Chapter 4: Air Pollution Consequences
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Haze is a manifestation of ______ smog and is a yellowish _____-gray haze
photochemical , brownish
Haze is an atmospheric phenomenon where ___, ___, and ___ particles in the air obscure the sky’s clarity
dust, smoke, dry
Haze forms due to the presence of small ___ droplets containing products of ____ reactions that occur among ____ in the air
water, chemical, pollutants
particles who diameter us about that of the wavelength of visible light, i.e., ___-___μm, can scatter light
0.4-0.8
When the air contains a ___ concentration of particles with diameters between __μm and __μm produce a haze
high, 0.1-1
___ and ____ are main components in Haze, with sulfate at ___% and Organic Carbon at __%
sulfate, organic carbon, 37%, 24%
The widespread of haze in the artic atmosphere during winter it due to _____ that originate from the burning of coal, especially in ___ and ____.
sulfate aerosols, russia, europe
___ particles are largely responsible for the haze in Los Angeles
fine
“natural” rain is the same as ____ rain
unpolluted
The term acid rain refers to precipitation that is significantly more ___ than “natural” (unpolluted) rain
acidic
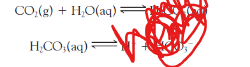
write the products
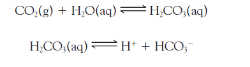
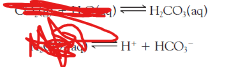
write the reactants for this reaction
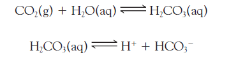
Acids deliver _____ ions to the solution
hydrogen
Bases deliver ____ ions to the solution
hydroxyl
Arrhenius acid-base reaction is limited to _____ solutions
aqueous
Not all bases contain the ____ ion
hydroxide
what bases do not contain OH-
NH3, SO4 2-, NO3 -
Bronsted-Lowery concept:
Acids are proton ___
Bases are proton ___
donors, acceptors
natural (unpolluted) rain has a pH of around ___?
5.6
any rain with a pH less than ___ is considered to be acid rain
5
The two predominant acids in acid rain are?
sulfuric acid, nitric acid (HNO3)
Acid rain is precipitated far downwind from the source of the corresponding primary pollutants ___ and ___
sulfur dioxide, SO2, and nitric oxide, NO
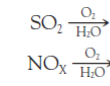
Write the products of the reaction
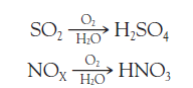
the extent to which acid rain affects biological life in a given area depends on the composition of the ___ and ___
soil, bedrock
If the bedrock is ____ or ____, the acid can be neutralized (buffered) since the rock are composed of ____, CaCO3, which act as a base and reacts with acid
limestone, chalk, calcium carbonate
areas strongly affected by acid rain are those having ___ or ___ bedrock since the soil there has little capacity to ____ the acid
granite, quartz, neutralize
acid rain leads to the damage of ___.
soil
When the pH of soil is lowered, plant nutrients such as ___, ___ and ___ ion are exchanged with pH and thereupon leached from it.
potassium, calcium, magnesium
China has serious acid rain problems due to its high emission of ___ from power plants.
SO2
what are the main sources formaldehyde in indoor pollution?
Cigarette smoke, fuel, glue and foam
Common three symptoms of acute formaldehyde exposure are
coughing, wheezing, chest pains
the rate of formaldehyde emission from synthetic materials increases with ____ and _____
temperature, relative humidity,
NO2 is responsible for the indoor concentrations of which compound?
a) nitrous acid
b) nitric acid
c) ammonia
d) urea
a
respiratory illness in children can be contributed to
a) formaldehyde
b) NO2
c) CO
d) asbestos
NO2
which pollutant is air toxic?
a) nitrous acid
b) formaldehyde
c) benzene
d) thermal NO
c
A significant fraction of benzene vapor occurs while
a) using stoves
b) driving
c) smoking
d) refueling
d
Which indoor pollutant is not a carcinogen?
a) formaldehyde
b) 1,3-butadiene
c) CO
d) none
c
Which is not a possible source of CO?
a) fuel
b) smoking
c) fabric
d) parking car
c
High levels of CO can cause?
a) headaches
b) fatigue
c) death
d) unconsciousness
a,b,c, and d
which indoor pollutant binds with hemoglobin?
a) NO2
b) CO
c) benzene
d) formaldehyde
b
Which is the main chemical compound of asbestos?
a) carbonate
b) silicate
c) zincate
d) granite
b
What metal cation is present in asbestos?
a) Zn
b) Si
c) Mg
d) Ca
c
Which asbestos causing cancer in humans is already well established?
a) chrysotile
b) amosite
c) actinolite
d) crocidolite
d
which are the application of asbestos?
a) insulation
b) automobile brake-bad lining
c) fireproofing material
d) all of them
d
Chrysotile, a popular asbestos, is primarily mined in
a) USA
b) India
c) Mexico
d) Kazakhstan
d
Which is the leading effect of asbestos?
a) headache
b) fatigue
c) mesothelioma
d) unconsciousness
c
which indoor pollution produces dozens of toxic substances?
a) asbestos
b) air toxic
c) formaldehyde
d) environmental tobacco smoke
d
Environmental tobacco smoke is also known as
a) first-hand smoke
b) second-hand smoke
c) long transport pollution
d) outdoor pollution
b
what are the sources and health effects formaldehyde.
glue, foam, tobacco smoke, and fuel.
coughing, wheezing, chest pains
what are the sources and health effects of benzene
riding in motor vehicles and refueling them at gas stations
increases the rate of leukemia
what are some sources and health effect of asbestos?
insulation, fireproofing material, automobile brake-pad lining, chrysotile
causes mesothelioma
explain how greenhouse gases influenced the Earth’s incoming and outgoing energy sources and contributed to global warming?
currently the planet is absorbing slightly more than it is emitting, thereby warming the planet and oceans
some gases in the air absorb IR light and therefore the IR emitted form Earth’s surface and atmosphere does not all escape directly to space
what is meant by ‘fixed carbon’.
Explain the atmospheric lifetime of CO2 in terms of net gain
the CO2 captured by the photosynthetic process is no longer free to function as a greenhouse gas.
carbon dioxide does not have an atmospheric sink. CO2’s net gain is continuously increased significantly over time due to fossil fuel combustion and well as burning tropical forests and cement production being released into the air.