Key Concepts in Antibiotic Development, Resistance, and Clostridioides difficile
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is the biggest challenge in antibiotic development?
The timeline mismatch; it takes ~12 years and $800M to develop a drug, but resistance can emerge in just 6 months.
What are the 5 primary targets for antibiotics?
1. Cell wall 2. Cell membrane 3. Protein synthesis 4. Nucleic acid synthesis 5. Metabolism.
What is the difference between Bacteriostatic and Bactericidal?
Bacteriostatic inhibits growth; Bactericidal kills the bacteria directly.
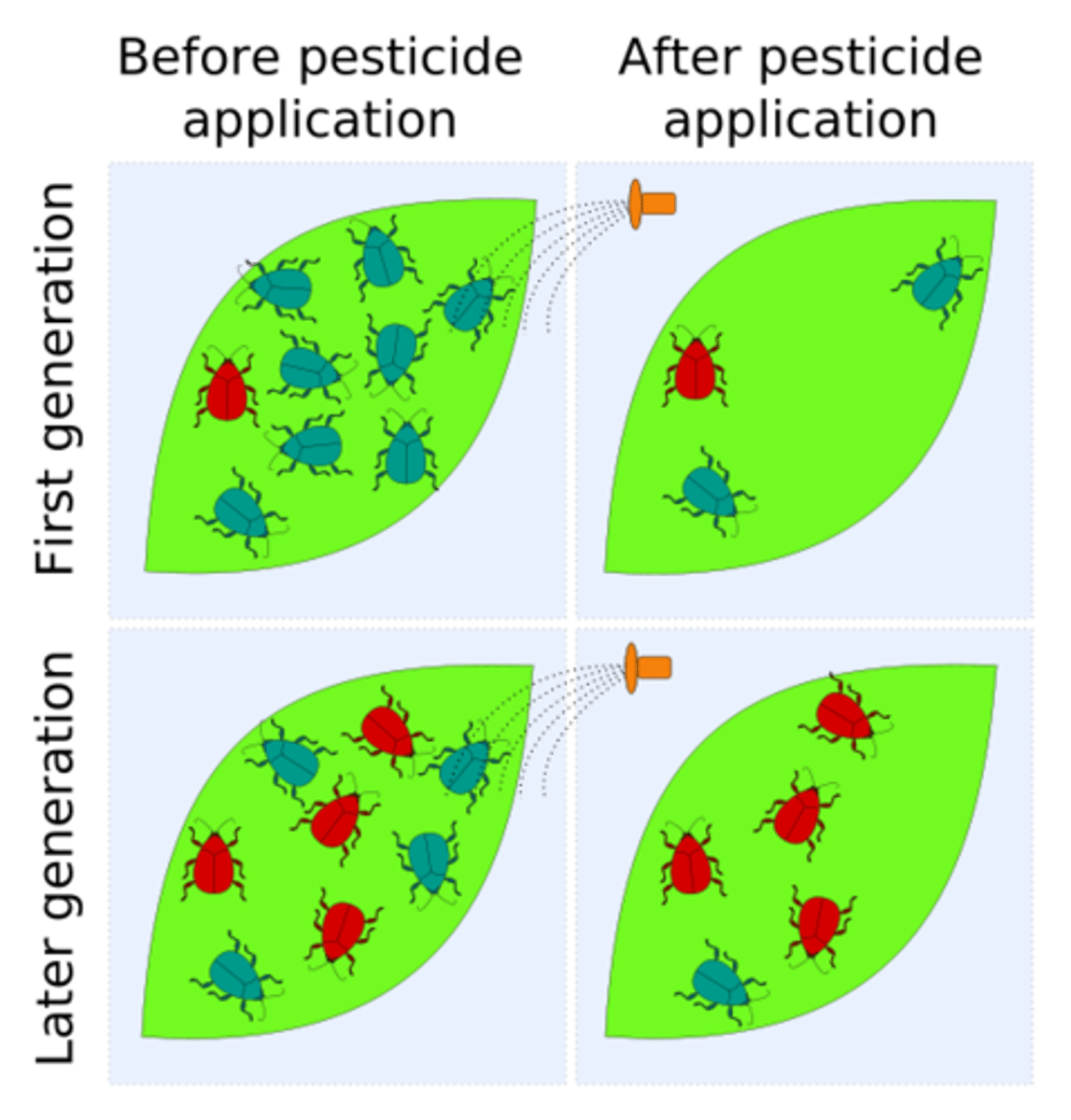
How does selective pressure drive resistance in hospitals?
Intensive antibiotic use kills susceptible bacteria, allowing resistant strains to survive and dominate.
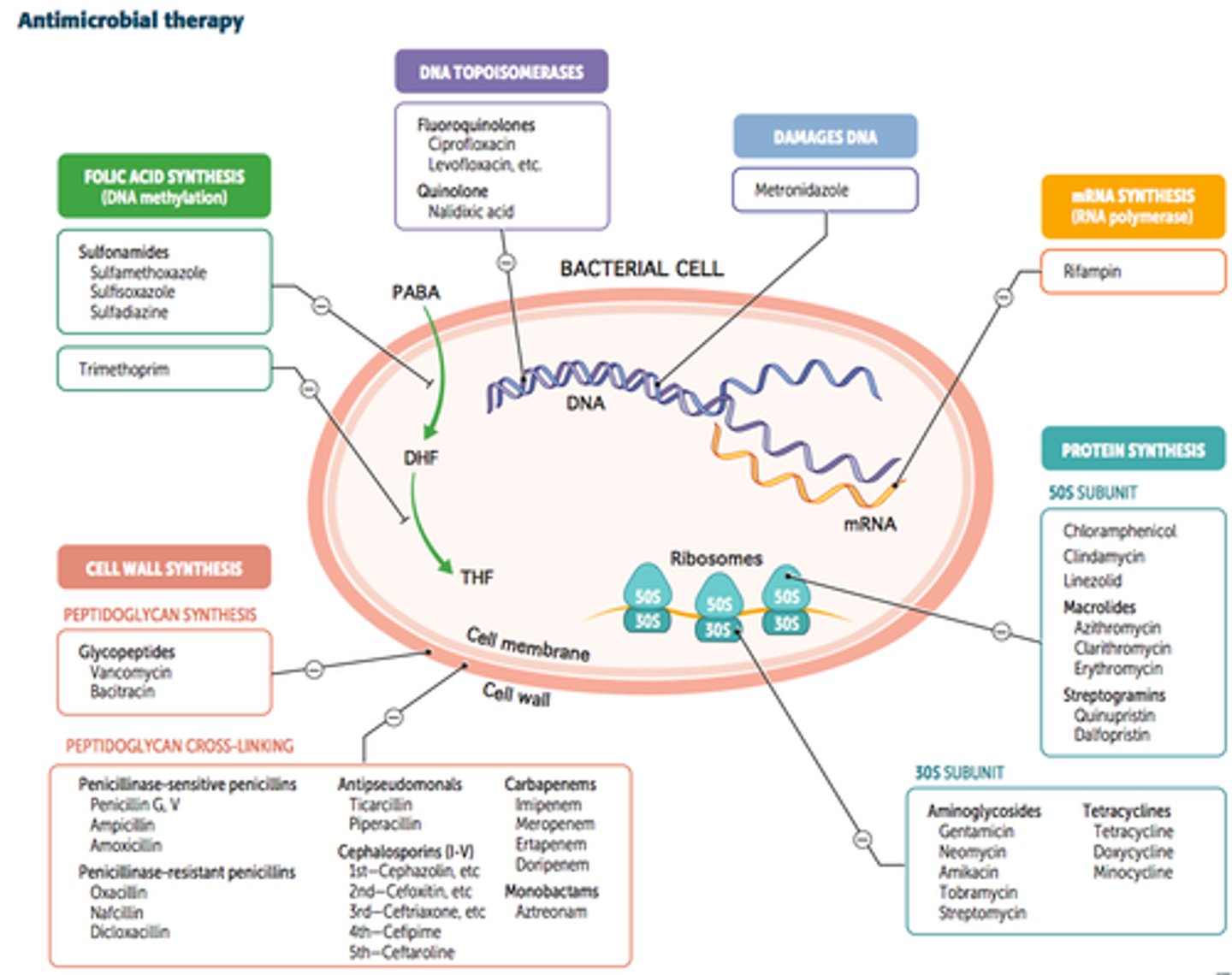
What are the 4 main mechanisms of bacterial resistance?
1. Efflux pumps 2. Reduced permeability 3. Target modification 4. Enzymatic inactivation.
How do β-lactamases work?
They are enzymes that hydrolyse the β-lactam bond, breaking the antibiotic ring before it can reach the cell wall.
How do bacteria resist Quinolones?
Through point mutations in the gene encoding DNA gyrase, modifying the drug target.
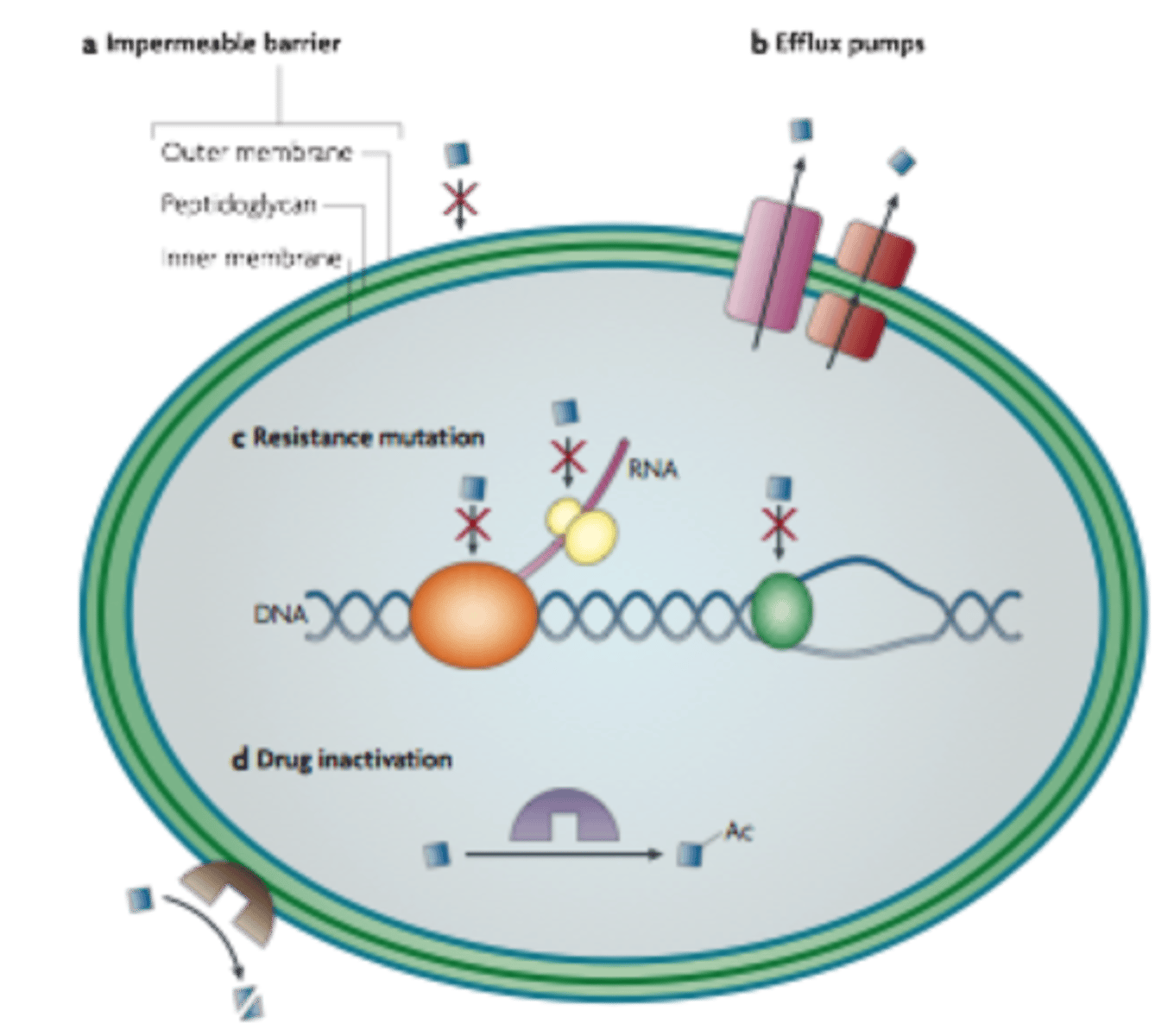
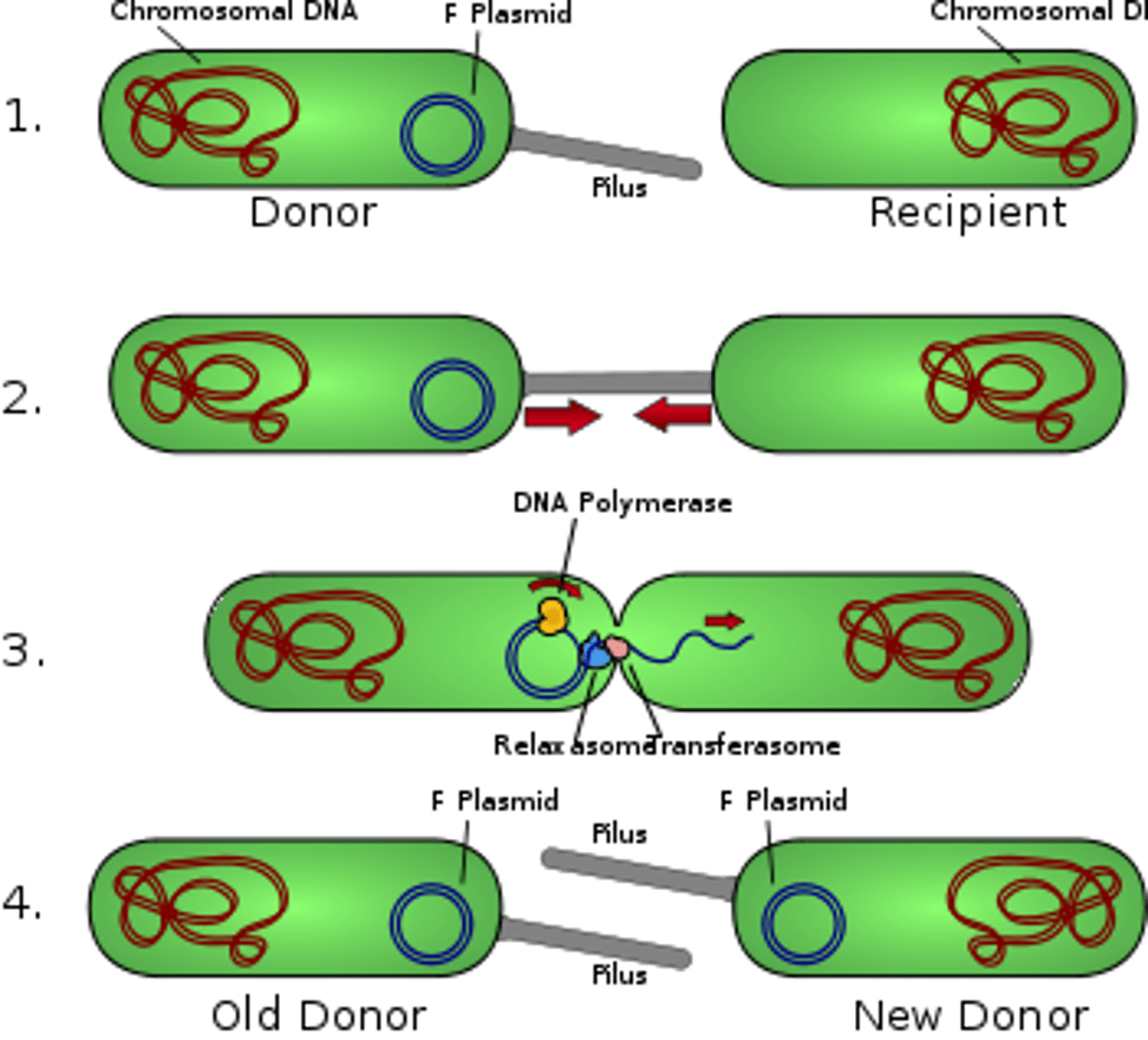
What is Horizontal Gene Transfer (HGT)?
The spread of resistance genes between different bacteria via Plasmids.
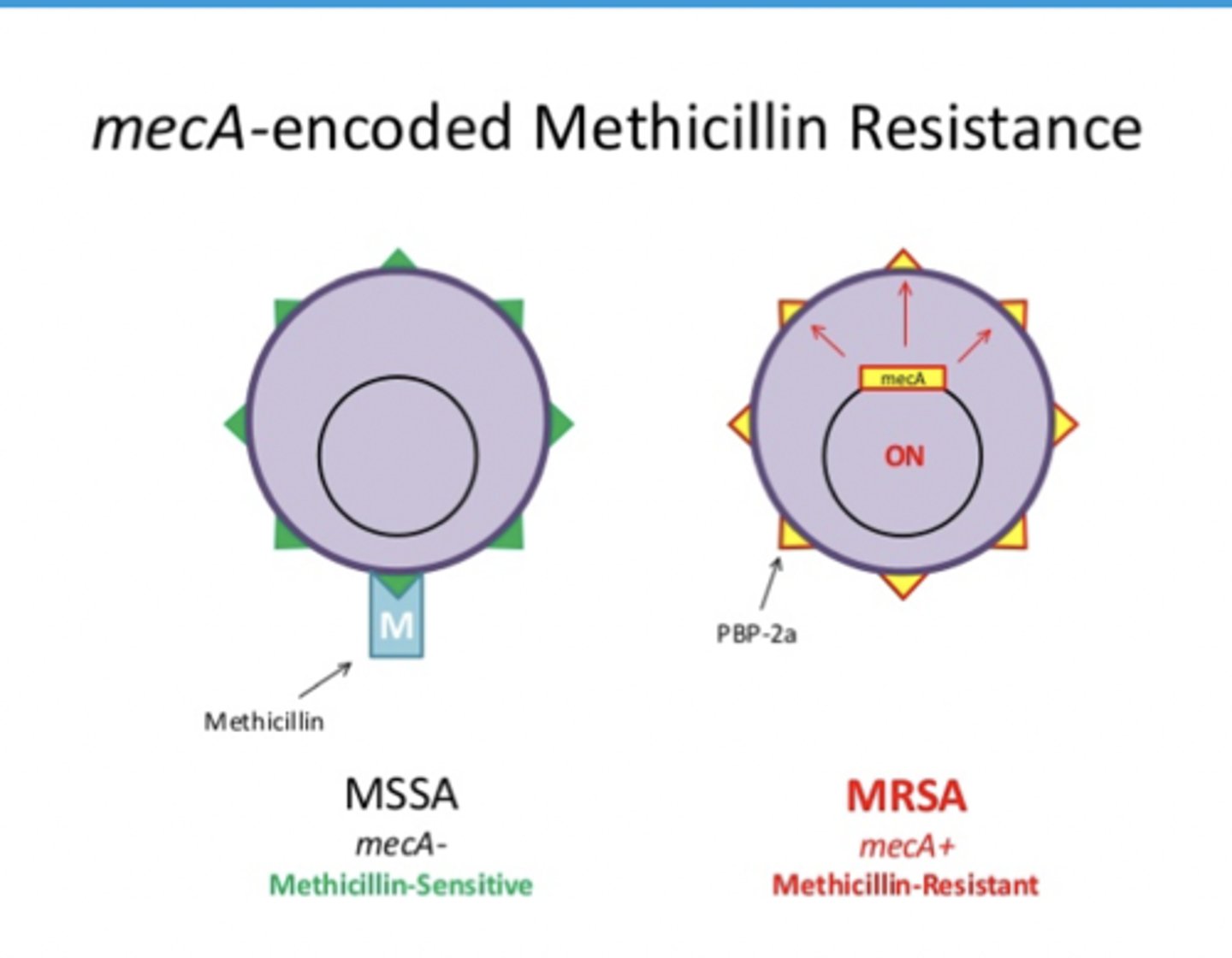
What defines MRSA?
Resistance to nearly all β-lactams due to the mecA gene, which encodes a low-affinity protein called PBP2a.
How is MRSA managed in a hospital ward?
Swab screening, patient isolation, and treatment with non-beta-lactam drugs like Vancomycin.
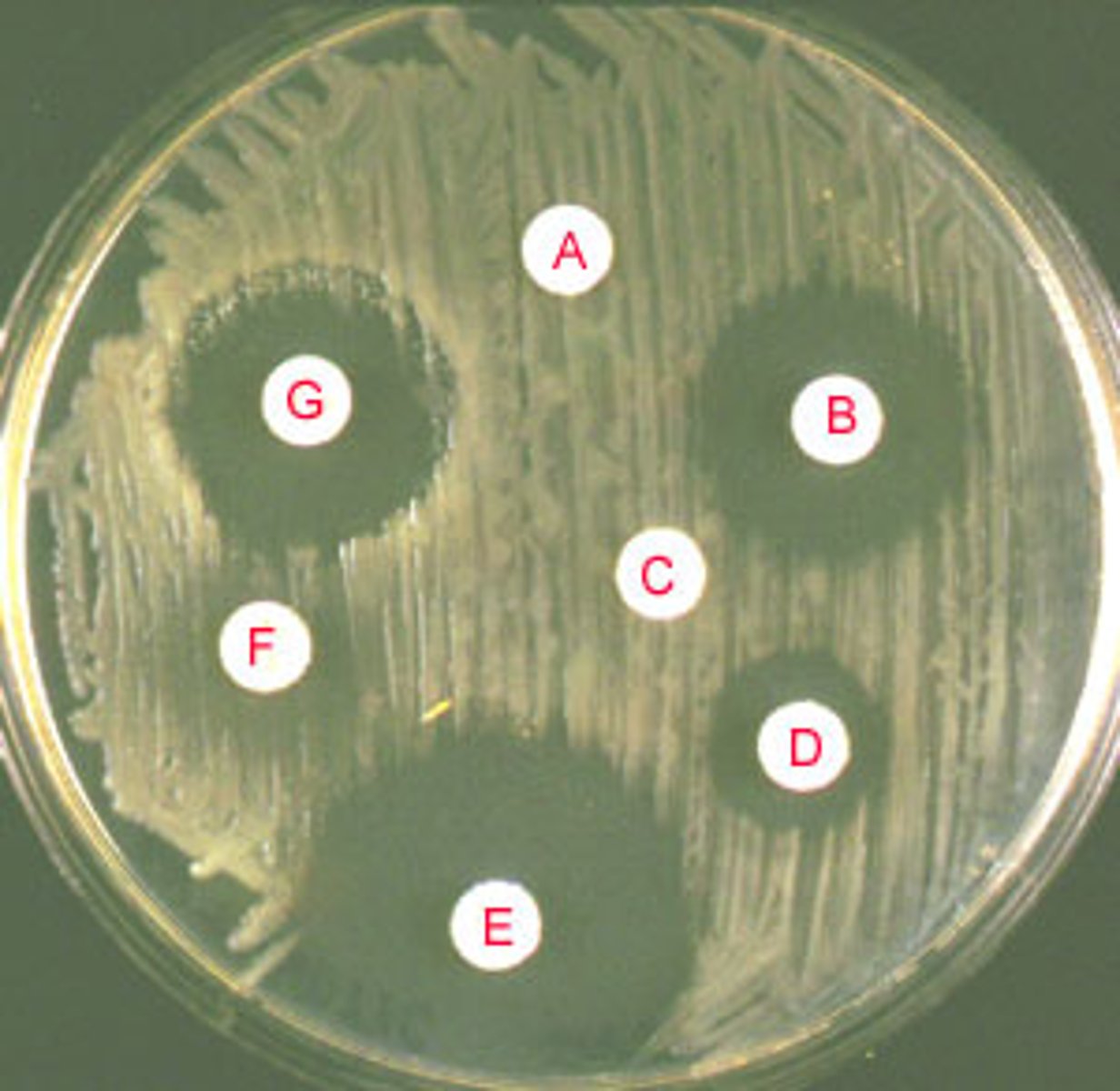
How do you interpret a Disc Diffusion (Kirby-Bauer) test?
A clear area indicates a Zone of Inhibition; no zone or a small zone means the bacteria are resistant.
Why does antibiotic use lead to C. diff (Clostridioides difficile)?
Broad-spectrum antibiotics wipe out good gut flora, allowing C. diff to overgrow and produce toxins.
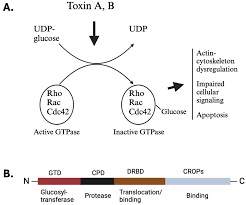
What are the two C. diff toxins and their roles?
Toxin A (Enterotoxin): Causes fluid leakage; Toxin B (Cytotoxin): Causes cell death and inflammation.
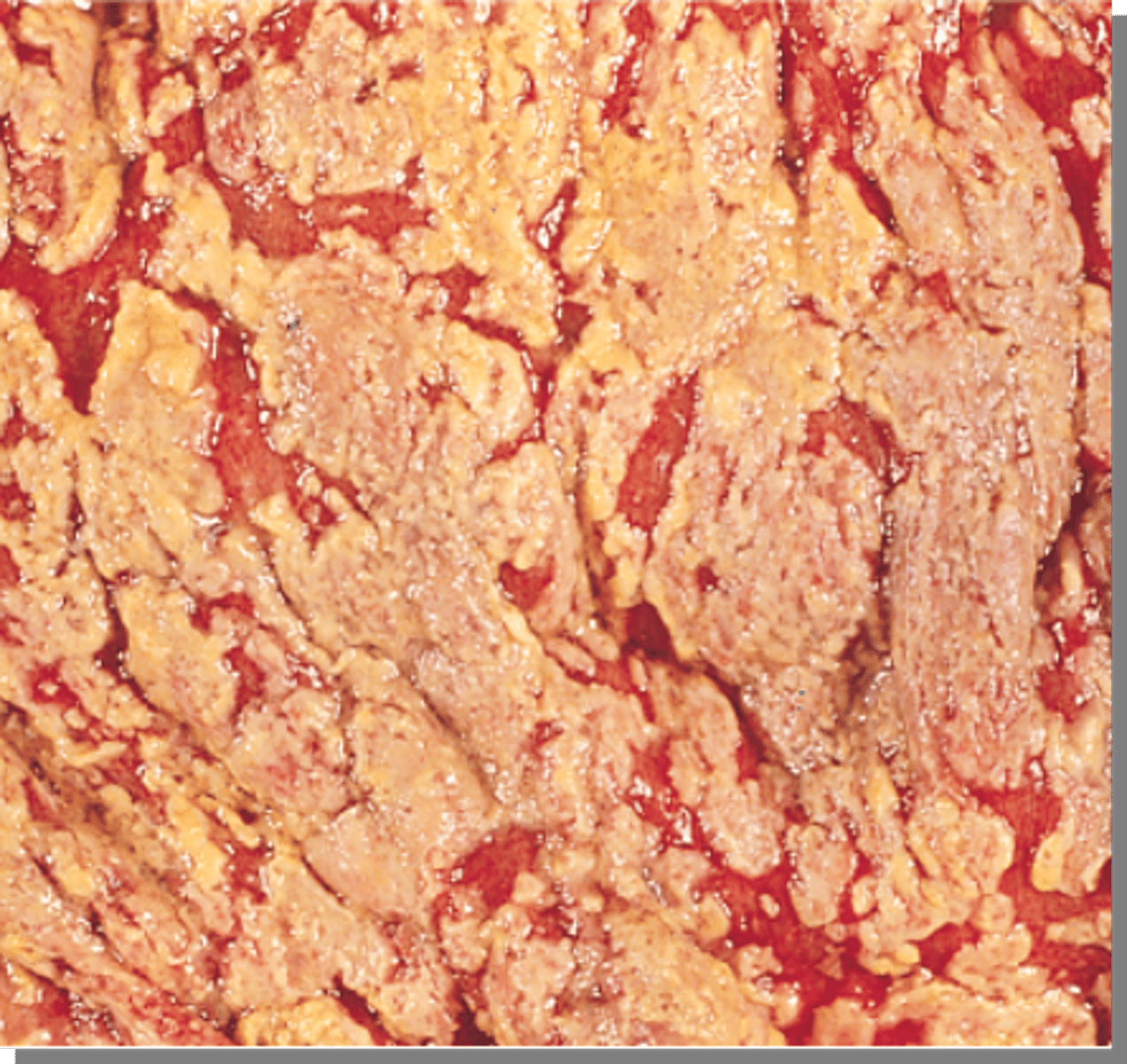
What is Pseudomembranous Colitis?
A severe C. diff complication showing yellow-white inflammatory plaques on the colon wall.
How is C. diff diagnosed in the lab?
Two-step testing: 1. GDH screening for the organism 2. Toxin EIA confirming the toxins are present.
What is the first clinical step in treating a C. diff infection?
Stop the causative antibiotic immediately, isolate the patient, and start oral Vancomycin or Fidaxomicin.