Ch. 11: The Self & Identity
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is the “self”?
All of the characteristics of a person
Self-understanding definition
How individuals represent their self
Developmental changes in self-understanding: Infancy (2)
Visual self-recognition: ~18-24 mo.
Self-awareness gradually develops: 2-3 yrs
Developmental changes in self-understanding in early childhood through adolescence
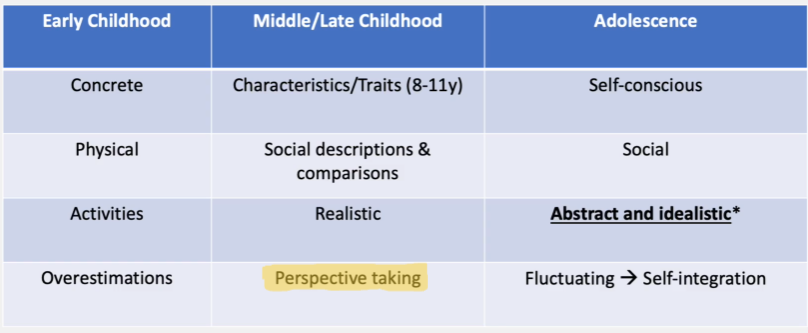
Why do young children overestimate the abilities? (4)
They don’t distinguish between actual and desired performance
Don’t distinguish from real and ideal self
Less frequent or lack social comparisons
Social comparisons alter self-understanding by forcing a child to consider their abilities relative to others
Developmental changes in self-understanding: Adolescence (5)
Ideal self
Possible self: what one hopes to be and dreads of becoming
Can be positive or negative
Real self – who a person actually is
Self-integration – self-understanding becomes more integrative, with the disparate parts of the self becoming more systematically pieced together
Developmental changes in self-understanding: Adulthood (3)
Expanded self-awareness
Revision of possible selves
Life revies of older adults
Self-esteem definition
A global (general) evaluation of the self
Self-concept definition
Domain-specific evaluation of the self
Developmental changes in self-esteem
Higher in early childhood, drops in adolescence, rises through the 60s then drops off
Self-regulation
Involves the ability to control one’s behavior without having to rely on others’ help
What is identity? (3)
A self-portrait
An understanding of oneself
Contains many different pieces
Components of identity (8)
Vocational/career identity
Political identity
Religious identity
Relationship identity
Achievement/intellectual identity
Sexual identity
Cultural/ethnic identity
Interests, personality, and physical identity
Erikson’s view of identity during adolescence (3)
Identity vs Identity Confusion
Fifth stage in his theory of development
Psychosocial Moratorium: Gap between childhood security and adult autonomy
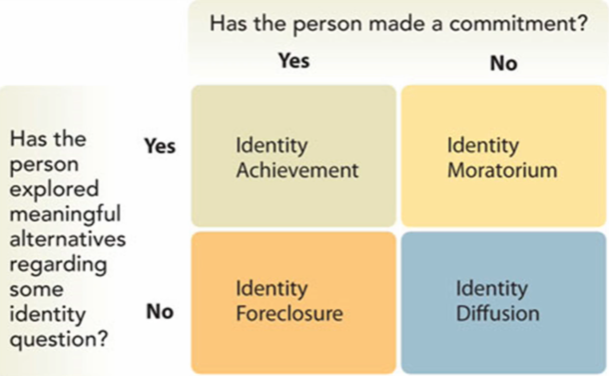
Erikson’s view & Marcia’s extension (3)
Crisis (Exploration): Period of identity development during which the individual is exploring alternatives
Identity confusion: Unsuccessful resolution of identity crisis
Commitment (decision): Personal investment in identity
Developmental changes in identity (6)
Key changes in identity in emerging adulthood (18-25 yrs)
Percentage of people in identity moratorium increases to 19, then declines
More stable in adulthood than in adolescence
MAMA cycle:
Moratorium → achievement → moratorium → achievement
Influenced by family, peers/romantic relationships, culture/ethnicity
Marcia’s four identity statuses
Family influence on identity (7)
Individuality
Self-assertion: Ability to communicate a particular point of view
Separateness: Ability to communicate how one is different from others
Connectedness
Mutuality: Sensitivity and respect for others’ point of view
Permeability: Openness to others’ point of view
Attachment likely plays a role
Personality: Stage vs trait theories (3)
Trait – personality consists of broad dispositions (traits) that tend to produce characteristic responses
Trait-situation interactions – context matters, and some traits are more stable in some people than in others
Stage-crisis view – adulthood has 3 main stages, which are surrounded by transition periods. Specific tasks and challenges are associated with each stage
Contemporary life-events approach (7)
Emphasizes how life events influence an individual’s development
Depends on:
The event
Mediating factors (physical health, family supports)
The individual’s adaptation to the life event (appraisal of threat, coping strats)
Life-stage context
Sociohistorical context
Generativity vs stagnation (3)
Erikson’s 7th stage of his life-span theory
Generativity – desire to leave a legacy to next generation
Stagnation – develops when individuals sense they’ve done nothing for the next generation
The Big Five
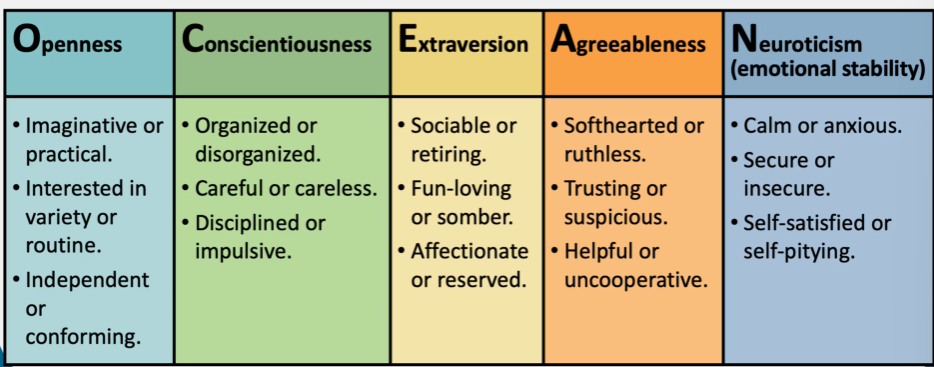
Personality: Stability & change (4)
Greatest change in big five occurs in early adulthood
Relative stability across adulthood – some characteristics change more than others
*Less change in personality occurs when it’s assessed in smaller time frames than in larger ones
Cumulative personality model of personality development – across time, people work with the environment in order to interact in ways that promote more stability in their personality