Node Analysis, Dependent Sources (Lecture 5.2/6.1 - Chap. 3-4)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
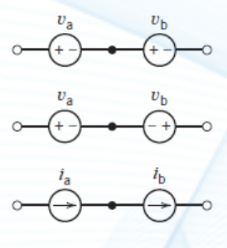
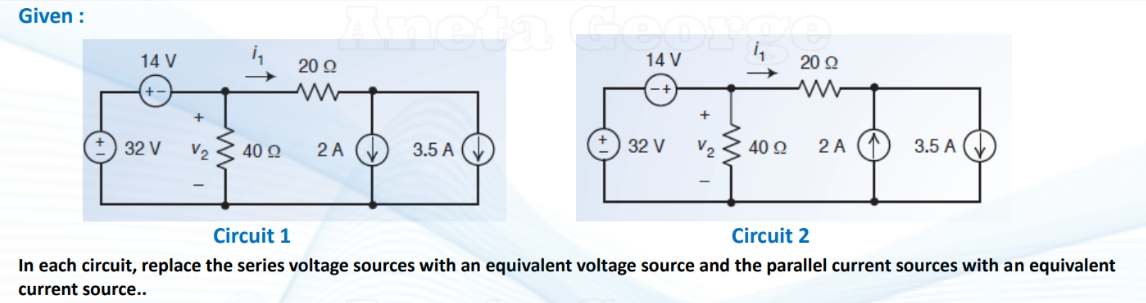
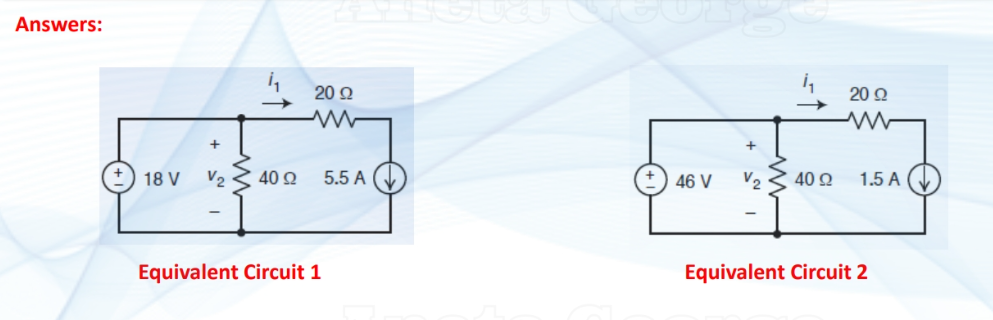
what are the equivalent of these three situations in a series circuit?
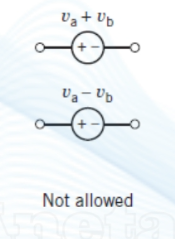
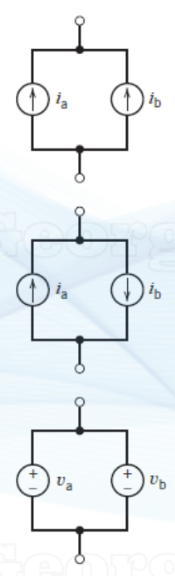
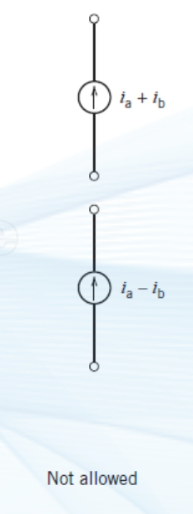
what are the equivalent of these three situations in a || circuit?
(keep the direction of the source that produces the larger current)
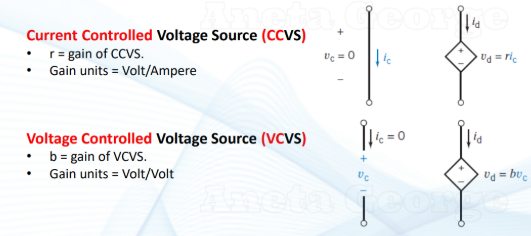
dependent source
models the situation where the voltage or current of one circuit elem is proportional to a voltage or current elsewhere
symbols for dependent voltage/current source

two types of dependent voltage sources (DVS)
gain = the constant
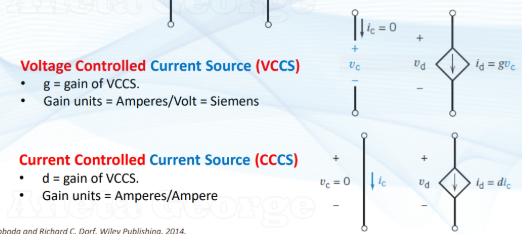
two types of dependent current sources (DCS)
gain = the constant
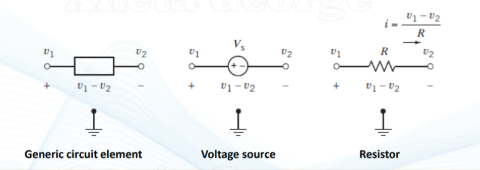
node voltages (v1, v2) and elem voltage (v1 - v2) for different types of circuit elems
rmbr to respect passive convention → v1 - v2, v1 comes first because the polarity is pos at v1, meaning it has a higher elec potential.
supernode (and when you can make one)

steps to analyzing a circuit using voltage nodes
express all voltages (including sources) as equations with voltage nodes
create supernodes if possible
apply KCL, KVL, with special focus given to unknown variables wanted by the question
solve through system of equations