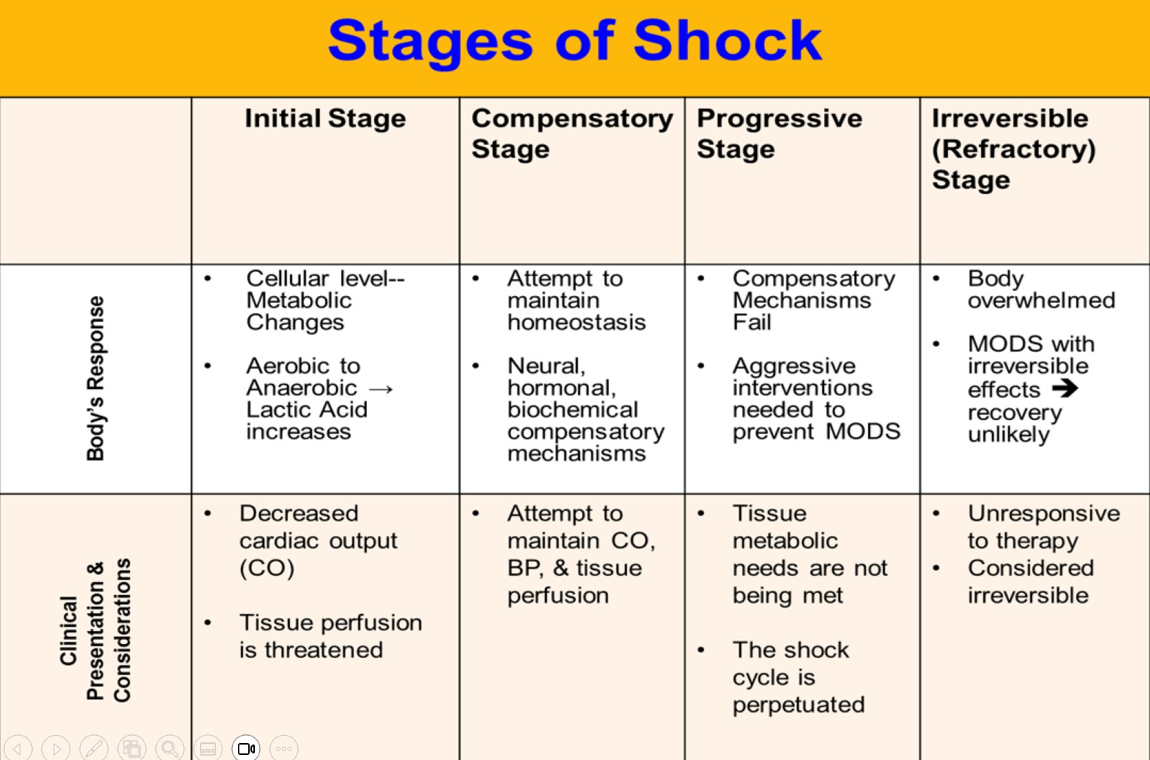
SIRS, MODS
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
my blood is dirty garbage WATERRRR
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
SIRS - abbreviation
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
MODS - abbreviation
Multi-organ dysfunction syndrome
DIC - abbreviation
Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy
What is SIRS?
Generalized and massive inflammatory dysfunction
Activation of leukocytes and endothelial cells
Release of infl. mediators and oxygen free radicals
Progression of SIRS
Exaggerated SIRS → Abnormalities in perfusion + hypoxia → Tissue destruction → MODS and Death
True or false:
SIRS is only caused by extracellular infections and toxins
FALSE
There are various triggers
Basically, anything that can result in an inflammatory response has the potential to become exaggerated
Can have infectious or noninfectious origins!
Physiologic responses resulting in SIRS
Vasodilation
Increased capillary permeability
Microvascular clotting
Temperature alteration
Clinical presentation of SIRS
Tachycardia
Tachypnea and/or hypocapnia
Leukocytosis or leukopenia
Fever or hypothermia
Can be VARIED!
Criteria for SIRS
Requires 2 or more of the following!!!!
Temperature
Greater than 100.4/38 or less than 96.8/36
Heart rate >90 bpm
RR > 20 bpm or PaCO2 < 32 mmHG
WBC
>12000 OR <4000
>10% immature bands
6 parameters to monitor in the cases of SIRS
RR
O2 sat
Systolic blood pressure
Pulse rate
LOC
Temperature
When SIRS is the result of an infection by an invading microorganism
Sepsis
Sepsis is characterized by _________ patient response along with new ____________ related to the infection.
Sepsis is characterized by dysregulated patient response along with new organ dysfunction related to the infection.
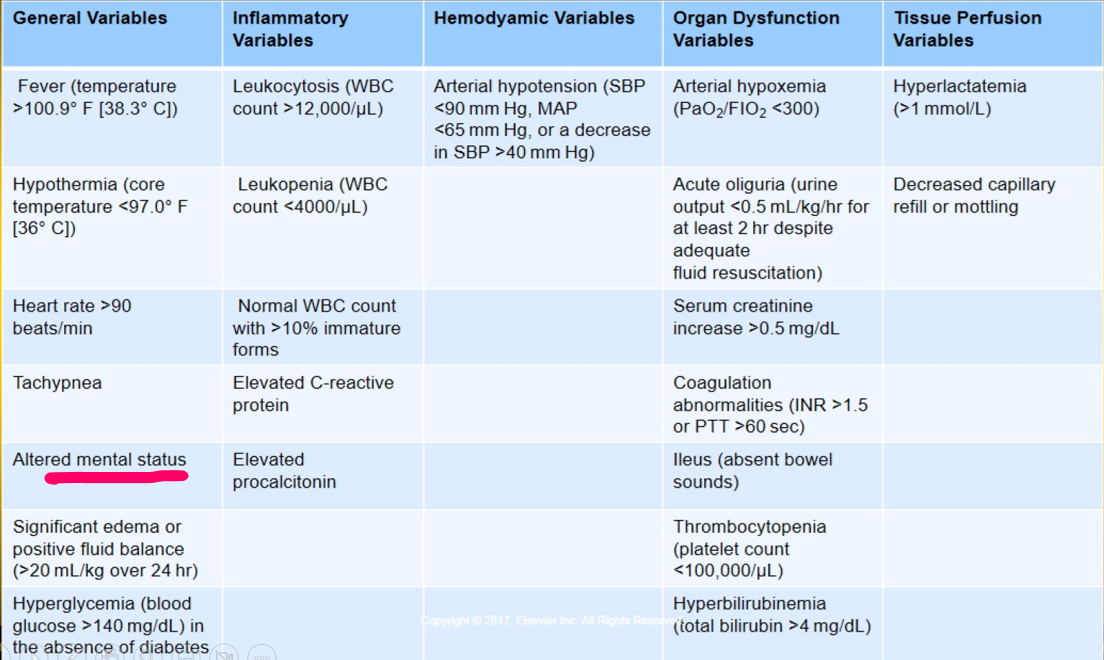
Diagnostic criteria for sepsis
Have a lot of the same as SIRS tho
Shock is characterized by _____ tissue perfusion and _______ cellular metabolism
Shock is characterized by decreased tissue perfusion and impaired cellular metabolism
(caused by massive vasodilation)
What conditions are associated with septic shock?
Pneumonia
Peritonitis
Urinary tract infection
Invasive procedures
Indwelling lines and catheters
What patients are at highest risk for developing septic shock?
Older adults
Chronic illnesses
Immunsuppressant therapy
Immunocompromised
Malnourshed
Debilitated
Critical care patients
What is septic shock?
Refractory hypotension despite fluid resuscitation requiring vasopressors
Inadequate tissue perfusion → Tissue hypoxia
Criteria for Sepsis (simplified lol)
Refractory hypotension
Hypotension despite fluid resuscitation
Sbp <90
MAP <70
SBP decreased more than 40 compared to baseline
Vasopressor-dependent post fluid replacement (under normal circumstances, they wouldn’t need the vasopressor after fluid replacement!)
Tissue hypoperfusion / MODS
Refractory hypotension
Hypotension even with fluid resuscitation
Characteristics
SBP <90
MAP <70
SBP decreased 40+mmHG compared to baseline
3 physiologic effects of septic shock
Massive vasodilation
Maldistribution of blood flow
Caused by increased capillary permeability
(think of a gardening hose with a few holes - Blood not exiting when you want it to!)
Myocardial decompensation (heart unable to meet demands)
How does the cardiovascular system attempt to compensate for septic shock?
SNS response → Epinephrine/Norepi
Make the heart work harder, pump harder, pump more
BP continues to drop
At the end, still results in narrowed pulse pressure
Early clinical presentation of septic shock
“Hot stage” - Looks like an infection
Tachycardia
Pulse = bounding
Wide pulse pressure
Warm/flushed, hyperthermia
Hyperpnea
Not decreased LOC, but altered
Oliguria
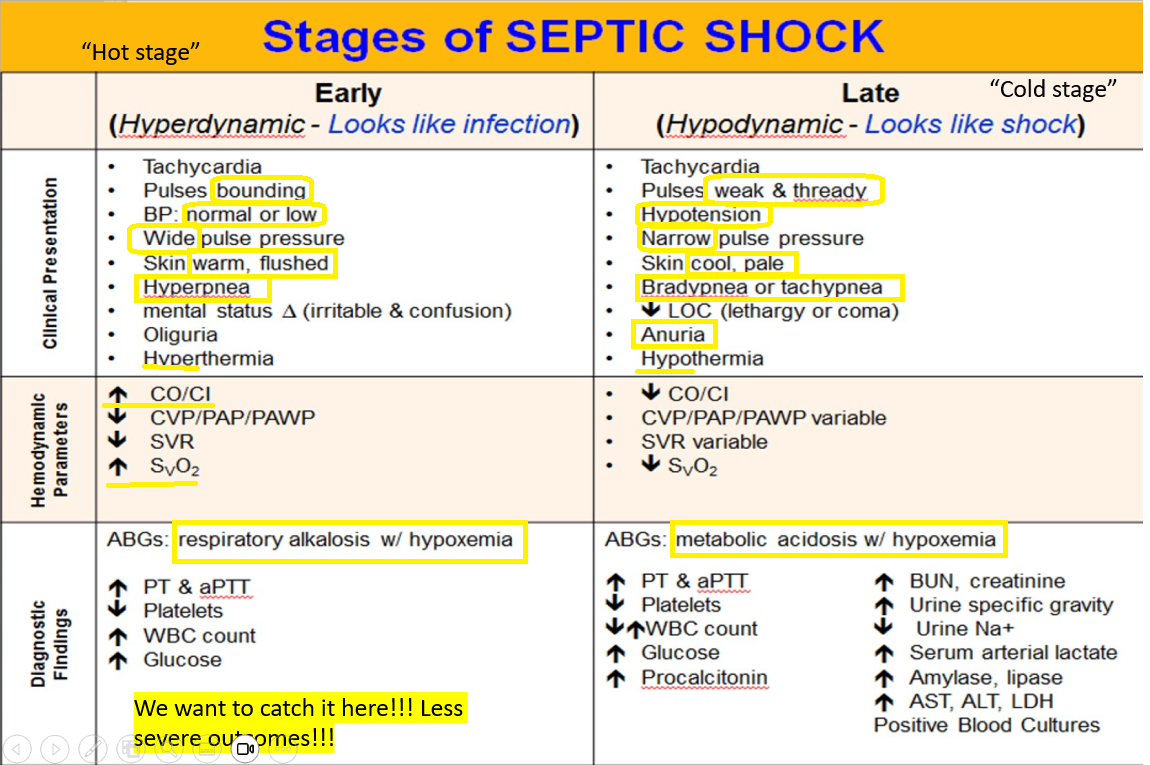
After observing a patients ABG results, you conclude that this patient is in early septic shock.
What is this patient exhibiting?
Respiratory alkalosis + hypoxemia
Late clinical findings of septic shock?
“Cold stage” - Looks like shock
Tachycardia
Pulse are weak and thready
Hypotension
Narrow pressure
Cool, pale, Hypothermia
Brady or Tachypnea
Anuria
Decreased LOC - lethargy or coma
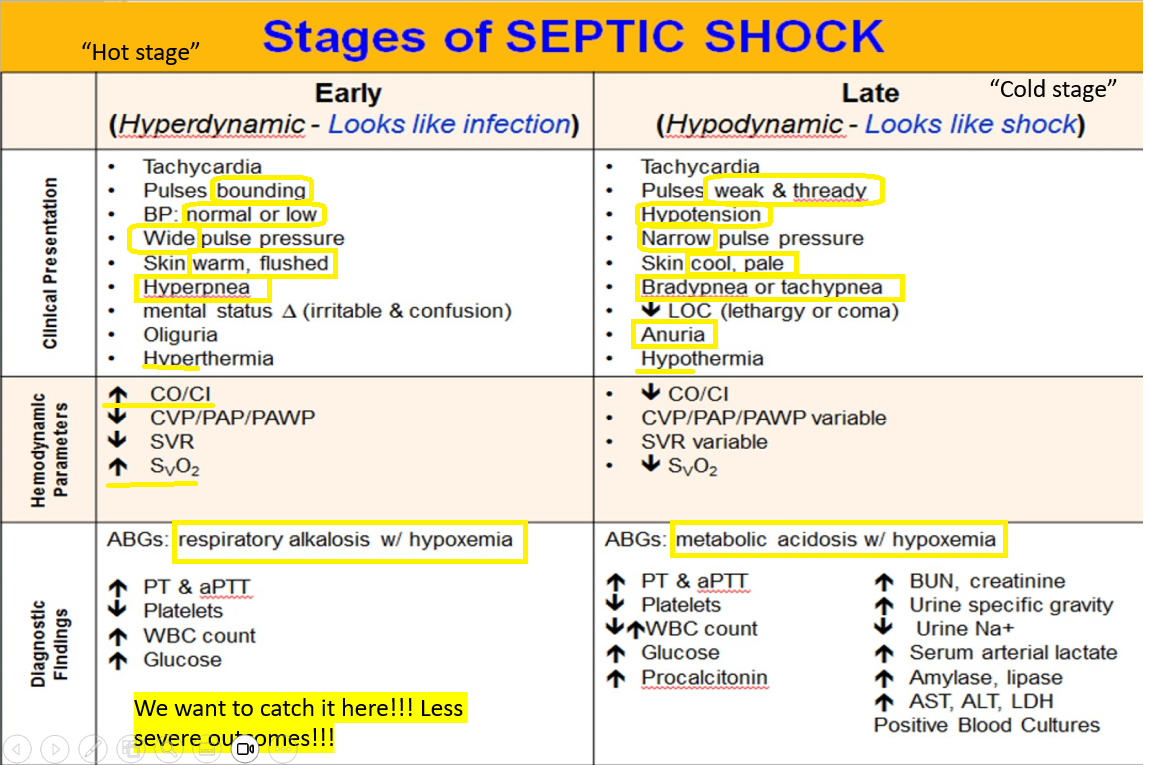
After observing a patients ABG results, the results support that this patient is in the late stage of septic shock.
What is this patient exhibiting?
Metabolic acidosis + hypoxemia
Hour 1 bundle for Sepsis and Septic Shock?
Upon recognition of sepsis/septic shock…
Measure lactate level. If elevated, remeasure
>2 mmol/L
Blood cultures (BEFORE ABX ADMIN)
Administer broad abx
Rapid admin of 30 mL/kg saline for hypotension OR lactate >4mmol/L
Apply vasopressors if hypotension persists to maintain MAP>65
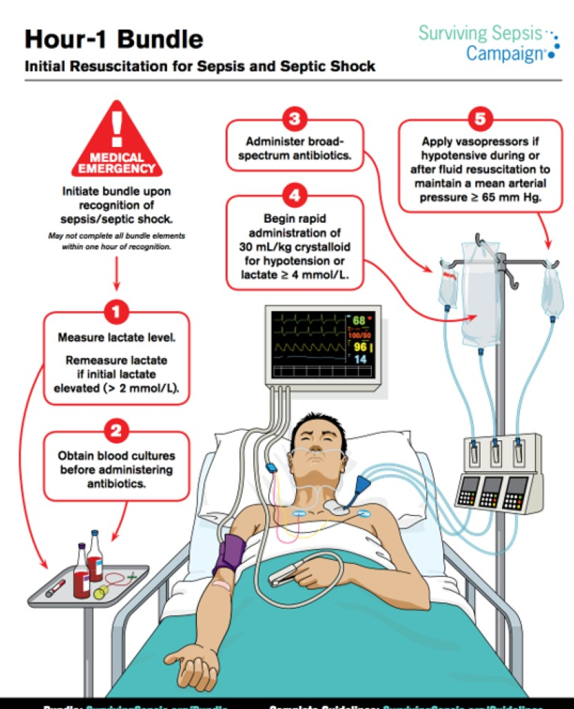
When is it recommended to administer antibiotics in the case of sepsis/septic shock?
Within 1 hour of recognition
In the 1-hour bundle, it is recommended to apply vasopressors to maintain a MAP >___
65
What vasopressor will most likely be recommended in the 1-hour bundle?
Dopamine
True or false:
MODS can result in SIRS
FALSE
Often, MODS is a complication of SIRS!
How does SIRS result in MODS?
Hypotension
Decreased perfusion
Microemboli formation
Redistribution and shunting of blood
SIRS and MODS - Respiratory manifestations
Bilateral fluffy infiltrates
Decreased compliance
Severe dyspnea
PaO2 <200
PAWP < 18
Pulmonary hypertension
Refractory hypoxemia
Tachypnea
V/Q mismatch
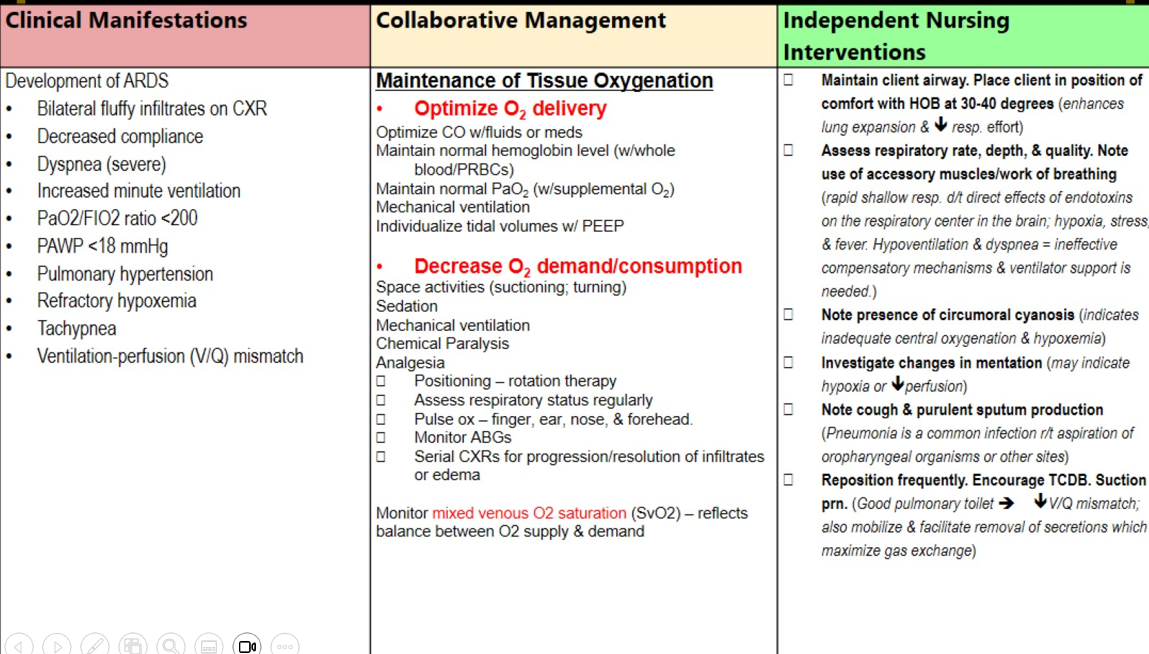
Management of respiratory failure in SIRS and MODS
Fluids, and meds
Whole blood
Supplemental O2, mechanical ventilation
Space nursing activities
Sedation
Analgesia
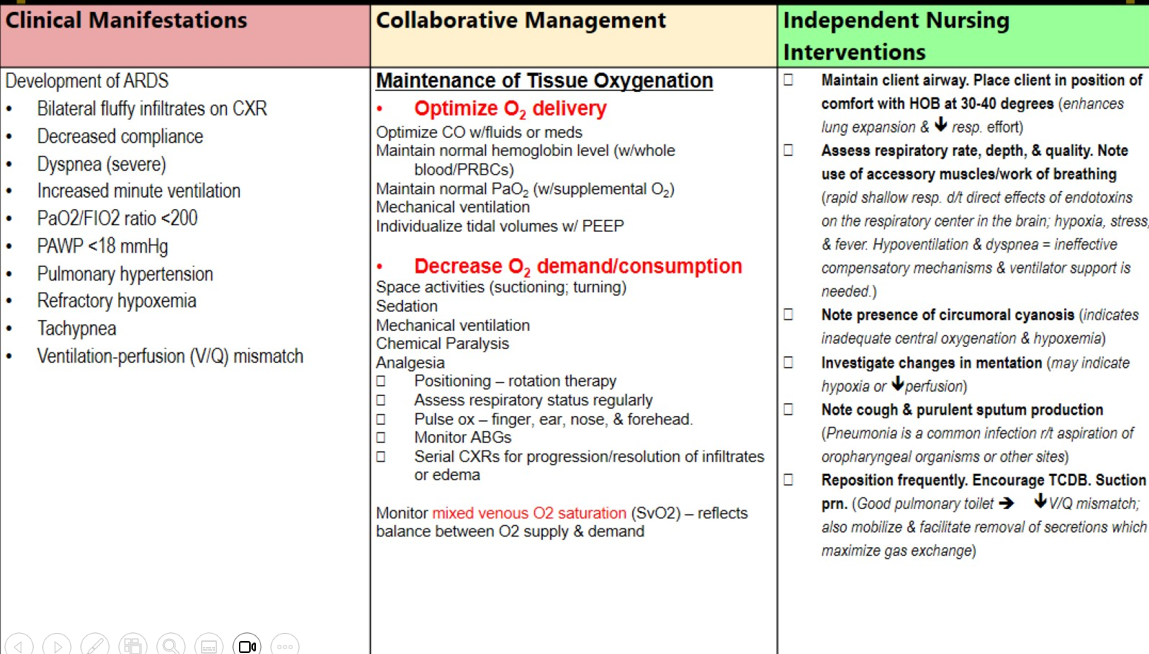
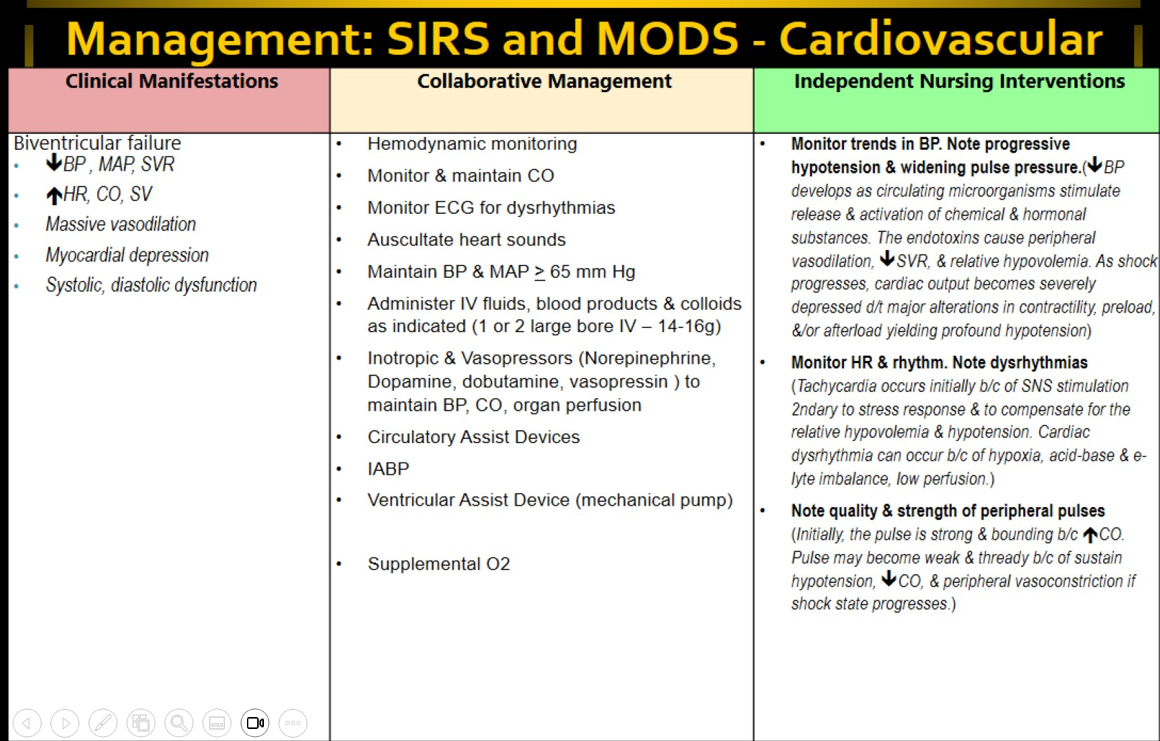
Clinical manifestations of cardiovascular failure in MODS and SIRS
Decreased BP, MAP, SVR
Increased HR, CO, SV
Massive vasodilation
Myocardial depression
Systolic and diastolic dysfunction
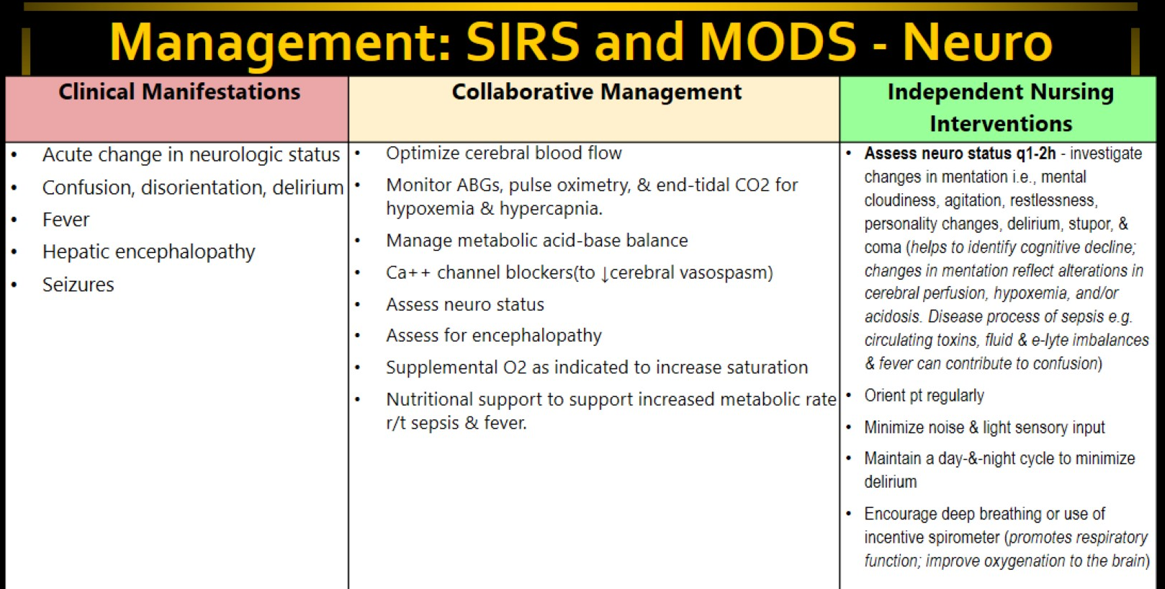
Management of Neuro failure/dysfunction in SIRS/MODS
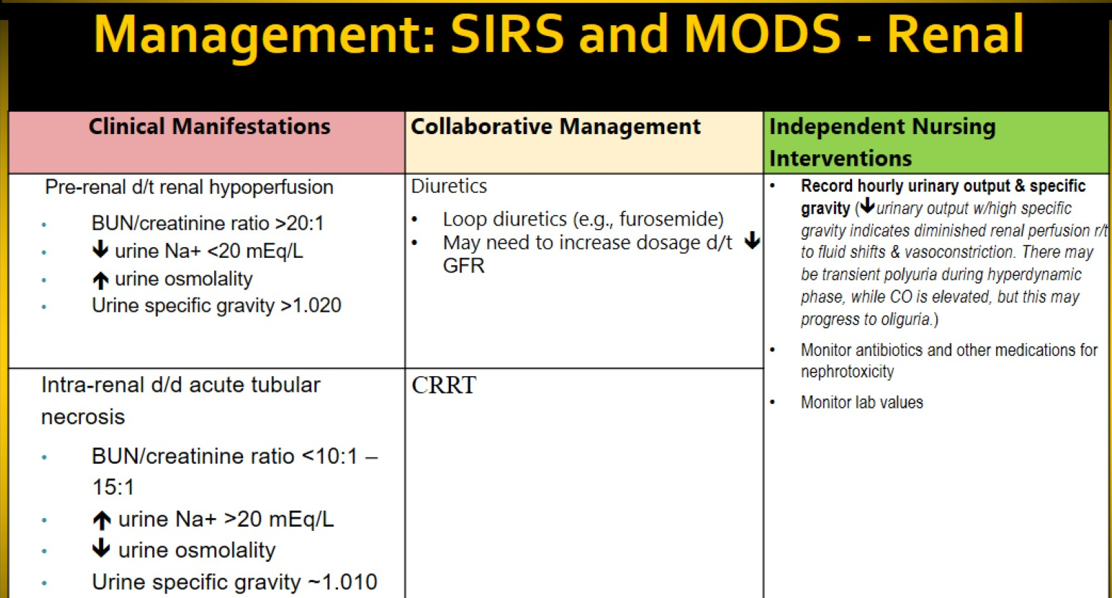
Management of renal failure/dysfunction in SIRS and MODS
Pre-renal (fluids not leaving) vs Intra-renal (fluids leaving too much)!!!