Codon Study Path
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Given the following traits, which domain does these traits belong to:
Does transcription and translation
Starts protein synthesis with unmodified methionine
Cell membranes have structural features that are distinct
Does not have cell walls
Reproduces via cell division
Does not have nuclei in cells
Unicellular
Archaea, because of the distinct cell membrane.
Imagine you could travel back in time and observe the last common ancestor of all eukaryotes. What are three characteristics you would find in this organism?
Membrane bound organelles, including a nucleus.
Mitochondria as a result of endosymbiosis.
Cytoskeleton and phagocytosis capability
Highly organized form with complex structures.
Which traits do bacterias have
DNA (circular, found in nucleoid), Cell Division through binary fission, Simple cytoskeleton system
Endosymbiont
An endosymbiont is an organism that lives inside another organism, forming an endosymbiosis.
BENEFIT and COST of an endosymbiotic relationship to HOST CELL
BENEFIT: New metabolic pathways for energy production COST: Energy needed to coordinate cellular functions due to differences in genetic material.
BENEFIT and COST of an endosymbiotic relationship to ENDOSYMBIONT
BENEFIT: Stable environment and protection from environment.
COST: Genomic reduction.
Synapomorphies
when species share the same traits that originated in a common ancestor and are inherited by all its descendants.
species share the same synapomorphies when
1. They come from a common ancestor that first evolved that trait. 2. The trait is inherited by all descendants of that ancestor. 3. The trait is not found in species outside of the group (it is unique to that lineage).
In a phylogenic tree: Synapomorphies
if two species or groups are part of the same branch/clade, and the branch is marked by a specific trait, that trait is a synapomorphy for that clade.
Profiera
Sponges
- Asymmetrical or radial
no true tissues
pores and canals for filter feeding
no nervous system and sessile as adults.
Cnidaria
Jellyfish, corals, sea anemones, hydra
radial symmetry
tissues present: ectoderm and endoderm
body structure: polyp (sessile) and medusa (free swimming)
single opening- gastrovascular cavity
Chordata
Vertebrates
Bilateral symmetry
tissues: ectoderm (protection + perception), mesoderm (movement + support + reproduction), endoderm (digestion + breathing + internal organ linings)
BENEFITS and CONSEQUENCES: Radial Symmetry
Good for sessile animals
efficient feeding from all sides
Limited mobility
no cephalization
less suited for complex behaviours.
BENEFITS and CONSEQUENCES: Bilateral Symmetry
enables cephalization
supports directional movement and favours complex organ systems and complex behaviours
requires more developmental complexity
needs greater energy investment in maintaining symmetry and organ systems.
more specialized body part = more prone to breaking
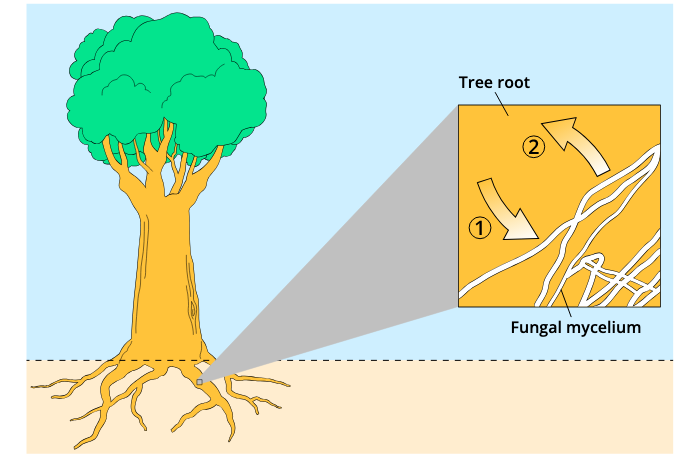
Tree to fungus (1); Fungus to Tree (2)
(1) C6H12O6 ; (2) hydrogen phosphate, water, nitrate
Cellulose cell walls
Provides structural support to plant (composed of carbohydrates and located outside cell membrane).
Chloroplasts
Allows for plant to capture sunlight and make own food.
Vascular tissue
Allows for more efficient water transport from roots to shoots.
Cuticle
Prevents plant from drying out with waxy covering.
Stomata
Allows for gas exchange.
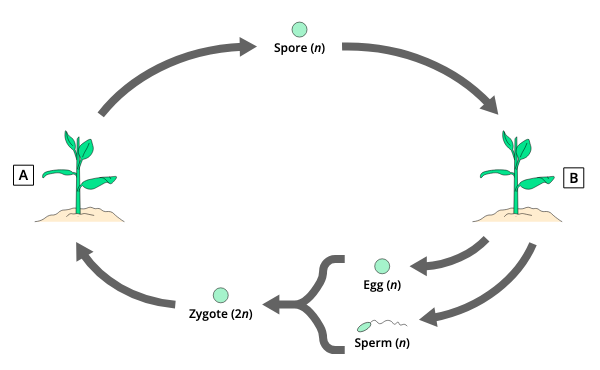
A ; B
Sporophyte- A is the diploid (2n) phase that produces spores ; Gametophyte- B is the haploid (n) phase that produces gametes
What part of a virus evolves?
its genetic material DNA or RNA changes though mutations.
Why do viruses evolve?
to better infect hosts, avoid immune systems, or resist treatments.
What cases natural selection in viruses?
Host immune responses, antiviral drugs, and how well the virus spreads.
Is evolving a reason to say viruses are alive?
Yes, because all living things evolve.
Why do some scientists say viruses are not alive?
Because viruses can’t grow or reproducce without a host.
What is one trait you can use to tell a virus from a bacterium?
Viruses cannot reproduce on their own—they must infect a host cell. Bacteria can reproduce by themselves using binary fission.
What is one trait you can use to tell a virus or bacterium from a protist?
Protists are eukaryotes, so they have a nucleus. Virus and bacteria do not have a nucleus.
Should you give an antibiotic if the infection is caused by a protist?
No, antibiotics only work on bacteria, not on protists like the one that causes malaria. You would need an antiparasiticor antimalarial drug instead.
Order of events on how the influenza virus life cycle occurs
Viral surface protein binds to a protein in the plasma membrane of the human cell.
A piece of the plasma membrane pieces off, bringing the vision inside the cell.
Viral RNA is inserted into the host cell nucleus.
RNAs are made during the viral genome.
RNA that codes for viral proteins move from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Viral proteins are synthesized using human ribosomes, tRNAs, and amino acids.
Copies of the viral genome are assembled into new visions, which bud from the cell’s plasma membrane.
Newly made visions travel to new host cells.