Anatomy and Physiology Vocabulary Review
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential vocabulary terms related to anatomy and physiology, providing definitions for important concepts discussed in the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
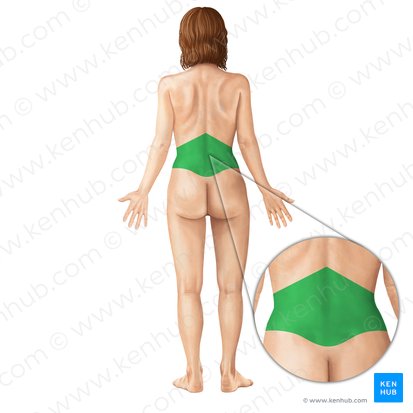
Lumbar
Relating to the lower back region, specifically the five vertebrae (L1-L5) in the lower spine.
Abdominal
The area of the body between the chest and pelvis, containing organs like the stomach and intestines.
Deep
Referring to structures that are farther from the surface of the body.
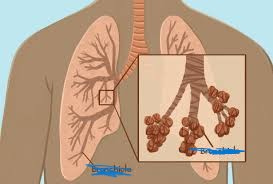
Lung
An organ in the respiratory system responsible for gas exchange.
Abduction
Movement of a limb away from the midline of the body.
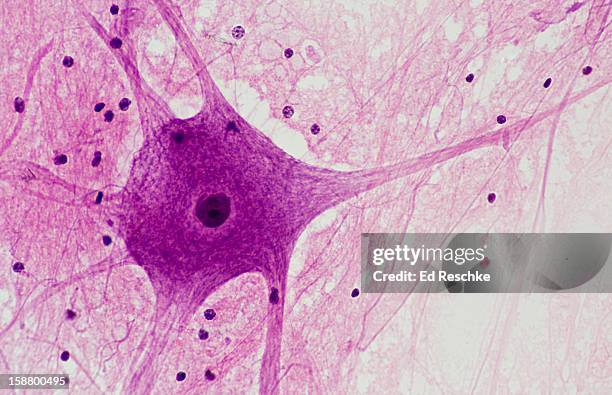
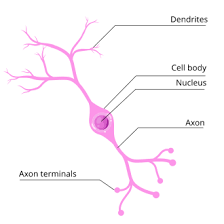
Dendrite
A branched extension of a neuron that receives signals from other neurons.
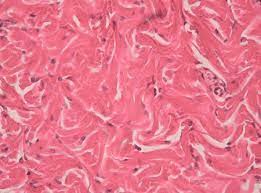
Dense irregular
A type of connective tissue with fibers arranged in various directions, providing strength in multiple directions.
Gallbladder
A small organ that stores bile produced by the liver.
Lysosome
An organelle containing enzymes that digest waste and cellular debris.
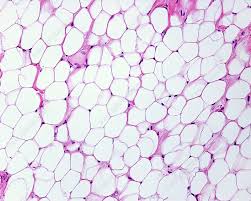
Adipose
Connective tissue that stores fat.
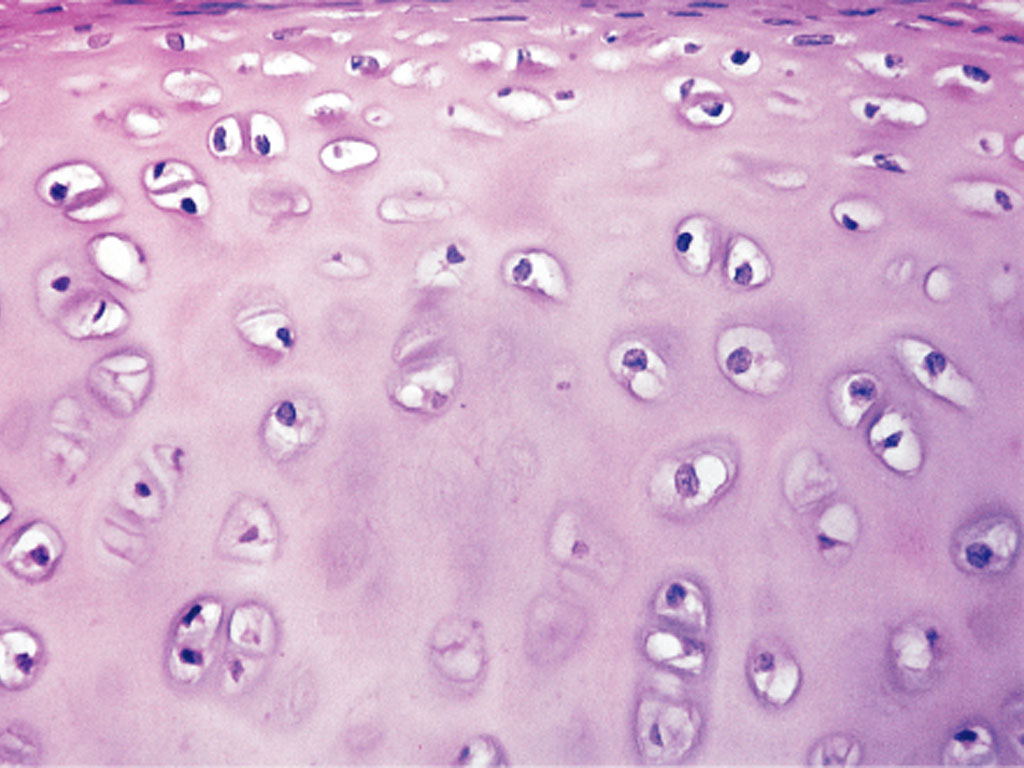
Hyaline cartilage
A translucent cartilage found in various parts of the body, including the joints and rib cage.
Mitochondrion
An organelle known as the powerhouse of the cell, producing energy through respiration.
Intercalated discs
Connections between cardiac muscle cells that facilitate synchronized contraction.
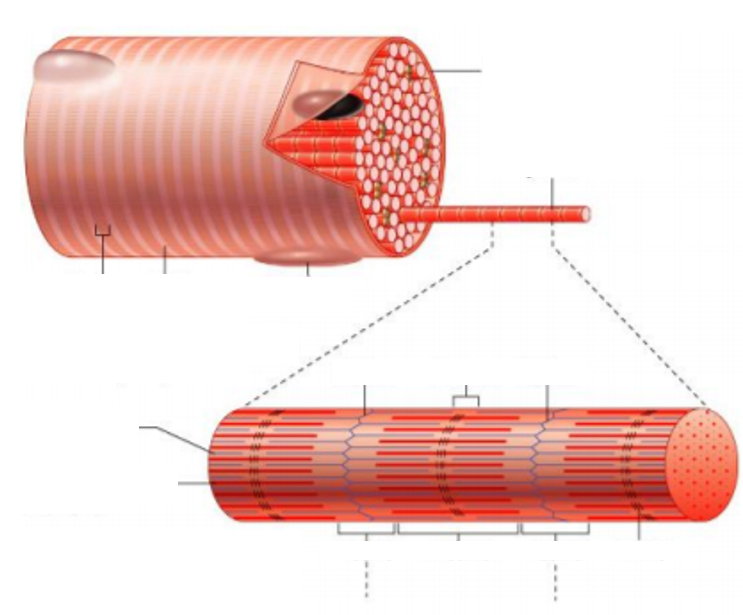
Myofibril
A basic rod-like unit of a muscle cell.
Efferent
Nerves that carry signals away from the central nervous system to effectors like muscles and glands.
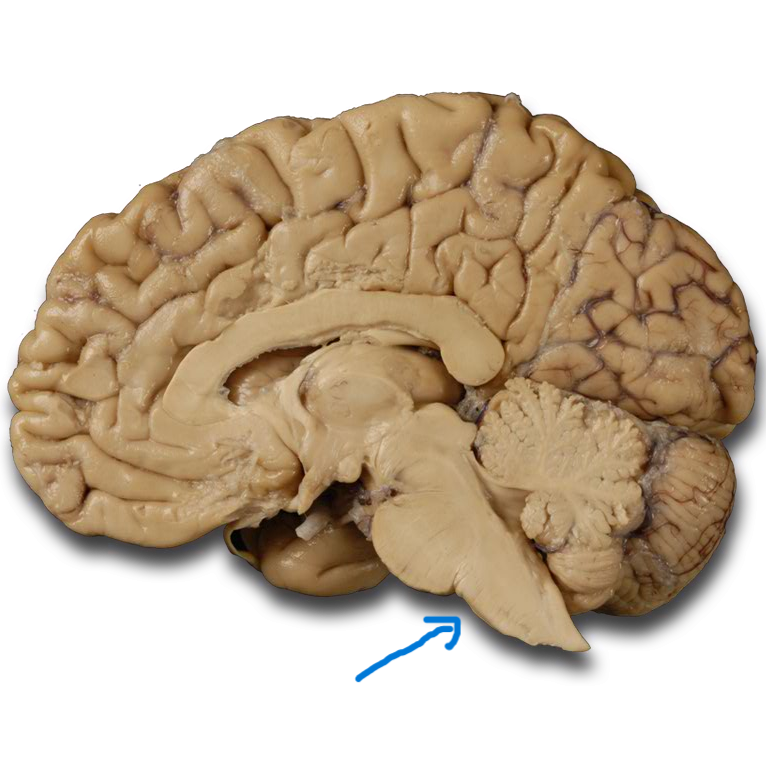
Medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that regulates vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
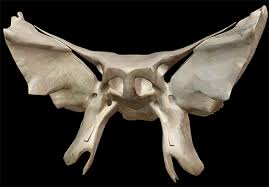
Sphenoid
A bone located at the base of the skull, shaped like a butterfly. sinus cavity
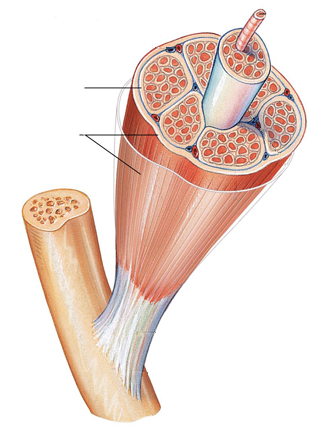
Fascia
A band or sheet of connective tissue that envelops, separates, or supports muscles or organs.
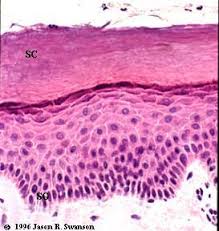
Stratum corneum
The outermost layer of the epidermis, consisting of dead cells that provide a barrier to the environment.
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment to the body or to a given reference point.
Apocrine sweat gland
A type of gland in the skin that secretes a thicker, milky fluid into hair follicles.
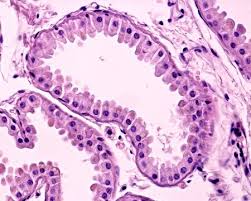
afferent
Referring to nerves or vessels that carry signals or blood towards a central organ or point, such as the heart or brain.
alveoli
Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
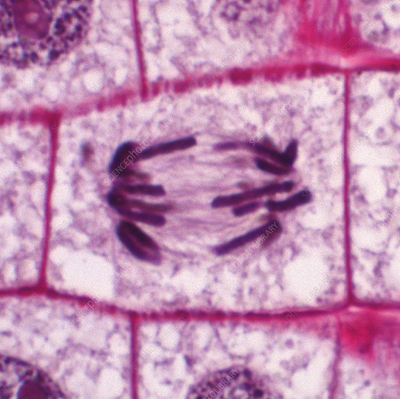
anaphase
The stage in mitosis or meiosis where chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
anaxonic
A type of neuron where all processes are similar and there are no distinct axons or dendrites. These neurons are primarily found in the brain and retina.
antagonist neuron
A type of neuron that inhibits the action of another neuron, playing a critical role in regulating neural activity and maintaining homeostasis.
anterior/ventral
Referring to the front side of the body or object in anatomical position.
apical
the surface of the cell that is exposed to the lumen or external environment, typically involved in absorption, secretion, and cell signaling.
basal
the surface of a cell that is oriented towards the underlying tissue or substrate, often involved in attachment and communication with other cells.
appendix
a small pouch connected to the large intestine
axon
the long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body.
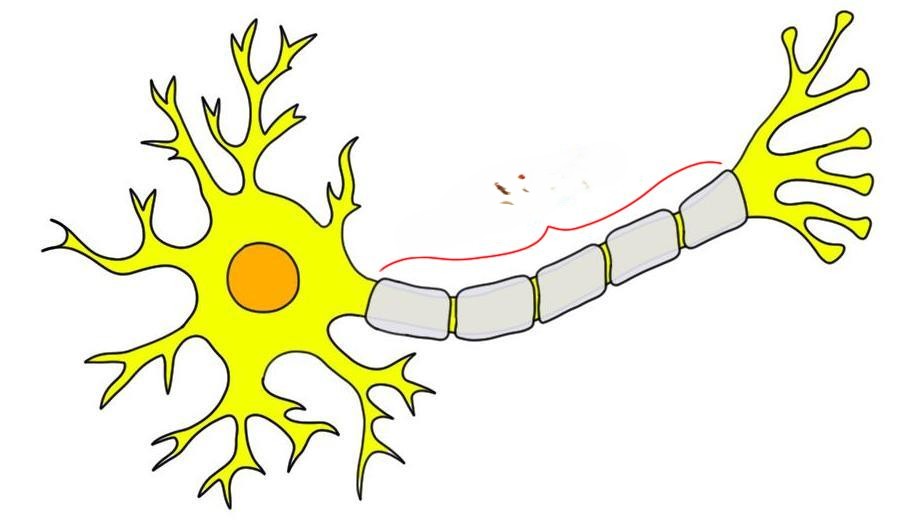
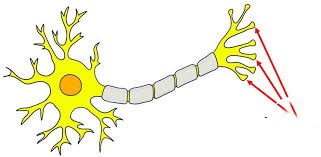
axon terminal
the specialized structure at the end of an axon that releases neurotransmitters to communicate with other neurons or target cells.
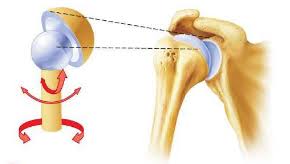
ball and socket
a type of joint that allows for multi-directional movement and rotation, typically found in the shoulder and hip.
bipennate
muscle fibers arranged on both sides of a central tendon

bipolar
a type of neuron that has two extensions, one axon and one dendrite, which allows for specific communication with other neurons.
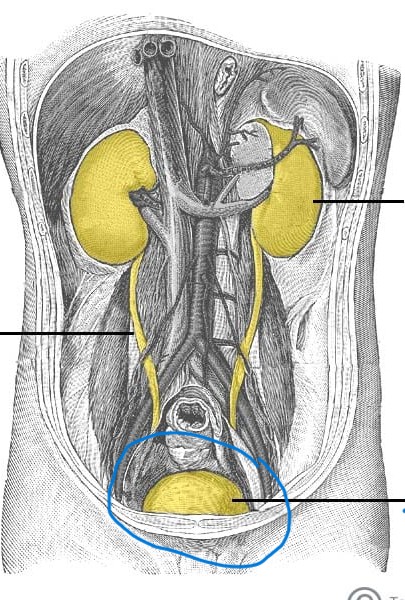
bladder
a muscular sac that stores urine before it is excreted from the body.
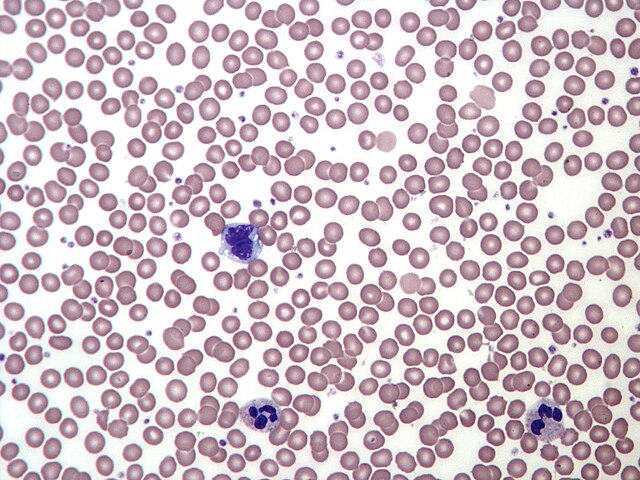
blood
a liquid connective tissue that carries oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body.
blood vessel
a tubular structure that carries blood throughout the body, including arteries, veins, and capillaries.
bone
a hard, dense connective tissue that forms the skeleton, providing structure, support, and protection for the body's organs.
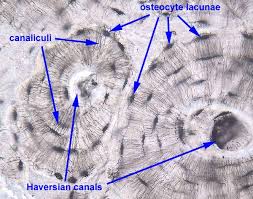
bony
relating to or composed of bone, providing structure and support in the skeletal system.
bronchiole