SBI3U plants unit review
1/67
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
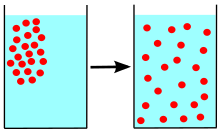
diffusion
molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
moves down a concentration gradient
is diffusion passive or active
passive
rate of diffusion can by influenced by
temperature
concentration gradient
diffusion is mainly used for
gases and liquids
osmosis
movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable memberone
is osmosis passive or active
passive
Osmosis is mainly used for
water and solutes
solute
a substance that's dissolved in a solvent
solvent
the substance that is doing the dissolving
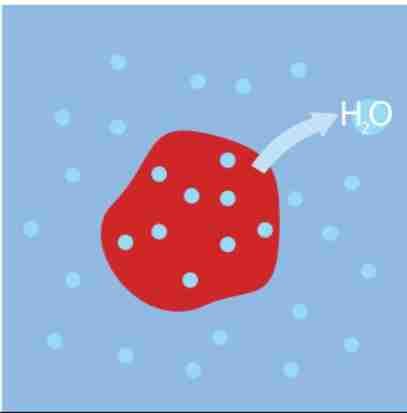
hypertonic
solute concentration is higher than that inside the cell
there's a net flow of water out of the cell
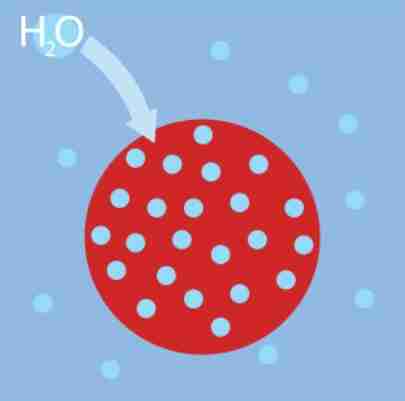
hypotonic
solute concentration outside the cell is lower than inside the cell
there will be a net flow of water into the cell

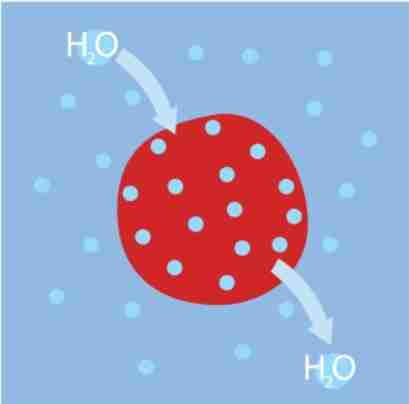
isotonic
solute concentration outside the cell is the same as the inside
there is no net flow of water in or out of the cell
cohesion
force of attraction between water molecules, that causes them to come together
adhesion
force of attraction between water molecules and a surface
water moves from the roots to the leaves in a tall tree due to:
transpiration
cohesion/adhesion of water
root pressure (osmosis)
whatever can dissolve in water is
polar
whatever CANNOT dissolve in water is
non-polar
active transport
the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration, which requires energy
tropism
a biological phenomenon indicating growth or turning movement of a plant in response to a environmental stimulus
phototropism
movement of plants in response to light
stems → positive tropism
roots → negative tropism
gravitropism/geotropism
movement of plants in response to gravity
stems → negatively gravitropic (they grow up)
roots → positively gravitropic (they grow down)
thigmotropism
plants moving in response to touch
hydrophilic
water-loving
hydrophobic
fearful of water
nastic movement
a growth response unrelated to direction of stimulus
types of plant hormones
auxin
cytokinins
gibberellins
ethylene
abscisic acid
where is auxin made?
in stem and root tips
how is auxin transported?
by diffusion
purpose of auxin
causes cell enlargement/elongation in shoots
causes upward growth over outward growth in shoots (apical dominance)
promotes formation of lateral and adventitious roots
restricts cell elongation in roots
prevents abscission (detachment) in fruits and leaves
causes fruit growth and development
results in differmentation and regeneration in vascular tissue
where is cytokinins made?
in root tips
how is cytokinins transported?
from roots to shoots via xylem
purpose of cytokinins
promotes cell division
delays leaf senescence (death)
promotes growth of lateral buds
where is gibberellin made?
in roots, shoot tips, and developing seeds
how is gibberellin transported?
by xylem and phloem
purpose of gibberellin
affects fruit development
can cause bolting (premature production of a flowering stem)
causes hyperelongation of shoots by stimulating cell division and elongation
breaks seed dormancy
where is ethylene made?
in most tissues in response to stress
how is ethylene transported?
by diffusion from site of synthesis
purpose of ethylene
Causes flowers to open
causes fruit to ripen
discourages cell expansion
causes leaf abcission (detachment of the leaf)
where is abscisic acid made?
in mature leaves, roots and seeds
how is abscisic acid transported?
from leaves in phloem and from the roots in xylem
purpose of abscisic acid
prevents seed germination
leaf abcission
causes seeds to fall
causes somata to close to prevent water loss
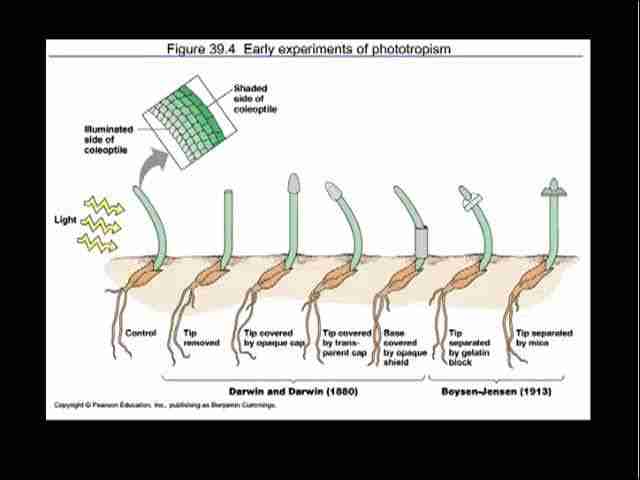
what was Darwin's experiments
Darwin conducted experiments on plants to study their responses to environmental stimuli, specifically investigating phototropism (response to light) and geotropism (response to gravity), and the role of plant hormones in growth and development.
statoliths
starch-filled organelles that help plants sense gravity
which hormone is a gas?
ethylene
cotyledon
is the first leaf that appears from a seed when it sprouts

plants with one cotyledon are
monocots
plants with two cotyledon are
dicots
types of vascular plants
angiosperms (flowering plants)
gymnosperms (confers, ferns)
xylem
carries water throughout the plant
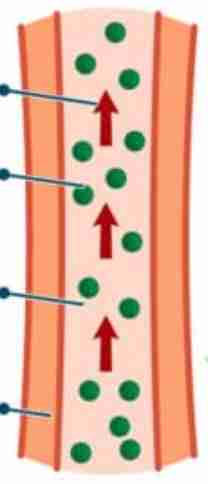
direction of xylem movement
up the plant
direction of phloem movement
up and down the plant
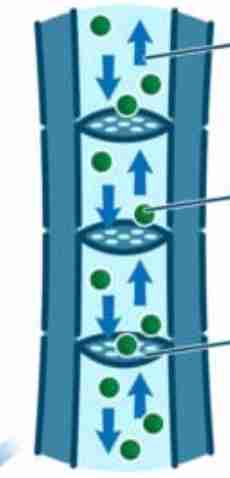
phloem is composed of
sieve tube elements
companion cells
phloem
carries mainly sugars and water
meristematic tissue
divides (by mitosis) to produce new cells
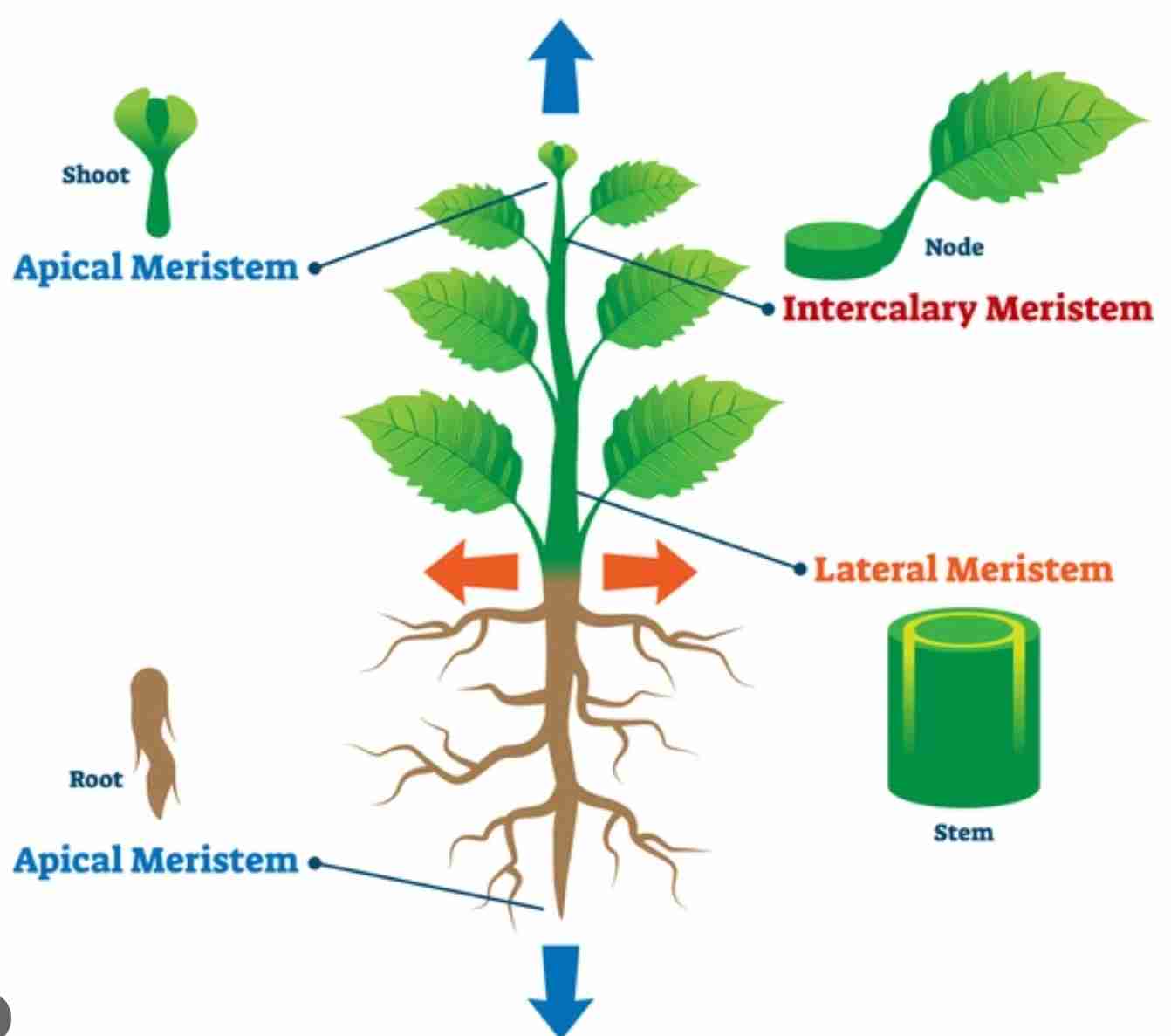
Apical Meristem Region and Intercalary Meristem
found of end of shoot and root tips
youngest cells found of the tip of the apical meristem
responsible for primary growth
vascular cambium
ring of dividing cells found between the xylem and phloem of ONLY DICOT PLANTS
causes secondary growth and produces secondary xylem and phloem
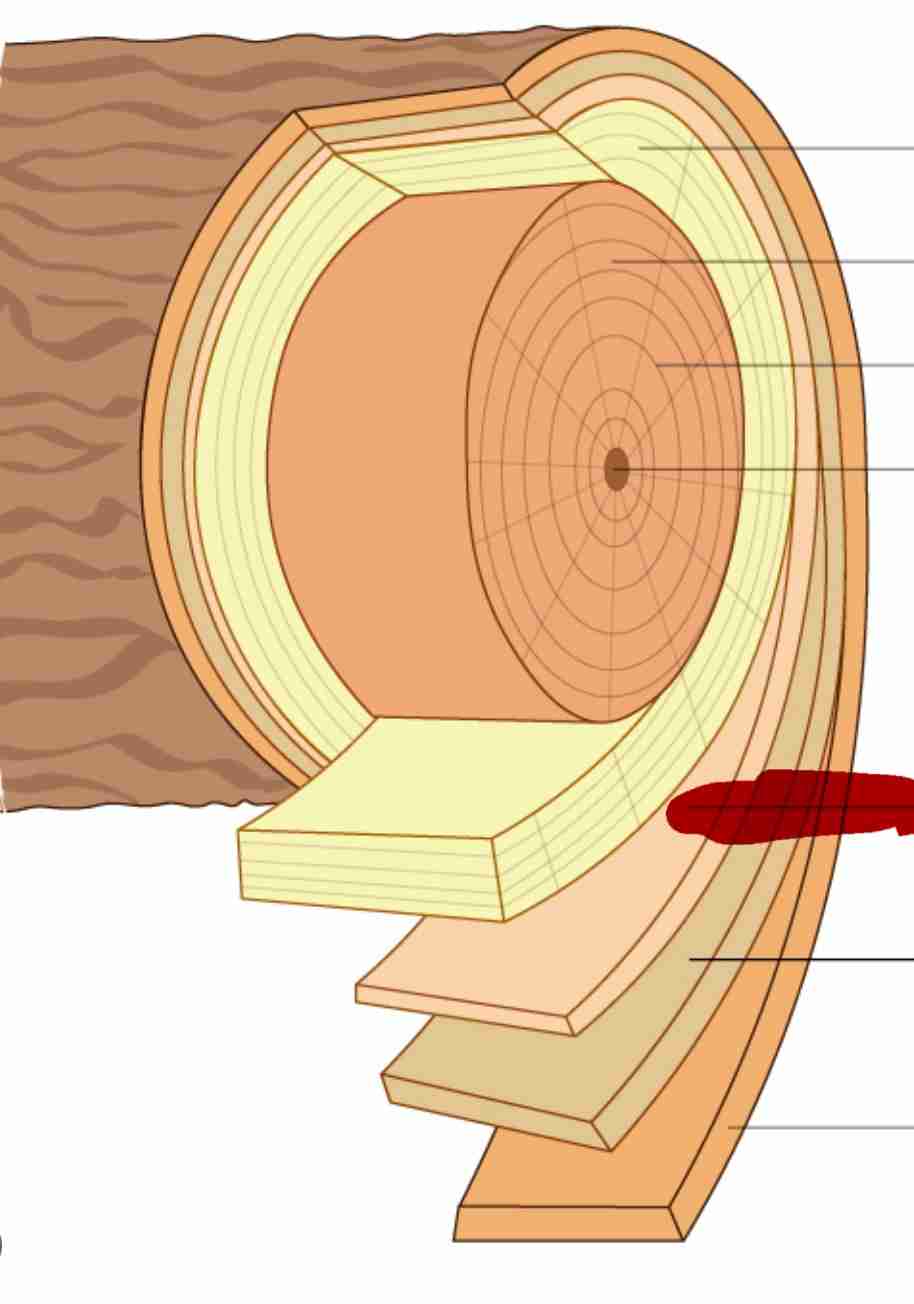
dicot stem
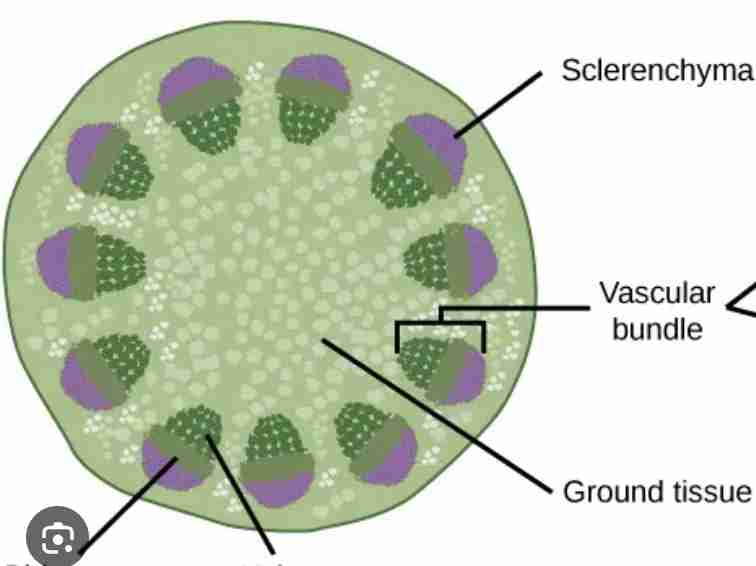
monocot stem
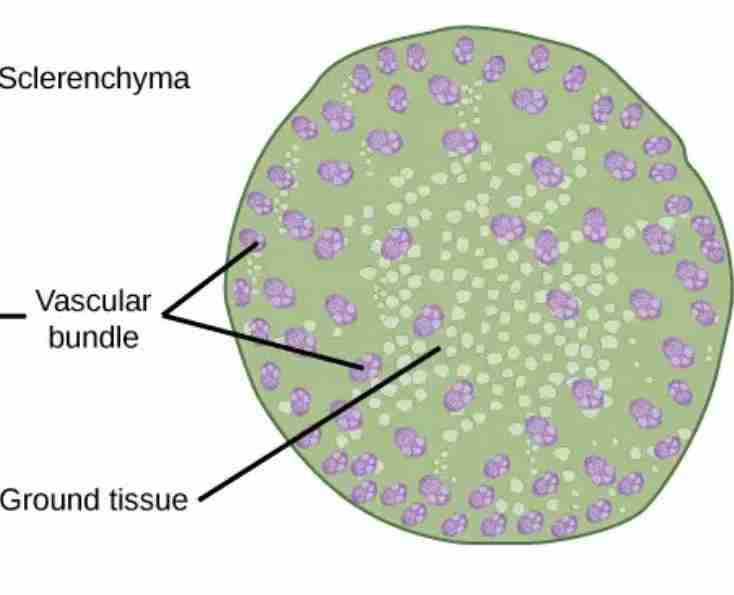
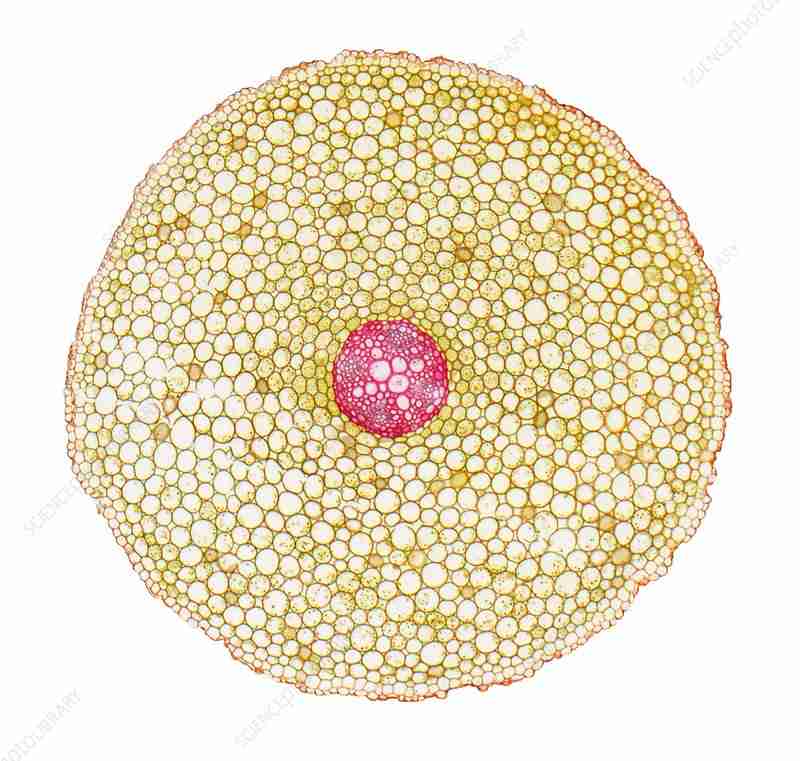
monocot root
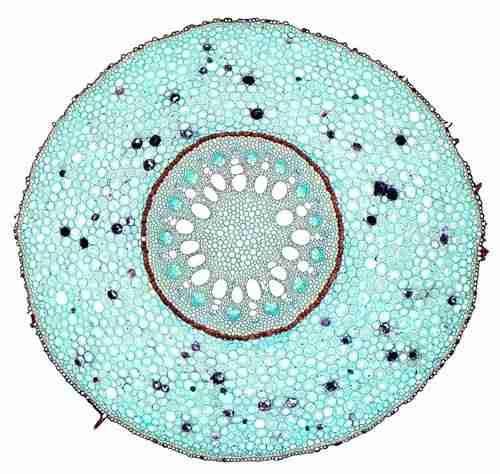
dicot root
cross-pollinating
pollination that includes 2 different plants
self-pollinating
pollination that only occurs in one plant
What is translocation?
is the process by which sugars and other organic nutrients are transported within the plant, primarily through the phloem.
What is transpiration?
the process through which moisture is carried from the roots of a plant to the leaves and released as water vapor into the atmosphere.
megasporangium
ovule
megasporocyte
megaspore mother cell
microsporocyte
microspore mother cell
microsporangium
pollen sac