Emotion
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
Emotion
physical and psychological reaction to some event
2
New cards
Valence
one way emotion is measured
= range from positive to negative
= range from positive to negative
3
New cards
Arousal
one way emotion is measured
= range from low to high intensity
= range from low to high intensity
4
New cards
Left Hemisphere
hemisphere of the brain that is associated with positive emotions
5
New cards
Right Hemisphere
hemisphere of the brain that is associated with negative emotions
* also processes facial expressions
* evolutionarily: makes sense because need to read faces
* it would be more dangerous to misread negative expressions like anger than happiness
* also processes facial expressions
* evolutionarily: makes sense because need to read faces
* it would be more dangerous to misread negative expressions like anger than happiness
6
New cards
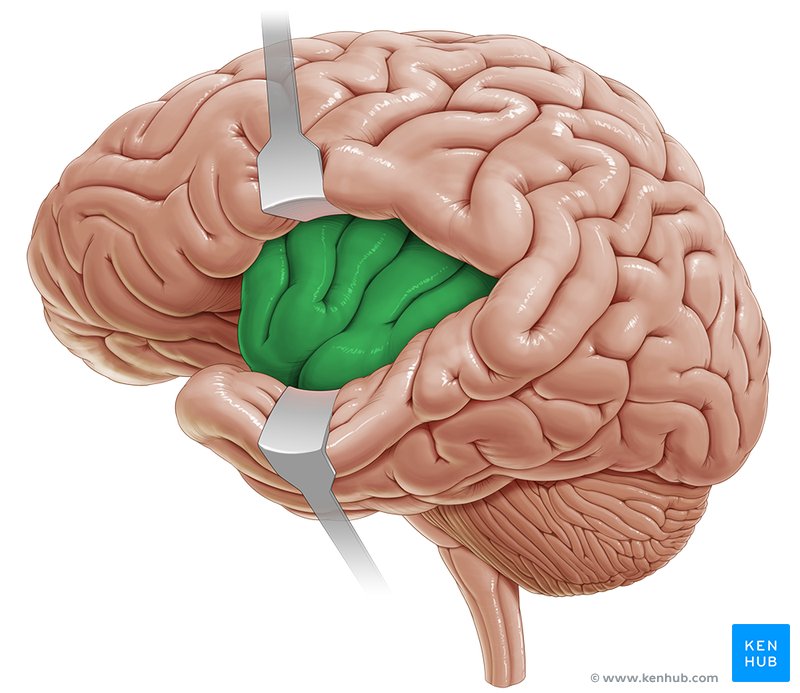
Insula
= neural center that works with somatosensory and gustatory cortex
* activated for negative social emotions
* lust, pride, disgust
* gustatory = disgust (sensation of bad taste)
* somatosensory = integrates bodily information (emptiness in stomach) with prefrontal cortex
* basically, helps interpret what body is feeling
\
\
region of cortex not visible from the surface view = is “**insula**ted”
* activated for negative social emotions
* lust, pride, disgust
* gustatory = disgust (sensation of bad taste)
* somatosensory = integrates bodily information (emptiness in stomach) with prefrontal cortex
* basically, helps interpret what body is feeling
\
\
region of cortex not visible from the surface view = is “**insula**ted”
7
New cards
Amygdala
= neural system for processing fearful and threatening stimuli
* detection of threat
* activation of appropriate fear-related behaviors
\
ex. this brain region/circuit is activated when seeing fearful face
* detection of threat
* activation of appropriate fear-related behaviors
\
ex. this brain region/circuit is activated when seeing fearful face
8
New cards
Reticular Formation
= regulatory center for sleep, alertness, fatigue
* helps determine arousal level/intensity of emotions
* helps determine arousal level/intensity of emotions
9
New cards
Serotonin
body's natural “feel good” neurotransmitter
* at normal levels, you feel more focused, emotionally stable, happier and calmer.
* Low levels are associated with depression
* at normal levels, you feel more focused, emotionally stable, happier and calmer.
* Low levels are associated with depression
10
New cards
Sympathetic Nervous System
activates the fight-or-flight response in threatening situations
* releases epinephrine
* releases epinephrine
11
New cards
to Prepare body for action
one purpose of emotions
ex. fear = danger = run away
ex. fear = danger = run away
12
New cards
to Help us learn
one purpose of emotions
* like operant conditioning
* positive experience → positive emotion → “I should do that again!”
* negative experience → negative emotion → “yeah, don’t do that again :(“
* like operant conditioning
* positive experience → positive emotion → “I should do that again!”
* negative experience → negative emotion → “yeah, don’t do that again :(“
13
New cards
to regulate social interactions
one purpose of emotions
* helps us react appropriately to others’ emotions
ex. if someone looks sad :( → “how can I help?”
if someone looks angry >:( → avoid, give them space
* helps us react appropriately to others’ emotions
ex. if someone looks sad :( → “how can I help?”
if someone looks angry >:( → avoid, give them space
14
New cards
James-Lange Theory
one of the emotion theories
= physiological response causes emotion
\
stimulus → physical reaction → emotion
ex. (see bear) → (heart racing) → (fear)
= physiological response causes emotion
\
stimulus → physical reaction → emotion
ex. (see bear) → (heart racing) → (fear)
15
New cards
Canon-Bard Theory
one of the emotion theories
= stimulus arriving at thalamus activates sympathetic nervous system, and ***SIMULTANEOUSLY*** alerts cerebral cortex of the stimulus
= we experience physiological and emotional reaction at same time
\
Think: standing next to a cannon that unexpectedly fires, leap into the air while expressing surprise at same time
\
stimulus → physical reaction + Emotion
ex. (see bear) → (heart racing) + (fear)
= stimulus arriving at thalamus activates sympathetic nervous system, and ***SIMULTANEOUSLY*** alerts cerebral cortex of the stimulus
= we experience physiological and emotional reaction at same time
\
Think: standing next to a cannon that unexpectedly fires, leap into the air while expressing surprise at same time
\
stimulus → physical reaction + Emotion
ex. (see bear) → (heart racing) + (fear)
16
New cards
Schachter-Singer (2-factor) Theory
one of the emotion theories
= individual can cognitively appraise identical physical sensations differently depending on the context
* first factor: physiological response
* second factor: cognitive response
\
stimulus → physical reaction + Cognition → Emotion
\
“is my heart racing because I’m looking at my date, or because I’m on a roller coaster?”
= individual can cognitively appraise identical physical sensations differently depending on the context
* first factor: physiological response
* second factor: cognitive response
\
stimulus → physical reaction + Cognition → Emotion
\
“is my heart racing because I’m looking at my date, or because I’m on a roller coaster?”
17
New cards
Opponent Process Theory
one of the emotion theories
= emotions are paired as opposites such as
* Happiness and sadness
* Fear and relief
* Pleasure and pain
When you experience one emotion, the other is temporarily inhibited. With repeated stimulus, the initial emotion becomes weaker, and the opposing emotion intensifies
\
ex.
1) first time sky diving = fear/anxiety
2) after completing it = don’t return to baseline normal, but have an opposed feeling of happiness/euphoria/relief
3) next time sky diving, fear (initial emotion) is reduced, but opposing emotion of elation just as or even more intense
\
ex.
1) Emergency room doctors = extreme levels of stress / adrenaline.
2) With time, however, stress decreases, and the rush of adrenaline may drive them to perform better instead of being stressed out.
= emotions are paired as opposites such as
* Happiness and sadness
* Fear and relief
* Pleasure and pain
When you experience one emotion, the other is temporarily inhibited. With repeated stimulus, the initial emotion becomes weaker, and the opposing emotion intensifies
\
ex.
1) first time sky diving = fear/anxiety
2) after completing it = don’t return to baseline normal, but have an opposed feeling of happiness/euphoria/relief
3) next time sky diving, fear (initial emotion) is reduced, but opposing emotion of elation just as or even more intense
\
ex.
1) Emergency room doctors = extreme levels of stress / adrenaline.
2) With time, however, stress decreases, and the rush of adrenaline may drive them to perform better instead of being stressed out.
18
New cards
Evolutionary Theory
one of the emotion theories
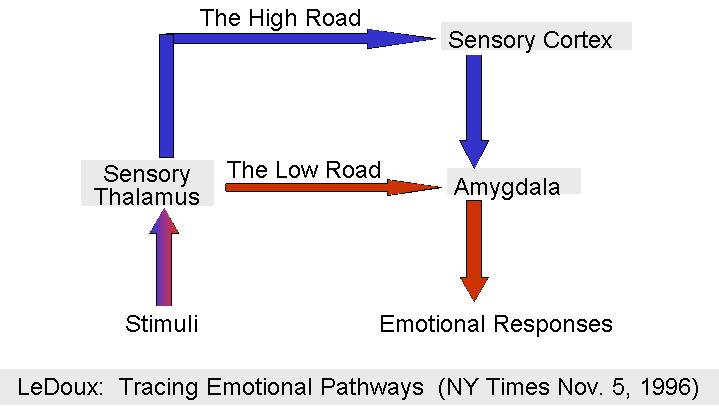
= emotions are evaluated along two roads: the "Low Road" and the "High Road"
= Emotions motivate people to respond quickly to stimuli in the environment, which helps improve the chances of success and survival.
\
Low:
= elicits defensive responses without conscious thought
* amygdala has evolved to process threats really fast
ex. visual input of a snake is received by thalamus, projected to the amygdala, which sends its signals directly to areas of the brain responsible for generating self defense behavior.
\
High:
= involves and indirect pathway to the amygdala. In this case thalamic info is transmitted to the sensory cortex where it is further processed and evaluated for level of threat prior to being sent to the amygdala.
* takes longer than low road
ex. sensory cortex recognizes that the “snake” is in fact just a wiggly stick → tells parasympathetic system to bring you back down
= emotions are evaluated along two roads: the "Low Road" and the "High Road"
= Emotions motivate people to respond quickly to stimuli in the environment, which helps improve the chances of success and survival.
\
Low:
= elicits defensive responses without conscious thought
* amygdala has evolved to process threats really fast
ex. visual input of a snake is received by thalamus, projected to the amygdala, which sends its signals directly to areas of the brain responsible for generating self defense behavior.
\
High:
= involves and indirect pathway to the amygdala. In this case thalamic info is transmitted to the sensory cortex where it is further processed and evaluated for level of threat prior to being sent to the amygdala.
* takes longer than low road
ex. sensory cortex recognizes that the “snake” is in fact just a wiggly stick → tells parasympathetic system to bring you back down
19
New cards
Primary/Universal Emotions
= a certain set of emotions that’s innate no matter your culture
anger, fear, happiness, sadness, disgust, love
* thought because of evolutionarily causes
* (disgust protects you from eating rotten stuff, wrinkling nose → closes nose from foul odors)
* (surprise → raise eyebrows / eyes widen → you can see better)
\
Evidence:
* blind (people who’ve never seen other’s expressions) also do them
* Ekman’s research gathered from people around the world
anger, fear, happiness, sadness, disgust, love
* thought because of evolutionarily causes
* (disgust protects you from eating rotten stuff, wrinkling nose → closes nose from foul odors)
* (surprise → raise eyebrows / eyes widen → you can see better)
\
Evidence:
* blind (people who’ve never seen other’s expressions) also do them
* Ekman’s research gathered from people around the world
20
New cards
Display Rules
different cultures have different ideas of what emotions are appropriate to express
ex. westerners think a firm handshake = outgoing/expressive
europeans think it customary to kiss and hug as greeting (but in US that would be weird)
ex. westerners think a firm handshake = outgoing/expressive
europeans think it customary to kiss and hug as greeting (but in US that would be weird)
21
New cards
Difference in nonverbal behavior between genders
* women have a higher sensitivity to nonverbal cues
* women have a higher emotional literacy and express more complex emotions
* girls are “allowed” to express stronger emotions than boys (social factor)
* although both genders experience empathy, women are more likely to express it
* women have a higher emotional literacy and express more complex emotions
* girls are “allowed” to express stronger emotions than boys (social factor)
* although both genders experience empathy, women are more likely to express it
22
New cards
Facial Feedback Effect
= tendency of facial muscle states to trigger corresponding feelings
\
ex. if someone forces a smile, induces happy feelings
\
* supports james-lange theory, that first physical response, then experience emotion
\
ex. if someone forces a smile, induces happy feelings
\
* supports james-lange theory, that first physical response, then experience emotion
23
New cards
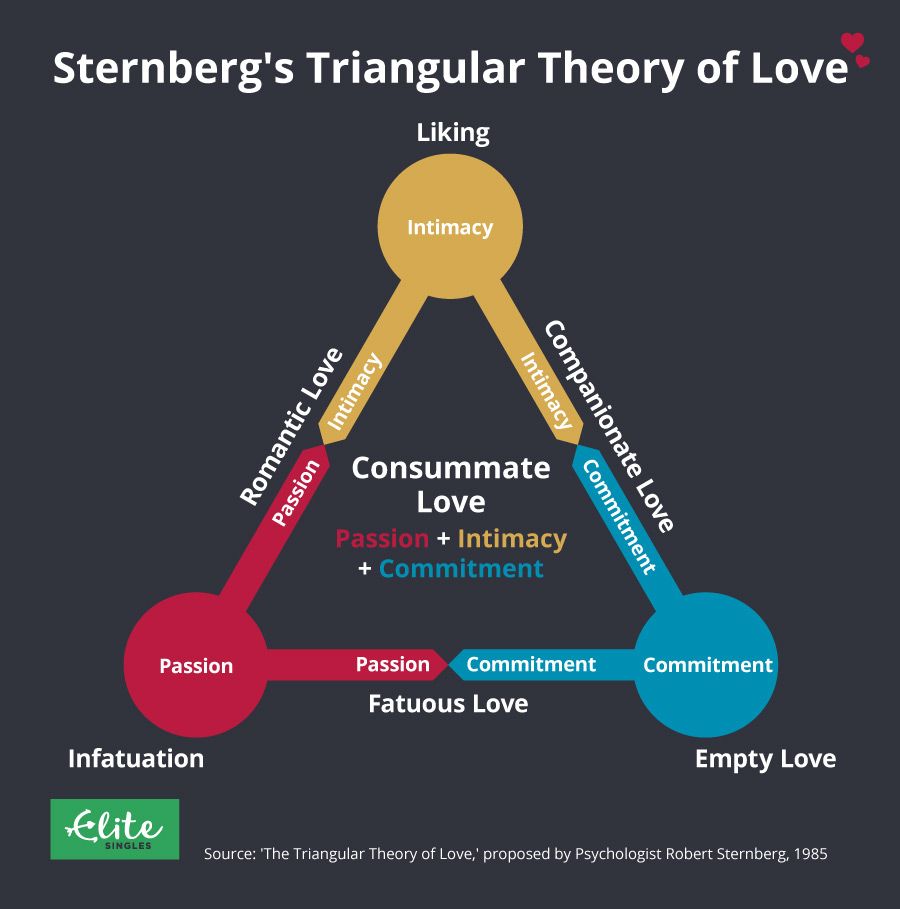
Sternberg’s Triangular Theory of Love
= “love is based on three different scales: intimacy, passion, and commitment”
\
* a relationship based on a single element is less likely to survive than one based on two or more
\
* a relationship based on a single element is less likely to survive than one based on two or more
24
New cards
Emotional Intelligence
the ability to:
* understand/control own emotions
* understand/react appropriately to others’ emotions
* understand that emotions impact decision making
* understand/control own emotions
* understand/react appropriately to others’ emotions
* understand that emotions impact decision making