Comprehensive Study Guide for BIOL 5330 Final Exam
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
EXAM 1: Which of the following is the correct order of parts of a gene?
a) Promoter - Start Codon - Exon - Intron - Stop Codon
b) Promoter - Start Codon - Intron - Exon - Stop Codon
c) Start Codon - Promoter - Intron - Exon - Stop Codon
d) Promoter - Intron - Exon
a) Promoter - Start Codon - Exon - Intron - Stop Codon
EXAM 1: An alternative form of a given gene at a single locus, which differs in DNA sequence and often results in altered protein expression is known as ______.
allele
EXAM 1: The observable properties of a trait is known as ________; while the genetic properties that produce a trait is known as its ________.
1. Phenotype
2. Genotype
EXAM 1: Which of the following is NOT a functional domain/motif found in proteins?
a) DNA binding domain
b) cellular targeting sequence
c) transmembrane domain
d) ligand domain
e) all of the above
d) ligand domain
EXAM 1: True or False? Heritable changes in gene expression that are NOT due to changes in DNA sequence could be due to epigenetic effects.
True
EXAM 1: Which of these are common epigenetic mechanisms we discussed in lecture?
a) regular non-coding RNAs (RNAi)
b) methylation
c) histone modifications
d) all of the above
d) all of the above
EXAM 1: True or False? A "loss of function" mutation has reduced a complete lack of normal gene function in control to a "gain of function" mutation that has gained or added a novel gene function.
True
EXAM 1: True or False? Mutagens produce different types of mutations in DNA
True
EXAM 1: True or False? One key point in the regulations of many transcription factors is localization to the mitochondria.
False
EXAM 1: True or False? Dimerization commonly plays a part of signal transduction pathways
True
EXAM 1: True or False? Inhibition and Activation can occur as part of the same signaling pathway
True
EXAM 1: True or False? Some signaling pathways act over long distances
True
EXAM 1: True or False? Experimental methods examining RNA expression levels do not directly examine protein levels
True
EXAM 1: Which of the following are advantageous reasons for having phosphorylation in a signal transduction pathway?
a) new proteins do not need to be synthesized
b) it is easily reversible
c) it can occur quickly
d) all of the above
d) all of the above
EXAM 1: A primary use of mutants by scientists in genetic studies is to help determine what?
The function of a gene
EXAM 1: Match the following alternations of the wild-type DNA sequence ATTGCAGCT with the type of mutation:
ATAGCT
deletion
EXAM 1: Match the following alternations of the wild-type DNA sequence ATTGCAGCT with the type of mutation:
ATTCAGCT
deletion
EXAM 1: Match the following alternations of the wild-type DNA sequence ATTGCAGCT with the type of mutation:
ATGTCAGCT
transposition
EXAM 1: Match the following alternations of the wild-type DNA sequence ATTGCAGCT with the type of mutation:
ATTGCTCAAGCT
insertion
EXAM 1: Match the following alternations of the wild-type DNA sequence ATTGCAGCT with the type of mutation:
AGTGCAGCT
substitution
EXAM 1: Which of these listed below is NOT a general type of mutation?
a) frameshift
b) adaptive
c) reversion
d) conditional
e) lever
e) lever mutation
*** EXAM 1: Effects of this mutation type can be stronger than a null mutation with complete loss of gene function
Dominant Negative
EXAM 1: Match the name with the described function: Reporter/Marker
Ability to track expression of a gene
EXAM 1: Match the name with the described function: Overexpression
Determine effects of too much ...
EXAM 1: Match the name with the described function: RNAi or Antisense
determine effects of reducing gene expression
EXAM 1: Match the name with the described function: TAG
ability to track expression of a protein
EXAM 1: When conducting a mutagenesis screen-- looking for a defect in a specific phenotype regardless of the particular gene involved is know as a ___________
Forward genetic screen
EXAM 1: Why use Homologous recombination or CRISPR instead of other methodologies to generate transgenic organisms?
Selectable Gene Targeting
EXAM 1: Which of the following might be a reason that you would decide to make a condition or inducible version of a transgenic organism?
a. all of these are good answers
b. you could control the gene expression in a specific spatial pattern
c. you could control the gene expression in a specific manner
d. you could control the gene expression in a specific temporal manner
a. all of these are good answers
EXAM 1: Enhancer elements can function by ___________
act on gene transcriptions from a distance of over 10,000 base pairs away
EXAM 1: This is NOT a feature of cis-regulatory elements?
Often composed of 5-25 amino acids
EXAM 1: Which of these is a major transcription factor class or family we discussed?
a. lecine finger
b. beta scaffolding
c. zinc finger
d. helix-binding
b. beta scaffolding
EXAM 1: Which of these is NOT a major signaling pathway involved in development?
a) alpha kinase
b) hedgehog
c) g-protein
d) beta-kinase
e) all of the above
f) alpha & beta kinase
f) alpha & beta kinase
EXAM 1: The Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) signaling pathway repeatedly makes use of which of the following processes in its signaling?
Phosphorylation
EXAM 1: what is a standard outcome at the end of a general transcription factor signaling pathway?
gene expression is activated
EXAM 1: what is a feature of the Notch signaling pathway that makes it different from the other signaling pathways that we discussed?
both the receptor becomes part of the signal pathways and the ligand a membrane spanning proteins
EXAM 1: Which of the following is NOT a mechanism for eliminating a signal in a signal transduction pathway once that signal has been initiated?
a) paracrine/autocrine loop
b) destruction of the receptor
c) negative signal of feedback loop
d) sequestration of the receptor
a) paracrine/autocrine loop
EXAM 1: This mechanism for maintaining a signal from a signal transduction pathway involves the activation of a signal from one cell, which then activates its neighboring cell, which then activates a signal in the original cell.
Paracrine loop
EXAM 1: Name and order the FOUR major parts of a general transcription factor signaling pathway
1. ligand
2. receptor
3. signaling cascade
4. transcription factors
EXAM 1. Which of the parts of signal transduction pathway is most likely to be the most complex?
3. signaling cascade
EXAM 1: match the characteristic or feature with whether it is likely to be found in a Model System or a Non-Model system.
A unique organism characteristic
Non-Model System
EXAM 1: match the characteristic or feature with whether it is likely to be found in a Model System or a Non-Model system.
Sequenced and well annotated genome
Model System
EXAM 1: match the characteristic or feature with whether it is likely to be found in a Model System or a Non-Model system.
Large Physical Size
Non-Model System
EXAM 1: match the characteristic or feature with whether it is likely to be found in a Model System or a Non-Model system.
Large Number of Progeny
Model System
EXAM 1: match the characteristic or feature with whether it is likely to be found in a Model System or a Non-Model system.
Abnormal Genetics
Non-Model System
EXAM 1: Match the characteristic to whether it would be General or Specific.
Ease of Use
General
EXAM 1: Match the characteristic to whether it would be General or Specific.
Rapid Generation Time
Specific
EXAM 1: Match the characteristic to whether it would be General or Specific.
Readily Available
General
EXAM 1: Match the characteristic to whether it would be General or Specific.
Ease of Data Generation
General
EXAM 1: Match the characteristic to whether it would be General or Specific.
Large Numbers of Progeny Produced
Specific
EXAM 1: Match the characteristic to whether it would be General or Specific.
Genome Sequenced and Annotated
Specific
EXAM 1: Indicate the Model System where each characteristic is a positive.
Short life cycle
Caenorhabditis elegans
EXAM 1: Indicate the Model System where each characteristic is a negative.
Short life cycle
Mus musculus - mouse
EXAM 1: Indicate the Model System where each characteristic is a negative.
Easy to care for
Mus musculus
EXAM 1: Indicate the Model System where each characteristic is a positive.
Easy to care for
Drosphila melanogaster
EXAM 1: Indicate the Model System where each characteristic is a positive.
Ability to see internal organs
Caenorhabditis elegans
EXAM 1: Indicate the Model System where each characteristic is a negative.
Ability to see internal organs
Drosphila melanogaster
EXAM 1: Which of the following is NOT an important factor to consider when designing a mutagenesis screen as we discussed?
a) mutation rate
b) organism
c) type of gene or phenotype
d) mechanisms of mutant screening
e) all of the above
e) all of the above
EXAM 1: This is a common feature used in the generation of transgenic organisms to help determine if it was successfully made transgenic?
A marker that can easily be selected
*** EXAM 2: Name the different tissue layers that are responsible for forming each of the following tissues/organ.
Digestive System or Gut
endoderm
*** EXAM 2: Name the different tissue layers that are responsible for forming each of the following tissues/organ.
Circulatory System & Muscles
Mesoderm
*** EXAM 2: Name the different tissue layers that are responsible for forming each of the following tissues/organ.
Nervous system & Skin
Ectoderm
EXAM 2: Why is it important for an organism to override an initial establishment of axis determination in a developing embryo?
In order to properly orient the developing organism to the enviornment
EXAM 2: Gastrulation involves the migration of cells which can occur in different patterns, yet during this process there is always the formation of a set of common layers known as?
Germ Layers
EXAM 2: Which of the following becomes the cue for default axis determination if all environmental cues are eliminated from a developing embryo?
Site or Sperm Entry in the Egg
*** EXAM 2: True or False? Transcription factors, such a B-catenin in Sea Urchin, often play an important role during early embryo development
True
EXAM 2: True or False? The first organ produced during organogenesis is an ANIMAL in the GUT
False
EXAM 2: True or False? Fertilization, as a developmental stage consists of MORE than one step/stage.
True
EXAM 2: True or False? Three basic tissue systems are established in the development both of plants and animals
True
EXAM 2: The neural tube formed during neurulation originates from what germ layer?
Ectoderm
EXAM 2: Name two different types of cell movements we discussed that occur during gastrulation
1. Delamination
2. Epiboly
EXAM 2: Which of the following best describes a meristem?
a. a group of stem cells
b. a region of the embryo that produces the epidermis
c. any plant cell with nucleus
d. a region of the plant containing stem cells where nearly all tissues & organs are derived.
e. all of the above
d. a region of the plant containing stem cells where nearly all tissues & organs are derived.
EXAM 2: Which of the following is NOT true about fate maps?
a. can only be made over the entire development of an organism
b. easier to generate in embryos
c. provide a lineage of cells from an early to later stage of development
d. construction require detailed understanding of the organism
a. can only be made over the entire development of an organism
EXAM 2: Which of the following is NOT a method or tool that has been used to construct fate maps?
a. realtime PCR
b. genetic markers
c. fluorescence dyes
d. physical alteration of cells
a. realtime PCR
*** EXAM 2: General mechanisms involved in regulating morphogen gradients that we discussed in lecture.
Possible Final Question: Morphogen gradients are regulated by a number of different mechanisms. List 3.
1. Cross Repression
2. Positive Feedback
3. Feed Forward Loop
EXAM 2: Which of the following is required to differentiate cells with a single morphogen?
a. presence of a morphogen gradient
b. morphogen response genes with different thresholds
c. all of these answers are essential
d. morphogen gradient responsive genes
e. presence of a morphogen
c. all of these answers are essential
EXAM 2: Which of the following is NOT one of the 4 maternal gene systems involved in coordinating control of embryo polarity in Drosphila?
a. dorsal-ventral system
b. anterior/posterior system
c) terminal system
d) segment system
d) segment system
EXAM 2: True or False? Multiple segment formation that divides a Drosphila embryo during developmental is a process that requires a single morphogen gradient.
False; requires MORE than one.
EXAM 2: True or False? Homeotic genes are key factors in evolutionary development because they can change identities of entire body parts of segments.
True
EXAM 2: Molecular parsimony is a process where duplicated genes can diverge in different ways. Name One outcomes:
1. gene loss
others:
2. degeneration
3. neofunctionalization
4. subfunctionalization
*** EXAM 2: Homologs are genes related to each other evolutionary. _______ are genes in different species that have evolved from a common ancestral gene through speciation, while ______ are genes within a genome that have occurred by gene duplication.
1. Orthologs
2. Paralogs
*** EXAM 2: There are 5 different general pathways we discussed by which environmental factors can alter phenotypes through differential gene expression, name 3:
1. Indirect Activation
2. Direct Activation
3. Modification of Genes
Others:
4. Methylation
5. Direct Activation or Signaling Pathways
*** EXAM 2: Macroevolutionary patterns of changes occur through changes in gene function or changes in gene expression.
Name 3 different types of changes in gene expression that lead to standard evolutionary developmental patterns of change
1. Heterotopy
2. Heterochromy
3. Heterotypy
Others: Heterometry
EXAM 2: Match all 6 points of the three major animal body axes.
1. Dorsal
2. ventral
3. Lateral-Right
4. Lateral-Left
5. Anterior
6. Posterior
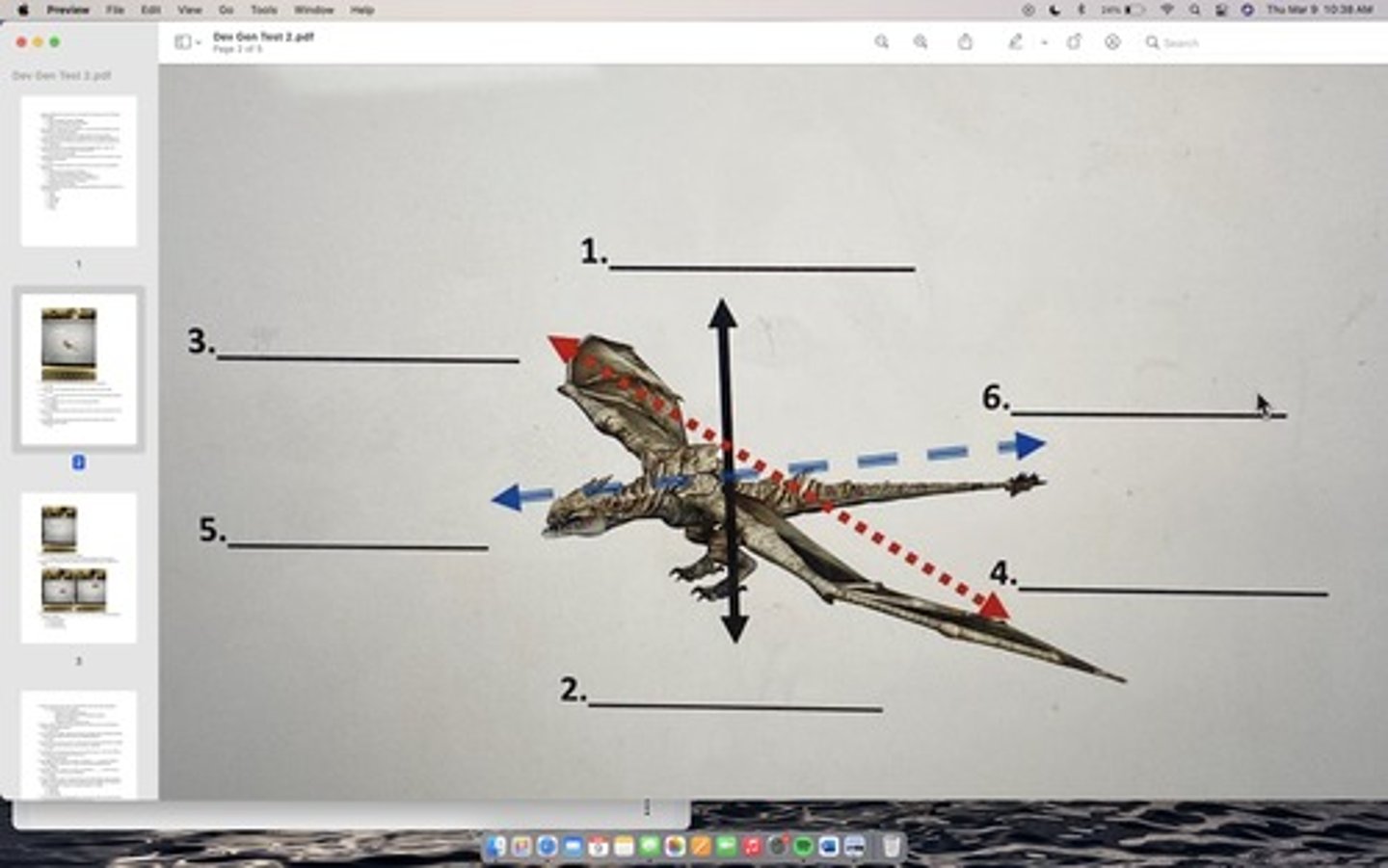
*** EXAM 2: Match the Developmental Stage to the best set of corresponding events.
Formation of the notochords
Neurulation
*** EXAM 2: Match the Developmental Stage to the best set of corresponding events.
Fusion of male & female gametes
Fertilization
*** EXAM 2: Match the Developmental Stage to the best set of corresponding events.
Formation of advanced organ structures
Organogenesis
*** EXAM 2: Match the Developmental Stage to the best set of corresponding events.
Formation of the germ layers
Gastrulation
*** EXAM 2: Match the Developmental Stage to the best set of corresponding events.
Rapid cell division
Cleavage
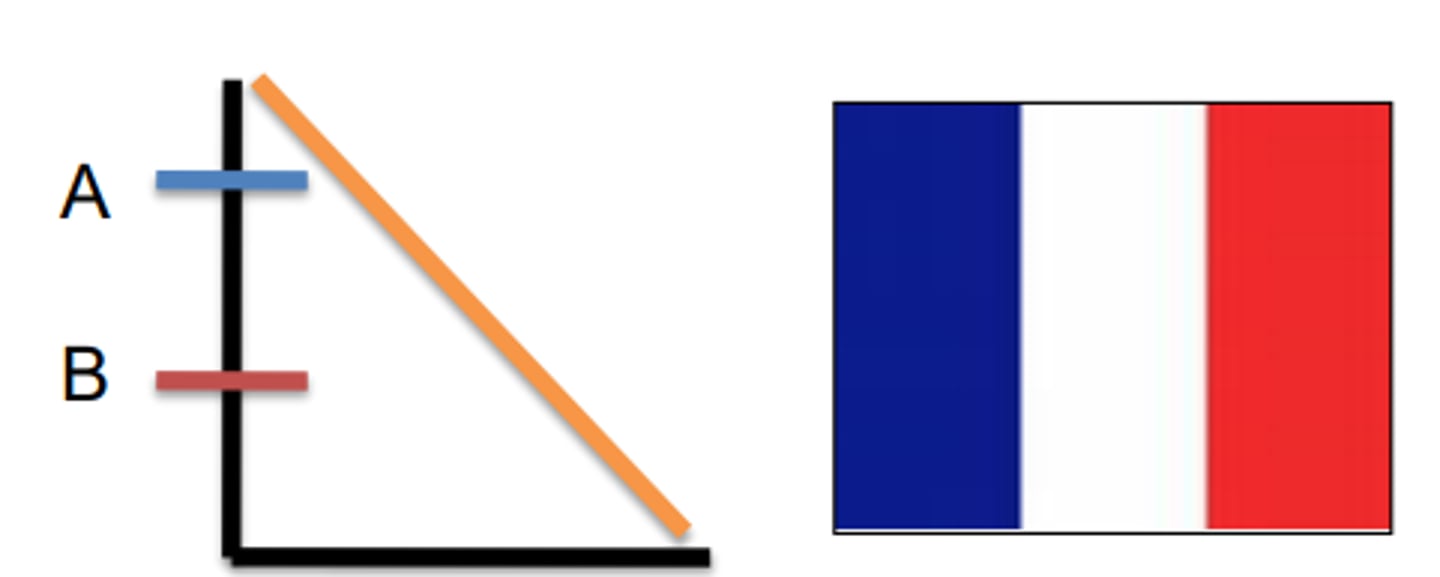
EXAM 2: What are the two different correct ways you could end up with a "French Flag" coloring-like phenotype in an embryo based on one morphogen and two thresholds.
1. Red default. White activated above B (covers red), Blue activated above A covers both Red and White
2. Blue default, Blue repressed below A and White activated, White repressed below B and Red activated
P.FINAL: Select the correct order of parts in a typical gene
5' UTR, Promoter, Exon, Intron, Exon, 3' UTR
P.FINAL: ___________ is the observable properties of an organism produced by its genotype
Phenotype
P.FINAL: a major reason we discussed for studying changed in phenotypes in mutant organisms is to determine the function of the mutated ___________
Gene
P.FINAL: indicate whether the following are terms used to describe either a gene or protein:
Promoter
Gene
P.FINAL: indicate whether the following are terms used to describe either a gene or protein:
Transmembrane Domain
Protein
P.FINAL: indicate whether the following are terms used to describe either a gene or protein:
TATA Box
Gene
P.FINAL: indicate whether the following are terms used to describe either a gene or protein:
Cellular Targeting Sequence
Protein
P.FINAL: the effect of this type of mutation can be more adverse or detrimental than a null mutation in which there is complete loss of gene function
dominant negative
P.FINAL: a major reason we discussed for studying changes in phenotypes in transgenic organisms is to determine the function of the altered _________
gene
P.FINAL: Which of the following is a specific benefit of using CRISPR methodology in genetics research?
a. single DNA strand replacement
b. site directed DNA editing
c. nuclear targeting
d. promotor editing
e. the ability to stop epigenetic effects
b. site directed DNA editing