Chemistry-Acid, Bases and salts
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms

Acid And Base
Acid Is Proton donor (H+) , and Base is the proton acceptor (OH-)

Dissociation
Release of H+ Ions in a solution from an acid making it acidic
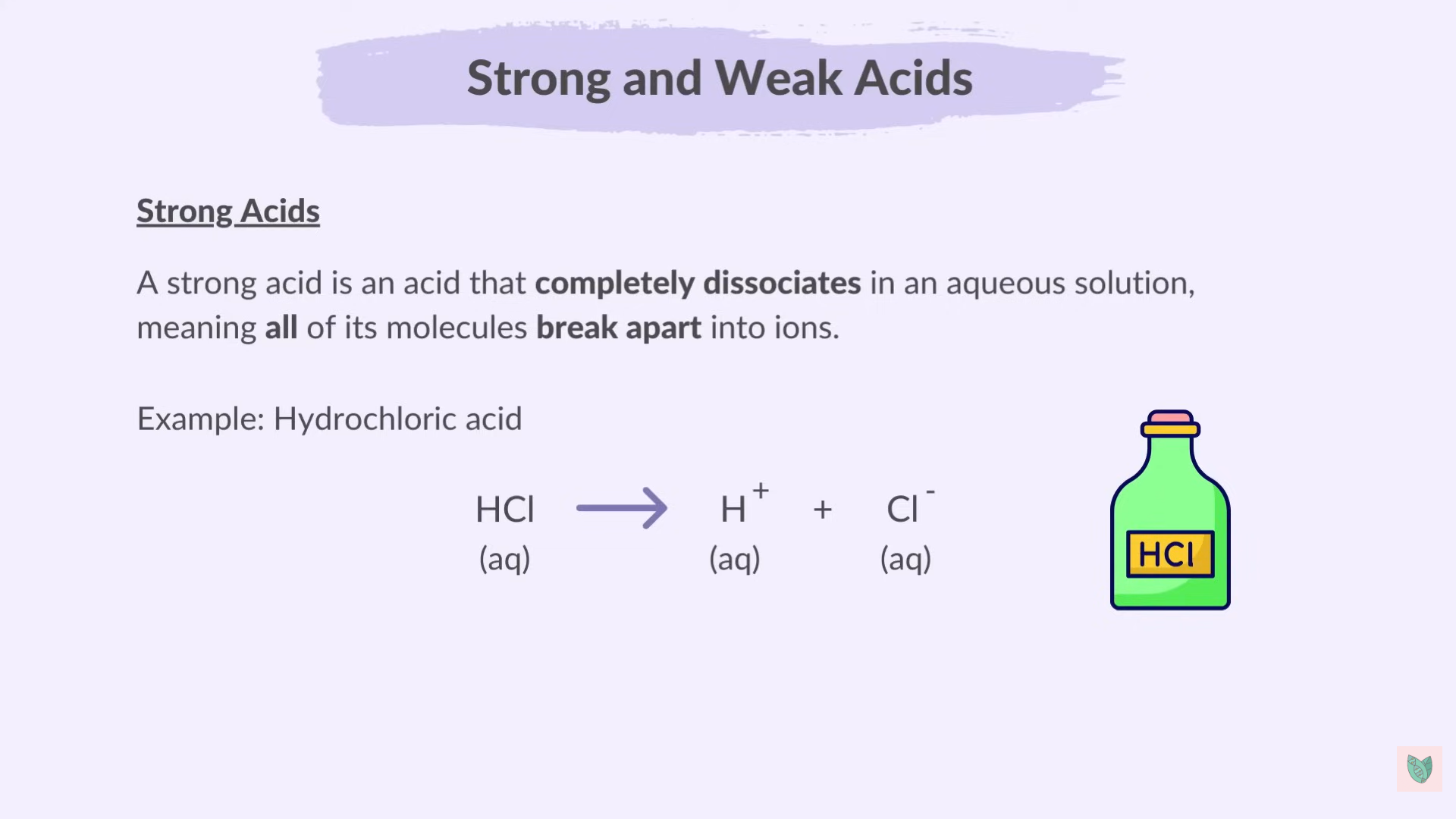
Strong And weak Acid
Strong acid completely Dissociates where Weak acid partially dissociates

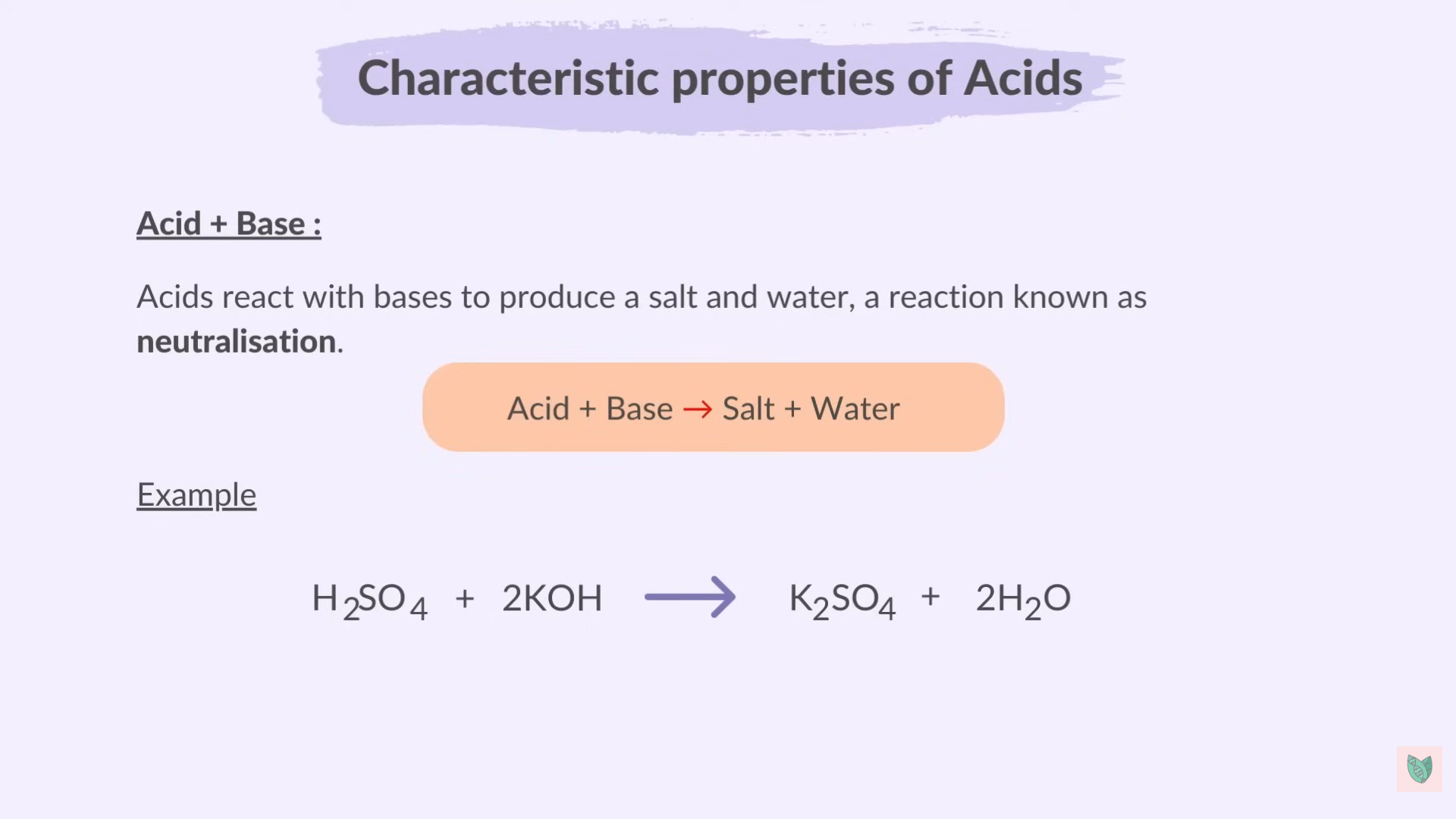
Reaction of Acids
Acid + Base > Salt + Water

Reaction of acid with carbonate
Acid + Carbonate > Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
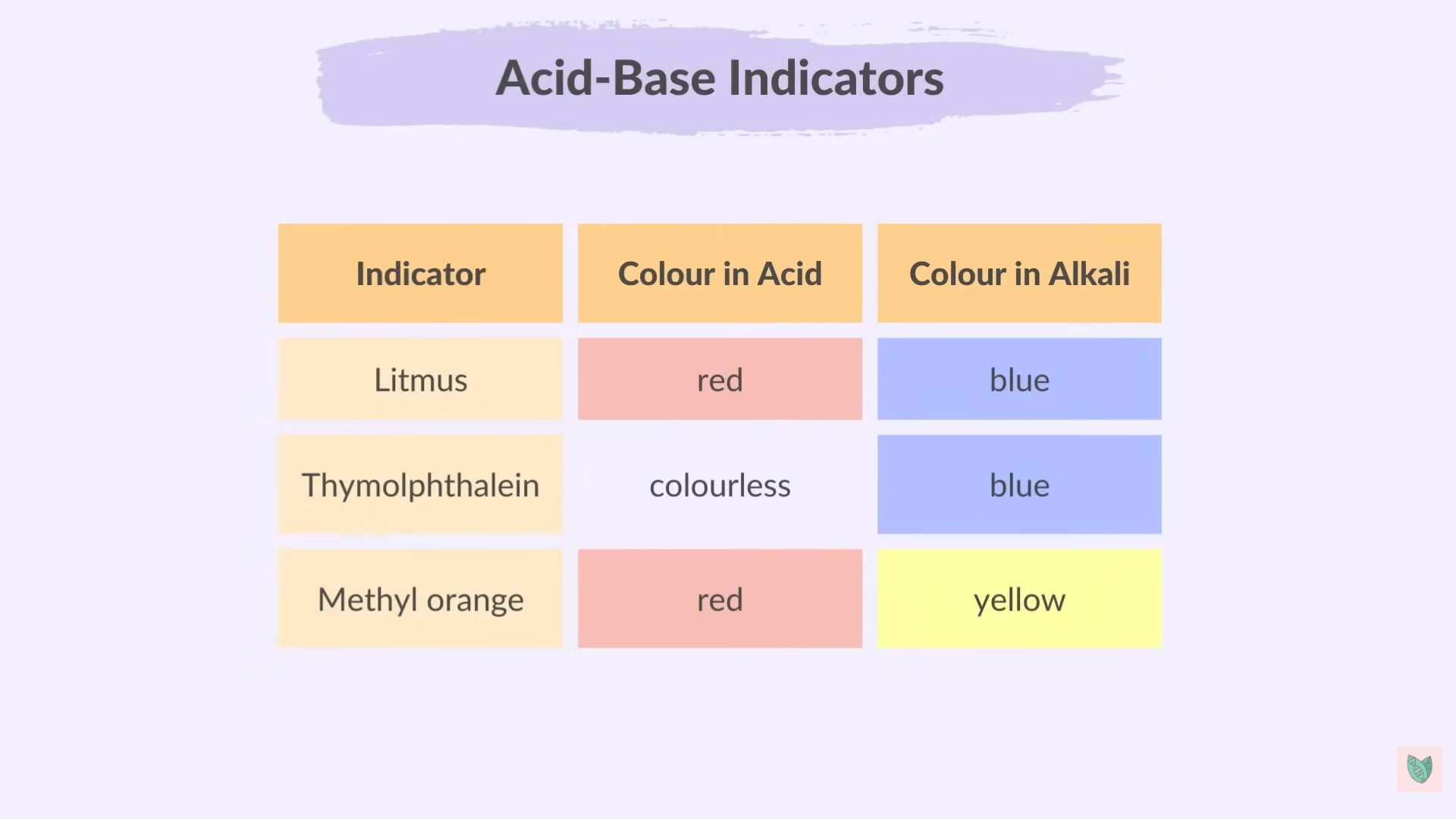
Indicators
Litmus
Methyl Orange ( Yellow in Base ) > ( Orange in Neutral) > (Pink/Red in Acid)
Thymolphthalein ( Blue in Base)
Phenolphthalein (Pink In Base)

Reaction of Bases
Base + Ammonium Salt > Salt + Water + Ammonia Gas

PH indicator
indicates how acidic or basic a substance is by Changing color

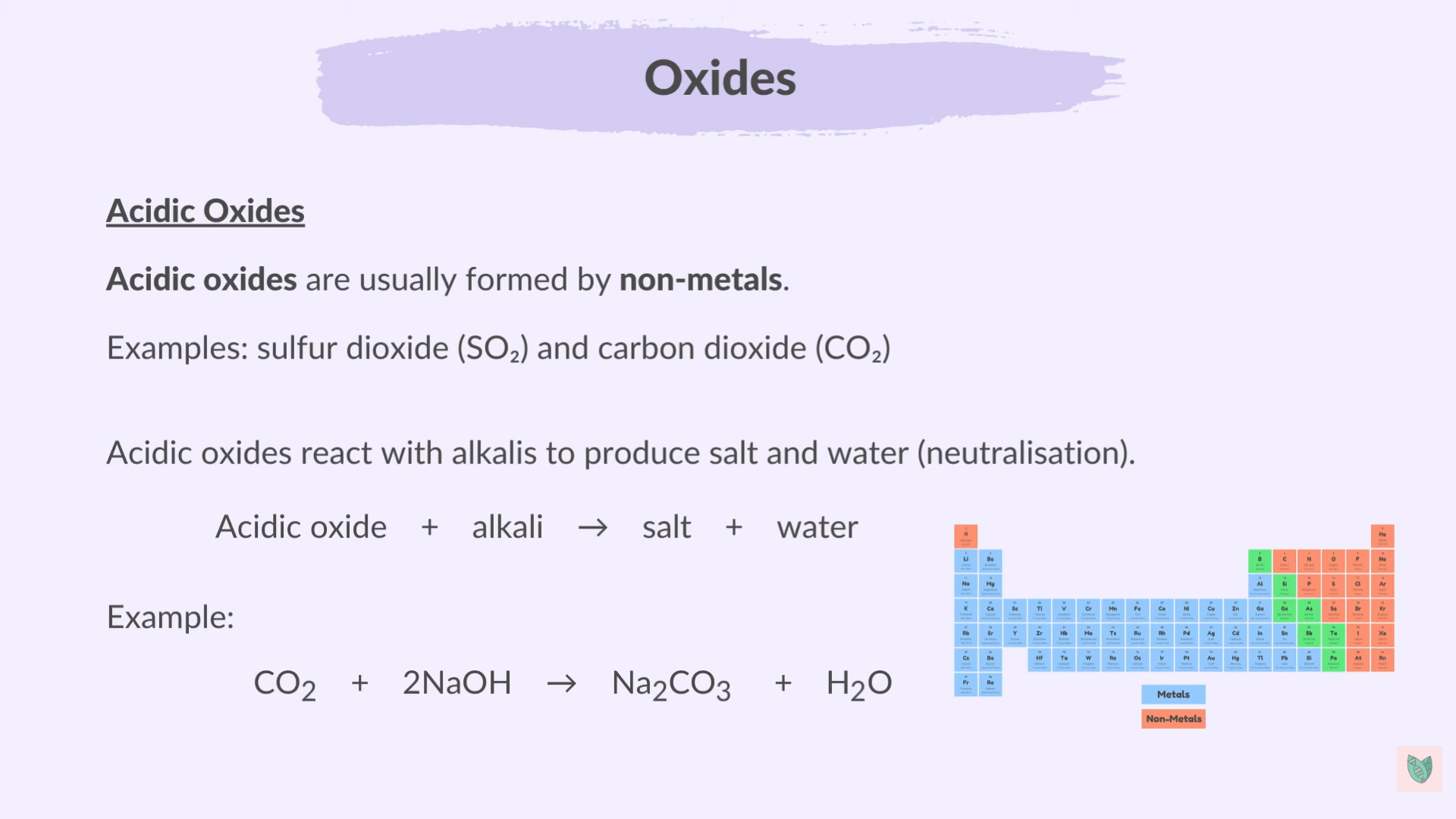
Oxides
Form when Metal or non-metal react with oxygen or Carbon dioxide
Non-metal Oxides are acidic
Metal Oxides are basic

Amphoteric Oxides
Are oxides that can react with both metals and non-metals , Examples:
Zinc Oxide
Aluminum Oxide

Preparing Soluble Salts
Done By several ways Depending on the Reactants , Example an Acid With:
Titration ( with an alkali)
excess metal
excess insoluble base
excess insoluble carbonate

Titration
Measuring Known volume of an alkali (needed: Conical Flask , Pipette)
Adding few drops of indicator (Methyl Orange And Thymolphthalein)
Add Acid Gradually till the colour Change Indicating neutralisation (needed: burette)
Record The volume
Repeat without indicator
Separartion forming Crystallise
Purification (Dry)

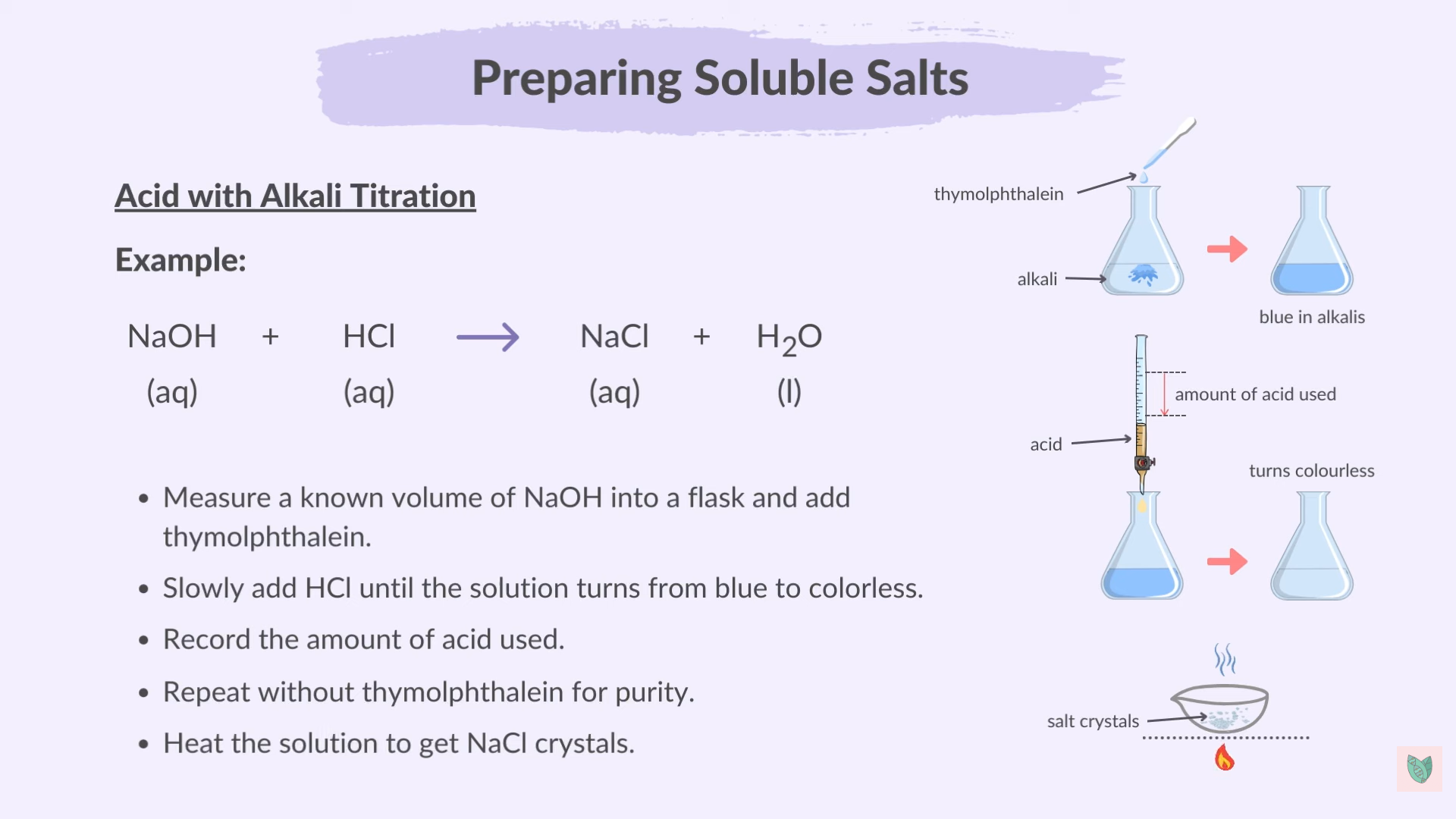
Example Of Titration
NaOH + HCl > NaCl + H2O

Preparing Insoluble Salts
Bring to soluble salts in distilled water
Mix them > Precipitate of insoluble salt forms
Separation
Purification


Example Of Precipitation
Zn + H2SO4 > ZnSO4 + H2

Hydrated And Anhydrous Salts
Crystals Can Chemically bond with water
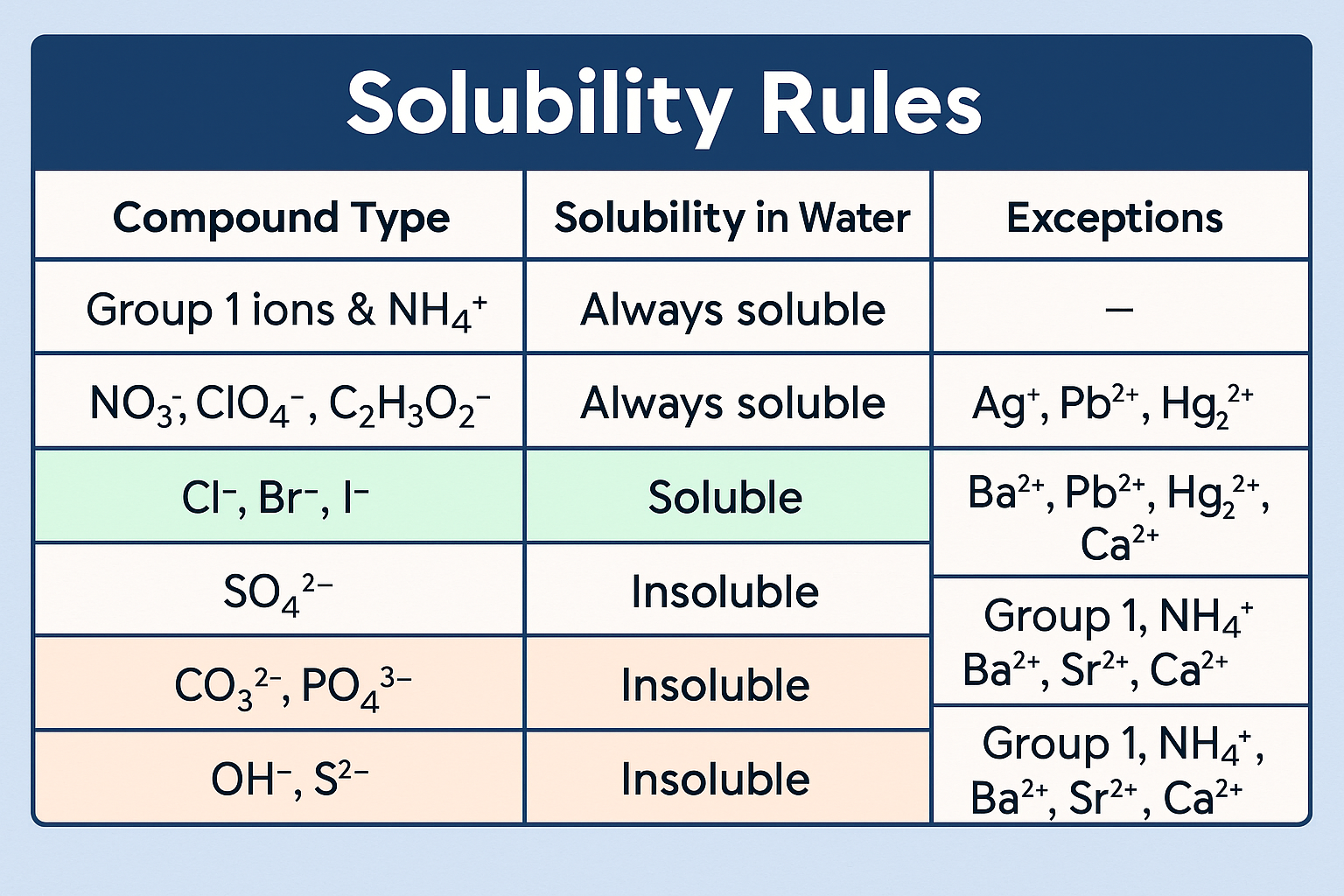
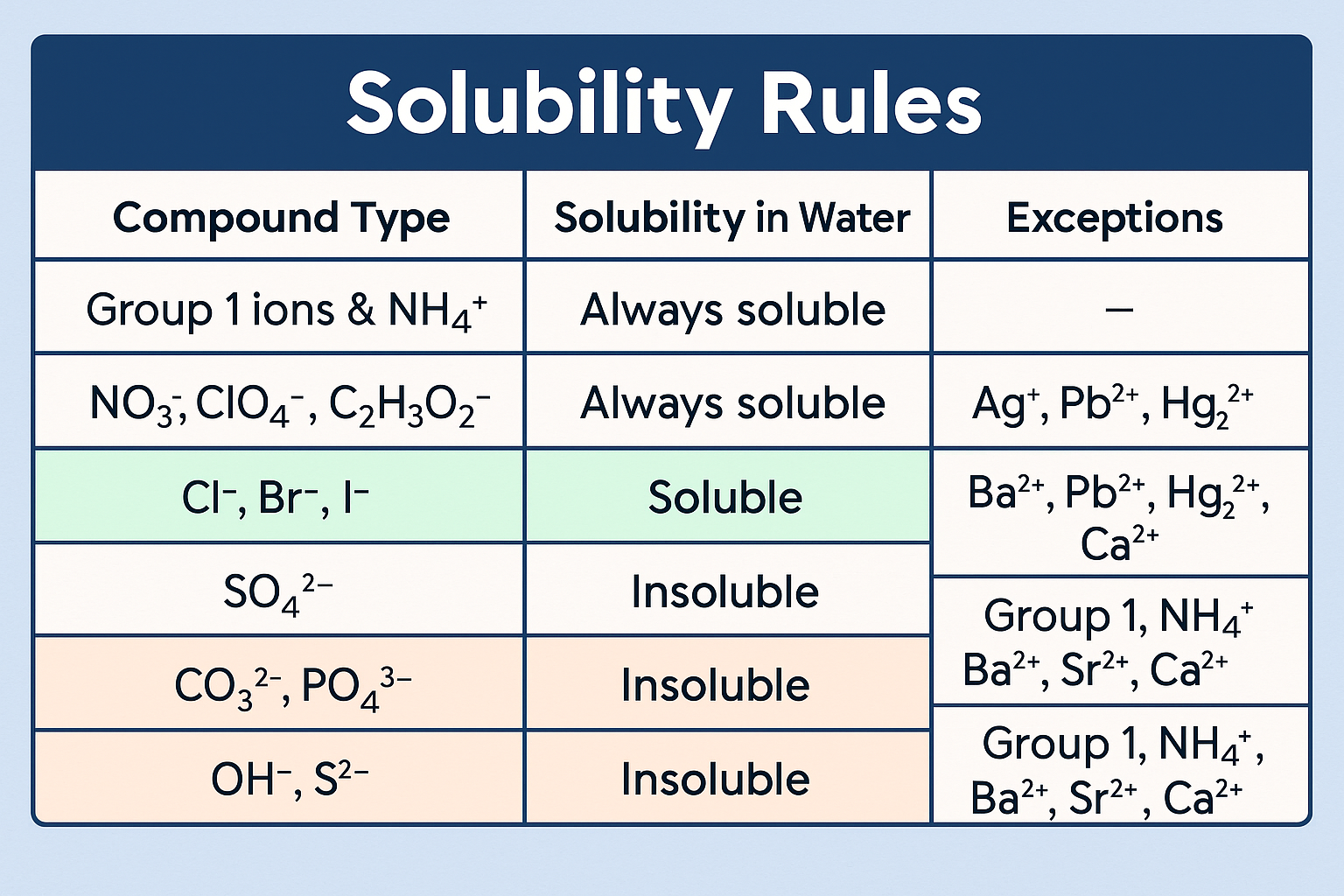
Solubility Rules
PMS > Pb + Mercury + Silver (All Nitrates are soluable)