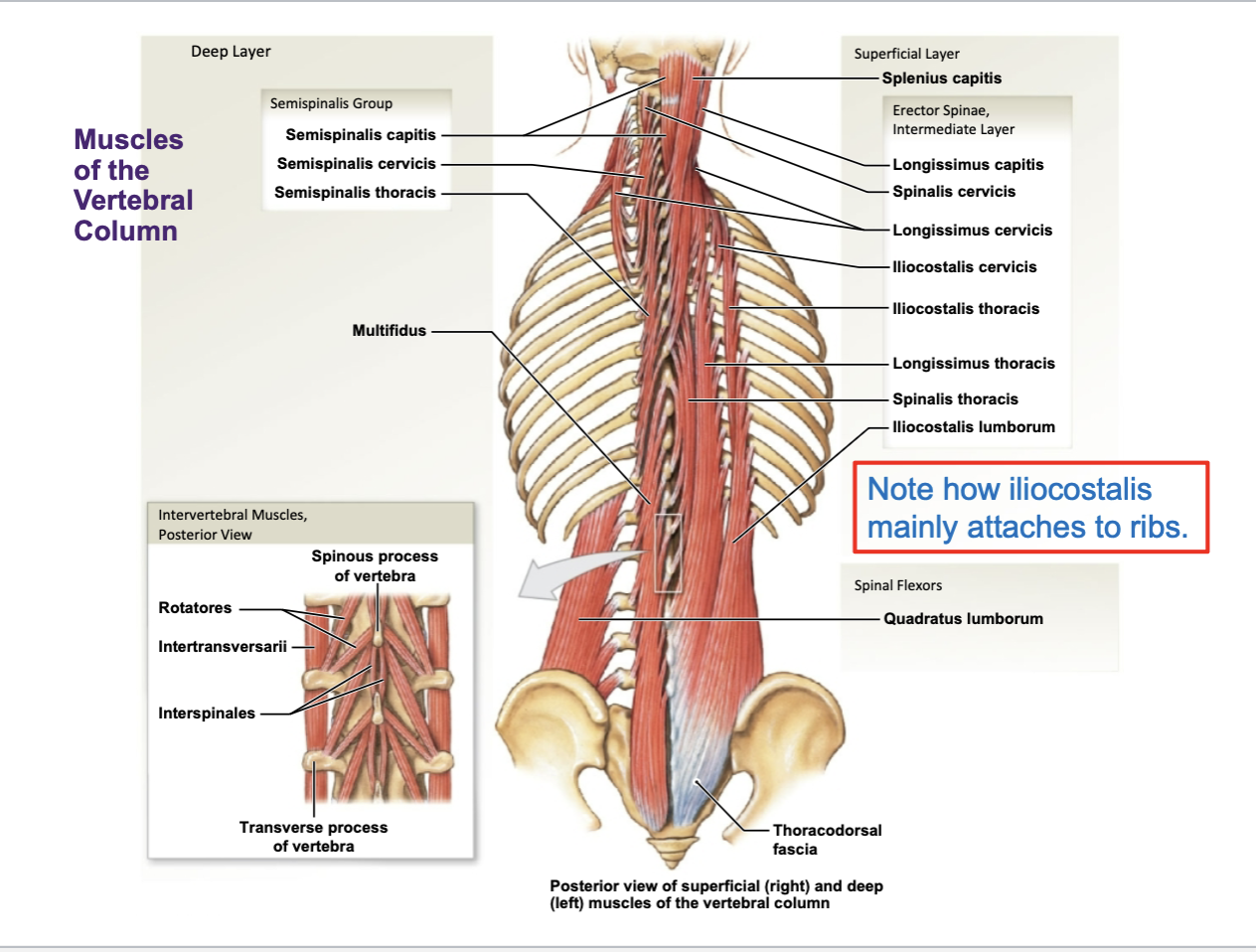
Bilateral and unilateral actions of erector spinae group:
bilateral movements: extension of vertebral column (straightening the back); in practice, these muscles are actually working to reduce the movement of the spinal column
Unilateral movements: lateral flexion and rotation to the same side
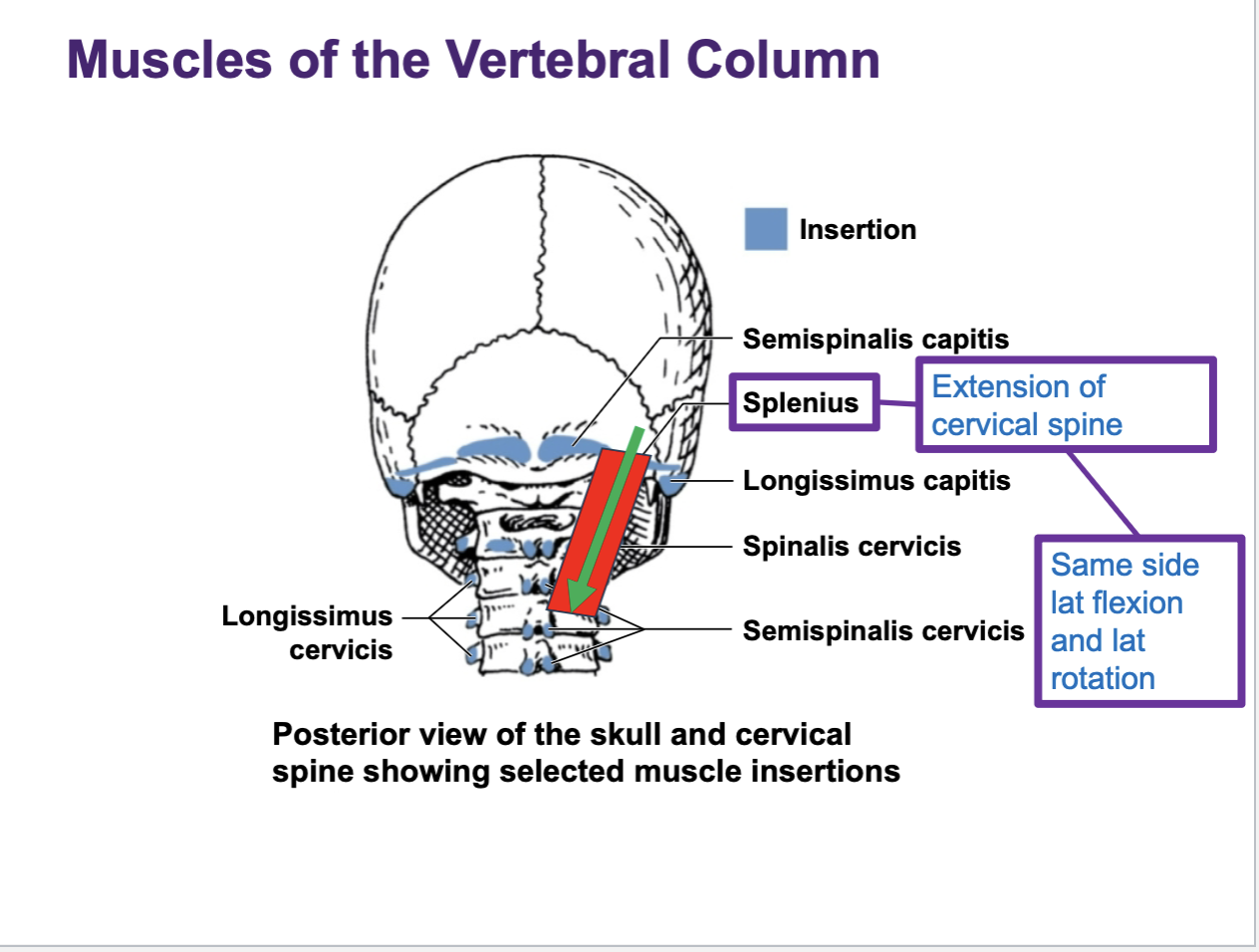
The splenius muscle are found
along the back of the neck
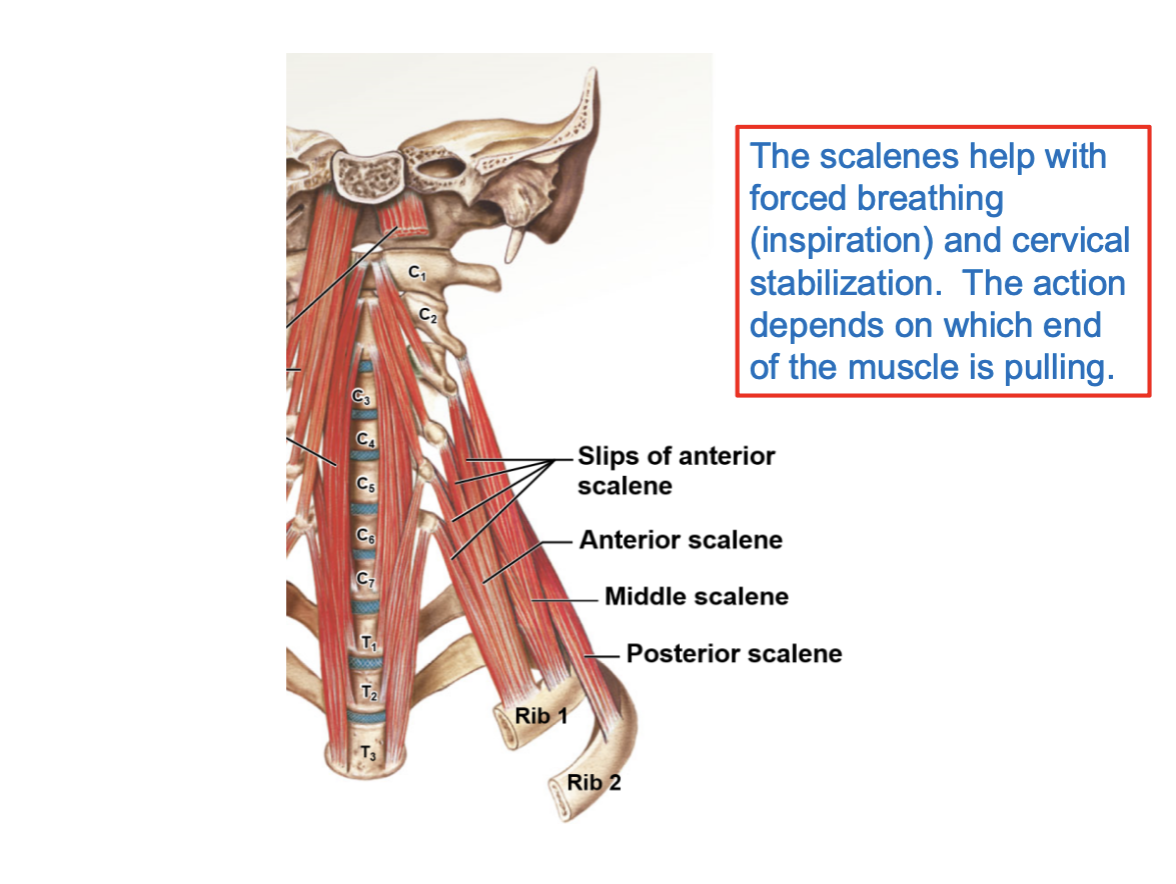
Scalene muscles exist in 3 segments:
anterior, middle, posterior
What do Scalene muscles help with
depending on the context and what movement the body is creating, they can assist with forced inspiration. Or, they can help w stabilizing the cervical spine or laterally flexing it.
Remember: the roots of the brachial plexus emerge b/w the anterior and middle scalene muscles
Intercostal muscles are
thin layers of muscle found in b/w adjacent ribs. Main ex of this group are the external intercostals and internal intercostals. The externals assist w forced inspiration. internals assist with forced expiration
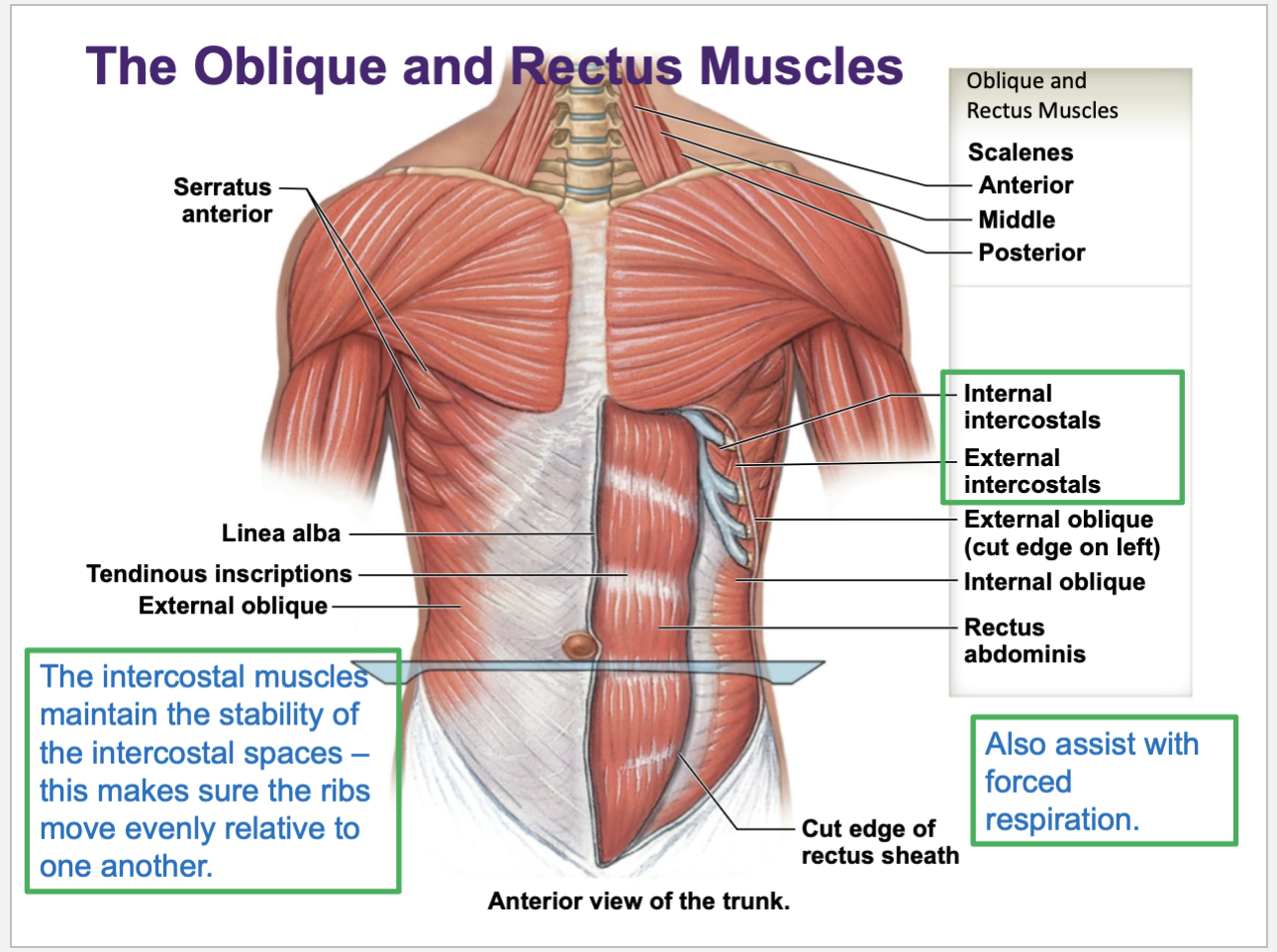
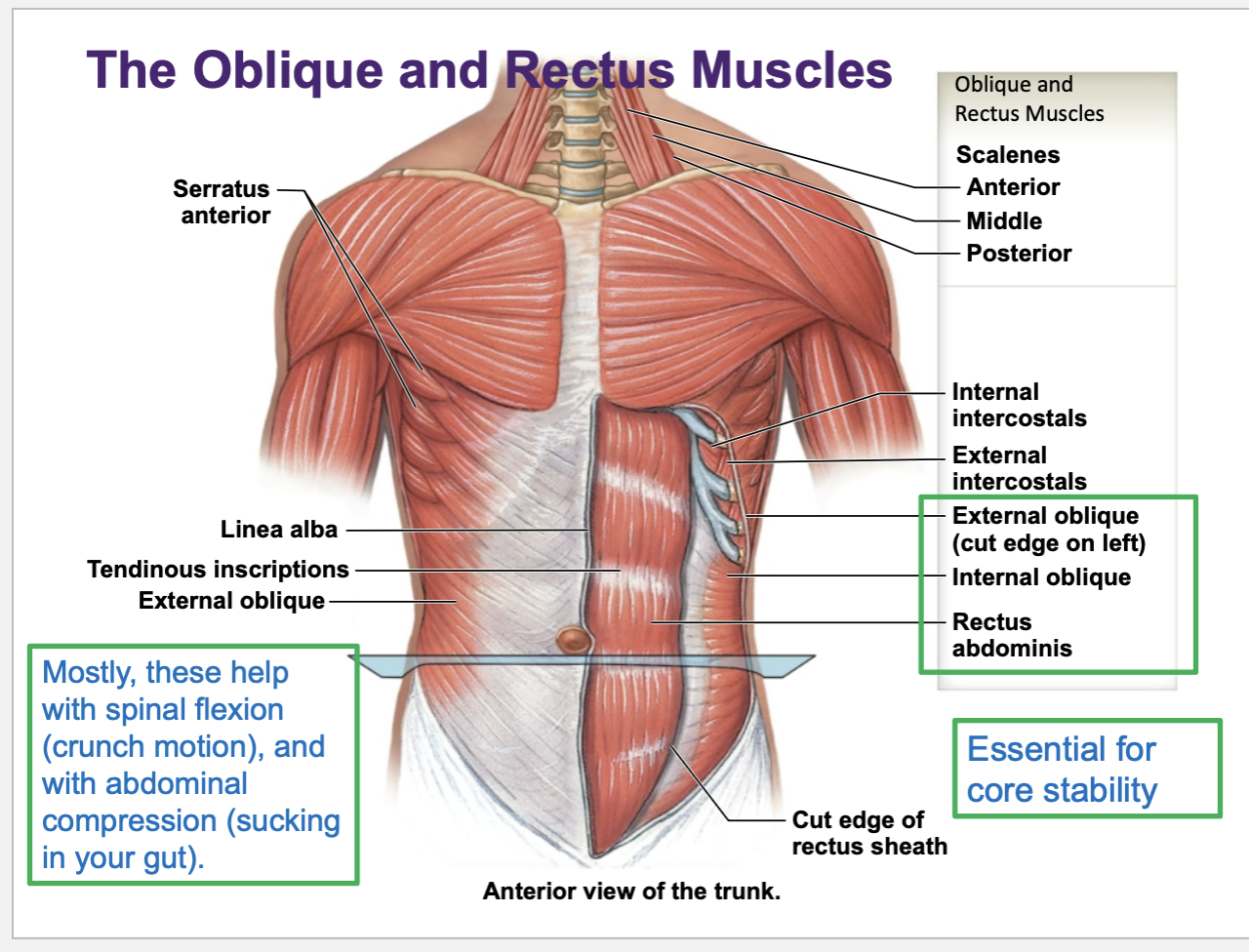
Names and functions of muscles of abdominal wall
External oblique, internal oblique, the rectus abdominis, and the transversus abdomens are the main abdominal wall muscles
Common functions are to flex the torso, or to create compression of the torso — this is basically sucking in ur gut to tighten the abdominal wall
movements of diaphragm during phases of breathing
Inspiration (Inhale/breathing in) = diaphragm contracts & descends to allow for lung expansion
Expiration (Exhale/breathing out) = diaphragm relaxes & ascends to allow for lung contraction
Weakness of pelvic floor muscles can lead to …
urinary incontinence (urinary leakage)