Unit Three: Absolute Monarchs (copy)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
1
New cards

Phillip II
King of Spain who built the Spanish Armada (Navy to attack protestant nations) - too bulky so they fail and Spain loses a lot of money (merchant ships attacked)
2
New cards

Roger Bacon
Creates the idea of Empiricism - “practice makes perfect” - learning takes place through experiences and learning from mistakes
3
New cards

Rene Descartes
Creates the idea of Rationalism - based on the idea of reason (“I think therefore I am”) - thinking and reading books
4
New cards

Mary Wollenscroft
Wrote A Vindication of the Rights of Women - one of the first feminists (women should go to school and university)
5
New cards

Thomas Hobbes
Wrote Leviathan - about absolute monarchs (uses scientific method and determines there’s a need) - people are naturally selfish so one person needs to make decisions to get things done as a nation
6
New cards

Louis XVI
Ruled from Versailles who was the grandfather of Louis the 16th
7
New cards
Catherine II
(“Catherine the Great”) - Queen of Russia who built schools for all citizens and abolished slavery
8
New cards

Elizabeth I
ruler during the golden age of England - stops war between Protestants and Catholics (Anglican Church) - not married so there’s no heir to the throne
9
New cards

Jean Jacques Rousseau
Wrote the Social Contract - government should be a choice (the people choose - democracy) - suffrage (the right the vote)
10
New cards

Louis XIV
French absolute monarch that built Versailles, a party city filled with tons of gold (very expensive) - known as “the Sun King” because everything revolves around him - when he runs out of money he raises taxes
11
New cards

Peter l
(“Peter the Great”) - Builds St. Petersburg, a tourist attraction that makes Russia more appealing (instead of being the “redneck country”). People begin to view Russia as a beautiful country
12
New cards

Immanuel Kant
Wrote A Critique of Pure Reason - inventor of metaphysics that uses science to prove God is real
13
New cards

Bernini
Boroque architect and artist who designed the Vatican
14
New cards

Frederick II
“The Great” - Prussian ruler who is a patron of arts and gives citizens some freedoms (mild form of democracy) - expands Prussian borders (very successful at war)
15
New cards

John Locke
Wrote Two Treatises of Government - all humans have Natural Rights (life, liberty, freedoms, property) that gov. needs to protect
16
New cards

Galileo
Invents to telescope which allows astronomers to test their theories - focuses on heliocentricism
\
Scientific Method - process used to test if theories are true or not
\
Wrote a book on heliocentrism that’s read by pope - brought before inquisition and chooses to recount his words instead of being executed
\
Scientific Method - process used to test if theories are true or not
\
Wrote a book on heliocentrism that’s read by pope - brought before inquisition and chooses to recount his words instead of being executed
17
New cards

Montesquieu
wrote The Spirit of the Laws - divide government between three branches (executive, legislative, judicial) - introduces checks and balances (veto, impeach, overrride)
18
New cards

Charles I
Son of James I that rules England as an Absolute Monarch - does whatever he wants - signs the petition of right and executes part of parliament when they follow it - executed by parliament after civil war
19
New cards

Israel Putnam
“Don’t fire until you see the whites of their eyes” - battle of bunker hill
20
New cards

George Washington
First president of the United States and head commander of colonials
21
New cards

Patrick Henry
Give me liberty or give me death - American attorney and founding father
22
New cards

Thomas Jefferson
author of the Declaration of Independence - third president
23
New cards

Maximilien Robespierre
Leader of the Committee of Public Safety - finds any enemies of the state and guillotines them (no one is safe) - Reign of terror
24
New cards

Arthur Wellesy
First Duke of Wellington who defeated Napoleon at the Battle of Waterloo
25
New cards

Thomas Paine
Wrote the book Common Sense - “no taxation without representation” - some people agree with this, some don’t (America splits into two groups)
26
New cards

Charles II
Son of Charles I who returns the monarchy to England in The Glorious Revolution (after Cromwell dies) - also known as the restoration
27
New cards

Oliver Cromwell
Puritan put as the Lord Protector of England after Civil War. Massacres Catholics in Ireland and Scotland (become calvanist or die) so they become under control of England. Rules by martial law (rules with army), passes calvanist laws - makes people mad.
28
New cards

Napoleon Bonaparte
Great military leader in France - first emperor in France - exiled to Elba and St. Helena Island
29
New cards

The Ambassadors
30
New cards

The Descent from the Cross
31
New cards

**The Crucifixion of Saint Peter - Caravaggio**
32
New cards
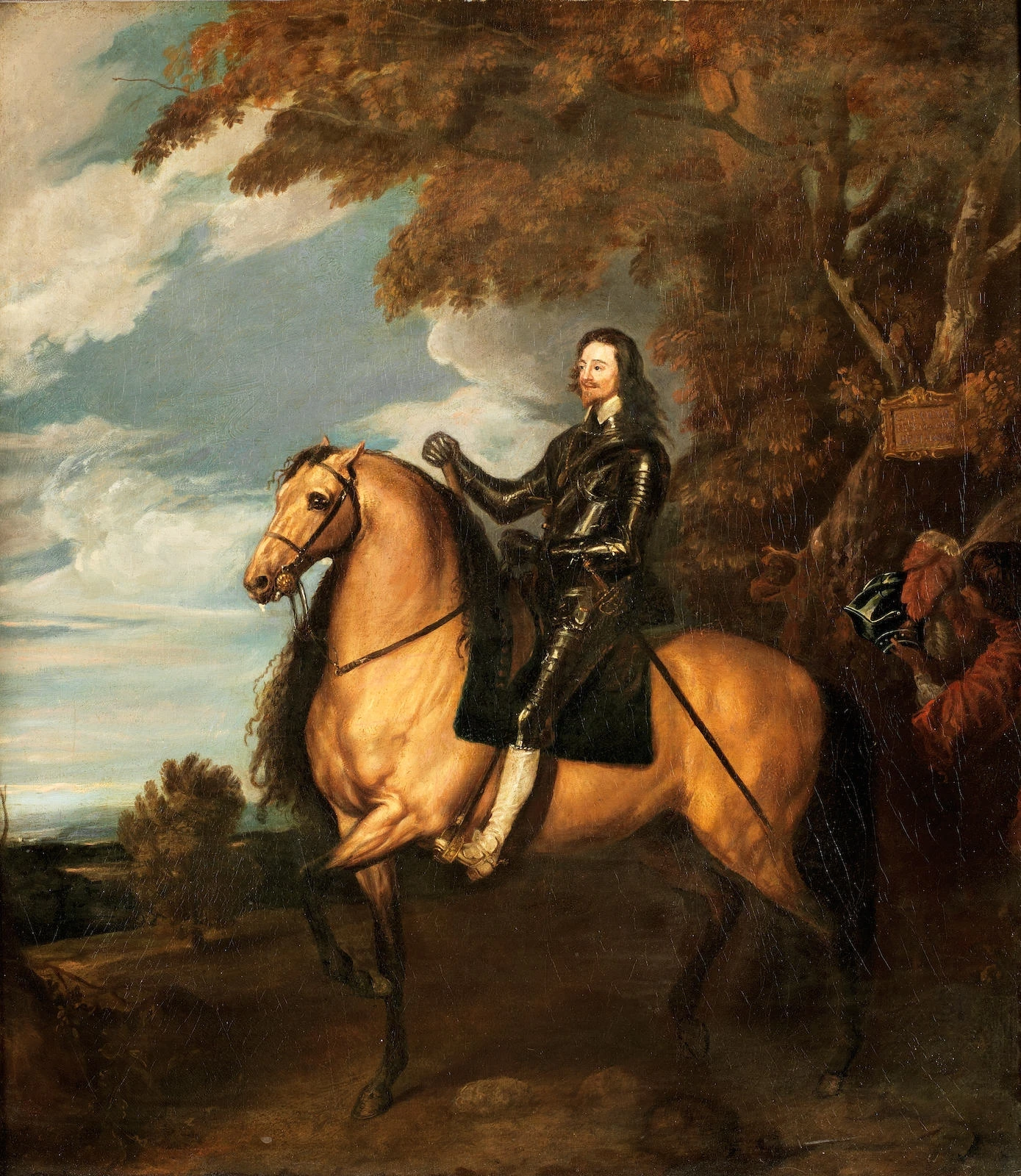

Equestrian portrait of Charles l
33
New cards
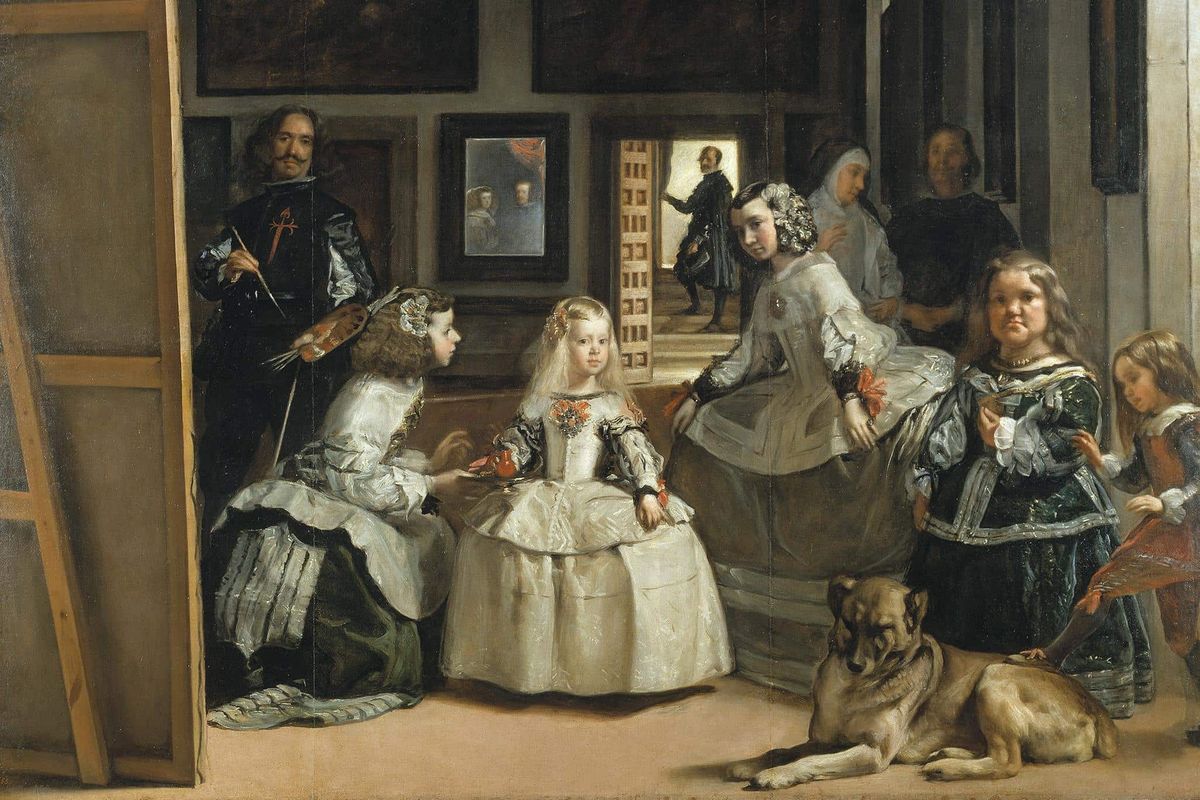

The Maids of Honor
34
New cards

The Burial of Count Orgaz
35
New cards

who was it painted by
El Greco
36
New cards
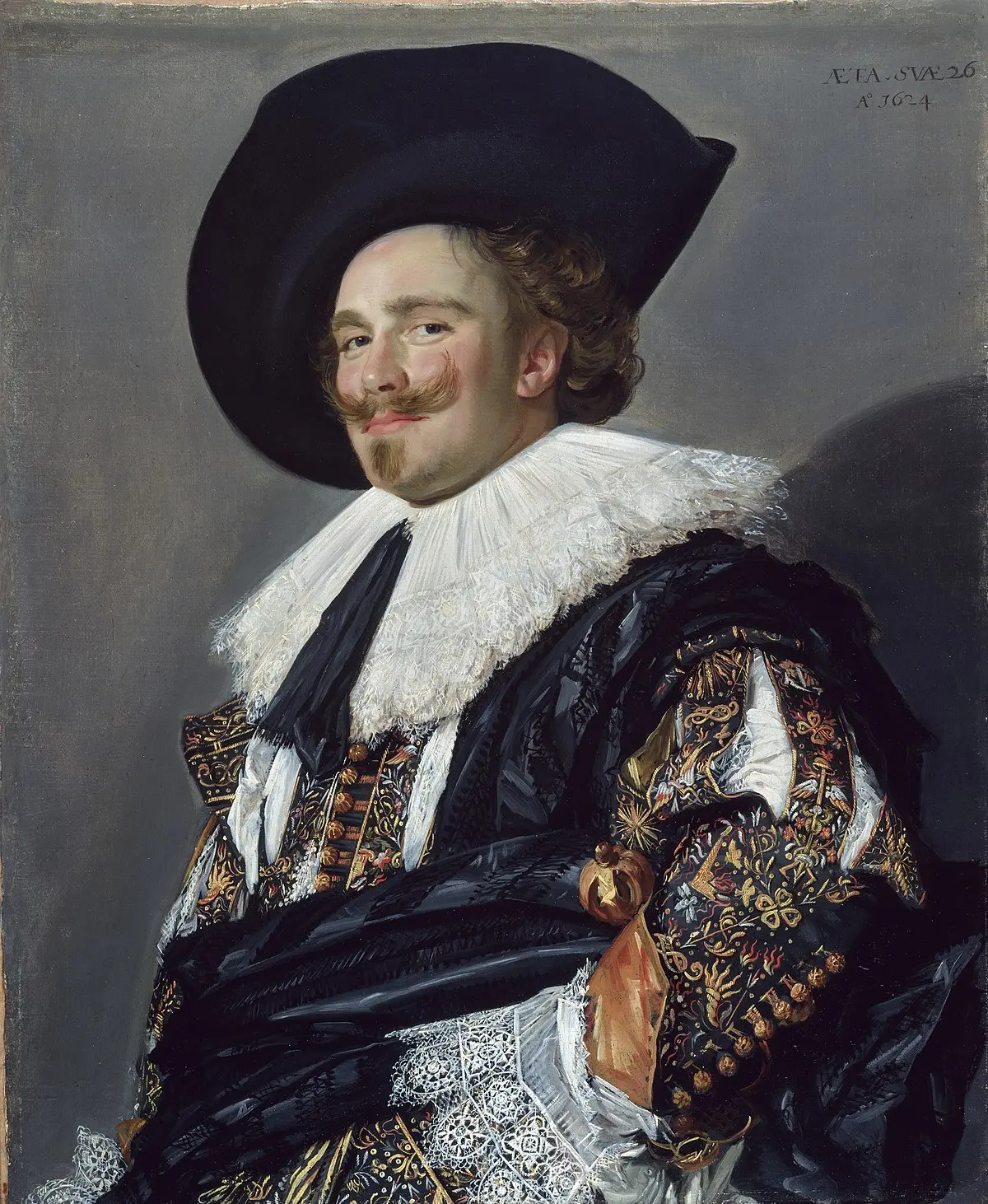

who was it painted by
Frans Hals
37
New cards
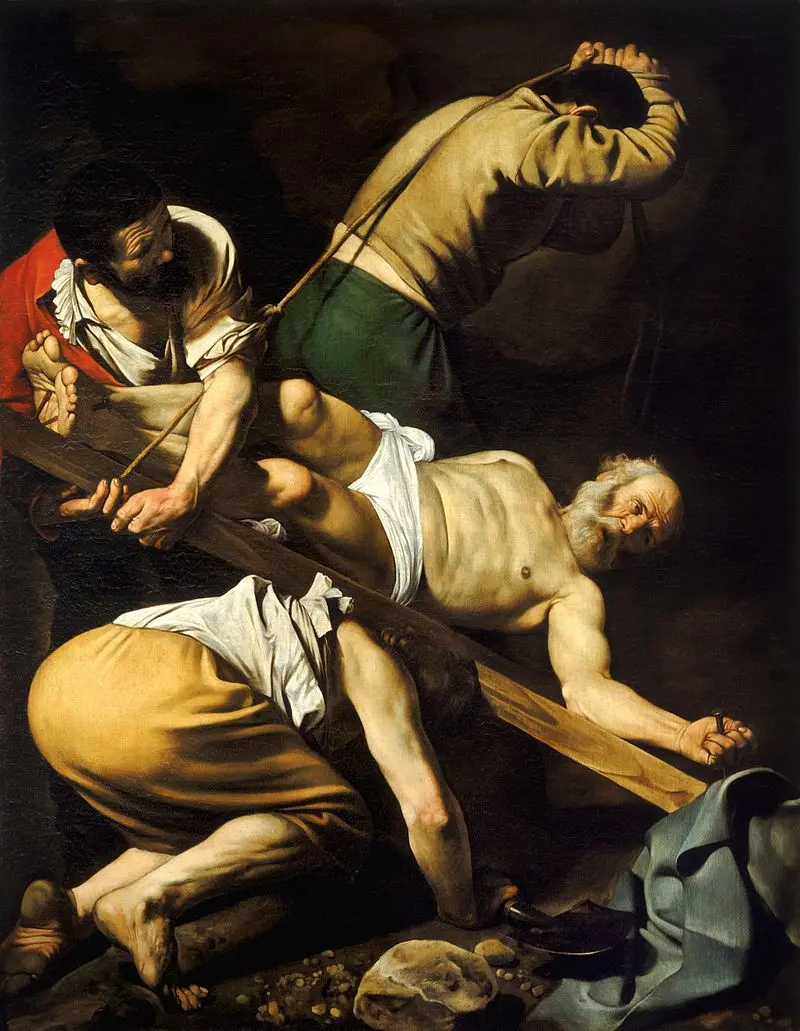

who was it painted by
Caravaggio
38
New cards
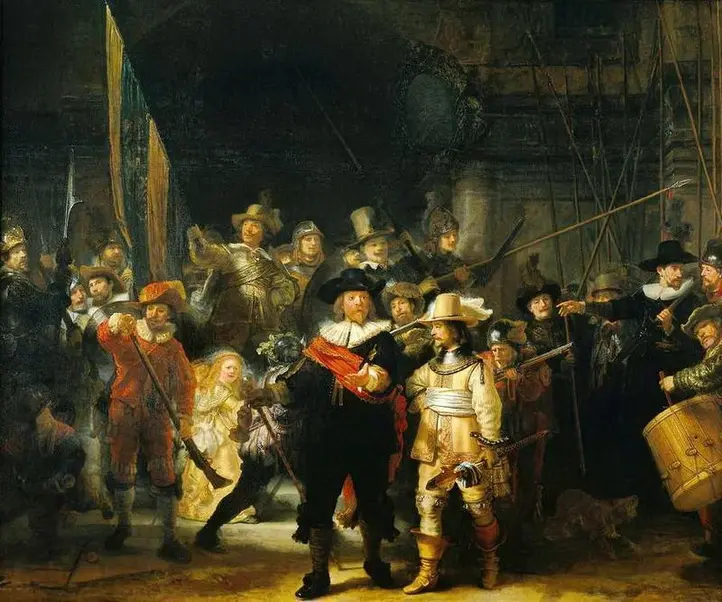

who was it painted by
Rembrandt van Rijn
39
New cards

who was it painted by
Jan Vermeer
40
New cards
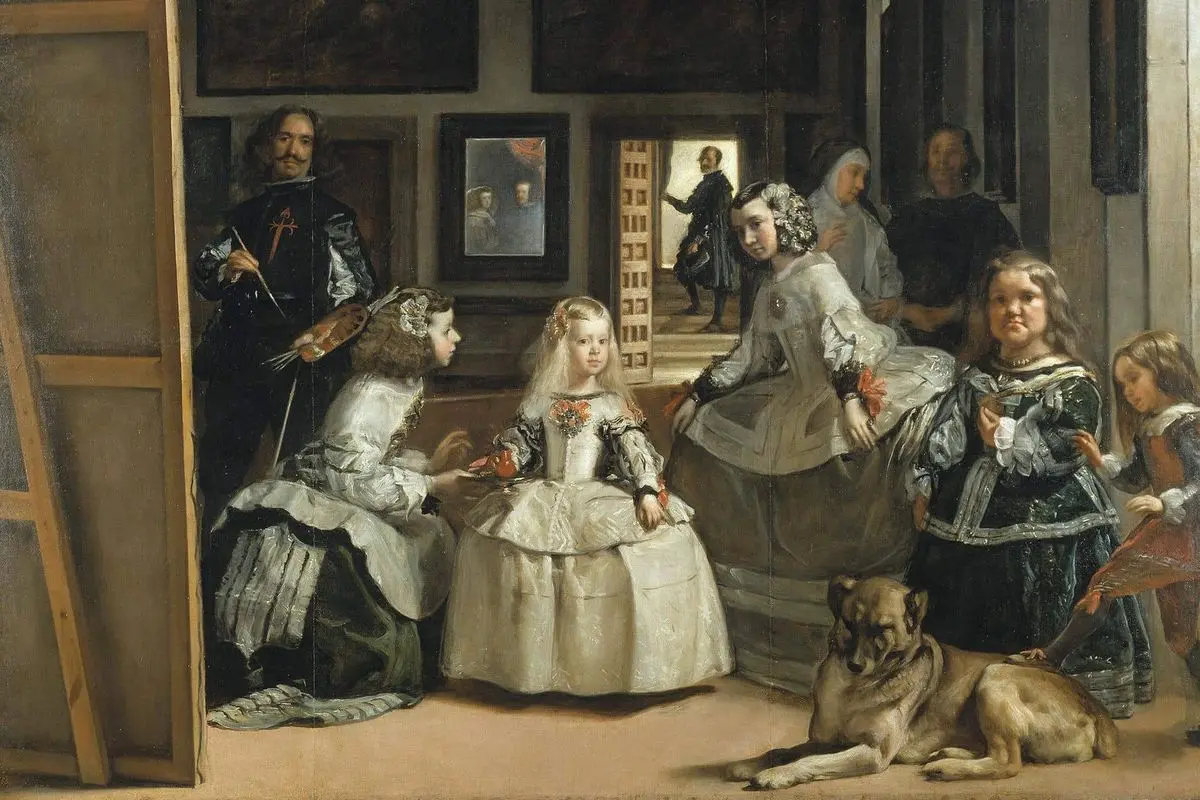

who was it painted by
Diego Valezquez
41
New cards

who was it painted by
Peter Paul Rubens
42
New cards
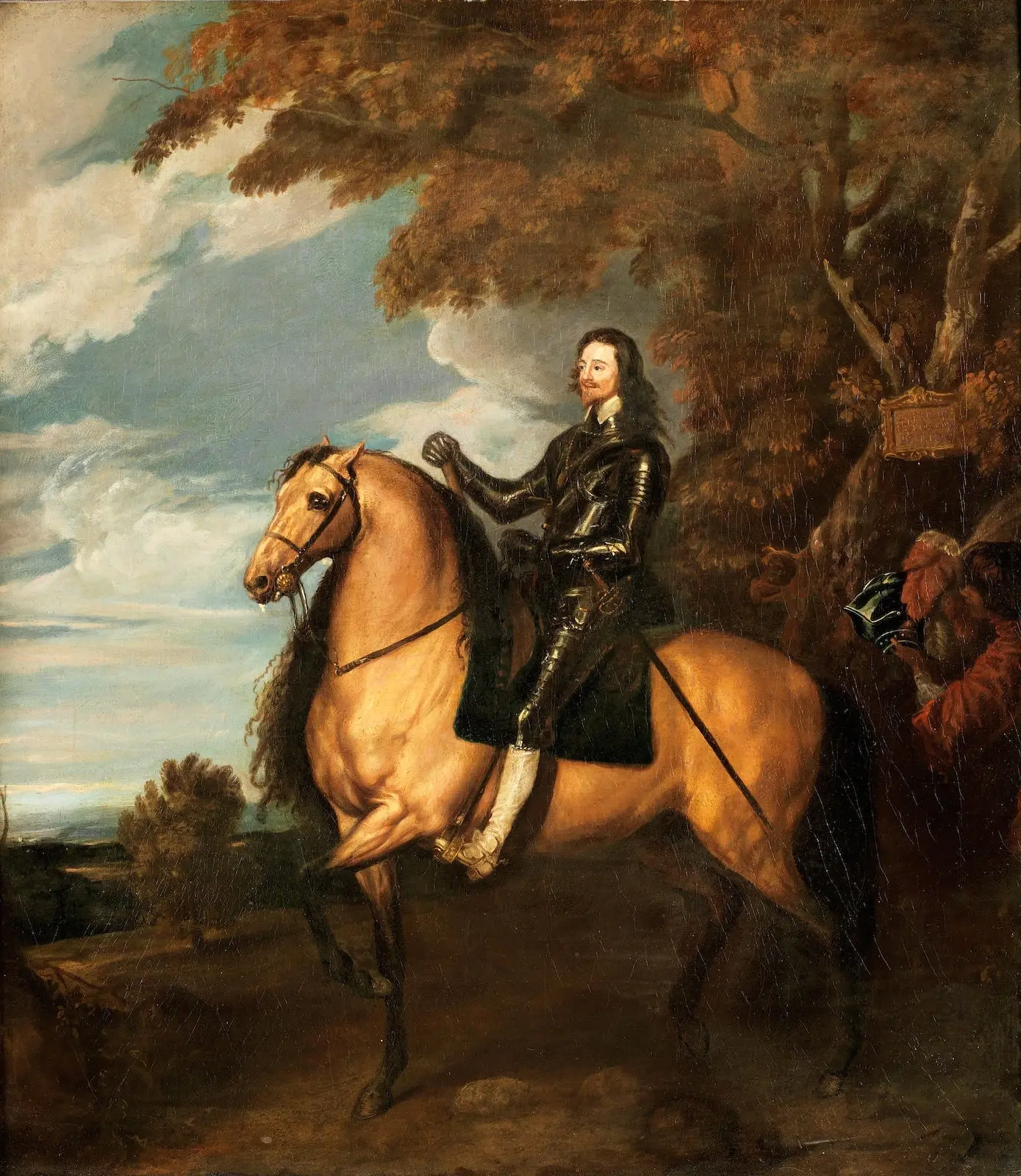

who was it painted by
Van Dyck
43
New cards
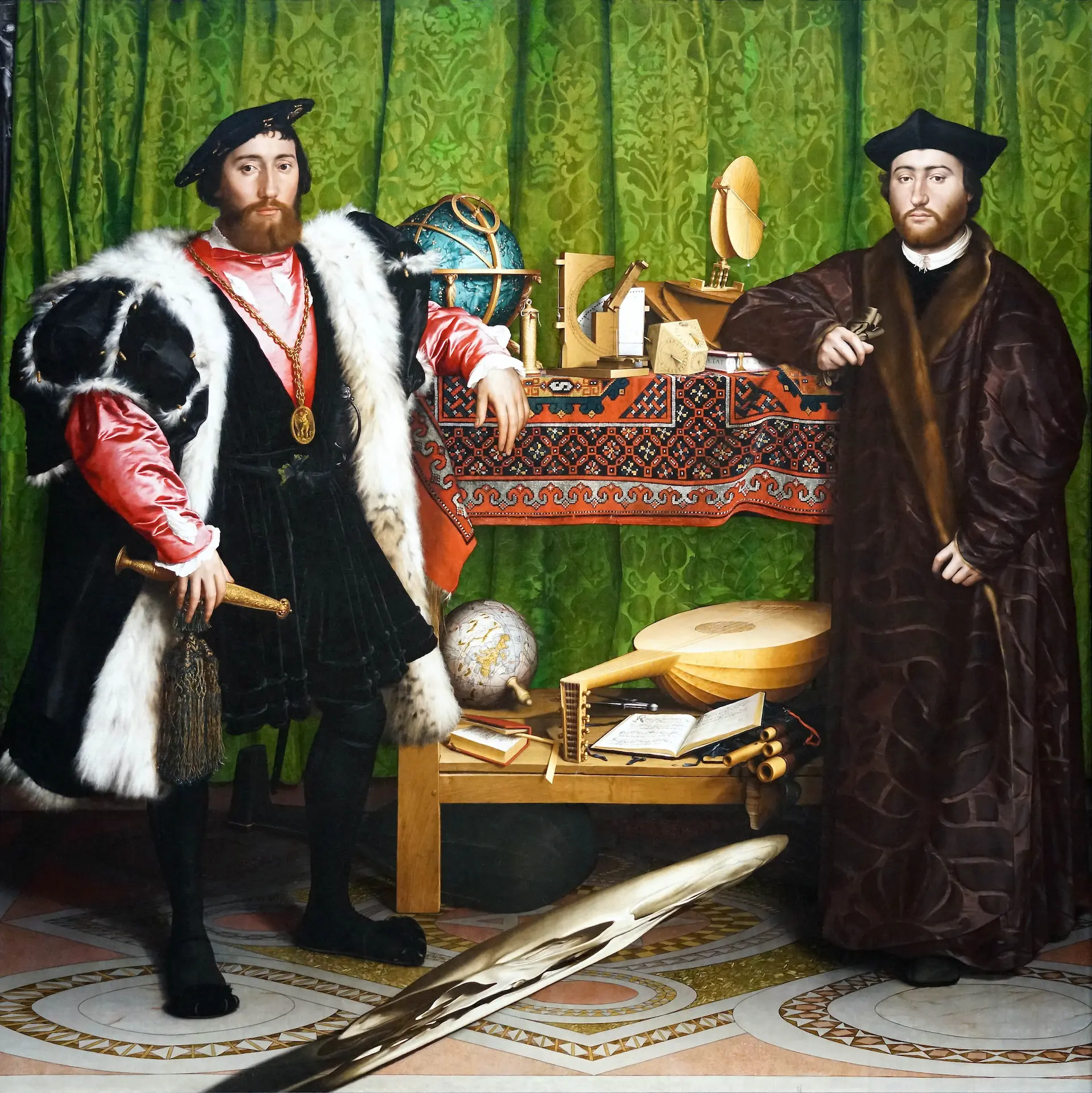

who was it painted by
Hans Holbein
44
New cards

who was it painted by
Nicholas Poussin
45
New cards

\
Laughing Cavalier
46
New cards

\
Et in Arcadia Ego
47
New cards

\
The Night Watch
48
New cards

\
Maid Pouring Milk
49
New cards
Political power during the age of absolutism
Absolute monarchs - total control
50
New cards
Religious Wars (Age of Absolutism)
Protestants vs. Catholics - civil wars and Protestant nations vs. Catholic nations
51
New cards
Spain - Age of absolutism
Hapsburg family - Phillip II was the King of Spain (spanish Armada)
\
Armada failing is a power vacuum - no Spanish power in New World so England can take over
\
30 years war - war against Germany (founder of Protestants) - huge failure so they lose more money
\
Spain is no longer a superpower
\
Armada failing is a power vacuum - no Spanish power in New World so England can take over
\
30 years war - war against Germany (founder of Protestants) - huge failure so they lose more money
\
Spain is no longer a superpower
52
New cards
France - Age of Absolutism
Bourbons - ruling family - King Louis XIV (sun king who built versailles)
53
New cards
England - Age of Absolutism
Tudors - ruling family - Queen Elizabeth I
\
British Navy defeats Spanish Armada, Shakespeare, Anglican church stops war
\
James I - reluctant ruler (king of scotland and distant cousin of elizabeth)
\
British Navy defeats Spanish Armada, Shakespeare, Anglican church stops war
\
James I - reluctant ruler (king of scotland and distant cousin of elizabeth)
54
New cards
Prussia (Poland) - Age of Absolutism
Hohenzollern - ruling family - Frederick the Great
55
New cards
Russia - Age of Absolutism
Romanov - ruling family - Peter the Great (St. Petersburg) and Catherine the Great (schools and outlaws slavery)
56
New cards
Scientific revolution
Scientists begin to challenge accepted knowledge
57
New cards
Science before Scientific Revolution
Based on Bible, Tradition, Alchemy (magic, potions, gold), and Astronomy
\
Ptolemy, Galen, Aristotle - “world’s greatest scientists” - Greek
\
Catholic Church feels threatened by S.R. (catholic country scientists sent before Inquisition)
\
Ptolemy, Galen, Aristotle - “world’s greatest scientists” - Greek
\
Catholic Church feels threatened by S.R. (catholic country scientists sent before Inquisition)
58
New cards
Factors leading to Scientific Revolution
Exploration - bringing new knowledge back
Renaissance - new ideas
Printing Press - vernacular, new learning
Universities - People are educated and discuss, test theories
\
Information is being shared
Renaissance - new ideas
Printing Press - vernacular, new learning
Universities - People are educated and discuss, test theories
\
Information is being shared
59
New cards
Rationalism
Rene Descartes comes up with the idea - based on the idea of reason (man has the ability to think and discover) - thinking and reading books
\
Cogito ergo sum - “i think therefore I am”
\
Cogito ergo sum - “i think therefore I am”
60
New cards
Empiricism
“Invented by Roger Bacon” - learning takes place through experience (practice makes perfect)
61
New cards
Nicolaus Copernicus
Polish (protestant country) Astronomer who invented heliocentric theory (planets revolve around the SUN)
62
New cards
Johannes Kepler
Swiss (protestant) astronomer who invented the laws of planetary motion - how the planets move
63
New cards
Andreas Vesalius
“Father of Anatomy” who was the first to sketch the total human body (skeleton, organs, muscles)
64
New cards
William Harvey
First to map out circulatory system (veins, arteries, heart)
65
New cards
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Inventor of the microscope who is the first to study microorganisms
66
New cards
Physics
Study of forces within nature
67
New cards
Sir Isaac Newton
Uses scientific method to invent calculus and PHYSICS - laws of motion, gravity, inertia
68
New cards
Enlightenment - Age of Reason
Using Scientific Method to challenge ideas, such as absolutism (is it a good form of government?)
69
New cards
Philosophes
“Lovers of Wisdom” - leading thinkers of this time period - writes books with an impact on society
70
New cards
Salon
Meeting place where people discuss new ideas (popular form of entertainment for men and women)
\
Explosion of knowledge because Philosophes develop new ideas at salons about government and other issues
\
Explosion of knowledge because Philosophes develop new ideas at salons about government and other issues
71
New cards
Branches of government at different levels
Branch - Federal, State, Local
\
Executive - President, Governor, Manager
Legislative - Congress, General Assembly, Town Council
Judicial - Supreme Court, Superior, Probate
\
Executive - President, Governor, Manager
Legislative - Congress, General Assembly, Town Council
Judicial - Supreme Court, Superior, Probate
72
New cards
Voltaire
Wrote Candide - satire about government
\
“I may disagree with what you have to say, but I will defend your right to say it”
\
Cares about liberties/freedoms people should have - especially freedom of speech
\
“I may disagree with what you have to say, but I will defend your right to say it”
\
Cares about liberties/freedoms people should have - especially freedom of speech
73
New cards
Denis Diderot
Wrote the Encyclopedia - 35 volume book with excerpts of the greatest ideas of Renaissance, Social Revolution, Philosophes, etc.
\
Mass produced in Vernacular
\
Mass produced in Vernacular
74
New cards
Enlightened Despots
Absolute monarchs who used ideas of the enlightenment to make positive changes in their nations
\
Building schools, outlawing slavery, religious freedom, etc.
\
Absolute monarchs who don’t embrace these ideas are overthrown - revolution
\
Building schools, outlawing slavery, religious freedom, etc.
\
Absolute monarchs who don’t embrace these ideas are overthrown - revolution
75
New cards
Baroque
A style of art and literature that exudes power - “the grand style”, larger than life - used to intimidate (ex. Versailles, Lorenzo Bernini)
76
New cards
Rococo
More playful, about ornate, delicate, gentle design - Antoine Watteau, Tiepolo (both famous rococo artists) - subject matter is lighter (landscape, people enjoying themselves)
77
New cards
Classical Composers - Baroque vs. Rococo?
Bach - Baroque (Chamber)
Handel - Baroque (Chamber)
Haydn - Baroque (Chamber)
Mozart - Rococo (Action in music)
Handel - Baroque (Chamber)
Haydn - Baroque (Chamber)
Mozart - Rococo (Action in music)
78
New cards
Henry Fielding
The History of Tom Jones - Satire about poverty (Raising awareness about solving this issue)
79
New cards
Jonathan Swift
Gulliver’s Travels - Satire about social classes and how people treat each other
80
New cards
Daniel Dafoe
Robinson Crusoe - Satire about slavery
81
New cards
Deism
Religion based on science - society operates on science, not “god making decisions”
\
God is an “all-seeing” eye
\
God is an “all-seeing” eye
82
New cards
Long Paliament
England was ruled by the people for 20+ years during James I rule because he was an absent monarch
83
New cards
Parliament Sections
Two Houses: House of Lords (wealthy landowners - seats passed to children) and House of Commons (everyone else
\
Prime Minister - Oversees Parliament and discusses decisions with the King
\
Prime Minister - Oversees Parliament and discusses decisions with the King
84
New cards
Petition of Right
Outlines the rights of Englishmen and limits the power of the king - Charles I threatened into signing it (reason why he starts the Civil War)
85
New cards
Cavaliers (English Civil War)
Supporters of King Charles I
86
New cards
Roundheads (English Civil War)
Supporters of Parliament (shaved their heads) - army led by Oliver Cromwell (known as New Model Army) - has many victories
87
New cards
English Civil War
Cavaliers vs. Roundheads - Roundheads win
88
New cards
Trial of Charles I
Charles is captured and put on trial in front of Parliament - his defense is Divine Right, but is convicted guilty because he signed the petition of right - executed (beheaded) and Oliver Cromwell is put into power
89
New cards
Constitutional Monarchy
There is a monarch but no one is above the law. Established in England with laws to ensure the civil war doesn’t happen again
90
New cards
Habeas Corpus (England)
All citizens get trial by jury, no cruel and unusual punishments
91
New cards
Bill of Rights (England)
List of freedoms that all English citizens get
92
New cards
Act of Union (England)
Creates a new country - Great Britain (England, Scotland, Ireland, Wales) - prevents a King from ruling two countries
93
New cards
Salutary Neglect (America)
Colonies seen as a way to make money for England - left to rule themselves (similar to Long Parliament)
94
New cards
French and Indian War
Wars between France and England over control of North American colonies - Great Britain wins (colonies help British Army fight - colonists get military experience)
95
New cards
End of Salutary Neglect
After French and Indian war, Britain gets very involved with the colonies
96
New cards
Navigation Acts
Known to the Colonists as the Intolerable Acts - laws that generate more money for Britain (taxes) - Britain feels justified bc they need money to cover war costs, and the Americans owe them because the war was to defend the Americans
97
New cards
Sons of Liberty
Against British and taxes (Patriots)
98
New cards
Tories
Supports the British Crown
99
New cards
Lexington and Concord
British hears weapons are being collected so they go to confiscate - Paul Revere alerts minutemen - the “Spark” of the American revolution (“the shot heard round the world”) - Sons of Liberty begin to form a serious military
100
New cards
Bunker Hill
For built by Patriots that was the first official battle of the American Revolution - British loses 800+ people due to their bad strategy (fights in lines, waits for officers before shooting) - patriots have to retreat when they run out of ammo but it’s a moral victory