L11 + L12 Multi-species dynamics: Predation and herbivory
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What are examples of couples oscillations?
Predator -> prey
Herbivore -> plant
Parasite -> host
What is the Lotka-Volterra model, that relates to predation and herbivory?
Captures how efficient a predator is at catching prey, and conversion of prey biomass into predator biomass
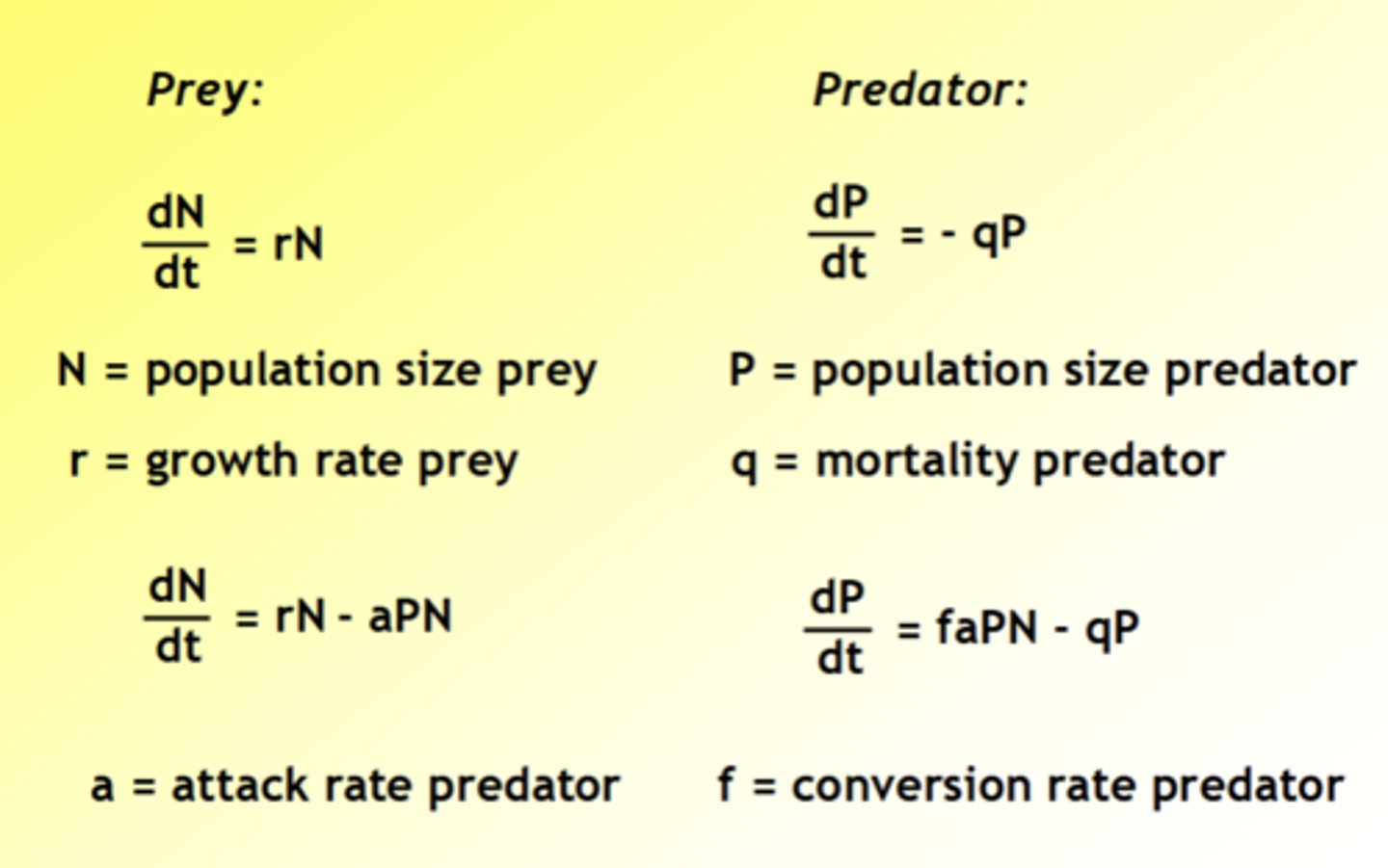
What are zero isoclines?
no change in population size
What are the 2 lotka-Volterra graphs?
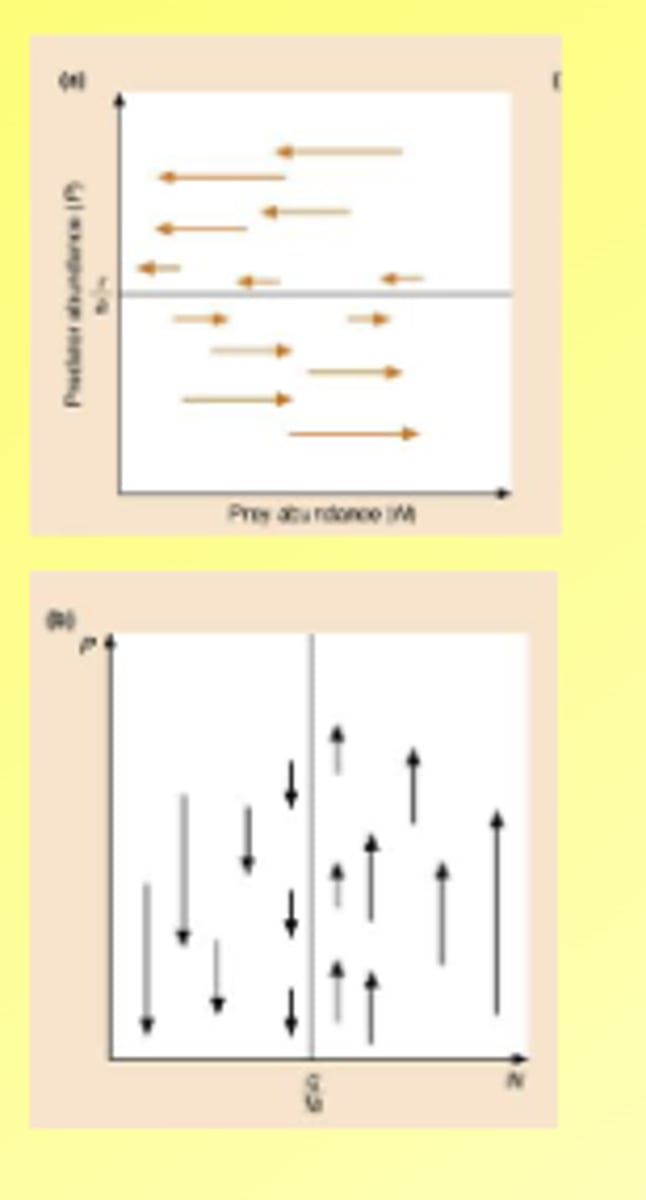
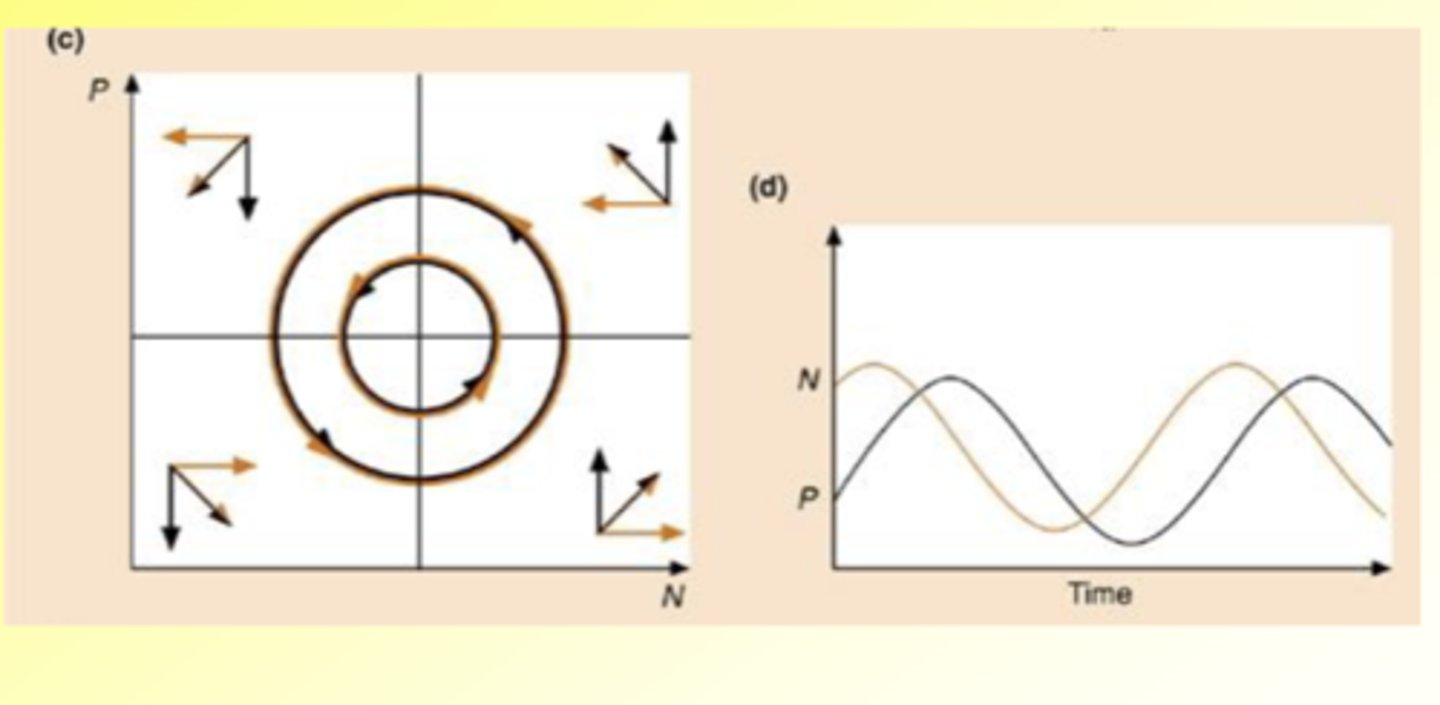
What happens when you overlay the graphs?
Coupled oscillations, with predator lagging behind prey
1st shows prey and predator
2nd shows against time
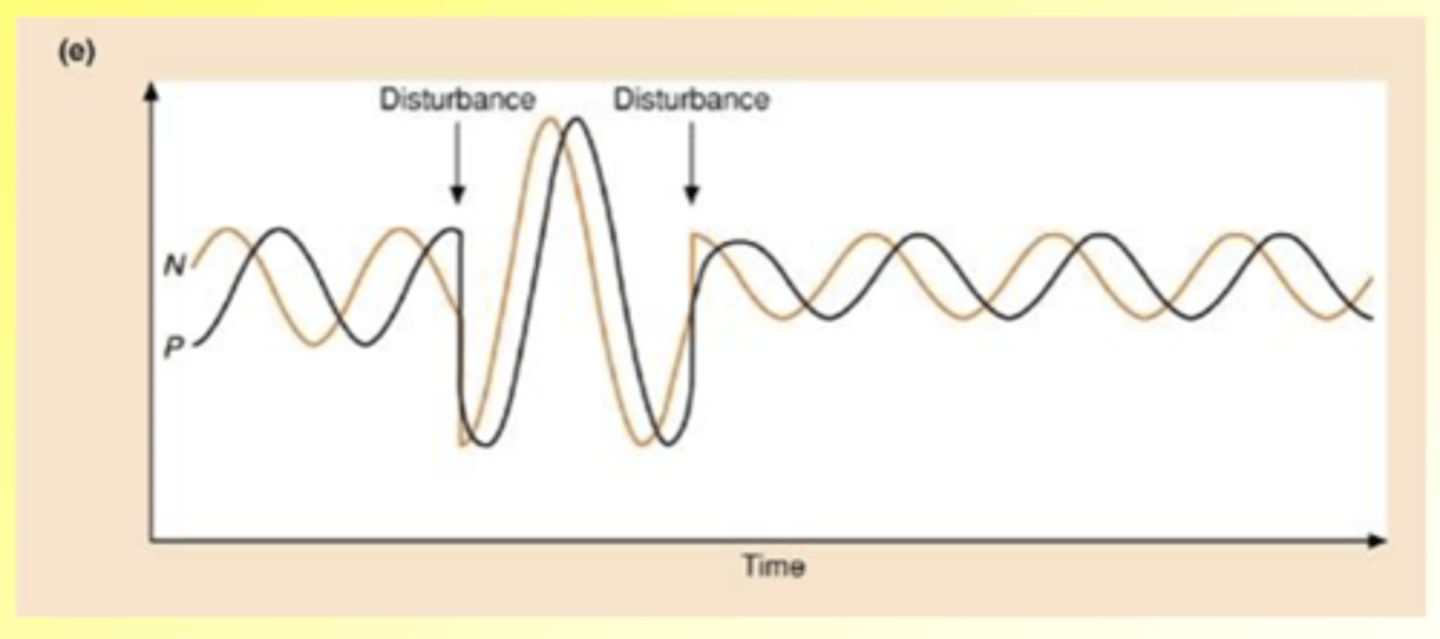
What happens when there is a disturbance in the lotka-volterra model?
Oscillations are unstable
What is a functional response?
Describes how consumption rate of predator reacts to change in prey numbers
What are the 3 types of functional response?
- Type I
- Type II
- Type III
What is a type 1 functional response?
Consumption rate increases linearly with prey abundance (until plateau is reached)
Type I functional response is assumed in LV equations (constant a = attack rate)
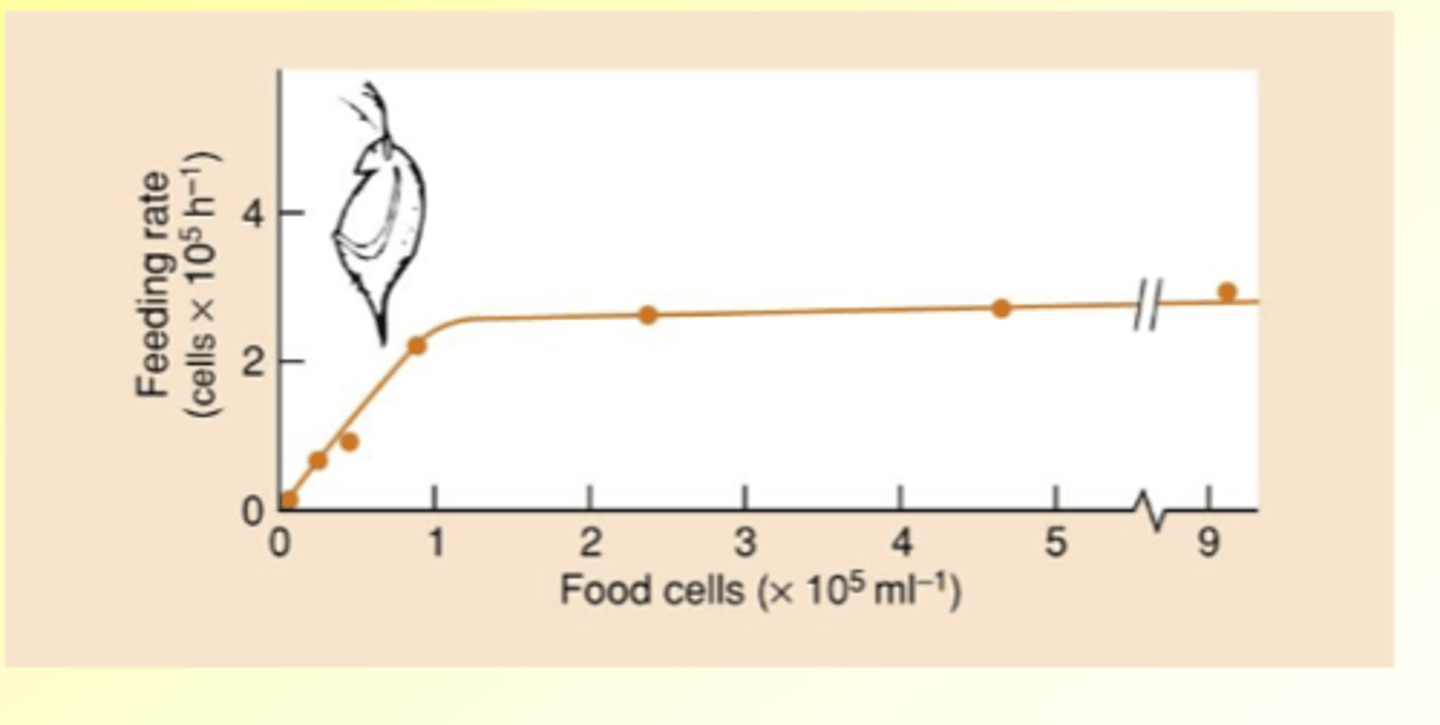
What is a type 2 functional response?
Consumption rate increases with prey abundance, but in a decelerating way
Caused by predator spending more time on handling prey than finding prey at high densities
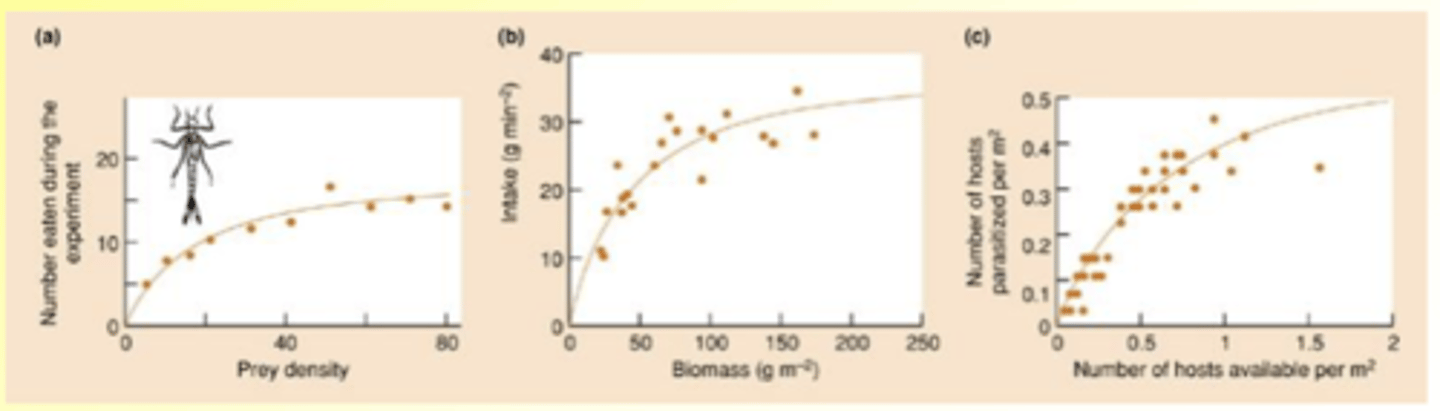
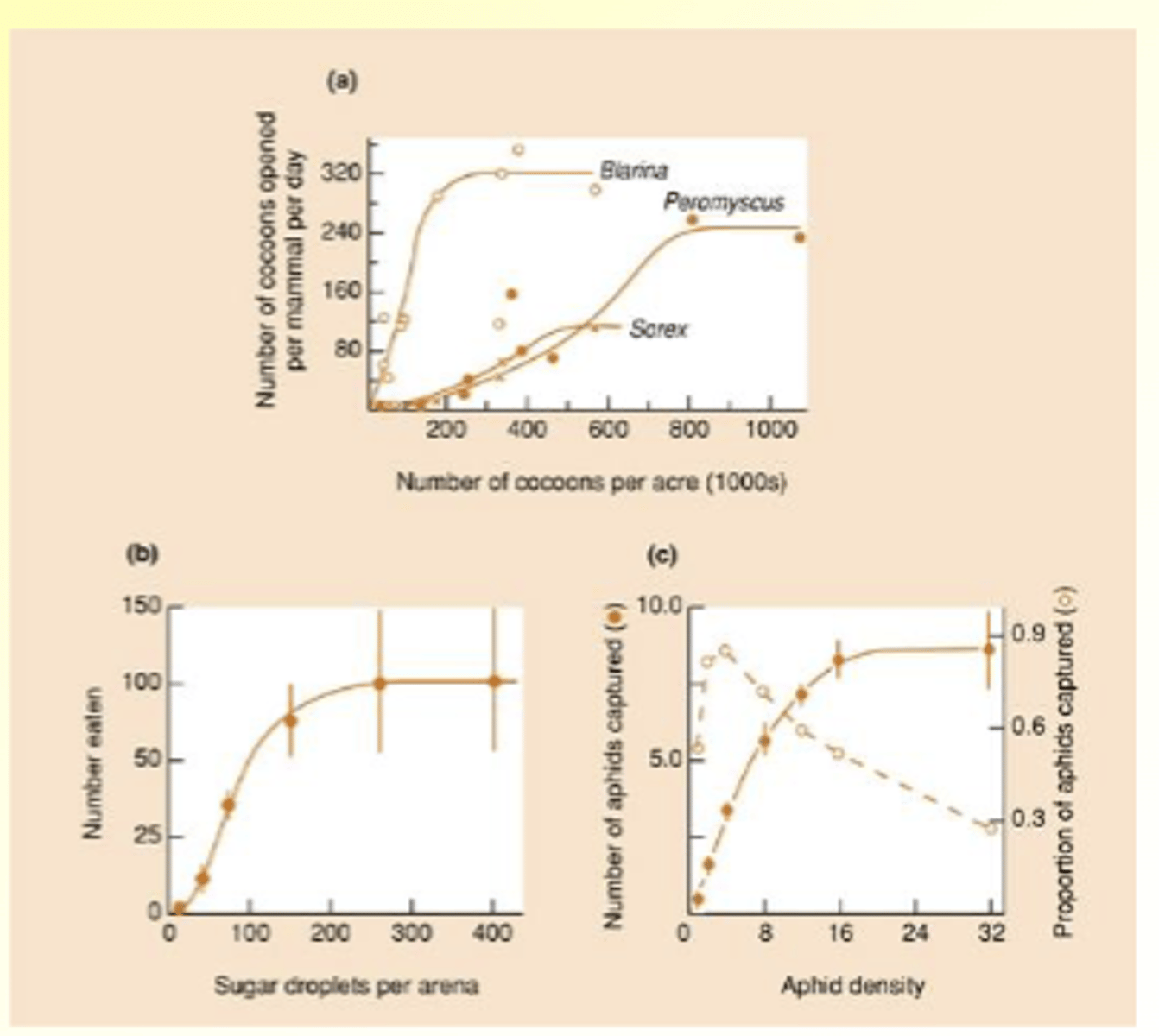
What is a type 3 functional response?
- Like type II at higher prey densities, but lower than expected at low prey densities
- Could be caused by 'switching'
- Leads to s-shaped ('sigmoidal') curve
- Refugium for prey at low densities
Will prey numbers vary across time and space?
yes
Where do predators aggregate?
where prey numbers are high
Refugia where prey numbers are low
How do we get stabilisation of oscillations?
through a negative feedback mechanism
What are features of herbivory - grazing?
Plant usually not killed
Large variation from strict monophagy (feeding on one species) to full polyphagy (feeding on lots)
What is the critical difference between predation and herbivory?
- plant not normally killed
- animal is
What do monophagous herbivores normally consist of?
- Small insects (exception is koala)
What do polyphagous herbivores usually consist of?
Large mammals (exception is locusts)
What is the strict monophagy of herbivory?
Plant abundance determined by herbivore traits; herbivore abundance by plant traits
Because herbivore is food-limited, the faster the plant grows, the faster the herbivore eats it
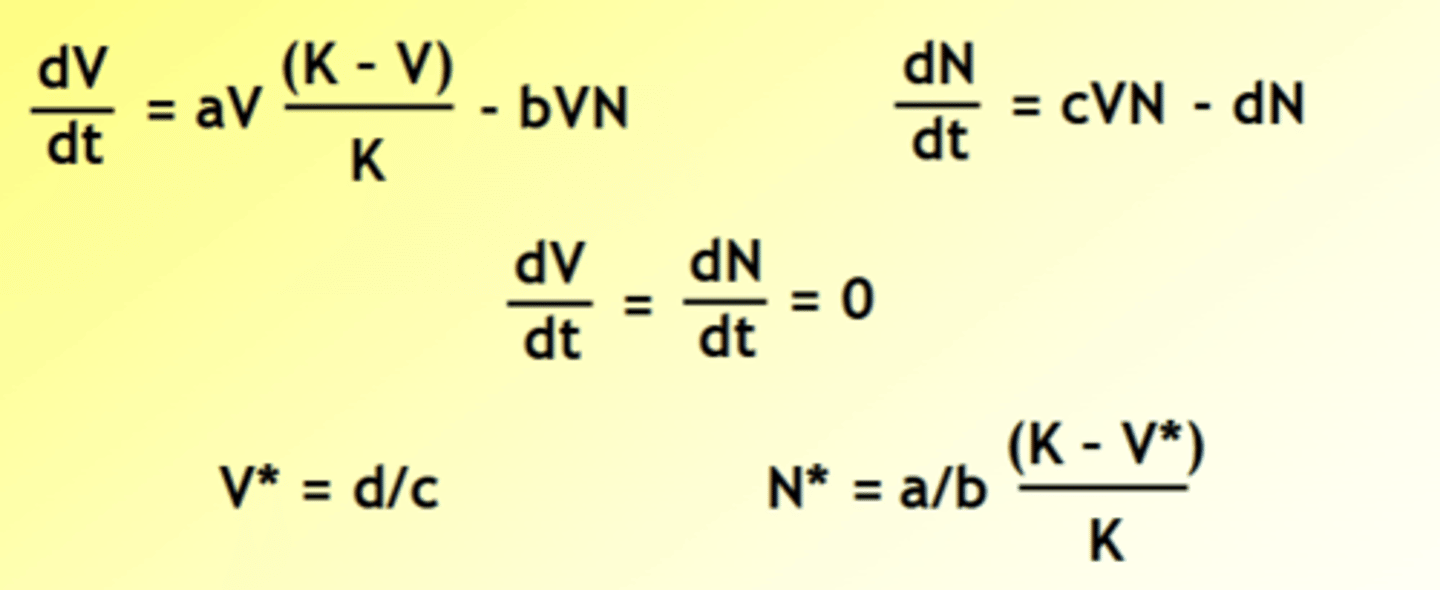
What happens if there is full polyphagy in herbivory?
- Herbivore is polyphagous, so abundance does not depend on focus plant -> constant rate of herbivory
- Plant abundance determined by plant and herbivore traits; the faster it grows, the higher its biomass
- Herbivore is not limited by focal plant
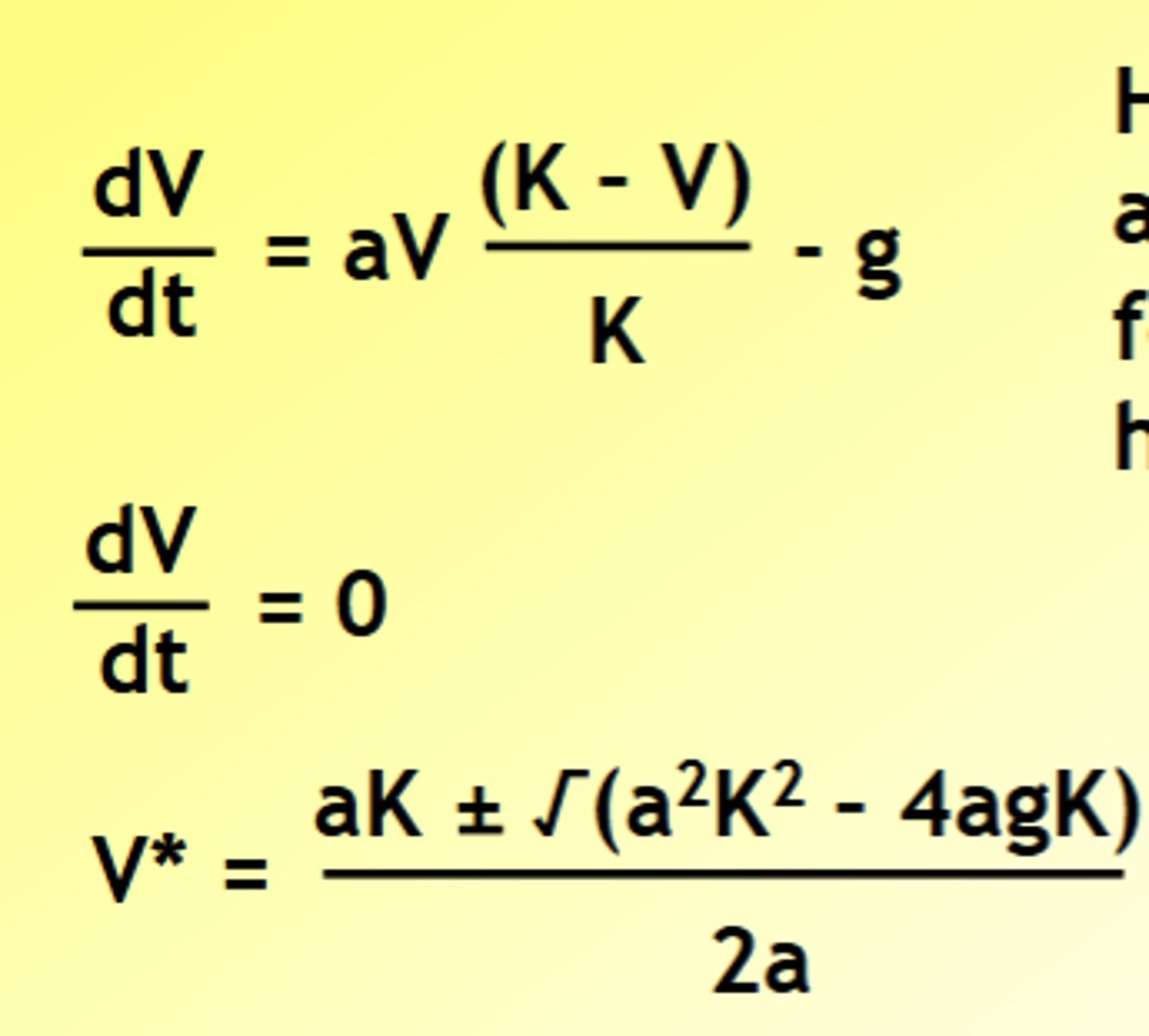
What is a trophic cascade?
when top consumers reduce the biomass of the next lowest trophic level and this reduction cascades down food chain
What control is it when predator pop increases, prey decreases and plant increases?
top-down control
When will bottom up control occur?
If dynamics driven by competition amongst plants
Plants decrease, prey decrease predator decrease
Do top-down and bottom-up control play a role on the species?
Both processes likely to play a role, with relative importance depending on the system
How can we try to understand what happens in natural systems?
construct food webs
Simplest food web:
"who eats whom"
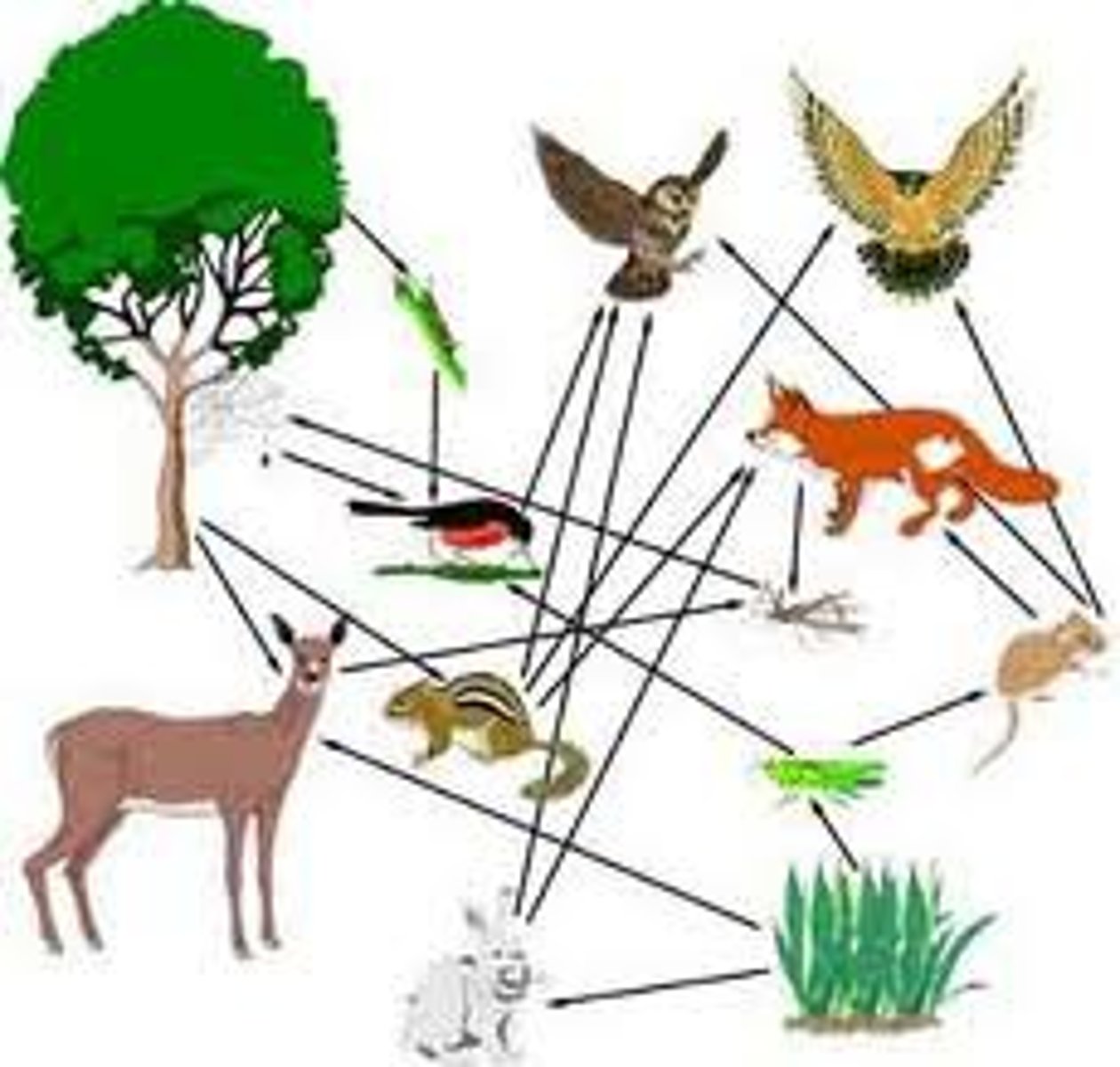
Is modelling a food web impossible?
yes as it is so complicated
What do people try to do instead of modelling a food web?
Characterise food webs, with aim of understanding stability (how resistant to change, how fast to revert back after change)

What is connectance?
fraction of all possible species pairs that are connected in the food web
Is there a relationship between species richness and conectance?
Yes but complex and not always significant
What is a keystone species?
Species whose impact is proportionally large relative to its abundance
Has a large beta ij with lote of species
Conceptually important, but difficult to measure objectively
Important for conservation
What are the 2 big problems with food webs?
Problem 1: doesnt necessarily taxonomic detail
- Not all 'groups' included
- Not all 'groups' equally detailed taxonomically
Problem 2: food web interactions basically 'yes' or 'no'
(i.e. βij not estimated)
What do quantitative food webs show?
Not only "who eats whom", but also "who eats how much of whom", "who is eaten how often by "whom"
What are indirect effects of complex food webs with many species?
- Intra-guild predation
- Apparent competition
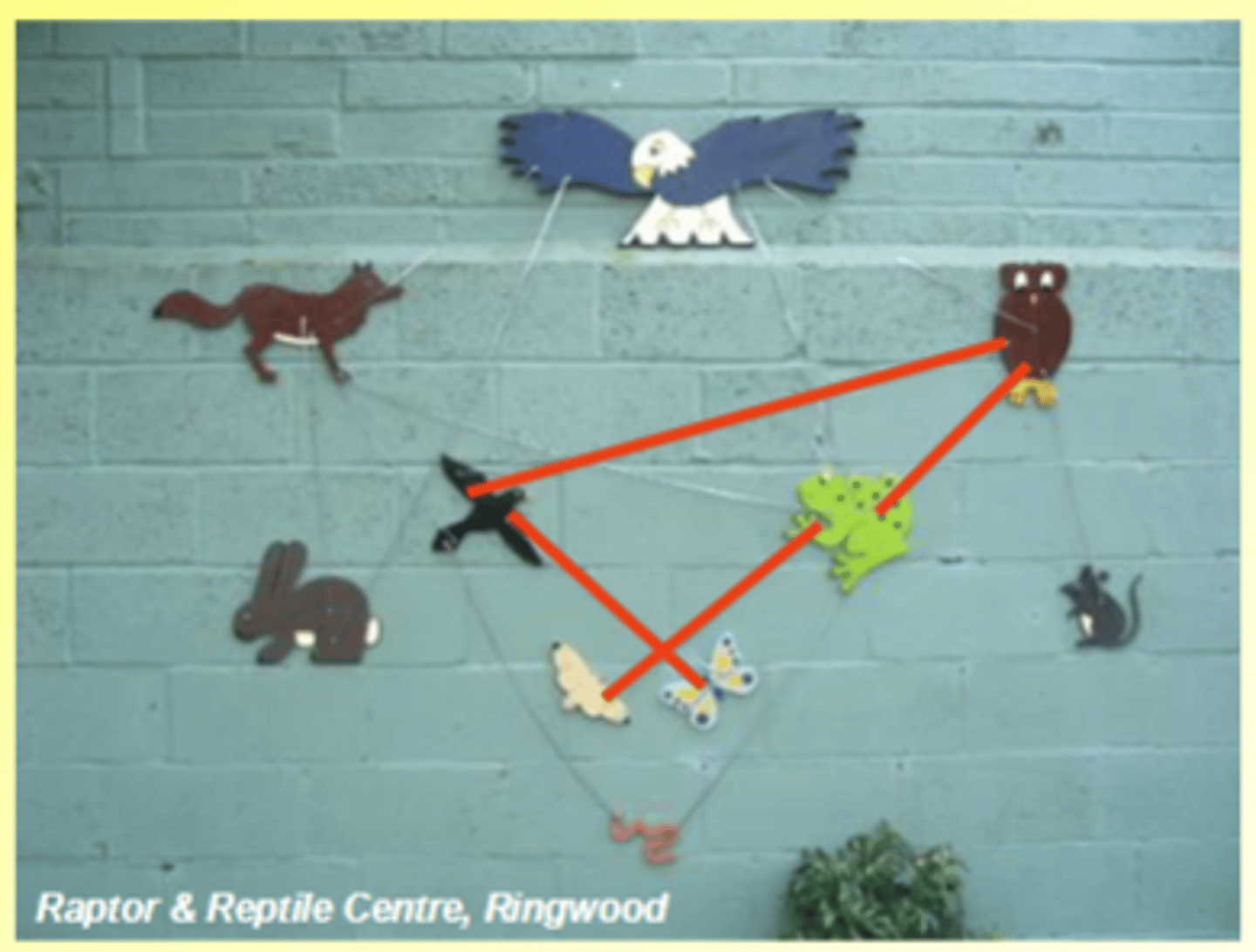
What is intra-guild predation?
Predator eats prey and predator of prey
Top predator has direct and indirect effect on middle trophic level
Raptor & Reptile Centre, Ringwood Top predator has direct and indirect effect on lower trophic level
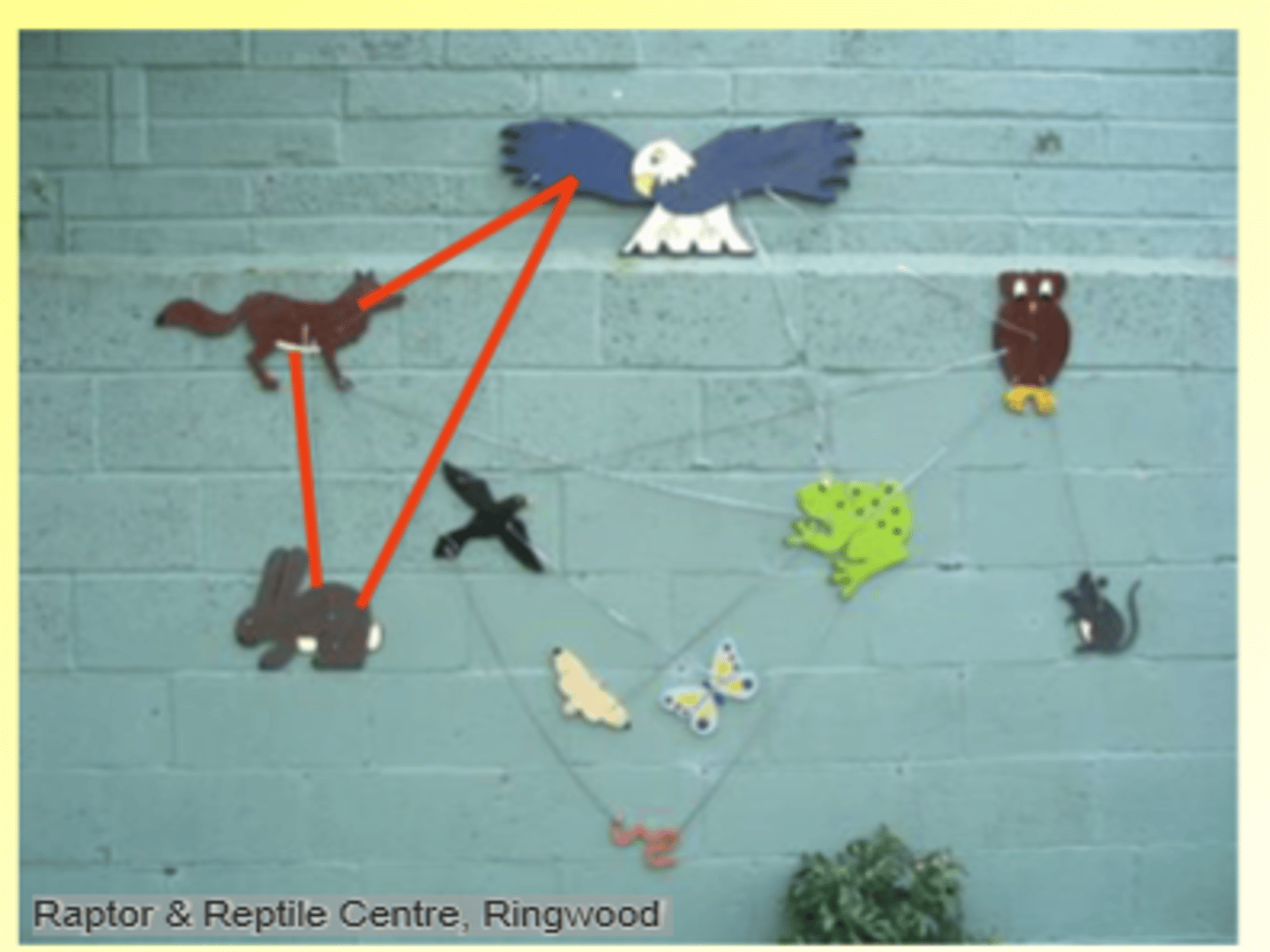

What is apparent competition?
Blackbird population increases
Owl population increases
Frog population decreases
Decrease of frog population as a result of increase in blackbird population looks like competition
But blackbirds and frogs do not share resource
