Anatomy Exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/334
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
335 Terms
1
New cards
What are organ systems?
integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, reproductive
2
New cards
What is the integumentary system?
skin
3
New cards
What is the skeletal system?
protects and supports body organs, and provides frameworks the muscles use to cause movement.
4
New cards
What is the muscular system?
Consists of skeletal muscles, tendons that connect muscles to bones, and ligaments that attach bones together to form joint
5
New cards
What is the nervous system?
Consists of the brain, spinal cord & nerves & it serves as the body's CONTROL SYSTEM
6
New cards
What is the endocrine system?
HORMONES!!
7
New cards
What is the cardiovascular system?
heart and blood vessels
8
New cards
What is the lymphatic system?
Lymph nodes, immune system
9
New cards
What is the respiratory system?
This system keeps the body's cells supplied with oxygen
10
New cards
What is the urinary system?
the excretory (urinary) system helps maintain the water & electrolyte balance in the body.
11
New cards
What is the digestive system?
consists of all organs from mouth to the anus involved in the ingestion and breakdown or processing of food.
12
New cards
What is the reproductive system?
Reproduce offspring- produce male sex cells (sperm) and female sex cells (oocytes)
13
New cards
What is homeostasis?
the ability of an organism to maintain consistent internal environment in response to changing internal or external conditions
14
New cards
What is an example of how humans maintain homeostasis?
body temperature--sweating, sickness--lymphatic system kicks in
15
New cards
What are the three components of homeostatic systems?
Receptor, Control Center, Effector
16
New cards
What is a condyle?
Large, smooth, rounded, oval structure
17
New cards
What is a facet
Small, flat, shallow surface
18
New cards
What is a head?
Prominent, rounded epiphysis
19
New cards
What is a trochlea?
Smooth, grooved, pulleylike process
20
New cards
What is an alveolus?
Deep pit or socket in the maxillae or mandible
21
New cards
What is a Fossa?
Flattened or shallow depression
22
New cards
What is a Sulcus?
Narrow groove
23
New cards
What is a Crest?
Narrow, prominent, ridgelike projection
24
New cards
What is a Epicondyle?
Projection adjacent to a condyle
25
New cards
What is a Line?
Low ridge
26
New cards
What is a process?
Any marked bony prominence
27
New cards
What is a Ramus?
Angular extension of a bone relative to the rest of the structure
28
New cards
What is a Spine?
Pointed, slender process
29
New cards
What is a Trochanter?
Massive, rough projection found only on the femur
30
New cards
What is a Tubercle?
Small, round projection
31
New cards
What is a Tuberosity?
Large, rough projection
32
New cards
What is a Meatus/Canal?
Passageway through the bone
33
New cards
What is a Fissure?
Narrow, slitlike opening through a bone
34
New cards
What is a Foramen?
Rounded passageway through the bone
35
New cards
What is a Sinus?
Cavity or hollow space in a bone
36
New cards
Clavicle
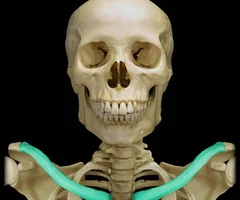
37
New cards
Scapula
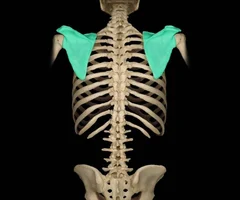
38
New cards
Humerus
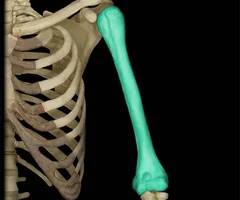
39
New cards
Carpals
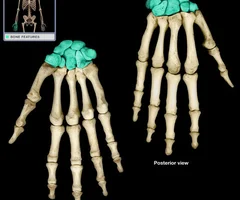
40
New cards
Radius
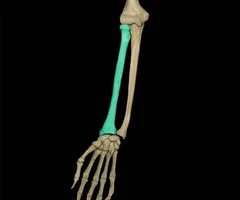
41
New cards
Metacarpals
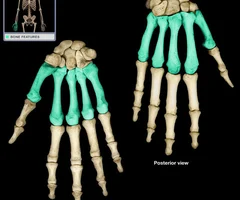
42
New cards
Ulna
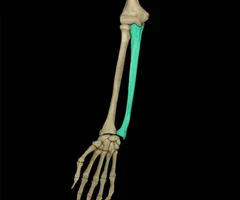
43
New cards
Phalanges
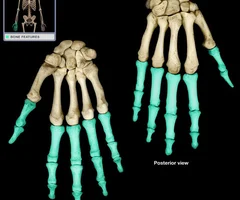
44
New cards
Os coaxe
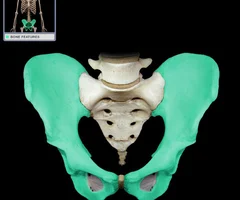
45
New cards
Femur
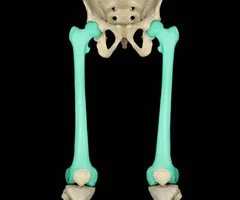
46
New cards
Tarsals
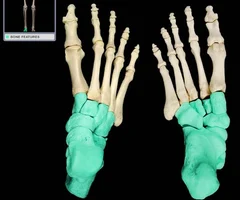
47
New cards
Patella
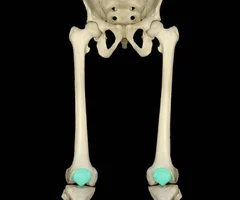
48
New cards
Tibia
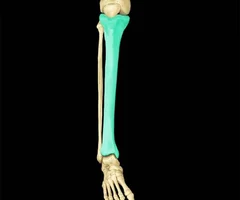
49
New cards
Fibula
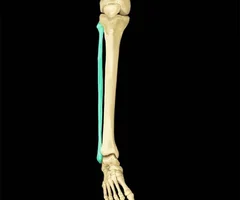
50
New cards
Frontal Bone
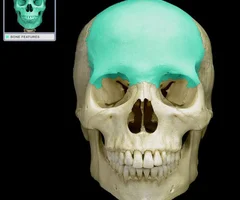
51
New cards
Parietal Bones
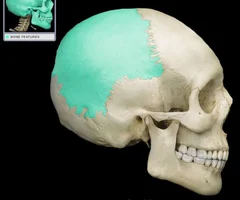
52
New cards
Temporal Bones
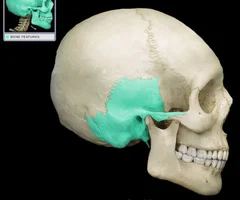
53
New cards
Occipital Bone
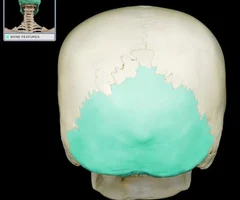
54
New cards
Sphenoid bone
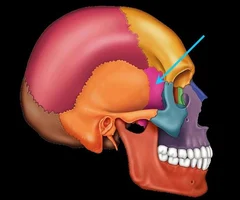
55
New cards
Ethmoid Bone
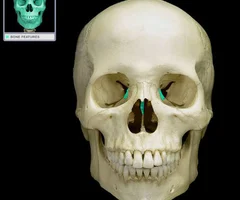
56
New cards
Zygomatic Bones
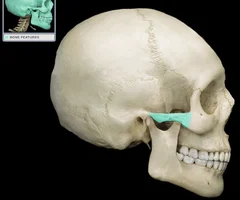
57
New cards
Lacrimal Bones
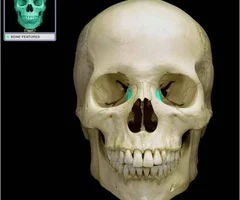
58
New cards
Nasal Bones
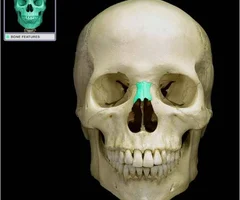
59
New cards
Vomer
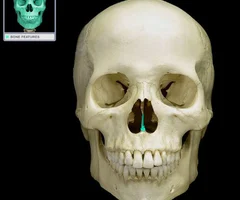
60
New cards
Inferior Nasal Conchae
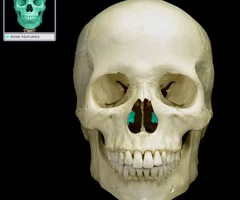
61
New cards
Palatine Bones
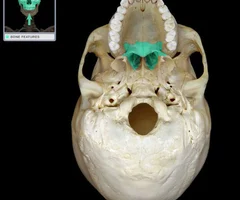
62
New cards
Maxillae
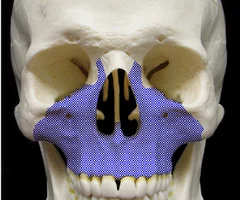
63
New cards
Mandible
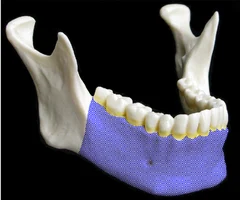
64
New cards
Malleus
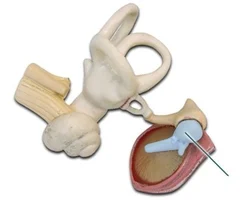
65
New cards
Incus
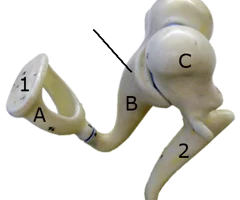
66
New cards
Stapes
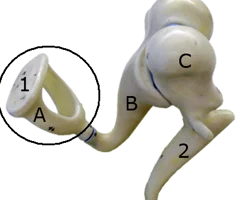
67
New cards
Hyoid Bone
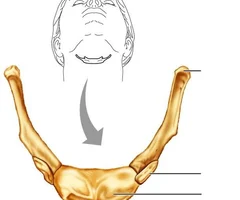
68
New cards
cervical vertebrae
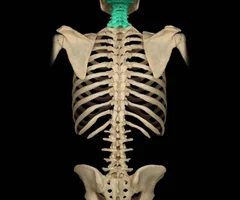
69
New cards
Thoracic Vertebrae
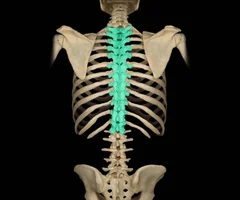
70
New cards
Lumbar Vertebrae
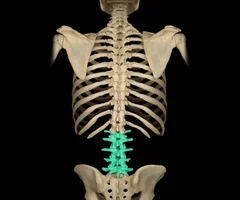
71
New cards
Sacrum
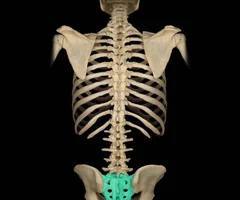
72
New cards
Coccyx
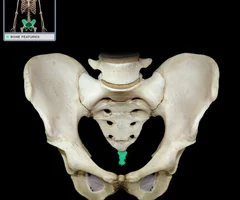
73
New cards
Sternum
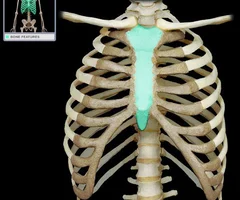
74
New cards
Ribs
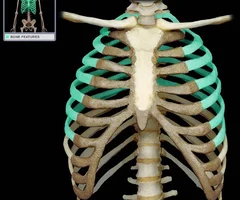
75
New cards
What are articulating surfaces?
condyle, facet, head, trochlea
76
New cards
What are depressions?
alveolus, fossa, sulcus
77
New cards
What are Projections?
crest, epicondyle, line, process, ramus, spine, trochanter, tubercle, tuberosity
78
New cards
What are openings and spaces?
canal, fissure, foramen, meatus, sinus
79
New cards
What are condyles?
large, smooth, rounded articulating oval structure
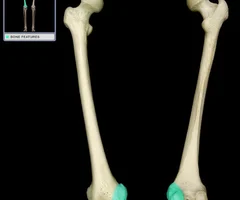
80
New cards
What are facets?
small, flat, shallow surface
81
New cards
What are heads?
prominent, rounded epiphysis
82
New cards
What are Trochiea?
smooth, grooved, pulley-like process
83
New cards
What is Etiology?
study of the cause of disease
84
New cards
What is Pathogenisis?
development of disease
85
New cards
What is anatomy?
The study of body structure
86
New cards
What is Physiology?
The study of body function
87
New cards
What is Microscopic Anatomy?
deals with structures too small to be seen with the naked eye
88
New cards
What is Cytology?
study of cells
89
New cards
What is Histology?
study of tissues
90
New cards
What is systematic anatomy?
body structure is studied system by system
91
New cards
What is Regional Anatomy?
specific regions of the body such as the head or chest
92
New cards
What is surface anatomy?
the study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin surface
93
New cards
What is comparative anatomy?
The comparison of body structures and how they vary among species
94
New cards
What is embryology anatomy?
developmental changes that occur before birth
95
New cards
What is Pathologic Anatomy/Pathology?
examines all anatomic changes resulting from disease
96
New cards
What is radiographic anatomy?
investigates internal structures visualized by scanning procedures
97
New cards
What is cardiovascular physiology?
functions of the heart and blood vessels
98
New cards
What is Neurophysiology?
explains the workings of the nervous system
99
New cards
What is respiratory physiology?
functions of the air passageways and lungs
100
New cards
What is reproductive physiology?
the functioning of reproductive hormones and the reproductive cycle