MIS 561 Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:18 AM on 12/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
1
New cards
All People Seem To Need Data Processing
Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical
2
New cards
7 application layer
- interface between the user's application and the network
- types of communication: email, file transfer, client/server
- types of communication: email, file transfer, client/server
3
New cards
6 presentation layer
- provides a context for communication between layers
- handles encryption, data conversion
- handles encryption, data conversion
4
New cards
5 session layer
- controls the dialogs between computers; also controls duplexing, termination, and restarts
- maintains order
- maintains order
5
New cards
4 transport layer
- provides end to end communication control
- ensures delivery of entire file/message
- ensures delivery of entire file/message
6
New cards
3 network layer
- provides connections between hosts on different networks
- routes data to different LANs and WANs based on network address
- routes data to different LANs and WANs based on network address
7
New cards
2 data link layer
- provides connections between hosts on the same network
- transmits packets from node to node based on station address
- transmits packets from node to node based on station address
8
New cards
1 physical layer
- describes electrical and physical specifications on devices
- electrical signals or cabling
- electrical signals or cabling
9
New cards
subnet mask
A 32-bit number assigned to each host for
dividing the 32-bit binary IP address into
network and node portions. (ex. 255.255.255.255)
dividing the 32-bit binary IP address into
network and node portions. (ex. 255.255.255.255)
10
New cards
default gateway
address that tells computer where the router is and allows computer to access the internet
11
New cards
internal/private ip address
- usually starts with a 10 or a 192 (class b and c addresses)
- routers give these ip addresses to private end users so that they can connect to the internet
- ex: ipad, laptops, computers, etc.
- routers give these ip addresses to private end users so that they can connect to the internet
- ex: ipad, laptops, computers, etc.
12
New cards
external/public ip address
- the ip address that is given to the router by the isp
- allows router to communicate w/ all other publicly available routers
- central area for internet, allows the internet to identify the router
- allows router to communicate w/ all other publicly available routers
- central area for internet, allows the internet to identify the router
13
New cards
common ports
- 25/2525/465/587 (STMP)
- 80/443 (HTTP)
- 110/995 (POP3)
- 143/993 (IMAP4)
- 23 (Telnet)
- 20, 21 (FTP)
- 53 (DNS)
- 389 (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
- 80/443 (HTTP)
- 110/995 (POP3)
- 143/993 (IMAP4)
- 23 (Telnet)
- 20, 21 (FTP)
- 53 (DNS)
- 389 (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
14
New cards
well known port
port number reserved for use by a particular application. allows a client to send a TCP or UDP segment to a server, to the correct destination port for that application.
15
New cards
registered port
port that can be used by network users and processes that are not considered standard processes. Default assignments of these ports must be registered with IANA.
16
New cards
dynamic (private) port
port number that can be assigned by a client or server as the need arises
17
New cards
inbound port
- port for when a connection was initiated from outside of your computer and traffic flows inward
- ex: a server that you own gets requests from people
- ex: a server that you own gets requests from people
18
New cards
outbound port
- port for when a connection was initiated from your computer and the traffic flows outward to the destination intended
- ex: connecting to a server
- ex: connecting to a server
19
New cards
switch
- a computer networking device that connects network segments
- occurs at layer 2 (Data Link)
- occurs at layer 2 (Data Link)
20
New cards
router
- a device that transfers data from one network to another in an intelligent way
- occurs at layer 3 (Network)
- occurs at layer 3 (Network)
21
New cards
hub
- a device that uses its ports to connect devices (computers, printers, etc.) together
- outdated
- occurs at layer 1 (Physical)
- outdated
- occurs at layer 1 (Physical)
22
New cards
dhcp server
- automatically provides and assigns ip addresses, default gateways, and subnet masks to devices
- handles having to find your own ip address, default gateway, and subnet masks every time you connect
- handles having to find your own ip address, default gateway, and subnet masks every time you connect
23
New cards
Some People Fear Birthdays
Segments, Packets, Frames, Bits.
24
New cards
segment
data in the transport layer
25
New cards
packet
data in the network layer
26
New cards
frame
data in the data link layer
27
New cards
bits
data in the physical layer
28
New cards
ipv4
- the dominant protocol for routing traffic on the Internet
- 32 bit
PROS
- simple prefixes
- system handling is good
CONS
- running out of addresses
- 32 bit
PROS
- simple prefixes
- system handling is good
CONS
- running out of addresses
29
New cards
ipv6
- a new protocol developed to replace IPv4, addressing the issue of IP address exhaustion
- 128 bit
PROS
- unique addresses
- no subnetting issues
CONS
- long addresses that can be hard to type
- computer routing issues
- 128 bit
PROS
- unique addresses
- no subnetting issues
CONS
- long addresses that can be hard to type
- computer routing issues
30
New cards
threat environment
the types of attackers and attacks that companies face
31
New cards
Sony data breach
2014 incident where malware installed on a company computer allowed hackers to steal scripts, emails, and personal information of employees and customers
32
New cards
hacking
unauthorized access, modification, or use of an electronic device or some element of a computer system
33
New cards
social engineering
- technique for breaching a system's security by exploiting human nature
- uses standard techniques to get users to give up info needed to gain access to a target system by getting preliminary info about a target organization and leveraging it to obtain additional info from system users
- uses standard techniques to get users to give up info needed to gain access to a target system by getting preliminary info about a target organization and leveraging it to obtain additional info from system users
34
New cards
denial of service attack (dos)
when hackers flood a website with so many requests for service that it slows down or crashes the site
35
New cards
cyberwarfare
State-sponsored activity designed to cripple and defeat another state or nation by damaging or disrupting its computers or networks
36
New cards
Cyberterrorism
politically motivated attacks on information systems
37
New cards
hacktivism
hacking that is intended as political activism
38
New cards
cybercriminal
Someone who attacks a computer system or network for financial gain
39
New cards
cryptography
the art of protecting information by transforming it into an unreadable format, called cipher text
40
New cards
initial authentication
authentication at the beginning of a communication session, before the two sides exchange working data.
41
New cards
public key encryption (asymmetric)
one key (public key) is used to encrypt a message, and another (private key) is used to decrypt the message
42
New cards
Kerckhoff's Law
law that says that in order to have confidentiality, communication partners only need to keep the key secret, not the cipher.
43
New cards
birthday attack
an attack that searches for any two digests that are the same.
44
New cards
data in transit
Any data sent over a network. It's common to encrypt sensitive data-in-transit.
45
New cards
data in use
Any data currently being used by a computer. Because the computer needs to process the data, it is not encrypted while in use.
46
New cards
data at rest
Data that is stored on electronic media.
47
New cards
worm
A destructive computer program that bores its way through a computer's files or through a computer's network.
48
New cards
virus
A program that is capable of copying itself and typically has a detrimental effect, such as corrupting the system or destroying data
49
New cards
malware
software that is intended to damage or disable computers and computer systems.
50
New cards
phising
an identity theft tool that appears in the form of an E-mail or pop-up message; usually looks like it's from a legitimate financial institution and prompts you to provide your personal infromation in order to fix a problem with your account
51
New cards
spearfishing
Phishing expedition that targets groups
52
New cards
trojan horse
a program that appears desirable but actually contains something harmful
53
New cards
payload
Malware delivered by social engineering and/or by exploiting vulnerability in software.
54
New cards
threat surface
The total set of penetrations of a boundary or perimeter that surrounds or contains systems elements.
55
New cards
logic bomb
A computer program or part of a program that lies dormant until it is triggered by a specific logical event.
56
New cards
shoulder surfing
Watching an authorized user enter a security code on a keypad.
57
New cards
eavesdropping
listening secretly to a conversation for the purpose of getting sensitive information
58
New cards
dumpster diving
combing through trash to identify valuable assets
59
New cards
baiting
When a malicious individual leaves malware-infected removable media, such as a USB drive or optical disc, lying around in plain view.
60
New cards
piggybacking
The process of connecting to a wireless network without the permission of the owner of the network.
61
New cards
wateringhole attack
A malicious attack that is directed toward a small group of specific individuals who visit the same website.
62
New cards
mantraps
63
New cards
pretexting
a form of social engineering in which the
64
New cards
privilege escalation
a network intrusion attack that takes advantage of programming errors or design flaws to grant the attacker elevated access to the network and its associated data and applications
65
New cards
backdoor attack
An attack that exploits an unprotected access method or pathway.
66
New cards
boot sector
________ viruses are often transmitted by a flash drive left in a USB port.
67
New cards
session hijacking
An attack in which an attacker attempts to impersonate the user by using his session token.
68
New cards
session theft
When an attacker attempts to steal a user's session using the owner's cookie and authentication information
69
New cards
tcp hijacking
A form of man-in-the-middle attack whereby the attacker inserts himself into TCP/IP-based communications.
70
New cards
spyware
software that enables a user to obtain covert information about another's computer activities by transmitting data covertly from their hard drive.
71
New cards
rootkits
a set of software tools that enable an unauthorized user to gain control of a computer system without being detected.
72
New cards
ransomware
a type of malicious software designed to block access to a computer system until a sum of money is paid.
73
New cards
adware
software that automatically displays or downloads advertising material (often unwanted) when a user is online.
74
New cards
grayware
software that isn't benign nor malicious and tends to behave improperly without serious consequences
75
New cards
teardrop attack
Attack that breaks apart packets into IP fragments, modifies them with overlapping and oversized payloads, and sends them to a victim machine to halt/freeze it
76
New cards
smurf attack
An attack that broadcasts a ping request to computers yet changes the address so that all responses are sent to the victim.
77
New cards
SYN flood attack
An attack that takes advantage of the 3 way handshake to flood servers
78
New cards
fraggle attack
Smurf attack variation that uses ports 7 & 19 to a broadcast address
79
New cards
ping flood attack
Ping utility used to send large number of echo request messages and overwhelms server
80
New cards
diversion theft
When a thief attempts to take responsibility for a shipment by diverting the delivery to a nearby location.
81
New cards
spear phising
a phishing method in which the emails are carefully designed to target a particular person or organization
82
New cards
whaling
A phishing attack that where the attacker attempts to compromise information about a specific highly valuable employee
83
New cards
vishing
a phone scam that attempts to defraud people by asking them to call a bogus telephone number to confirm their account information
84
New cards
malicious insider
An employee or contractor who attempts to gain financially and/or disrupt a company's information systems and business operations
85
New cards
CIAAAN
- Confidentiality: information kept private and secure
- Integrity: data not modified, deleted, or added
- Availability: systems available to whom requires them
- Authenticity: providing verification of the identities
- Accountability: assurance by recording identities and activities
- Non-repudiation: assuring the identities of the parties in a transaction
- Integrity: data not modified, deleted, or added
- Availability: systems available to whom requires them
- Authenticity: providing verification of the identities
- Accountability: assurance by recording identities and activities
- Non-repudiation: assuring the identities of the parties in a transaction
86
New cards
symmetric encryption
- type of encryption where only one key is used to encrypt and decrypt electronic information
- require a shorter key length to be secure
- faster than asymmetric encryption
- require a shorter key length to be secure
- faster than asymmetric encryption
87
New cards
cipher suite
a complete, packaged set of methods (algorithms) needed to secure a network connection through SSL/TLS (ex: Cisco AnyConnect)
88
New cards
cipher suite negotiation
method for establishing secure communication
- stage 1: selecting security methods and parameters
- stage 2: authentication
- stage 3: keying
- stage 1: selecting security methods and parameters
- stage 2: authentication
- stage 3: keying
89
New cards
hashing (hashing vs encryption)
- used for signing plaintext
- 1 way, non-reversible
- ex: taking a person's finger-print
-ex: used for storing Windows passwords or verifying an ISO file
- 1 way, non-reversible
- ex: taking a person's finger-print
-ex: used for storing Windows passwords or verifying an ISO file
90
New cards
encryption (hashing vs encryption)
- used for encoding plaintext
- 2 way, reversible
- ex: putting a lock on a box
-ex: using an ATM and needing info to be protected
- 2 way, reversible
- ex: putting a lock on a box
-ex: using an ATM and needing info to be protected
91
New cards
transposition cipher (transition vs substitution)
symmetric cipher that does not change individual letters or bits of a plaintext, but it changes their order
92
New cards
substitution cipher (transition vs substitution)
symmetric cipher that substitutes one letter (or bit) for another in each place of a plaintext
93
New cards
electronic signature
- used to verify that someone intended to sign something, the identity was verified, and that the document did not change after the signature was made
94
New cards
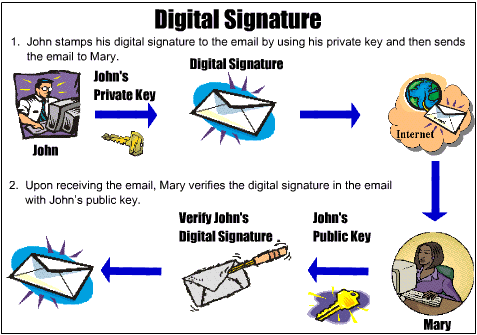
digital signature
- a code digitally signed by a company or person that verifies who sent a message
- sender selects the file they want to send, then their computer creates a hash for it.
- the hash value is encrypted with the sender's private key and is sent to the receiver
- the receiver gets the file, opens it in the correct app, and the app verifies that it was digitally signed
- the receiver's computer decrypts the digital signature using the sender's public key
- sender selects the file they want to send, then their computer creates a hash for it.
- the hash value is encrypted with the sender's private key and is sent to the receiver
- the receiver gets the file, opens it in the correct app, and the app verifies that it was digitally signed
- the receiver's computer decrypts the digital signature using the sender's public key
95
New cards
digital certification
- used to validate the authenticity and integrity of a message
- generates a hash of a message and encrypts it using the sender's private key. Then, the message is signed and sent to the recipient
- The recipient generates their own hash of the message and decrypts the sender's hash using the sender's public key
- If both hashes match the document wasn't modified and the sender was authenticated
- generates a hash of a message and encrypts it using the sender's private key. Then, the message is signed and sent to the recipient
- The recipient generates their own hash of the message and decrypts the sender's hash using the sender's public key
- If both hashes match the document wasn't modified and the sender was authenticated
96
New cards
one time pad (OTP)
secure method of encryption information that involves using random generated key only once
97
New cards
botnets
- a logical computer network of zombies under the control of an attacker
- controlled via a handler (compromised hosts used to manage large groups of bots)
- controlled via a handler (compromised hosts used to manage large groups of bots)
98
New cards
zombies
- computers that have been taken control by hackers
- used to directly attack victims
- can floor victims with different requests and can be updated for new functionality
- used to directly attack victims
- can floor victims with different requests and can be updated for new functionality
99
New cards
macro
viruses that infect the macros in office documents
100
New cards
program
a detailed plan or procedure for solving a problem with a computer