Abnormal Psych Exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/279
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:32 AM on 11/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
280 Terms
1
New cards
behavioral medicine
knowledge derived from behavioral science is applied to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of medical problems
2
New cards
health psychology
study of psychological factors that promote and maintain health, as well as health care systems and health policy
3
New cards
2 primary paths psychological and social factors influence health
- psychological factors influence biological processes
- behavioral patterns increase disease risk
- behavioral patterns increase disease risk
4
New cards
______ % of the leading causes of death in the US are linked to behavioral/lifestyle patterns
50%
5
New cards
examples of lifestyle patterns that can lead to death
* smoking
* poor eating habits
* lack of exercise
* insufficient injury control
* poor eating habits
* lack of exercise
* insufficient injury control
6
New cards
General adaptation syndrome (GAS) - theory of stress response
* Phase 1 - alarm response (to immediate danger)
* Phase 2 - resistance (attempt to cope with stress)
* Phase 3 - exhaustion (body suffers damage with stress that lasts too long)
* Phase 2 - resistance (attempt to cope with stress)
* Phase 3 - exhaustion (body suffers damage with stress that lasts too long)
7
New cards
Physiology of stress
- Stress activates HPA axis
- hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) and stimulates pituitary gland
- pituitary gland activates adrenal gland, secreting cortisol
- hippocampus turns off stress response
- hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) and stimulates pituitary gland
- pituitary gland activates adrenal gland, secreting cortisol
- hippocampus turns off stress response
8
New cards
what happens to hippocampus by chronic stress
it becomes damaged by chronic secretion of cortisol
9
New cards
social status in animals
- subordinate animals have chronically high levels of stress, which compromises ability to respond to stress over time, and leads to compromised immune system
- benefit of high social status: predictability and controllability of environment
- benefit of high social status: predictability and controllability of environment
10
New cards
diagram of contributions to stress response
as sense of control or ability to cope increases, our feelings range along continuum from depression, anxiety, stress, to excitement
11
New cards
psychoneuroimmunology
psychological influences on neurological component of immune response
12
New cards
what happened when rats where given sugar water
- rats given sugar water with a drug that suppresses immune system
- later, sugar water along suppressed immune system
- later, sugar water along suppressed immune system
13
New cards
immune system function
identify and eliminate foreign materials (antigens)
14
New cards
2 parts of immune system
- humoral
- cellular
includes white blood cells (leukocytes), B and T cells (lymphocytes), and macrophages
- cellular
includes white blood cells (leukocytes), B and T cells (lymphocytes), and macrophages
15
New cards
macrophages
- body's first line of defense
- surround antigens and destroy them
- signal lymphocytes
- surround antigens and destroy them
- signal lymphocytes
16
New cards
lymphocyte B cells
- in humoral
- release molecules that seek antigens in blood with purpose of neutralizing them
- produce immunoglobulins that act as antibodies, which combine with antigens to neutralize them
- release molecules that seek antigens in blood with purpose of neutralizing them
- produce immunoglobulins that act as antibodies, which combine with antigens to neutralize them
17
New cards
memory B cells
created so next time antigen is encountered, immune response is faster
18
New cards
lymphocyte T cells
- cellular part
- don't produce antibodies
- killer T cells destroy viruses and cancer cells
- memory T cells created to speed up response to same antigen
- T4 cells (helper T cells) enhance immune response by signaling B cells to produce antibodies and tell other T cells to destroy antigen
- suppressor T cells suppress production of antibodies by B cells when not needed
- don't produce antibodies
- killer T cells destroy viruses and cancer cells
- memory T cells created to speed up response to same antigen
- T4 cells (helper T cells) enhance immune response by signaling B cells to produce antibodies and tell other T cells to destroy antigen
- suppressor T cells suppress production of antibodies by B cells when not needed
19
New cards
what happens with too many T4 cells
helper T cells overreact and attack normal cells
20
New cards
in developing world, most die within _______ of AIDS
1 year
21
New cards
what is best treatment for AIDS
- highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)
- suppresses virus, slows progression and decreased mortality
- severe side effects
- suppresses virus, slows progression and decreased mortality
- severe side effects
22
New cards
US AIDS cases by mode of transmission
- male to male sexual contact: _____%
- heterosexual contact: ______ %
- injection drug use: _________%
- other: _______%
- male to male sexual contact: _____%
- heterosexual contact: ______ %
- injection drug use: _________%
- other: _______%
50%; 32%; 17%; 1%
23
New cards
what exacerbates AIDS progression
- high stress
- low social suppor
- low social suppor
24
New cards
outcomes of cognitive-behavioral stress-management (CBSM) in those with AIDS
- increased T-helper cells
- lower antibodies
- enhanced psychological adjustment
- lower antibodies
- enhanced psychological adjustment
25
New cards
psychoncology
study of psychological factors in cancer
26
New cards
psychological and behavioral contributions to etiology and maintenance of cancer
- perceived lack of control
- poor coping responses
- stressful life events
- life-style risk behaviors
- poor coping responses
- stressful life events
- life-style risk behaviors
27
New cards
psychological factors impact cancer risk by impacting functions such as
- immune function
- viral actviity
- DNA repair processes
- Gene expression
- viral actviity
- DNA repair processes
- Gene expression
28
New cards
psychosocial treatments for cancer improve
- health habits
- treatment adherence
- endocrine function
- stress response/coping
- treatment adherence
- endocrine function
- stress response/coping
29
New cards
what is hypertension
high blood pressure
30
New cards
hypertension increases the risk for
- heart disease
- kidney disease
because it taxes blood vessels
- kidney disease
because it taxes blood vessels
31
New cards
hypertension prevalence
- 27.6% of North Americans aged 35-64
- African Americans have 2x greater risk because of experiences of stereotype threat o
- African Americans have 2x greater risk because of experiences of stereotype threat o
32
New cards
risk factors for hypertension
- excessive sodium intake
- sympathetic arousal
- stress level
- expressed anger
- hostility
- sympathetic arousal
- stress level
- expressed anger
- hostility
33
New cards
psychological factors that have been used to explain individual differences in blood pressure
- personality
- coping style
- level of stress
- coping style
- level of stress
34
New cards
psychological factors that contribute to cardiovascular disease
- loneliness
- depression
- feelings of uncontrollability
- depression
- feelings of uncontrollability
35
New cards
coronary heart disease
blockage of arteries supplying blood to heart
36
New cards
psychological and behavioral risk factors associated with coronary heart disease
- stress, anxiety, anger
- poor coping skills
- low social support
- poor coping skills
- low social support
37
New cards
what is CHD linked to
- type A behavior pattern (anger, excessive drive and competitiveness, impatience, accelerated speech, agitated motor activity)
- chronic negative affect, low socioeconomic status, and stressful experiences
- chronic negative affect, low socioeconomic status, and stressful experiences
38
New cards
what factors reduce risk of CHD
positive emotions and optimistic style
39
New cards
reverse capacity model for risk factors for CHD
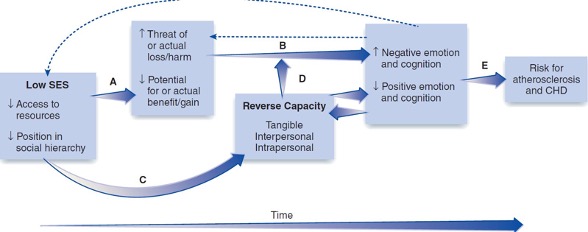
40
New cards
acute pain
follows an injury and disappears once injury heals/effectively treated
41
New cards
chronic pain
may begin with acute episode but doesn't decrease over time
42
New cards
pain behaviors
limping, complaining, avoiding activities
43
New cards
why is severity of pain not a good predictor of one's reaction to it
some experience intense pain and continue to work productively, rarely seek medical service, and lead normal lives
44
New cards
chronic pain is worsened by
- low perceived control
- negative emotion
- poor coping skills
- low social support
- negative emotion
- poor coping skills
- low social support
45
New cards
pain behaviors may be increased by
- compensation (e.g., paid time off)
- social reinforcement (sympathy)
- social reinforcement (sympathy)
46
New cards
gate control theory of pain
neurological processes (anxiety, fear, intense concentration) affect the degree to which pain is detected
- negative emotions - message from brain is to be vigilant against danger
- positive emotions - brain sends inhibitory signal to close gate
- negative emotions - message from brain is to be vigilant against danger
- positive emotions - brain sends inhibitory signal to close gate
47
New cards
endogenous (natural) opioids
- pain-inhibiting natural chemicals that may be increased by exercise
- called endorphins
- called endorphins
48
New cards
why do females have additional pain-regulation mechanisms
- to facilitate childbirth
- neurochemistry may be based on estrogen-dependent neuronal system
- neurochemistry may be based on estrogen-dependent neuronal system
49
New cards
nature of chronic fatigue
- lack of energy and fatigue that doesn't improve with adequate sleep
- may have aches and pains or low fever
- may have aches and pains or low fever
50
New cards
symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome
- subjective memory impairment
- sore throat
- tender lymph nodes
- muscle pain
- joint pain
- headache
- unrefreshing sleep
- malaise lasting more than 24 hours
- sore throat
- tender lymph nodes
- muscle pain
- joint pain
- headache
- unrefreshing sleep
- malaise lasting more than 24 hours
51
New cards
causes of chronic fatigue syndrome
- unknown
- may be response to stress
- may be response to stress
52
New cards
treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome
- medications ineffective
- CBT helpful (includes increasing activity, regulating rest, and stress reduction)
- CBT helpful (includes increasing activity, regulating rest, and stress reduction)
53
New cards
Core beliefs of someone with chronic fatigue syndrome
I am inadequate
54
New cards
lifestyle of someone with chronic fatigue syndrome
- achievement-oriented and hard working
- puts on brave face
- doesn't ask for help
- puts on brave face
- doesn't ask for help
55
New cards
thoughts of someone with chronic fatigue syndrome
- I must be physically ill
- i'm making myself worse
- there's nothing I can do
- I should try harder to cope
- I can beat this
- i'm making myself worse
- there's nothing I can do
- I should try harder to cope
- I can beat this
56
New cards
biofeedback
- psychosocial treatment of physical disorder
- monitor and control bodily responses (heart rate, blood pressure, muscle tension, EEG rhythms)
- increase sense of control
- improves patient's ability to control bodily processes
- monitor and control bodily responses (heart rate, blood pressure, muscle tension, EEG rhythms)
- increase sense of control
- improves patient's ability to control bodily processes
57
New cards
relaxation and meditation
- psychosocial treatment of physical disorder
- progressive muscle relaxation
- transcendental meditation: focuses attention on repeated mantra
- increased sense of control and mastery
- may improve headache, hypertension, acute and chronic pain
- progressive muscle relaxation
- transcendental meditation: focuses attention on repeated mantra
- increased sense of control and mastery
- may improve headache, hypertension, acute and chronic pain
58
New cards
comprehensive stress and pain reduction program
- monitor and identify stressful events (times, intensity, triggers)
- monitor somatic symptoms
- muscle relaxation
- cognitive therapy
- increase coping strategies (time management, assertiveness training)
- more effective than individual components
- monitor somatic symptoms
- muscle relaxation
- cognitive therapy
- increase coping strategies (time management, assertiveness training)
- more effective than individual components
59
New cards
drugs vs. stress reduction programs
- medication decreases efficacy of comprehensive programs
- high relapse when stopped
- tolerance built over time
- high relapse when stopped
- tolerance built over time
60
New cards
coping through denial
- denial about physical condition can be helpful
- helpful at early stages
- later, more helpful to face situation
- helpful at early stages
- later, more helpful to face situation
61
New cards
what is the leading cause of death from ages 1-45
accidents
62
New cards
injury prevention
- repeated warnings not enough
- programmatic efforts needed (teach children to escape fires and cross streets)
- programmatic efforts needed (teach children to escape fires and cross streets)
63
New cards
AIDS prevention
- preventable by changing behaviors (safe-sex, sanitary use of needles, regular check-ups, strong peer support programs)
64
New cards
smoking cessation in China
- capitalize on family relationships (children persuade fathers to stop)
- distribute anti-smoking literature
- target at-risk populations
- distribute anti-smoking literature
- target at-risk populations
65
New cards
stanford three community study
- looking to reduce risk factors of CHD
- conducted in 3 similar communities
- each community either got: no intervention, media blitz, media blitz plus face-to-face intervention
- highest benefit from media blitz plus live intervention
- conducted in 3 similar communities
- each community either got: no intervention, media blitz, media blitz plus face-to-face intervention
- highest benefit from media blitz plus live intervention
66
New cards
what is abnormal sexual behavior?
- normative facts and statistics
- cultural considerations
- gender differences in sexual behavior and attitudes
- cultural considerations
- gender differences in sexual behavior and attitudes
67
New cards
how many partners in a lifetime and past year
- 15 or more (lifetime): men = 21.4%, female = 8.3%
- 4 or more (past year): men = 6%; female = 2.9%
- 4 or more (past year): men = 6%; female = 2.9%
68
New cards
homosexual sex attraction or behavior statistics
men = 10%
women = 9%
women = 9%
69
New cards
sex in age 75-85 statistics
men = 38.5% active
female = 16.7% active
female = 16.7% active
70
New cards
gender differences in masturbation
men = 72% report ever masturbating
female = 42% report ever masturbating
- males masturbation may be easier and physical gratification more emphasized for men
female = 42% report ever masturbating
- males masturbation may be easier and physical gratification more emphasized for men
71
New cards
gender differences in casual premarital sex
men are more permissive, but the gap is shrinking
72
New cards
gender differences in elements of satisfaction
- women are more likely to seek demonstrations of love and intimacy
- men are more likely to focus on arousal
- men are more likely to focus on arousal
73
New cards
no differences in gender differences of
- acceptability of homosexuality
- acceptability of masturbation
- importance of sexual satisfaction
- acceptability of masturbation
- importance of sexual satisfaction
74
New cards
sexual self-schemas
beliefs about one's own sexuality
75
New cards
gender differences in sexual beliefs
- females more likely to value experience of passionate and romantic feelings
- minority of females hold embarrassed, conservative, or self-conscious views toward sex
- males have fewer negative core beliefs about sex
- men are more likely to emphasize dominance and aggression
- minority of females hold embarrassed, conservative, or self-conscious views toward sex
- males have fewer negative core beliefs about sex
- men are more likely to emphasize dominance and aggression
76
New cards
cultural differences on views on sexuality in children
- Sambia believe receiving semen contributes to development in children (emphasize homosexual oral sex between young boys)
- Munda emphasize mild heterosexual activity (mutual masturbation) among cohabitating children
- Munda emphasize mild heterosexual activity (mutual masturbation) among cohabitating children
77
New cards
development of sexual orientation
- bio-psycho-social influences
- homosexuality (only small genetic component: 50% of identical twins raised together do NOT share same sexual orientation)
- homosexuality (only small genetic component: 50% of identical twins raised together do NOT share same sexual orientation)
78
New cards
why did DSM III remove homosexuality as a disorder
- no physiological differences in arousal between gay and straight
- no difference in rate of psychological disturbance
- gender identity confusion no more common in homosexuals
- lack of full societal acceptance and different behaviors, homosexual sexual concerns differ from heterosexuals' concerns
- no difference in rate of psychological disturbance
- gender identity confusion no more common in homosexuals
- lack of full societal acceptance and different behaviors, homosexual sexual concerns differ from heterosexuals' concerns
79
New cards
sexual dysfunctions
- involve desire, arousal, and/or orgasm
- pain associated with sex can lead to additional dysfunction
- pain associated with sex can lead to additional dysfunction
80
New cards
sexual dysfunction present for how long to make a diagnosis
6+ months
81
New cards
desire phase
sexual urges occur in response to sexual cues or fantasies
82
New cards
arousal stage
sense of sexual pleasure and physiological signs of sexual arousal
83
New cards
plateau phase
brief period occurs before orgasm
84
New cards
orgasm phase
- in males, feelings of inevitability of ejaculation, followed by ejaculation
- females, contractions of walls of lower third of vagina
- females, contractions of walls of lower third of vagina
85
New cards
resolution phase
decrease in arousal after orgasm (particularly in men)
86
New cards
prevalence of sexual dysfunctions
- common and not always distressing
- 40% of men have difficulty with erection/ejaculation, 63% of women have problems with arousal/orgasm
- 40% of men have difficulty with erection/ejaculation, 63% of women have problems with arousal/orgasm
87
New cards
classification of sexual dysfunctions
- lifelong vs. acquired
- generalized vs. situational
- psychological factors alone
- psychological factors combined with medical condition
- generalized vs. situational
- psychological factors alone
- psychological factors combined with medical condition
88
New cards
lifelong
chronic condition present during person's entire sexual life
89
New cards
acquired
disorder begins after sex has been normal
90
New cards
generalized
occurs every time individual attempts sex
91
New cards
situational
occurs with some partners or at certain times
92
New cards
desire disorders in men/women
- men: hypoactive sexual desire
- women: female sexual interest/arousal disorder
- women: female sexual interest/arousal disorder
93
New cards
arousal disorders in men/women
- men: erectile disorder
- women: female sexual interest/arousal disorder
- women: female sexual interest/arousal disorder
94
New cards
orgasm disorder in men/women
- men: erectile disorder
- women: female sexual interest/arousal disorder
- women: female sexual interest/arousal disorder
95
New cards
pain disorder in women
- genito-pelvic pain/penetration disorder (ex: vaginismus)
96
New cards
male hypoactive sexual desire disorder statistics
- accounts for half of all complaints at sexuality clinics
- affects 5% of men
- affects 5% of men
97
New cards
DSM-5 for male hypoactive sexual desire disorder
1. persistently or recurrently deficient (or absent) sexual/erotic thoughts or fantasies and desire for sexual activity
2. symptoms have persisted for minimum of 6 months
3. symptoms cause distress in individual
4. sexual dysfunction not better explained by nonsexual disorder or consequence of relationship distress or other stressors and isn't attributable to medication or other medical condition
specify whether: lifelong or acquired type
specify whether: generalized or situational type
2. symptoms have persisted for minimum of 6 months
3. symptoms cause distress in individual
4. sexual dysfunction not better explained by nonsexual disorder or consequence of relationship distress or other stressors and isn't attributable to medication or other medical condition
specify whether: lifelong or acquired type
specify whether: generalized or situational type
98
New cards
erectile disorder
- difficulty achieving or maintaining erection
- sexual desire intact
- sexual desire intact
99
New cards
statistics for erectile disorder
- most common problem for which men seek treatment
- prevalence increases with age (60% of men over 60 experience erectile dysfunction)
- prevalence increases with age (60% of men over 60 experience erectile dysfunction)
100
New cards
female sexual interest/arousal disorder prevalence
prevalence decreases with age