Physics Forces and Motion
1/44
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1. set up the apparatus
2. measure the length of the spring without any hanging masses
3. hang a mass of 100g on the spring
4. measure the new length of the spring
5. calculate the extension of the spring (the increased length)
6. repeat and increase the mass in increments of 100g
* this is because force = change in momentum/time
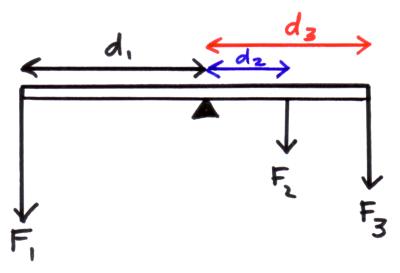
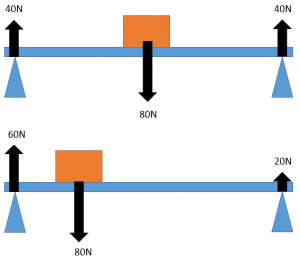
* Moment = force x perpendicular distance from pivot
* If the the distance from the pivot is less on the left hand side it means that the force must be greater to compensate for the larger distance on the right hand side.
average speed =
distance moved / time taken
acceleration =
change in velocity/time taken
how to find the acceleration from a velocity-time graph
measure the gradeint
how to determine the distance traveled
area underneath the graph
v² =
u² + 2 a x s
final speed =
initial speed + 2 x acceleration x distance moved
difference between an electrostatic force and a gravitational force
electrostatic force is a force between objects that have an electric charge, gravitational force is a force between objects that have mass
electrostatic force can either be attractive or repulsive and is much greater than gravitational force
electrostatic force depends on the medium whereas gravitational force is independent of the medium
what is the difference between a vector quantity and a scalar quantity?
Vector quantities have magnitude and direction, like velocity. Scalar quantities have only magnitude, like speed.
what is friction?
a force that opposes motion
f = (relationship between unbalanced force, mass and acceleration)
m x a
weight =
mass x gravitational field strength
stopping distance =
thinking distance + braking distance
factors that affect thinking distance
speed, alcohol, tiredness
factors that affect braking distance
icy road, worn tires, speed
how do falling objects reach terminal velocity?
As an object falls, air resistance increases until it equals gravity. At this point, the object stops accelerating and reaches a constant speed called terminal velocity.
As an object falls, air resistance increases until it equals gravity. at this point, the object stops accelerating and reaches a constant speed called terminal velocity