Motivation
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/53
Last updated 11:43 PM on 4/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
Need
= something that is required for survival
ex. food, belonging
ex. food, belonging
2
New cards
Drive
= a physical or psychological state that propels animals to fulfill a need
ex. hunger
ex. hunger
3
New cards
Motivation
= a process that starts, guides, and continues a behavior until a goal is
achieved
* motivated behaviors are **intentional** and **goal-directed**
\
ex. eating when we feel hunger
achieved
* motivated behaviors are **intentional** and **goal-directed**
\
ex. eating when we feel hunger
4
New cards
Instinct Theory
a theory of motivation
= automatic, innate behaviors in response to a physical need
* is an early, simplistic theory (Darwin + William James)
= automatic, innate behaviors in response to a physical need
* is an early, simplistic theory (Darwin + William James)
5
New cards
Fixed-Action Patterns
= a behavior seen in an entire species that is automatically triggered by a stimulus (and followed through until completion)
ex. change in sunlight → bird migration
\
* pretty much discredited (obsolete) except for some reflexes (ex. rooting reflex for infants)
ex. change in sunlight → bird migration
\
* pretty much discredited (obsolete) except for some reflexes (ex. rooting reflex for infants)
6
New cards
Drive Reduction Theory
a theory of motivation
= individuals engage in certain behaviors to satisfy a biological drive (to maintain homeostasis)
Need → Drive → Drive-Reducing Behavior →__Homeostasis__ achieved!
\
* Employs Negative Reinforcement (do a behavior, eat, to reduce unpleasant feelings, hunger)
= individuals engage in certain behaviors to satisfy a biological drive (to maintain homeostasis)
Need → Drive → Drive-Reducing Behavior →__Homeostasis__ achieved!
\
* Employs Negative Reinforcement (do a behavior, eat, to reduce unpleasant feelings, hunger)
7
New cards
Arousal Theory
a theory of motivation
= behaviors are driven to maintain certain levels of stimulation/arousal
* diff people need diff levels of stimulation (couch potato vs. adrenaline junkie)
= behaviors are driven to maintain certain levels of stimulation/arousal
* diff people need diff levels of stimulation (couch potato vs. adrenaline junkie)
8
New cards
Yerkes-Dodson Law
= there is a relationship between arousal levels and optimal performance on a task
* the best level of arousal depends on the difficulty of the task
Easy task → requires high arousal/stimulation
ex. going for a run (repetitive, boring) → putting on music (increases attention/interest)
hard task → requires low arousal/stimulation
ex. driving (needs attention) → turning off music (incresaes concentration, decreases too much stimulation)
\
**SO, this law implies that “we need** ***some*** **stress for optimal performance (but not too much)”**
* the best level of arousal depends on the difficulty of the task
Easy task → requires high arousal/stimulation
ex. going for a run (repetitive, boring) → putting on music (increases attention/interest)
hard task → requires low arousal/stimulation
ex. driving (needs attention) → turning off music (incresaes concentration, decreases too much stimulation)
\
**SO, this law implies that “we need** ***some*** **stress for optimal performance (but not too much)”**
9
New cards
Incentive Theory
a theory of motivation
= behaviors are driven by incentives
* explains why we still do things even though they don’t satisfy biological needs
= behaviors are driven by incentives
* explains why we still do things even though they don’t satisfy biological needs
10
New cards
Intrinsic Motivation
part of the Incentive Theory of motivation
= doing something for passion/curiosity/enjoyment (no reward)
* contributes to a sense of accomplishment/autonomy
= doing something for passion/curiosity/enjoyment (no reward)
* contributes to a sense of accomplishment/autonomy
11
New cards
Extrinsic Motivation
part of the Incentive Theory of motivation
= doing something to get a reward
= doing something to get a reward
12
New cards
Overjustification
when extrinsic motivation overrides intrinsic motivation
\
ex. when you used to love reading, but school assigned it as homework, so it’s not fun anymore
\
ex. when you used to love reading, but school assigned it as homework, so it’s not fun anymore
13
New cards
Humanistic Theory
(Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs)
(Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs)
a theory of motivation
= behaviors are driven by 5 different levels of needs
* start at bottom (basic biological survival needs), then move up as those are fulfilled (social)
* most fulfill bottom, reaching top is harder
= behaviors are driven by 5 different levels of needs
* start at bottom (basic biological survival needs), then move up as those are fulfilled (social)
* most fulfill bottom, reaching top is harder
14
New cards
Physiological Needs
1st level of Maslow’s
* food, water, warmth, rest
* basic need
* food, water, warmth, rest
* basic need
15
New cards
Safety Needs
2nd level of Maslow’s
* security
* basic need
* security
* basic need
16
New cards
Belongingness and Love
3rd level of Maslow’s
* intimate relationships, friendships
* psychological Need
* intimate relationships, friendships
* psychological Need
17
New cards
Esteem Needs
4th level of Maslow’s
* prestige and feeling of accomplishment
* Psychological Need
* prestige and feeling of accomplishment
* Psychological Need
18
New cards
Self-Actualization
5th level of Maslow’s
= living to your potential to achieve your goals and dreams (personal growth)
* creative activities
= living to your potential to achieve your goals and dreams (personal growth)
* creative activities
19
New cards
Self-Transcendence
6th\* level of Maslow’s
= seeks to further a cause beyond the self and to experience connection beyonf the boundaries of the self
* spiritual needs, cosmos
= seeks to further a cause beyond the self and to experience connection beyonf the boundaries of the self
* spiritual needs, cosmos
20
New cards
Flow
= state of optimal experience
* “in the zone”
* don’t notice criticism/anxiety/time passing
* activities that put people in this state are both highly challenging and also within the person’s abilities (high abilities)
* dopamine levels increase in this state
* “in the zone”
* don’t notice criticism/anxiety/time passing
* activities that put people in this state are both highly challenging and also within the person’s abilities (high abilities)
* dopamine levels increase in this state
21
New cards
Cognitive Theories
= how we think affects how we behave
22
New cards
Self Efficacy
a cognitive theory
= a person’s belief that their effort contributes to success
* people who think they’ll accomplish something tend to work harder/persist at even difficult problems
* “hard work pays off”
= a person’s belief that their effort contributes to success
* people who think they’ll accomplish something tend to work harder/persist at even difficult problems
* “hard work pays off”
23
New cards
Cognitive Consistency
a cognitive theory
= behaving in ways that match our beliefs
ex. President of SADD doesn’t drink and drive
* opposite of cognitive dissoncance
= behaving in ways that match our beliefs
ex. President of SADD doesn’t drink and drive
* opposite of cognitive dissoncance
24
New cards
Cognitive Dissonance
a cognitive theory
= discrepancy in behavior and beliefs
ex. smoking even though they know smoking causes cancer
ex. eating meat even though like animals
* causes anxiety
* can be reduced by either changing behavior (stopping smoking/eating meat) OR by changing beliefs (justifying that you’re eating “veal” instead of “baby cow”)
* so they match
= discrepancy in behavior and beliefs
ex. smoking even though they know smoking causes cancer
ex. eating meat even though like animals
* causes anxiety
* can be reduced by either changing behavior (stopping smoking/eating meat) OR by changing beliefs (justifying that you’re eating “veal” instead of “baby cow”)
* so they match
25
New cards
Self-Determination Theory
= there are 3 needs people must meet to be engaged in life and have persistence
\
1) Competence = mastery
2) Autonomy = Control over life
3) Relatedness = interactions with others, care and be cared for
\
if 3 not met, then: aggression, unhappiness, mental disorders
\
* associated with positive psychology and resilience
\
1) Competence = mastery
2) Autonomy = Control over life
3) Relatedness = interactions with others, care and be cared for
\
if 3 not met, then: aggression, unhappiness, mental disorders
\
* associated with positive psychology and resilience
26
New cards
Competence
1 of the 3 needs of self-determination theory
= mastery
= mastery
27
New cards
Autonomy
1 of the 3 needs of self-determination theory
= Control over life
= Control over life
28
New cards
Relatedness
1 of the 3 needs of self-determination theory
= interactions with others, care and be cared for
= interactions with others, care and be cared for
29
New cards
lateral hypothalamus
known as the hunger center,
* stimulates feeding
(Electrical stimulation of the __ ____ _ results in **ravenous** eating behavior)
* stimulates feeding
(Electrical stimulation of the __ ____ _ results in **ravenous** eating behavior)
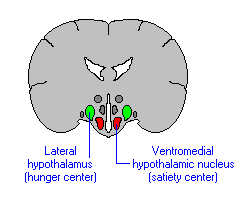
30
New cards
ventromedial hypothalamus
brain structure integral to glucose regulation and appetite
* tells you how satiated you are
* tells you how satiated you are
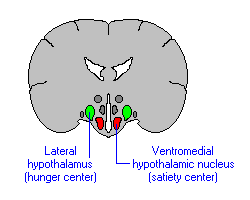
31
New cards
Leptin
a hormone secreted by fat cells to reduce appetite
\
Think: “**Lessens”** appetite
\
Think: “**Lessens”** appetite
32
New cards
Ghrelin
hormone that stimulates brain
“I’m hungry”
* secreted by an empty stomach
* works with the lateral hypothalamus
Think: “**Growlin**” stomach (cuz you’re hungry)
“I’m hungry”
* secreted by an empty stomach
* works with the lateral hypothalamus
Think: “**Growlin**” stomach (cuz you’re hungry)
33
New cards
obesity
= condition of having excess body fat resulting in overweight
* could lead to diabetes type 2
* hard on heart, knees, joints
* could lead to diabetes type 2
* hard on heart, knees, joints
34
New cards
Weight Set
once you reach this point at a certain age, body will settle on an ideal set point
* if you try to change it, homeostasis will work against you and try to revert back to ____
* body bases this set point on fat cells, genetics, etc.
* if you try to change it, homeostasis will work against you and try to revert back to ____
* body bases this set point on fat cells, genetics, etc.
35
New cards
cultural aspect of eating
an aspect of eating
* “eating is involved in a lot of social events”
* “let’s grab coffee/lunch”
* also involved in coping (comfort foods/boredom)
* “eating is involved in a lot of social events”
* “let’s grab coffee/lunch”
* also involved in coping (comfort foods/boredom)
36
New cards
Excitement
1st stage of sexual response cycle
* clitoris/penis swell
* arousal increases steadily
* clitoris/penis swell
* arousal increases steadily
37
New cards
Plateau
2nd stage of sexual response cycle
* breathing/pulse increase
* secretion from vagina and penis
* arousal steadies
* breathing/pulse increase
* secretion from vagina and penis
* arousal steadies
38
New cards
Orgasm
3rd stage of sexual response cycle
* muscle contractions across the body
* pleasurable feeling of sexual release
* arousal peaks
* muscle contractions across the body
* pleasurable feeling of sexual release
* arousal peaks
39
New cards
Resolution
4th stage of sexual response cycle
* arousal levels return to normal
* men have a longer refractory period
* while women, after a short time, can go through cycle again
* arousal levels return to normal
* men have a longer refractory period
* while women, after a short time, can go through cycle again
40
New cards
CBT for Sexual Dysfunction
= cognitive-behavioral therapy
* usually treats erectile dysfunction
* involves education, sensate focus, stimulus control, sexual skills training, and cognitive restructuring (the core component of cognitive therapy: to challenge dysfunctional sexual beliefs)
* usually treats erectile dysfunction
* involves education, sensate focus, stimulus control, sexual skills training, and cognitive restructuring (the core component of cognitive therapy: to challenge dysfunctional sexual beliefs)
41
New cards
Kinsey’s studies on sexuality concluded that:
“sexual orientation is a continuum that varies with time”
42
New cards
Buss’s sexual strategies theory
humans evolved complex short-term and long-term mating strategies
43
New cards
sexual orientation
an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions to men, women, or both sexes
44
New cards
estrogen
* hormone produced mainly by the ovaries
* act as the principal female sex hormones
* induces estrus in female mammals and secondary female sexual characteristics in humans
* act as the principal female sex hormones
* induces estrus in female mammals and secondary female sexual characteristics in humans
45
New cards
testosterone
* male sex hormone
* stimulates the development of male reproductive organs,
* and secondary sex characteristics, (such as beard, bone, and muscle growth)
* stimulates the development of male reproductive organs,
* and secondary sex characteristics, (such as beard, bone, and muscle growth)
46
New cards
dopamine
neurotransmitter that plays a role as a “reward center”
* memory, motivation, mood, attention
* memory, motivation, mood, attention
47
New cards
oxytocin
\
* traditionally associated with sex, breastfeeding, and childbirth,
* BUT almost any form of social bonding or positive physical contact can trigger _____ release
* traditionally associated with sex, breastfeeding, and childbirth,
* BUT almost any form of social bonding or positive physical contact can trigger _____ release
48
New cards
sexual schemas
blueprints for what we define as our role in:
* sexual expression,
* sexual orientation,
* sexual behaviors,
* sexual desires
* sexual expression,
* sexual orientation,
* sexual behaviors,
* sexual desires
49
New cards
Need for achievement
= psychological drive to accomplish things
* relates to the competence part of self-determination theory
* can be either extrinsic or intrinsic
* older siblings usually have a high level of this
* relates to the competence part of self-determination theory
* can be either extrinsic or intrinsic
* older siblings usually have a high level of this
50
New cards
Need to Belong
= desire to be accepted by people you care about
* related to the relatedness part of self-determination theory
\
too low = pathological/sociopath = don’t care about societal rules
* ex. I’m going to set my neighbor’s house on fire! what fun!!
too high = pathological/sociopath = know it’s wrong, but go to extreme lengths to please others (and react strongly to being excluded)
* related to the relatedness part of self-determination theory
\
too low = pathological/sociopath = don’t care about societal rules
* ex. I’m going to set my neighbor’s house on fire! what fun!!
too high = pathological/sociopath = know it’s wrong, but go to extreme lengths to please others (and react strongly to being excluded)
51
New cards
Need for Aggression
* \
* evolutionarily makes sense: needed to protect offspring/territory/food
* evolutionarily makes sense: needed to protect offspring/territory/food
52
New cards
Hostile Aggression
= a type of aggression carried out for its own sake with the intention of causing harm
* maladaptive coping
ex. road rage, punching walls
\
* opposite of instrumental aggression
* maladaptive coping
ex. road rage, punching walls
\
* opposite of instrumental aggression
53
New cards
Instrumental Aggression
= a type of aggression used in the process of achieving a goal other than the aggression itself
* pre-meditated aggression and controlled (used for strategy as an __instrument__)
ex. being aggressive in the court room but not while playing with toddler
* opposite of hostile aggression
* pre-meditated aggression and controlled (used for strategy as an __instrument__)
ex. being aggressive in the court room but not while playing with toddler
* opposite of hostile aggression
54
New cards
Need for Power
= need to have an impact on other people
ex. class president, captain, etc.
\
* tends to be linked with instrumental aggression
ex. class president, captain, etc.
\
* tends to be linked with instrumental aggression