CAM Psych 2 FINAL: Personality disorders; psychogenic nonepileptic seizure; dissociative disorders; somatic symptom and related disorders; sexual dysfunctions and paraphilic disorders
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Cluster A personality d/o include
Schizoid
Schizotypal
Paranoid PD
Cluster A personality d/o - patients seem
Peculiar, eccentric, or withdrawn
SUSPECT mnemonic paranoid personality d/o
SUSPECT
Spousal infidelity suspected
Unforgiving (bears grudges)
Suspicious
Perceives attacks (and reacts quickly)
Enemy or friend? (suspects associates and friends)
Confiding in others is feared
Threats perceived in benign events
DISTANT mnemonic for schizoid personality disorder
DISTANT
Detached or flattened affect
Indifferent to criticism or praise
Sexual experiences of little interest
Tasks done solitarily
Absence of close friends
Neither desires nor enjoys close relationships
Takes pleasure in few activities
Schizoid =
AVOID
Difference b/e schizotypal and schizoid
Schizotypal PD has eccentric behavior or magical thinking,
Schizoid does not
Schizotypal PD tx
Psychotherapy with development of social skills
Cognitive-perceptual disturbances may benefit from low-dose second generation antipsychotic short-term
ME PECULIAR mnemonic schizotypal PD
ME PECULIAR
Magical thinking
Experiences unusual perceptions
Paranoid ideation
Eccentric behavior or appearance
Constricted or inappropriate affect
Unusual thinking or speech
Lacks close friends
Ideas of reference
Anxiety in social situations
Rule out psychotic or autism spectrum disorders
Cluster B personality disorders include
Antisocial
Borderline
Histrionic
Narcissistic
Cluster B personality disorders seem
Emotional
Inconsistent
Dramatic
Antisocial PD mnemonic: CORRUPT
CORRUPT
Cannot conform to law
Obligations Ignored
Reckless disregard for safety
Remorseless
Underhanded (deceitful)
Planning Insufficient (impulsive)
Temper (irritable and aggressive)
Antisocial PD begins in childhood as ___ d/o
Conduct d/o
- May have hx of hurting animals or starting fires
- Violations of law
Tx of Antisocial PD
Psychotherapy usually ineffective
Medication for comorbid conditions
Antisocial PD - inc morbidity d/t
SUD
Trauma
Suicide
Homicide
Antisocial pd - individual must be how old for dx?
18
What is the most commonly diagnosed personality disorder in psychiatric inpatients?
A.Antisocial personality disorder
B.Borderline personality disorder
C.Schizoid personality disorder
D.Schizotypal personality disorder
B.Borderline personality disorder
Tx of choice for BPD
Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT)
Meds are adjunct—mood stabilizers and low-dose antipsychotic meds
- Of the personality disorders-- meds are most successful in BPD
IMPULSE mnemonic BPD
IMPULSIVE
Impulsive
Moodiness
Paranoia or dissociation under stress
Unstable self-image
Labile intense relationships
Suicidal gestures
Inappropriate anger
Vulnerability to abandonment
Emptiness (feelings of)
Histrionic PD defense mechanism of
REGRESSION -> revert to childlike behaviors
ACTRESS mnemonic Histrionic personality disorder
ACTRESSS
Appearance focused
Center of attention
Theatrical
Relationships (believed to be more intimate than they are)
Easily influenced
Seductive behavior
Shallow emotions
Speech (impressionistic and vague)
Describe the course of narcissistic PD
Chronic, higher incidence of depression in midlife due to their high value on power and youthfulness, depressed when do not get recognition they think they deserve
GRANDIOSE mnemonic for Narcissistic PD
GRANDIOSE
Grandiose
Requires attention
Arrogant
Need to be special
Dreams of success and power
Interpersonally exploitative
Others (unable to recognize feelings/needs of)
Sense of entitlement
Envious
What are the cluster c disorders
Avoidant
Dependent
Obsessive compulsive PD
in cluster C PD, Patients seem
fearful or anxious
Most effective tx for avoidant PD
Psychotherapy
Avoidant PD mnemonic: CRINGES
CRINGES
Criticism or rejection preoccupies thoughts in social situations
Restraint in relationships due to fear of shame
Inhibited in new relationships
Needs to be sure of being liked before engaging socially
Gets around occupational activities with need for interpersonal contact
Embarrassment prevents new activity or taking risks
Self viewed as unappealing or inferior
Problems with what in dependent personality d/o
employment - difficulty acting independently or w/o close supervision
Tx of choice for dependent personality d/o
Psychotherapy ToC
Others
- CBT with assertiveness and social skills training
- Meds for comorbid anxiety, depression
RELIANCE mnemonic for dependent personality d/o
RELIANCE
Reassurance required
Expressing disagreement difficult
Life responsibilities assumed by others
Initiating projects difficult
Alone (feels helpless and uncomfortable when alone)
Nurturance (goes to excessive lengths to obtain)
Companionship sought urgently when a relationship ends
Exaggerated fears of being left to care for self
Obsessive compulsive PD mnemonic SCRIMPER
SCRIMPER
Stubborn
Cannot discard worthless objects
Rule obsessed
Inflexible
Miserly
Perfectionistic
Excludes leisure due to devotion to work
Reluctant to delegate to others
Dissociative amnesia often after
trauma - stressful and traumatic events
Mainstay tx for dissociative amnesia
Psychotherapy
Meds not effective
Dissociative amnesia DSM - an inability to recall...
An inability to recall important autobiographical information, usually of a traumatic or stressful nature, that is inconsistent with ordinary forgetting.
Dissociative amnesia- what is w/ dissociative fugue
Apparently purposeful travel or bewildered wandering that is associated with amnesia for identity or for other important autobiographical information.
Characteristics of somatic sx disorder
Distressing somatic sxs:
- Abn thoughts
- Feelings
- Behaviors
- Multiple somatic sxs (pain is common)
Dx criteria for somatic sx d/o: one or more somatic sxs that are
Distressing or result in significant disruption of daily life
Dx criteria for somatic sx d/o: B. Excessive thoughts, feelings, or behaviors related to the somatic symptoms or associated health concerns as manifested by at least one of the following:
1. Disproportionate and persistent thoughts about the seriousness of one's symptoms.
2. Persistently high level of anxiety about health or symptoms.
3. Excessive time and energy devoted to these symptoms or health concerns.
somatic sx d/o persistent specification is marked if duration is more than ___ months
6
Specification criteria for somatic sx d/o: Persistant and ____
With predominant pain: This specifier is for individuals whose somatic symptoms predominantly involve pain.
Tx for somatic sx d/o
- One PCP -> have regularly scheduled visits
- Address psychological issues slowly due to resistance for MH care
- Psychotherapy: CBT
- Pharmacotherapy: Dual action agents (5-HT and NE) TCA, SSRIs/SNRIs
Conversion d/o also known as
Functional Neurological Sx D/o
Tx conversion d/o
Education
CBT w/ or w/o PT
Common sxs of conversion d/o
Paralysis
Weakness
Blindness
Mutism
Sensory complaints (paresthesias)
Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES), globus sensation
Conversion d/o DSM: A. One or more symptoms of altered voluntary ____ or ___ function.
Motor or sensory
Difference b/e PNES and epileptic seizure
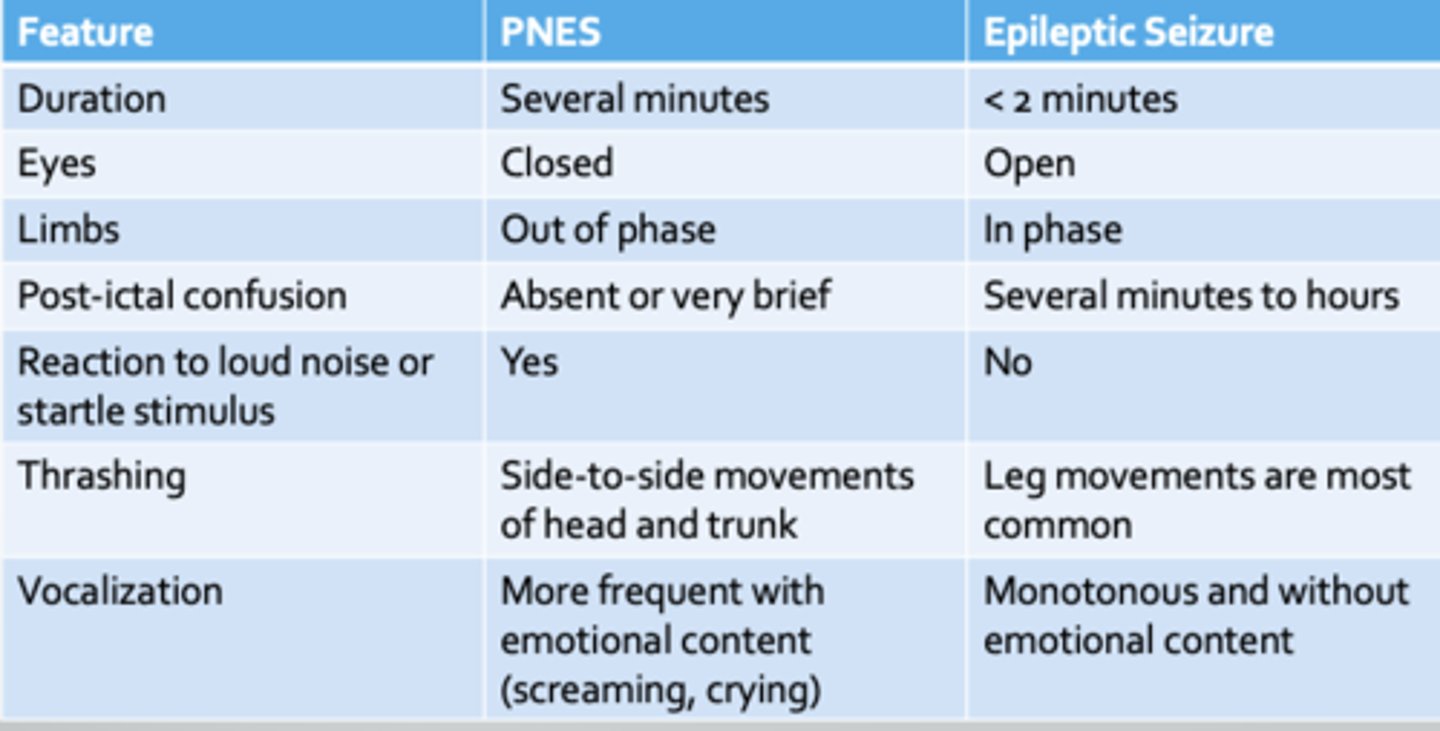
Illness anxiety d/o tx
- One PCP and regularly scheduled visits
- Psychotherapy-CBT
- Treat comorbid depression, anxiety—SSRIs, etc.
Illness anxiety d/o: ___ with having or acquiring a serious illness
Preoccupation
Are somatic sxs present in illness anxiety d/o
Somatic symptoms are not present or, if present, are only mild in intensity. If another medical condition is present or there is a high risk for developing a medical condition (e.g., strong family history is present), the preoccupation is clearly excessive or disproportionate.
Describe DSM for Illness anxiety d/o
A. Preoccupation with having or acquiring a serious illness.
B. Somatic symptoms are not present or, if present, are only mild in intensity. If another medical condition is present or there is a high risk for developing a medical condition (e.g., strong family history is present), the preoccupation is clearly excessive or disproportionate.
C. There is a high level of anxiety about health, and the individual is easily alarmed about personal health status.
D. The individual performs excessive health-related behaviors (e.g., repeatedly checks his or her body for signs of illness) or exhibits maladaptive avoidance (e.g., avoids doctor appointments and hospitals).
Facticious d/o - common deigned sxs
Hallucinations, depression,
fever,
infection, hypoglycemia, abdominal pain, seizures,
hematuria
Mgnt of factious d/o
Collect collateral info
Collaborate w/ other providers
non-threatening confrontation
Facticious d/o used to be known as
Munchhausen syndrome by proxy
Facticious disorder DSM - (A-C)
A. Falsification of physical or psychological signs or symptoms, or induction of injury or disease, associated with identified deception.
B. The individual presents himself or herself to others as ill, impaired, or injured.
C. The deceptive behavior is evident even in the absence of obvious external rewards.
is malingering considered a mental illness
no
What is malingering
The conscious feigning for sxs for some secondary gain
- Avoiding incarceration
- Monetary compensation
Mgnt of malingering
Neuropsych testing to assess further
TOMM (test of memory malingering)
Validity Indicator Profile (VIP)
Manage to pt underlying distress
Gentle confrontation may be necessary - pt may leave AMA
Gender dysphoria - the pathology is NOT the gender diversity itself, but rather the
Distress caused by incongruence b/e the gender a person was assigned to at birth and their identified gender
tx of gender dysphoria
- gender affirming psychotherapy
- Tx comorbid conditions with psychotherapy, meds as appropriate
- Family support
- Support patient in transitioning they desire (society, medical, surgical)
Surgical sex reassignment for gender dysphoria can be performed when
performed after living 1 year in the desired gender role and 1 year of continuous hormone therapy
At least how many months duration of gender dysphoria to get dx
6 months
tx for Female sexual interest disorder
- CBT, relationship therapy, trauma therapy depending on issues
- Education, Stimulation, Devices to increase erotic stimuli
- Meds - FDA approved two medications for hypoactive sexual desire d/o in premenopausal women - Filbanserin and Bremelanotide
Filbanserin is a
Serotonin receptor 1a agonist / serotonin receptor 2A antagonist
What inc hypotension and LOC if taken with Filbanserin
Alcohol
- skip dose if >3 drinks
Bremelanotide selectively activates
Melanocortin receptor NTs
SE of Bremelanotide
Inc BP
Decreasing HR
Focal hyperpigmentation
Nausea
Can you drink alc when on Bremelanotide
yes
How many sxs do you need to be dx with FSIAD
at least 3
tx for male hypoactive sexual desire d/o
CBT
Relationship therapy
Trauma therapy depending on issues
Stress reduction
Meds for male hypoactive sexual desire d/o
Testosterone therapy
Bupropion
Treatment of erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation if present—
- Sildenafil (Viagra)
- Tadalafil (Cialis)
Treatment of premature ejaculation: SSRIs
Dx of male hypoactive sexual desire d/o
Persistently or recurrently deficient (or absent) sexual/erotic thoughts or fantasies and desire for sexual activity. The judgment of deficiency is made by the clinician
what is paraphilic d/o
Engagement in unusual sexual activities and/or preoccupation with unusual sexual urges or fantasies for at least 6 months that are---acted on with a nonconsenting person or cause significant distress or impairment in functioning
MC paraphilic d/o
voyeuristic and pedophilic d/o
Poor prognostic for paraphilic d/o
Multiple paraphilias, onset at early age, comorbid SUD, high frequency of behavior, referral by law enforcement
Dx for paraphilic d/o
Difficult
Can use CBT
Social skills training
12 step programs
Group therapy
Controversial medications used to decrease sex drive and fantasies in paraphilic d/o
Antiandrogens, long-acting gonadotropin-releasing hormones, SSRIs, naltrexone
Fetishistic d/o
Sexual arousal from either the use of nonliving objects (pantyhose/shoes) or non genital body parts
Sexual masochism d/o
sexual arousal from act of being humiliated, beaten, bound, or made to suffer
Sexual sadism d/o
sexual arousal from the physical or psychological suffering of another
Exhibitionistic d/o
Sexual arousal from exposure of one's genitals to an unsuspecting person
Frotteuristic d/o
Sexual arousal from touching or rubbing against a nonconsenting person