ASC 305 - Equine Anatomy Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ASC 305 - Equine Anatomy (University Of Kentucky) Exam 2 Study Guide
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
1
New cards
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary, Striated and Branched | Specialized and Found only in the Heart
2
New cards
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary and Non-Striated | Found in the Digestive Tract, Arteries/Veins, and other Body Systems (Respiratory, Reproductive, Etc)
3
New cards
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary And Striated | 50% Of The Horse’s Body | What The Horse Uses For Locomotion
4
New cards
Stages Of Muscles
Contraction (shortening of muscle fibers) and Relaxation (return to neutral position of muscle fibers)
5
New cards
Components Of Muscles
* Central Fleshy and Contractile “Muscle Body”
* 2 Tendons, One at Each End of the Muscle
* Nerve to Stimulate It
* Blood Supply through an Artery and Vein
* 2 Tendons, One at Each End of the Muscle
* Nerve to Stimulate It
* Blood Supply through an Artery and Vein
6
New cards
Muscles can not ----, they can only ----.
Muscles can not push, they can only pull.
7
New cards
Epimysium
Muscle Belly Protective Membrane
8
New cards
Perimysium
Fascicle Protective Membrane
9
New cards
Endomysium
Muscle Fiber/Cell Protective Membrane
10
New cards
Myofibrils
Muscle Fibers are made up of a Bunch Of…
11
New cards
Actin & Myosin
Two Myofilaments that actually interact to cause Contraction.
12
New cards
Sarcomere
A Repeating area that contains the two myofilaments (actin & myosin). Shortening of the area occurs as the myofilaments move closer together.
13
New cards
Flexion, Flexors
The angle of the joint is made narrower. Muscles that have the prime function of closing the angle of a joint are called “-----”.
14
New cards
Extension, Extensors
The angle of the joint is widened. Muscles pass over the apex of the joint, and are called “-----”.
15
New cards
Adduction, Adductors
Muslces draw the limb toward the mid-line of the body. Muscles are called “----”.
16
New cards
Abduction, Abductors
Muscles lead the limb away from the mid-line of the body. Muscles are called “-----”.
17
New cards
Type I Fiber (Red Endurance Muscle)
High Oxygen Usage Capacity, Slow Response Time, Low Power, Narrow Muscle Fiber Thickness, Slow Fatigue
18
New cards
Type IIX (White Sprint Muscle)
Low Oxygen Usage Capacity, Quick Response Time, High Power, Thick Muscle Fiber Thickness, Quick Fatigue
19
New cards
Type IIA (White Sprint Muscle)
Medium Oxygen Usage Capacity, Medium Response Time, Medium Power, Medium Muscle Fiber Thickness, Medium Fatigue
20
New cards
Aerobic
* Uses Oxygen
* Complete Glucose Breakdown
* Produces CO2 and Water
* Releases Relatively Large Amount of Energy
* Complete Glucose Breakdown
* Produces CO2 and Water
* Releases Relatively Large Amount of Energy
21
New cards
Anaerobic
* Does NOT Use Oxygen
* Glucose is NOT completely broken down
* Produces Lactic Acid (By-Product)
* Releases A Small Amount Of Energy
* Glucose is NOT completely broken down
* Produces Lactic Acid (By-Product)
* Releases A Small Amount Of Energy
22
New cards
**Triceps Brachii**
Shoulder: Flex
Elbow: Extend
*Long Head*
Origination Point: Caudel surface of scapula
*Lateral Head*
Origination Point: Lateral side of femur
*Medial Head*
Origination Point: Distal medial side of the humerus
Insertion Point (the same for all): Proximal side of Electranon Tuberosity
Shoulder: Flex
Elbow: Extend
*Long Head*
Origination Point: Caudel surface of scapula
*Lateral Head*
Origination Point: Lateral side of femur
*Medial Head*
Origination Point: Distal medial side of the humerus
Insertion Point (the same for all): Proximal side of Electranon Tuberosity
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert?
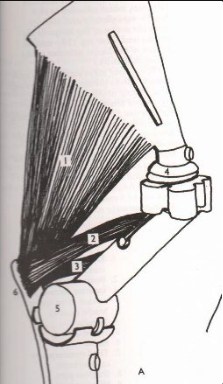
23
New cards
**Superficial Digital Flexor**
Knee: Flex
Lower Leg: Flex
Origination Point: Distal End Of The Humerus
Insertion Point: 4 Insertion Points (2 - Distal Of P1, 2 - Proximal of P2)
Knee: Flex
Lower Leg: Flex
Origination Point: Distal End Of The Humerus
Insertion Point: 4 Insertion Points (2 - Distal Of P1, 2 - Proximal of P2)
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (1)
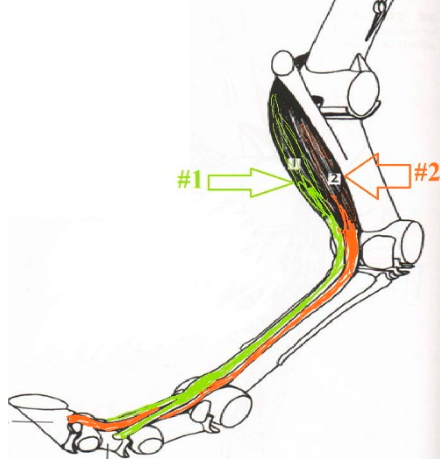
24
New cards
**Supraspinatus**
Shoulder: Extend
Origination Point: Superaspinous Fossa
Insertion Point: (1) Greater Tubrical on the Cranial Side (2) Lesser Tubrical on the Cranial Medial Side
Shoulder: Extend
Origination Point: Superaspinous Fossa
Insertion Point: (1) Greater Tubrical on the Cranial Side (2) Lesser Tubrical on the Cranial Medial Side
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert?
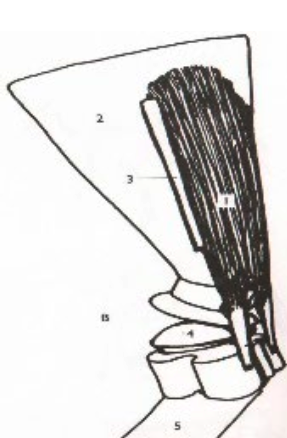
25
New cards
**Brachialis**
Elbow: Flex
Origination Point: Under lesser tubricale caudel medial side (goes under the deltoid tuberosity)
Insertion Point:under the medial tuberosity of radius (medial)
Elbow: Flex
Origination Point: Under lesser tubricale caudel medial side (goes under the deltoid tuberosity)
Insertion Point:under the medial tuberosity of radius (medial)
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (1)
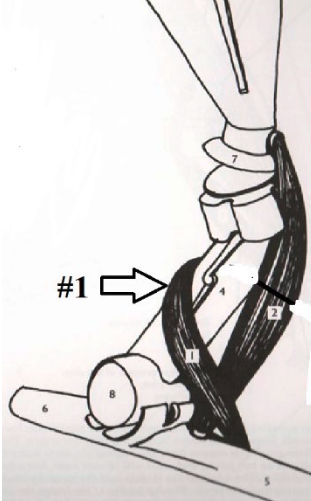
26
New cards
**Intraspinatus**
Shoulder: Flex
Origination Point: Infraspinous Fossa
Insertion Point: Greater Tubrical Caudal
Shoulder: Flex
Origination Point: Infraspinous Fossa
Insertion Point: Greater Tubrical Caudal
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert?
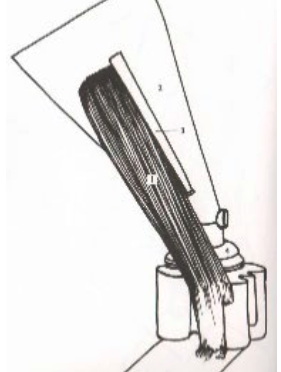
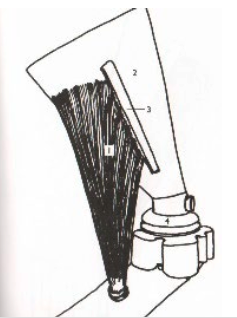
27
New cards
**Flexor Carpi Ulnaris**
Elbow (Minor): Extend
Knee: Flex
Origination Point: Medial Side of the humerus
Insertion Point: 2nd Metacarpal Proximal Medial End
Elbow (Minor): Extend
Knee: Flex
Origination Point: Medial Side of the humerus
Insertion Point: 2nd Metacarpal Proximal Medial End
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (3)
28
New cards
**Extensor Carpi Radialis**
Elbow: Flex
Knee: Extend
Origination Point: Lateral distal side of humerus
Insertion Point: Third metacarpal at proximal dorsal surface
Elbow: Flex
Knee: Extend
Origination Point: Lateral distal side of humerus
Insertion Point: Third metacarpal at proximal dorsal surface
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (1)
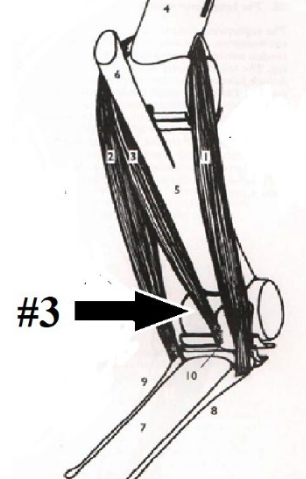
29
New cards
**Deltoid**
Shoulder: Flex
Origination Point: Infraspinous Fossa (on top of the infraspinatus)
Insertion Point: Deltoid Tuberosity
Shoulder: Flex
Origination Point: Infraspinous Fossa (on top of the infraspinatus)
Insertion Point: Deltoid Tuberosity
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert?
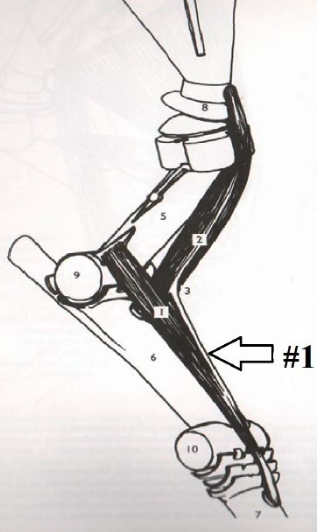
30
New cards
**Common Digital Extensor Tendon**
Knee: Extend
Lower Leg: Extend
Origination Point: Elbow Joint
Insertion Point: Extensor Process of P3
Knee: Extend
Lower Leg: Extend
Origination Point: Elbow Joint
Insertion Point: Extensor Process of P3
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (1)
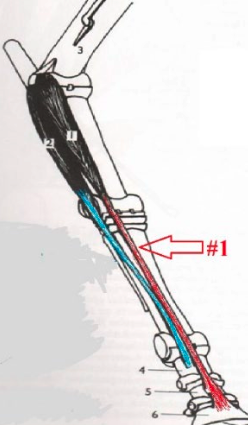
31
New cards
**Biceps Brachii**
Shoulder: Extend
Elbow: Flex
Origination Point: Super Glenod Tuberitcal
Insertion Point: Medial Tuberosity
Shoulder: Extend
Elbow: Flex
Origination Point: Super Glenod Tuberitcal
Insertion Point: Medial Tuberosity
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert?
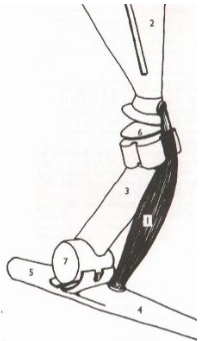
32
New cards
**Lateral Ulna**
Elbow (Minor): Extend
Knee: Flex
Origination Point: Distal lateral side of humerus
Insertion Point: 4th Metacarpal Proximal Lateral End & Accessory Carpal
Elbow (Minor): Extend
Knee: Flex
Origination Point: Distal lateral side of humerus
Insertion Point: 4th Metacarpal Proximal Lateral End & Accessory Carpal
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (1)
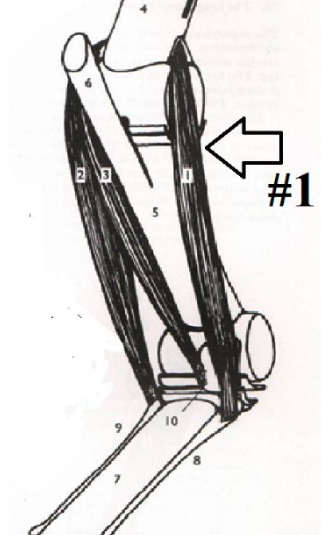
33
New cards
**Flexor Carpi Radialis**
Elbow (Minor): Extend
Knee: Flex
Origination Point: Medial distal end of the humerus
Insertion Point: 2nd Metacarpal Proximal Medial End
Elbow (Minor): Extend
Knee: Flex
Origination Point: Medial distal end of the humerus
Insertion Point: 2nd Metacarpal Proximal Medial End
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (2)
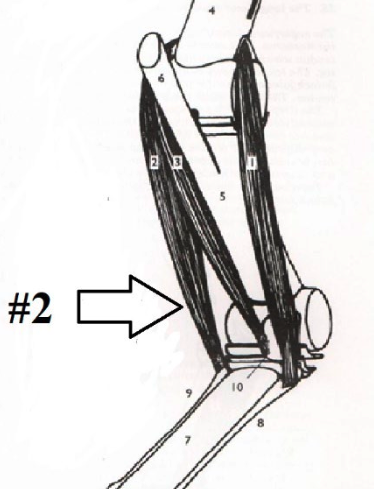
34
New cards
**Lateral Digital Extensor**
Knee: Extend
Lower Leg: Extend
Origination Point: Lateral Proximal End of the Radius
Insertion Point: Dorsal Surface of Long Pasturn
Knee: Extend
Lower Leg: Extend
Origination Point: Lateral Proximal End of the Radius
Insertion Point: Dorsal Surface of Long Pasturn
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (2)
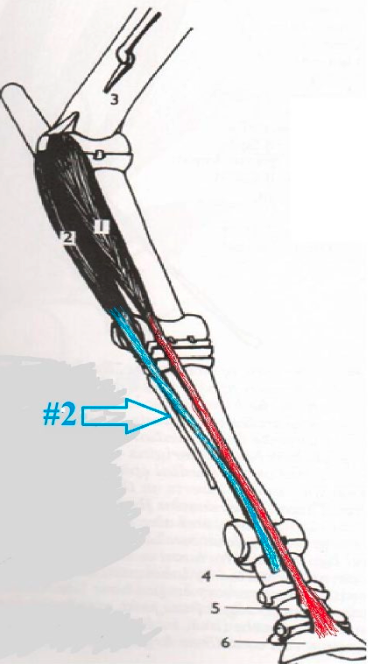
35
New cards
Subscapularis & Teres Major
What two muscles flex the shoulder?
36
New cards
**Omotransversaius**
Origination Point: Cervical Vertebrae (Transverse Processes)
Insertion Point: Lateral Side Of Humerus
Origination Point: Cervical Vertebrae (Transverse Processes)
Insertion Point: Lateral Side Of Humerus
What is the **blue** muscle and where does it originate and insert?
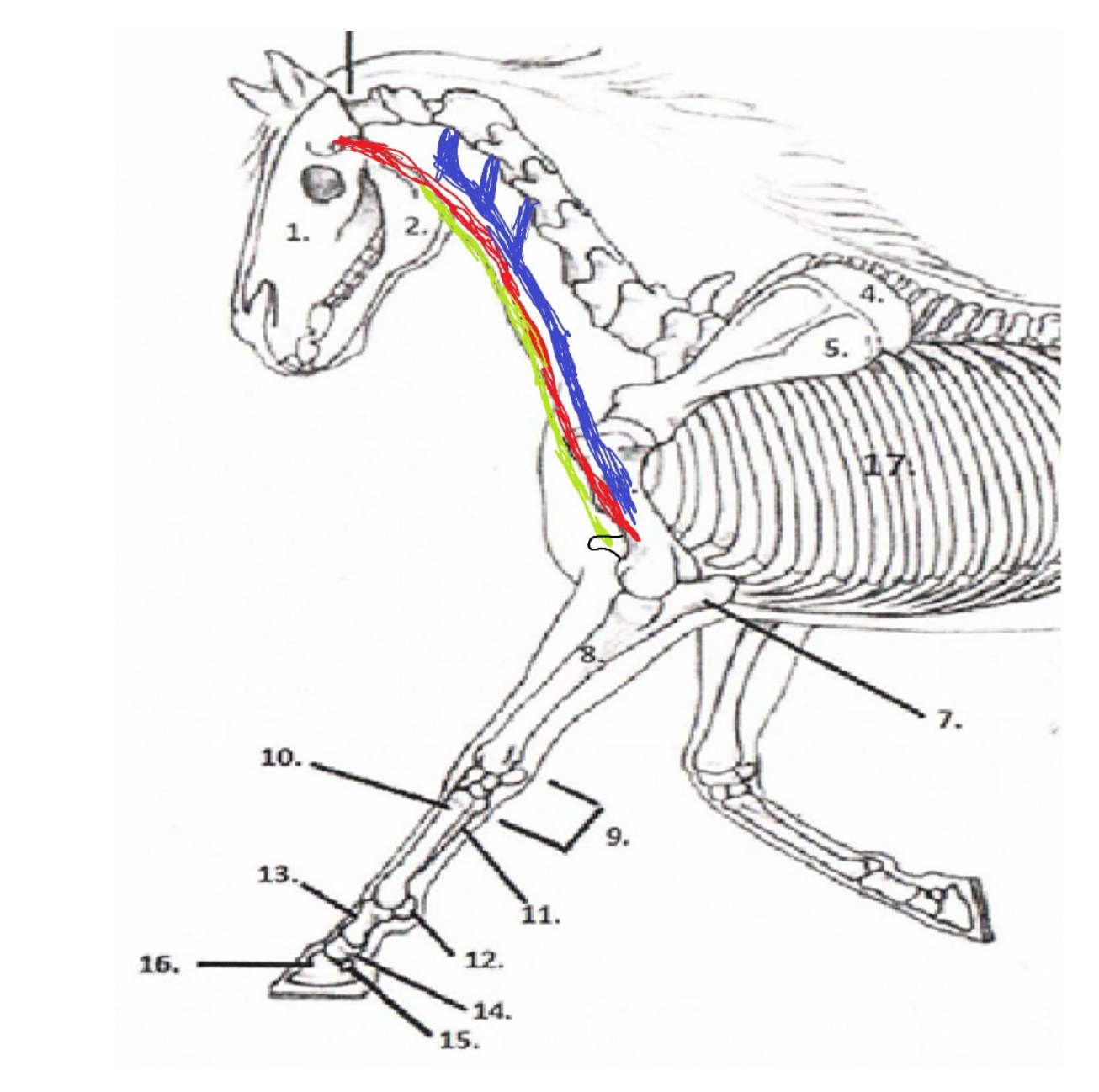
37
New cards
**Brachiocephalicus**
Origination Point: Temporal Bone
Insertion Point: Lateral Side Of The Humerus
Origination Point: Temporal Bone
Insertion Point: Lateral Side Of The Humerus
What is the **red** muscle and where does it originate and insert?
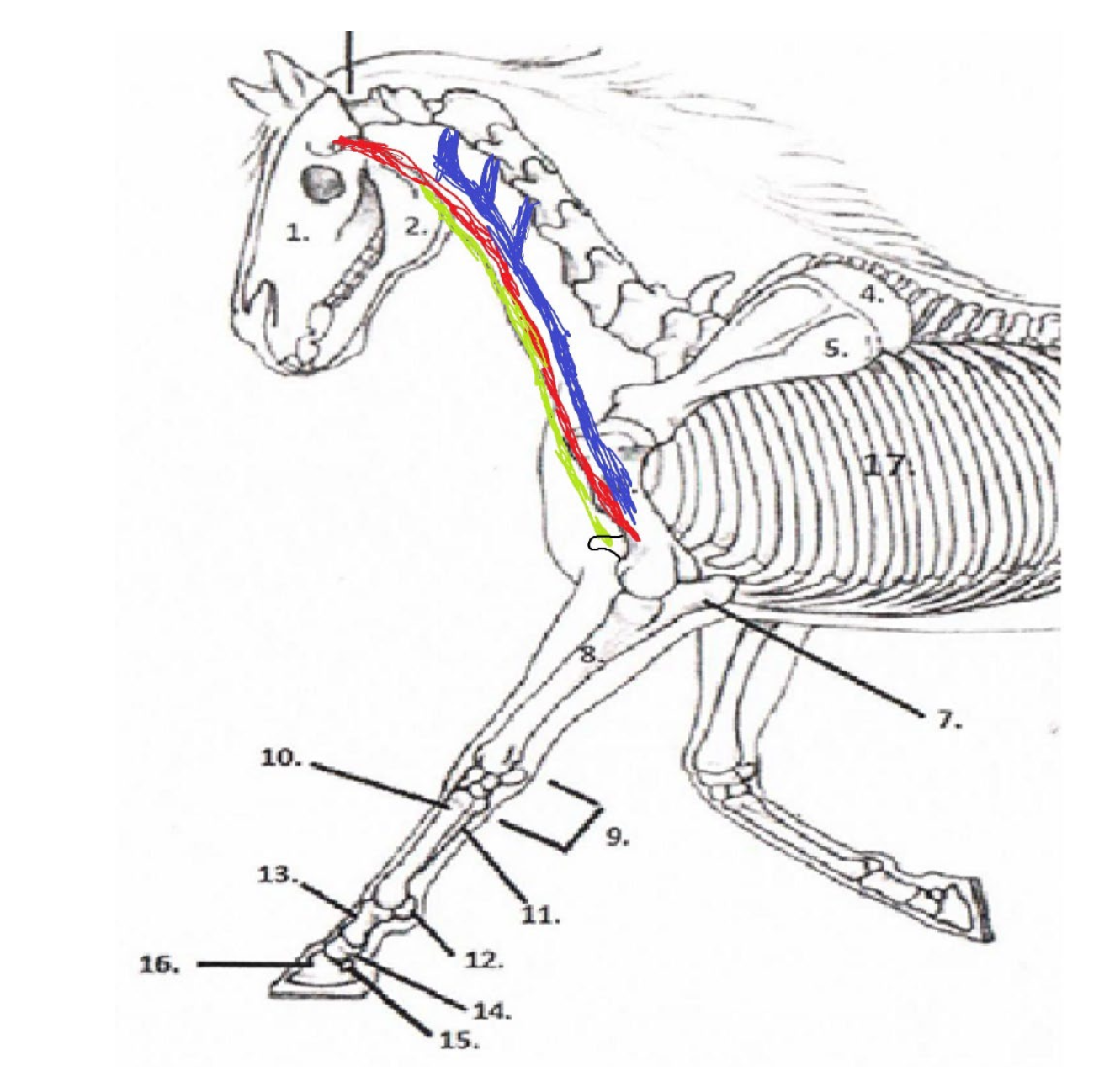
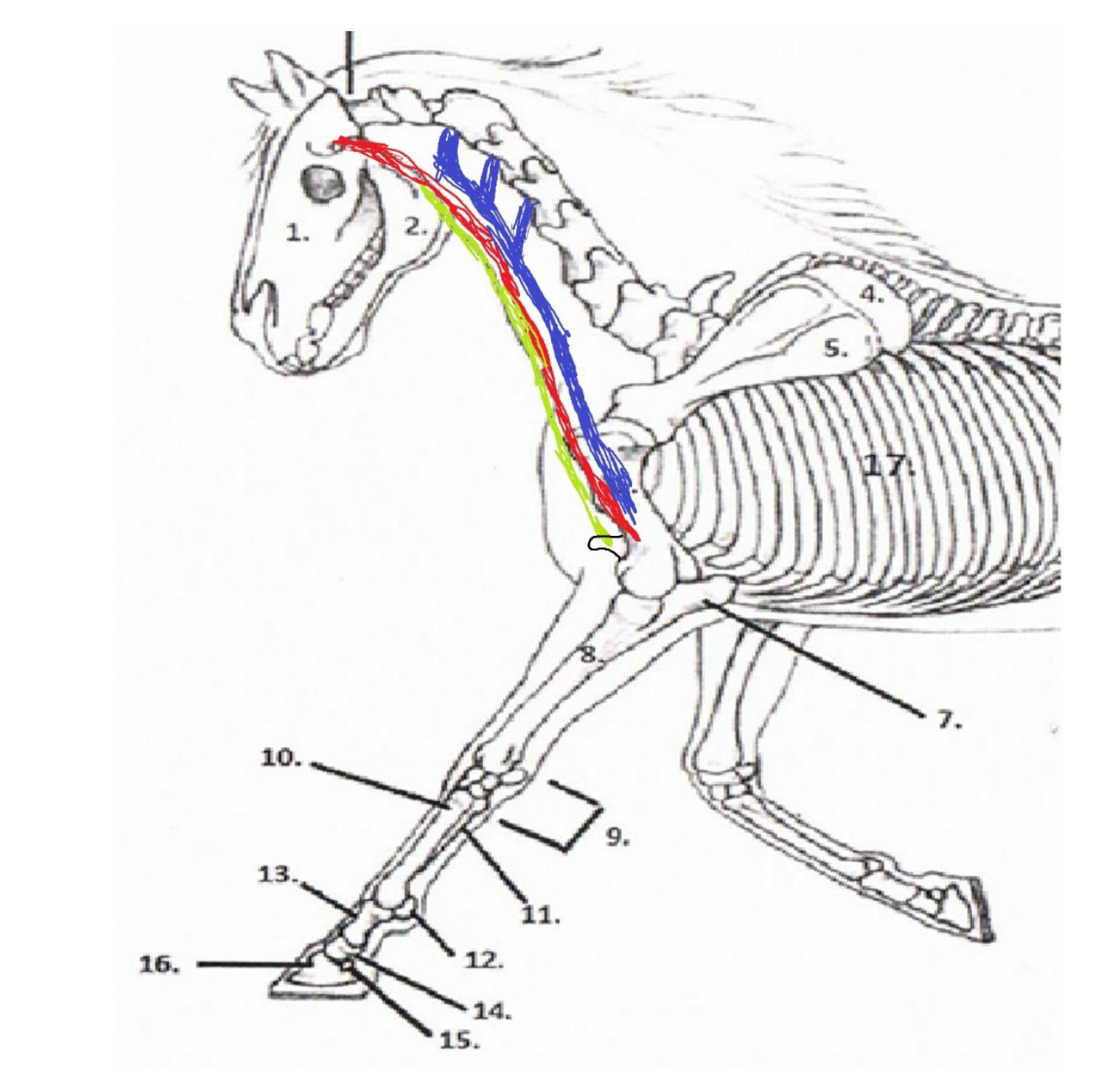
38
New cards
Sternomandibularis
Origination Point: Mandible
Insertion Point: Sternum
Origination Point: Mandible
Insertion Point: Sternum
What is the **green** muscle and where does it originate and insert?
39
New cards
Brachiocephalicus & Sternomandibularis
Which two muscles make up the jugular groove of the horse?
40
New cards
Brachiocephalicus & Sternomandibularis
Which of the three lower neck muscles can directly lower the head?
41
New cards
Sternomandibularis
Which of the lower neck muscles discussed in class move the horses’s leg by contracting?
42
New cards
Sternomandibaris - pull head down (both muscles)
Left Brachiocephalicus - to pull head to the left (left side muscle only) and down (both muscles)
Left Omnotransverarius - to pull neck down (both muscles) and to the left (left side muscle only)
Left Brachiocephalicus - to pull head to the left (left side muscle only) and down (both muscles)
Left Omnotransverarius - to pull neck down (both muscles) and to the left (left side muscle only)
My horse is trying to reach a carrot on the ground and to the left side of its body. Which lower neck muscles will it use to get the carrot?
43
New cards
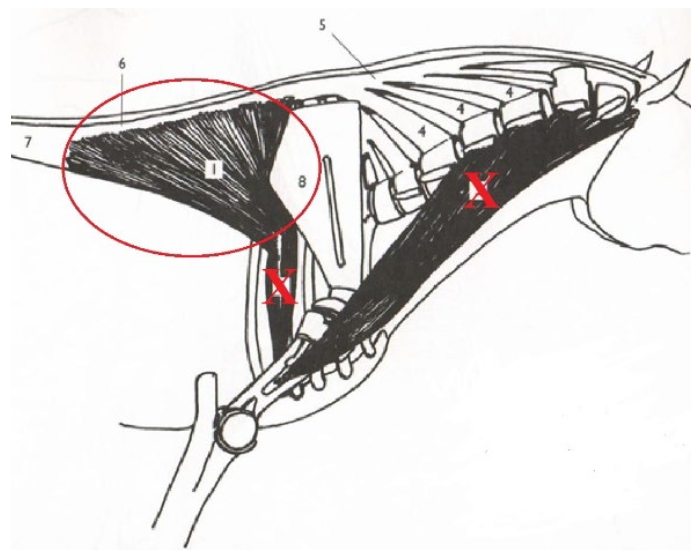
**Latissimus Dorsi**
Shoulder: Flex
Stabilizes Dorsal/Proximal End of Scapula
Origination: Along the supraspinous ligament (thoracic & some lumbar)
Insertion: Binds with (2) Teres Major (muscle) tuberosity
Shoulder: Flex
Stabilizes Dorsal/Proximal End of Scapula
Origination: Along the supraspinous ligament (thoracic & some lumbar)
Insertion: Binds with (2) Teres Major (muscle) tuberosity
What is this muscle? What is it’s purpose? Where does it originate and insert?
44
New cards
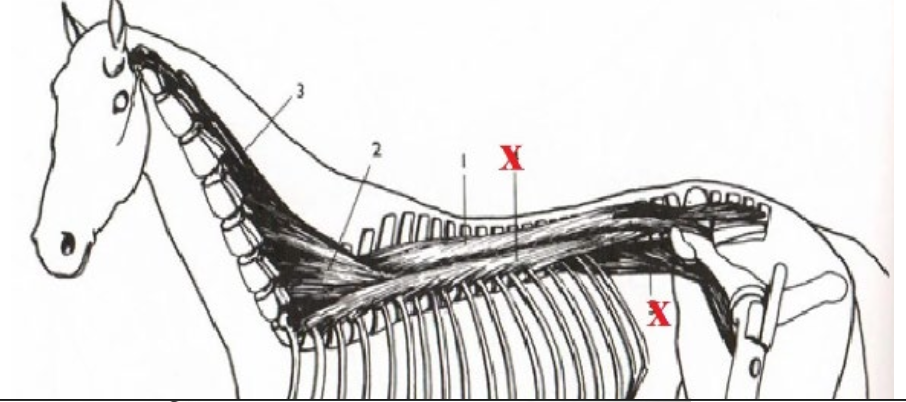
**Longissimus Dorsi**
Connects head, neck, withers, back, loin, and group together through vertebrae allowing connected movement. Pulls spine dorsally.
Origination: Sacrum/Pelvis at Multiple Locations
Insertion: Temporal Bone
Connects head, neck, withers, back, loin, and group together through vertebrae allowing connected movement. Pulls spine dorsally.
Origination: Sacrum/Pelvis at Multiple Locations
Insertion: Temporal Bone
What is this muscle? What is it’s purpose? Where does it originate and insert?
45
New cards
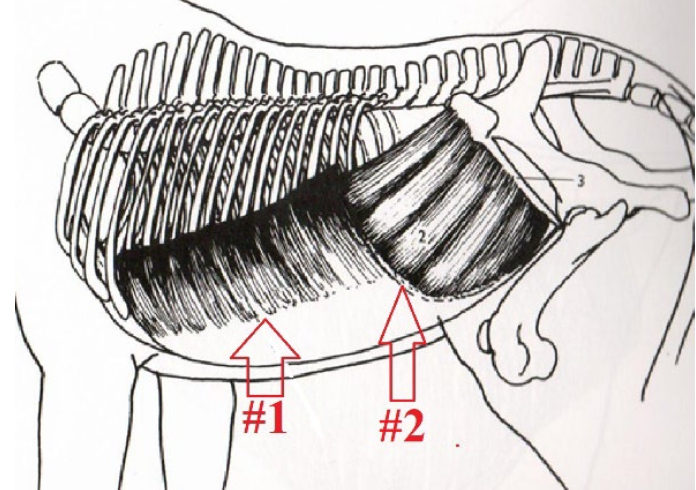
**External and Internal Oblique Abdominal Muscles**
Part of the bowstring effect. Helps to round the horses’s spine, by pulling ribs/sternum and pelvis closer together.
*External*
Origination: Lateral/Ventral Side of Ribs
Insertion: Coccytuberosity/Pubis/Illium
I*nternal*
Origination: False Ribs
Insertion: Cranial Edge of Illium
Part of the bowstring effect. Helps to round the horses’s spine, by pulling ribs/sternum and pelvis closer together.
*External*
Origination: Lateral/Ventral Side of Ribs
Insertion: Coccytuberosity/Pubis/Illium
I*nternal*
Origination: False Ribs
Insertion: Cranial Edge of Illium
What is this muscle? What is its purpose? Where does it originate and insert? (1 & 2)
46
New cards
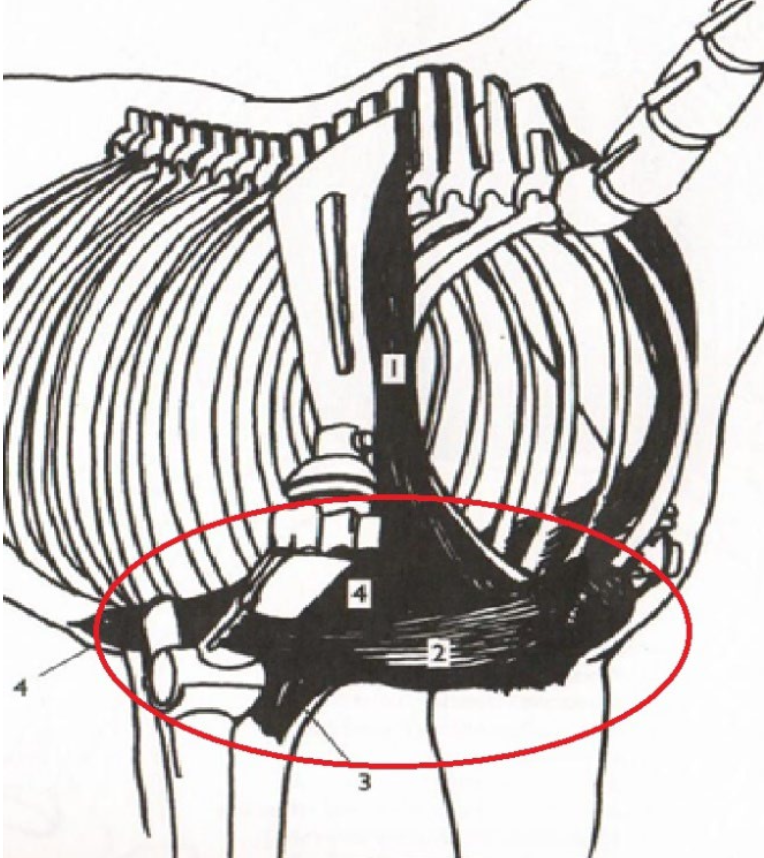
**Pectoral Muscles**
Part of the trampoline effect. “Catch” the axial skeleton. Adduct front legs.
Origination: Sternum
Insertion: Humerus
Part of the trampoline effect. “Catch” the axial skeleton. Adduct front legs.
Origination: Sternum
Insertion: Humerus
What is this muscle? What is it’s purpose? Where does it originate and insert? (Group Of Muscles)
47
New cards
**Psoas Minor and Iliopsoas**
Help to round lumbar spine. Tilts pelvis allows horse to reach under itself further with handles. Connect spine to pelvic limb.
*Psoas Minor*
Origination: Ventral of T16-L2
Insertion: Ventral Surface of Illium
*Illiopsoas*
Origination: Ventral Side of Transverse Processes of Lumbar
Insertion: Lesser Trochanter Lateral Side Of Femur
Help to round lumbar spine. Tilts pelvis allows horse to reach under itself further with handles. Connect spine to pelvic limb.
*Psoas Minor*
Origination: Ventral of T16-L2
Insertion: Ventral Surface of Illium
*Illiopsoas*
Origination: Ventral Side of Transverse Processes of Lumbar
Insertion: Lesser Trochanter Lateral Side Of Femur
What is this muscle? What is it’s purpose? Where does it originate and insert? (Two Muscles)
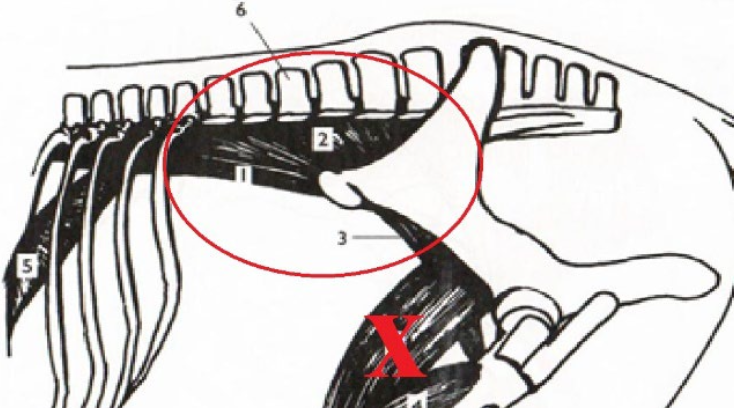
48
New cards
**Serratus Ventralis**
Part of the trampoline effect. Contract to pull axial skeleton up towards the dorsal surface.
(1) Origination: The transverse & cervical verterbrae
(2) Origination:
Both Insert in the the medial side of the scapula
Part of the trampoline effect. Contract to pull axial skeleton up towards the dorsal surface.
(1) Origination: The transverse & cervical verterbrae
(2) Origination:
Both Insert in the the medial side of the scapula
What is this muscle? What is it’s purpose? Where does it originate and insert? (1&2)
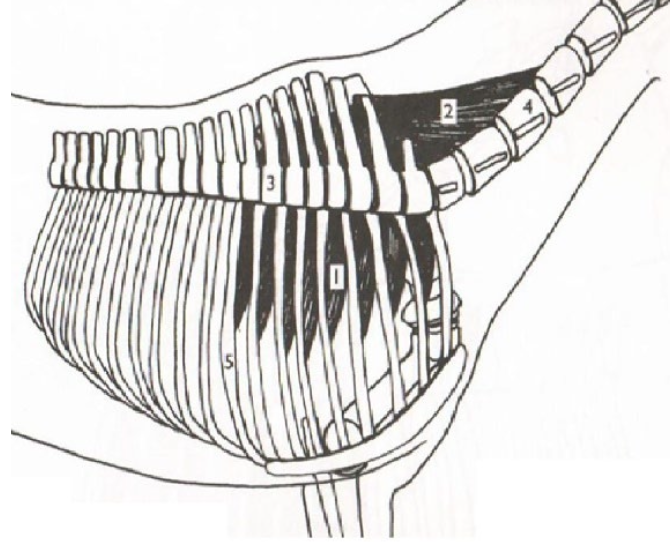
49
New cards
**Spinalis**
Connects thoracic and lumbar vertebrae and supports/stabilizes their spinous processes. Pulls vertebrae dorsally when contracts.
Origination: Sacrum/Pelvis Multiple
Insertion: Temporal Bone
Connects thoracic and lumbar vertebrae and supports/stabilizes their spinous processes. Pulls vertebrae dorsally when contracts.
Origination: Sacrum/Pelvis Multiple
Insertion: Temporal Bone
What is this muscle? What is it’s purpose? Where does it originate and insert?
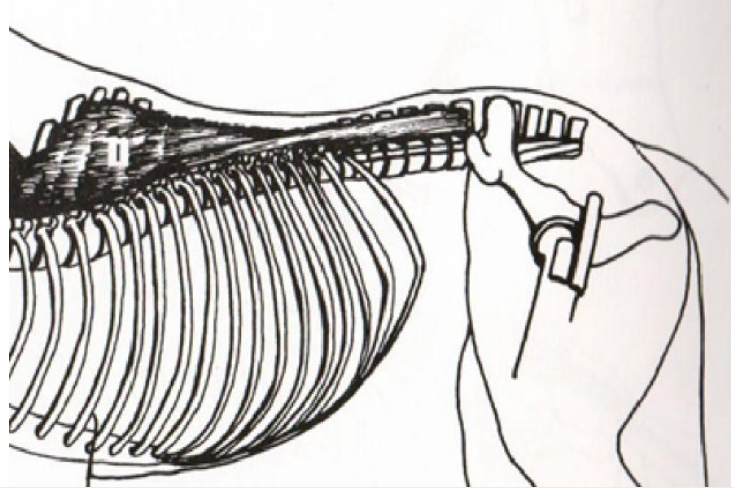
50
New cards
**Trapezius**
Cervical (Cranial) Portion - Rotate scapula forward (extending shoulder joint). Pulls scapula dorsally.
Origination: The Nuchal Ligament
Insertion: Cranial Part of the Spine of Scapula
Thoracic (Caudal) Portion - Rotate scapula backwards (flexing shoulder joint). Pulls scapula dorsally.
Origination: Supraspinous Ligament
Insertion: Caudal Part of the Spina of Scapula
Cervical (Cranial) Portion - Rotate scapula forward (extending shoulder joint). Pulls scapula dorsally.
Origination: The Nuchal Ligament
Insertion: Cranial Part of the Spine of Scapula
Thoracic (Caudal) Portion - Rotate scapula backwards (flexing shoulder joint). Pulls scapula dorsally.
Origination: Supraspinous Ligament
Insertion: Caudal Part of the Spina of Scapula
What is this muscle? What is it’s purpose? Where does it originate and insert?
51
New cards
**Rectus Abdominus**
Part of the bowstring effect. Helps round spine through connection to sternum, ribs, and pelvis.
Origination: Ventral Surface of the First Couple True Ribs
Insertion: Pelvis, Cranial/Ventral Surface
Part of the bowstring effect. Helps round spine through connection to sternum, ribs, and pelvis.
Origination: Ventral Surface of the First Couple True Ribs
Insertion: Pelvis, Cranial/Ventral Surface
What is this muscle? What is it’s purpose? Where does it originate and insert? (1)
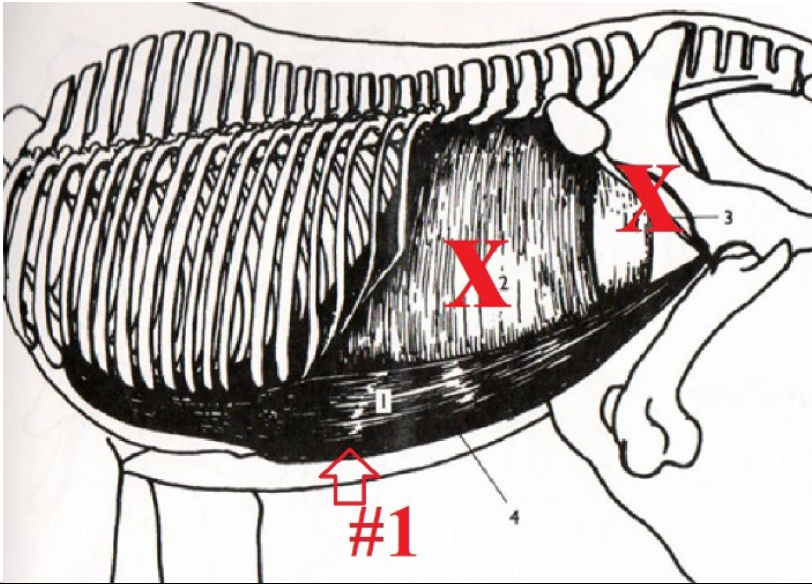
52
New cards
The bowstring effect is when muscles along the dorsal surface of the horse’s body are balanced by abdominal muscles to allow slight rounding of the spine so that the horse can fully extend its hind legs under its body. Muscles involved are the Spinalis, Longissimus doors, Internal oblique abdominal muscle, external oblique abdominal muscles, and rectus abdominus.
What is the bowstring effect? What muscles are involved?
53
New cards
Catch - Pectoral Muscles
Spring Up - Serratus Ventralis
Spring Up - Serratus Ventralis
With every step, the horses’s axial skeleton acts like a trampoline between the front legs. What muscles “catch” the axial skeleton? What muscles “spring up” the axial skeleton with each step?
54
New cards
The thoracic sling is a combination of muscles, tendons, and ligaments that connect the thoracic skeleton to the axial skeleton. It is needed because horses do not have a joint connecting their thoracic limb to their axial skeleton (no collarbone). Pectorals, Serratus Ventralis, Trapezius, Rhombiodius, Latissimus doors are examples of muscles that are part of the thoracic sling.
What is the thoracic sling? Why is it needed?
55
New cards
1. Latissimus Dorsi
2. Longissimus Dorsi
3. Spinalis
4. Trapezius (Thoracic Portion)
List four back/neck muscles that could be negatively affected by poor saddle fit.
56
New cards
* Serratus Ventralis
* Subscapularis
* Infraspinatus
* Deltoid
* Trapezius
* Subscapularis
* Infraspinatus
* Deltoid
* Trapezius
List these muscles from deepest to most superficial: Deltoid, Infraspinatus, Trapezius, Ventralis, Subscapularis
57
New cards
* Interspinous Ligaments
* Spinalis
* Longissimus dorsi
* Latissimus dorsi
* Tapezius
* Spinalis
* Longissimus dorsi
* Latissimus dorsi
* Tapezius
List these muscles from deepest to most superficial: Longissimus dorsi, Tapezius, Spinalis, Latissimus dorsi, Interspinous Ligaments
58
New cards
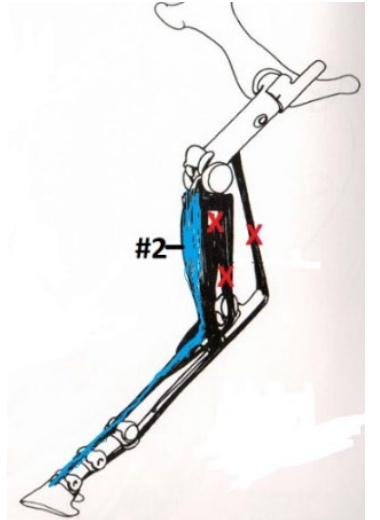
Common Digital Extensor Muscle
Lower Leg: Extends
Tarsus: Flexes
Origination: Cranial, Proximal, Lateral end of the Tibia
Insertion: Extensor Process of P3
Lower Leg: Extends
Tarsus: Flexes
Origination: Cranial, Proximal, Lateral end of the Tibia
Insertion: Extensor Process of P3
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (2)
59
New cards
Peroneus Tertius
Stifle & Hock (Flexes)
Part of the Reciprocal Apparatus. Connects the stifle and hock in the hind leg. When one extends, so does the other (this occurs due to interactions with the SSDF muscle/tendon).
Origination: Lateral Condyle of Femur
Insertion: Dorsal Surface of 3rd Metatarsal AND Deep Within Cranial Hock Bones
Stifle & Hock (Flexes)
Part of the Reciprocal Apparatus. Connects the stifle and hock in the hind leg. When one extends, so does the other (this occurs due to interactions with the SSDF muscle/tendon).
Origination: Lateral Condyle of Femur
Insertion: Dorsal Surface of 3rd Metatarsal AND Deep Within Cranial Hock Bones
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (1)
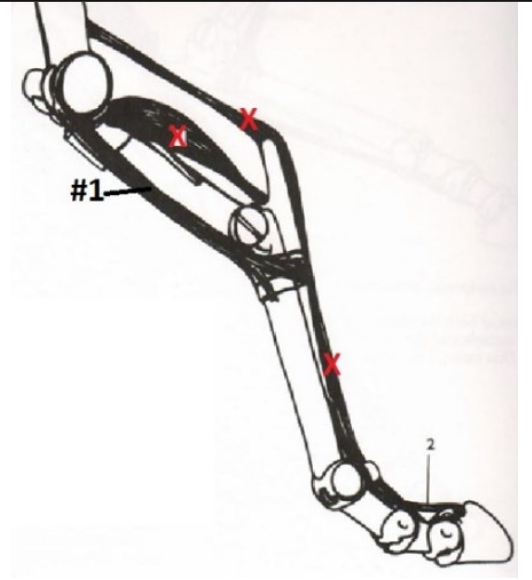
60
New cards
Biceps Femoris
Hip & Stifle (and hock via reciprocal apparatus)
Extends the hip and stifle (and therefore the hock). Abducts the hind limb.
Origination: Lateral Side of Sacral Vertebrae & Ischiatic Tuberosity
Insertion: Fascia
Hip & Stifle (and hock via reciprocal apparatus)
Extends the hip and stifle (and therefore the hock). Abducts the hind limb.
Origination: Lateral Side of Sacral Vertebrae & Ischiatic Tuberosity
Insertion: Fascia
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert?
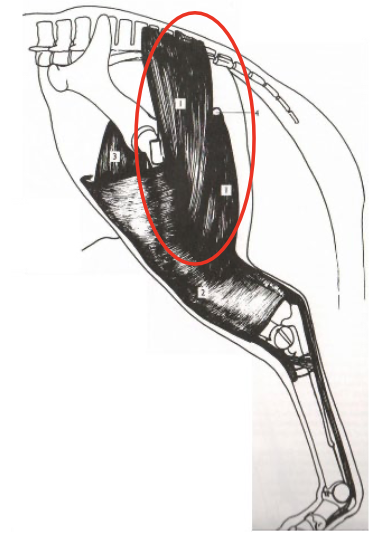
61
New cards
Quadriceps Femoris
Stifle (and indirectly hock, through reciprocal apparatus) extends. Minor effect on hip flexes.
Origination: Cranial End of Pelvis & Cranial End of Femur
Insertion: Cranial Proximal End of Tibia
Stifle (and indirectly hock, through reciprocal apparatus) extends. Minor effect on hip flexes.
Origination: Cranial End of Pelvis & Cranial End of Femur
Insertion: Cranial Proximal End of Tibia
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert?
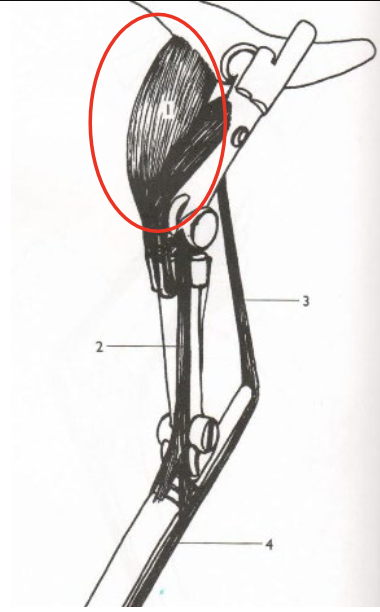
62
New cards
Semitendinosus & Semimembranosus
Hip, Stifle, and Hock
Weight Baring: Extends the hip, stifle, and hock
Non Weight Baring: Flexes the stifle, hock
Adduction of the Hind Leg
*Semitendinosus*
Origination: Sacrum & Ischiatic Tuberosity
Insertion: Medial, Cranial, Proximal End of the Tibia & Fascia
*Semimembranosus*
Origination: Ischiatic Tuberosity
Insertion: Medial, Cranial, Proximal End of the Tibia & Fascia
Hip, Stifle, and Hock
Weight Baring: Extends the hip, stifle, and hock
Non Weight Baring: Flexes the stifle, hock
Adduction of the Hind Leg
*Semitendinosus*
Origination: Sacrum & Ischiatic Tuberosity
Insertion: Medial, Cranial, Proximal End of the Tibia & Fascia
*Semimembranosus*
Origination: Ischiatic Tuberosity
Insertion: Medial, Cranial, Proximal End of the Tibia & Fascia
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert?
63
New cards
Superficial Digital Flexor Muscle/Tendon
Stifle, Hock, and Lower Leg
Connects the stifle, hock, fetlock, and pastern joints in the hind leg.
Without pernoneus teritius this muscle would flex the stifle, extend the hock, and flex the lower leg.
Reality: Works with the peroneus tertius as part of the reciprocal apparatus
Origination: Intercondylar Fossa of Femur
Insertion: Calcaneus + Distal End of P2 (2 points) Proximal End of P2 (2 points) Four Total Insertion Points
Stifle, Hock, and Lower Leg
Connects the stifle, hock, fetlock, and pastern joints in the hind leg.
Without pernoneus teritius this muscle would flex the stifle, extend the hock, and flex the lower leg.
Reality: Works with the peroneus tertius as part of the reciprocal apparatus
Origination: Intercondylar Fossa of Femur
Insertion: Calcaneus + Distal End of P2 (2 points) Proximal End of P2 (2 points) Four Total Insertion Points
What is this muscle? What joints does it move? Where does it originate and insert? (1)
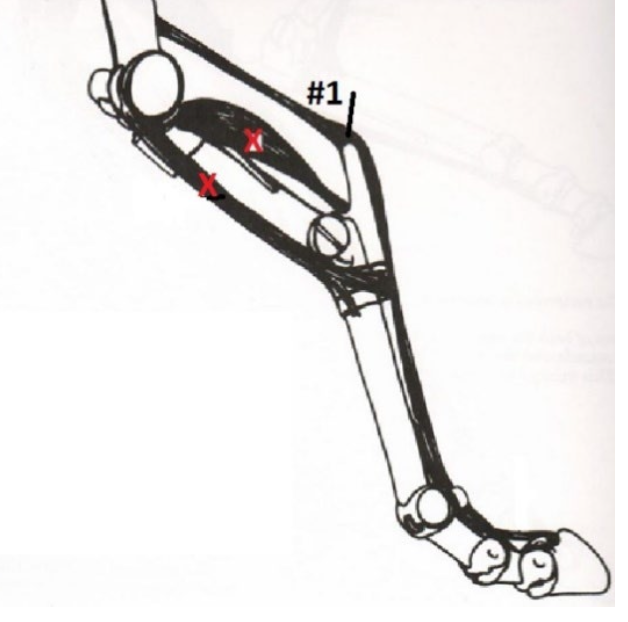
64
New cards
Reciprocal Apparatus
Connection of Stifle and Hock
* One Flexes, So Does The Other
* One Extends, So Does The Other
* One Flexes, So Does The Other
* One Extends, So Does The Other
65
New cards
Fascia
Normal Purpose?
* Allows Muscles To Slide With Minimal Friction
* Can Stretch
How is Fascia used differently in the hind leg?
* Superficial Layer: Encloses entirety of muscles in that area
* Deeper Layer: Wrap individual muscles or muscle groups
ALSO provides an insertion point. for powerful muscles of the hindquarters.
* Allows Muscles To Slide With Minimal Friction
* Can Stretch
How is Fascia used differently in the hind leg?
* Superficial Layer: Encloses entirety of muscles in that area
* Deeper Layer: Wrap individual muscles or muscle groups
ALSO provides an insertion point. for powerful muscles of the hindquarters.
66
New cards
* Pectineus
* Adductor
* Gracilis
* Sartorius
* Adductor
* Gracilis
* Sartorius
What are the hind muscles that cause adduction?
67
New cards
Muscle
Tendons connect ----- to bone.
68
New cards
Spinalis
What muscle is positioned **between** the **longissimus dorsi** and the spinous process of the **thoracic vertebrae**?
69
New cards
False
The Deltoid, Triceps Brachii, and Biceps Brachia cause extension in the shoulder joint. True or False?
70
New cards
Supraspinous Fossa
The supraspinatus muscle originates in the -----.
71
New cards
True
Both the supraspinatus and infraspinatus abduct the horse’s leg. True or False?
72
New cards
False
Both the supraspinatus and infraspinatus insert into the lesser tubercle. True or False?
73
New cards
The Infraspinous Fossa
The Deltoid originates in -----.
74
New cards
False
The extensor carpi radialis inserts into the accessory bone. True or False?
75
New cards
False
Ligaments cause movement with the assistance of muscles. True or False?
76
New cards
False
Tendons are able to both push and pull. True or False?
77
New cards
Fascia
Thin layers of connective tissue that cover board areas of muscles are called -----.
78
New cards
P3
The deep digital flexor tendon attaches to -----.
79
New cards
False
Lower leg flexor tendons can be found on the cranial/dorsal, lateral surface of the leg. True or False?
80
New cards
Thoracic Sling
The series of muscles that attach the front limb to the axial skeleton is called the -----.
81
New cards
Ventral Longitudinal
The ----- ligament keeps the ventral surface of the vertebrae equidistant to one-another.
82
New cards
False
Muscles can push and pull. True or False?
83
New cards
False
Skeletal muscles are involuntary and striated.
84
New cards
Mineral Storage
Which of the following is NOT a function of skeletal muscle?
* Produce Heat By Shivering
* Move Skeleton
* Mineral Storage
* Support Skeleton
* Produce Heat By Shivering
* Move Skeleton
* Mineral Storage
* Support Skeleton
85
New cards
Draw In Towards The Midline
Adduction means to….
86
New cards
Type I
Which of the following are “slow-twitch” muscle fibers?
* Type IIA
* Type I
* Type IIX
* Type IIA
* Type I
* Type IIX
87
New cards
Releases Large Amounts Of Energy
Which of these is TRUE of aerobic exercise?
* Releases Large Amounts Of Energy
* Glucose Not Fully Broken Down
* Releases A Small Amount Of Energy
* Does Not Use Oxygen
* Releases Large Amounts Of Energy
* Glucose Not Fully Broken Down
* Releases A Small Amount Of Energy
* Does Not Use Oxygen
88
New cards
True
Lactic Acid is produced by anaerobic exercise. True or False?
89
New cards
Brachialis
The muscle that wraps around the humerus is the…
90
New cards
False
The deltoid attaches to the trees major tuberosity. True or False?
91
New cards
False
The lateral digital extensor tendon is positioned directly next to the deep digital flexor tendon on the lateral side. True and False?
92
New cards
Brachiocephalicus
The ----- forms the supper portion of the jugular groove.
93
New cards
True
The rhomboideus pulls the neck up. True or False?
94
New cards
True
The trapezius can cause the scapula to swing back and forth depending on what portion is contracting. True or False?
95
New cards
Serratus Ventralis
Which of the following is part of the thoracic sling?
* Deltoid
* Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon
* Serratus Ventralis
* Subscapular Membranosis
* Deltoid
* Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon
* Serratus Ventralis
* Subscapular Membranosis
96
New cards
True
Pectoral muscles help “catch” downward motion of the axial skeleton. True or False?
97
New cards
Psoas Minor & Iliopsoas
What muscles(s) that connect the pelvis to the ventral surface of the lumbar (and caudal thoracic) vertebrae are the…
98
New cards
Hollow
The weight of a rider will naturally ----- the back of a horse.
99
New cards
External & Internal Abdominal Oblique
Which of the following helps prevent the spine from becoming too hollow?
100
New cards
Extends
The biceps femurs ----- the hip and stifle.