Adaptive Immunity
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Adaptive immunity
the acquired ability to recognize and destroy a particular pathogen or its products
Antigen
elicits adaptive immune response; reacts with antibodies and T-cell receptors (TRCs)
Antigen presenting cells (APCs)
engulf, process, and present antigens to lymphocytes (B and T cells)
Macrophages and dendritic cells
TCRs interact with APCs
T cell-mediated immunity
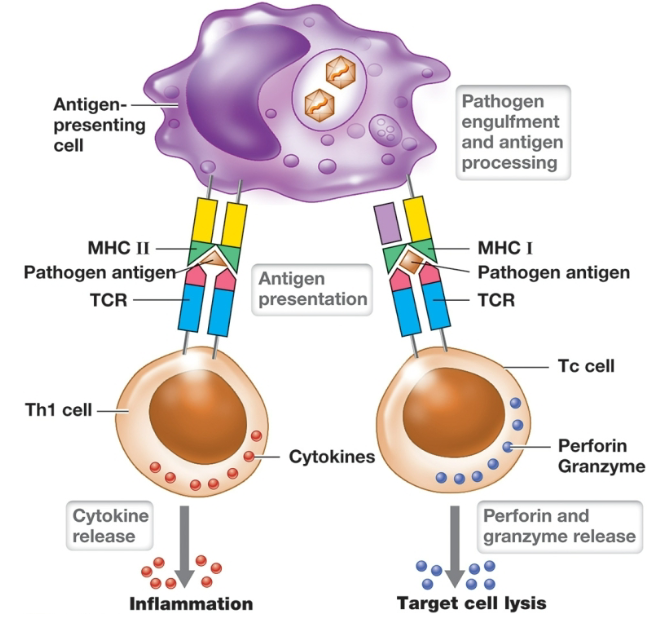
T cells
T-helper (Th) cells
Cytotoxic T (Tc) cells
T-helper cells
Interacts with MHC II complexes
enhance inflammation
Cytotoxic T cells
recognize antigen presented by MHC I protein on an infected cell
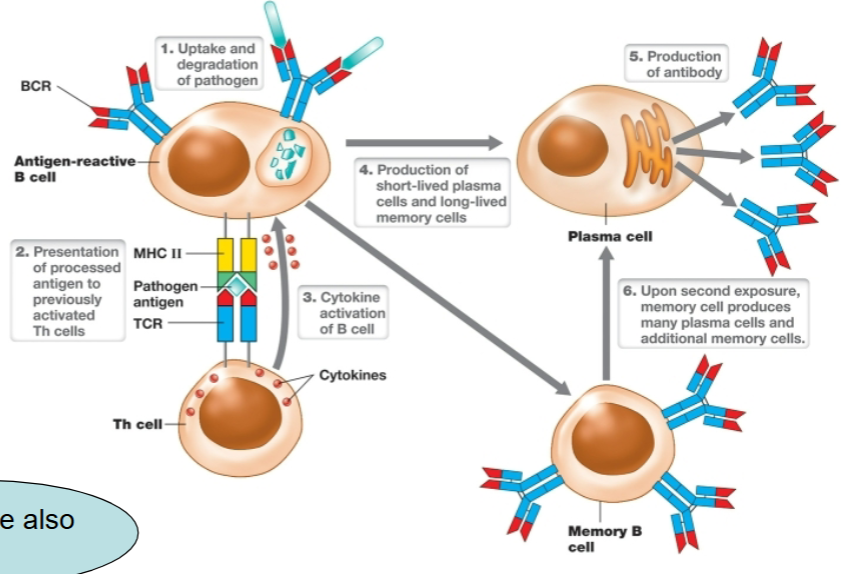
B cells
interact with antigens
present antigen to T cells
specific
Antibodies
are soluble proteins made by B cells in response to exposure to non-self antigens
Antibody - mediated immunity
Antibody classes
differentiated by amino acid sequence
each antibody has a specific function
IgG and IgM are found in blood
IgM
primary response to exposure
slow response
low titer
IgG
secondary response to exposure
fast response
high titer
Specificity
lymphocytes have surface receptors that interact with specific antigens
Memory
the ability to have a faster and stronger immunity due to subsequent exposure to the same antigen
Self Tolerance
adaptive immunity not being able to attack self-antigens
Natural immunity
receiving antibody directly from nature (ex: infection, genes)
Artificial immunity
artificially receiving the antibody (ex: vaccines, antivenom)
Active immunity
something causes our body produces the antibody
Passive immunity
receives antibody directly