ib econ- 3.5: monetary policy
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits: https://www.econinja.net/macroeconomics/3-5-monetary-policy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
what is monetary policy?
refers to the governments use of interest rates and the money supply to influence the level of aggregate demand and economic activity. usually done by the country’s central bank.
what are the goals of monetary policy?
low and stable rate of inflation (2% for most developed countries)
low unemployment
reduce business cycle fluctuations
promote a stable economic environment
external balance (imports = exports)
what is a nominal interest rate?
the actual interest rate of a loan, regardless of inflation
what is a real interest rate?
the interest rate of a loan adjusted to the inflation rate
how do you calculate real interest rate?
nominal interest rate - inflation
This means that in times of high inflation, there might be a negative real interest rate: The borrower pays interest, but it is lower than the inflation rate so the bank loses the real value of the loan.
what are examples of expansionary monetary policy (when you want to expand the economy)?
decrease minimum reserve ratio (so commercial banks can lend out more)
decrease the central bank interest rate (so commercial banks can take out cheaper loans and hopefully pass this on to consumers and firms - this is not that effective, commercial banks often retain their interest rates to increase profit margins)
buy government bonds (so there is more money in the economy)
buy corporate bonds (aka quantitative easing, so there is more money in the economy)
what is contractionary monetary policy? what are examples of it?
for when you want to slow the economy down. this is usually done to lower inflation rates, but it will also drag down real gdp with it.
increase the minimum reserve ratio
increase the central bank interest rate
sell government bonds
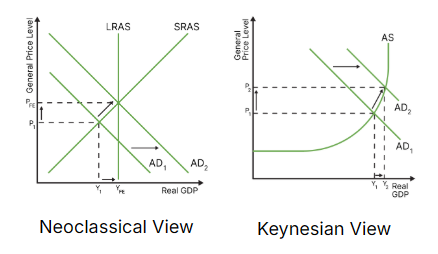
draw the diagram for expansionary monetary policy (neoclassical and keynesian)
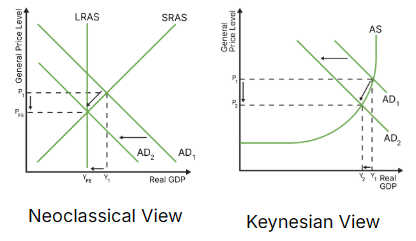
draw the diagram for contractionary monetary policy (neoclassical and keynesian)
what are the strengths of monetary policy?
incremental, flexible, and easily reversible: can be quickly done by the central bank
short time lags: most central banks are independent of the government’s politics. they were designed this way so policies can be implemented quickly without votes and bureaucracy
what are the weaknesses of monetary policy?
the effectiveness of lowering interest rates decreases as they tend towards 0: when interest rates are already very low, it is hard to lower them further. other forms of monetary policy then need to be used, but they can be more expensive.
low consumer and business confidence: the implementation of monetary policy can often reduce confidence in markets such as housing, reducing consumption and investment