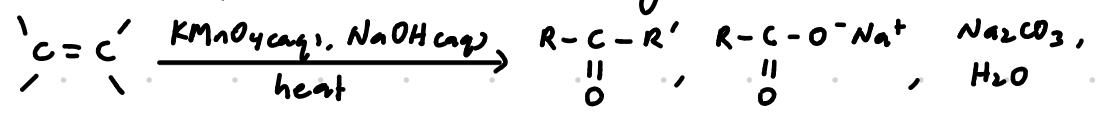Alkenes_Reagents and conditions
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Electrophilic addition of hydrogen halides
Reagents: HX (g)
Conditions: dry HX(g), room temp
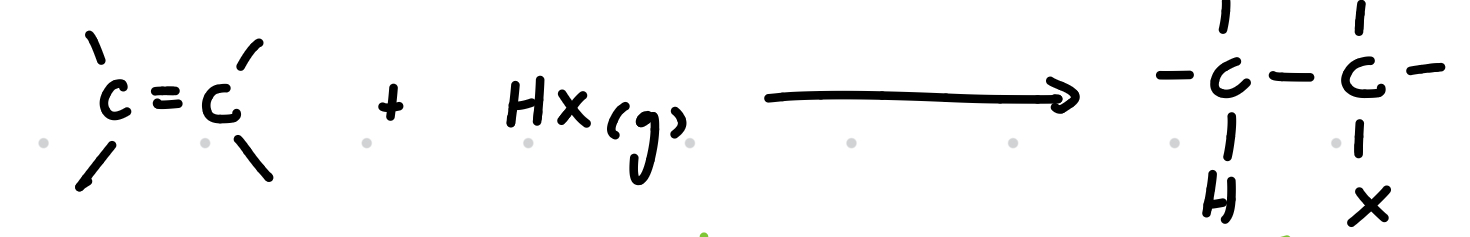
Electrophilic addition of steam
Reagents: H2O(g)
Conditions: conc. H3PO4 catalyst

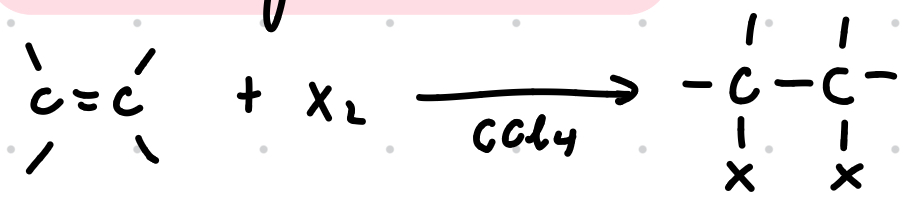
Electrophilic addition of halogens in CCl4
Reagents: X2 dissolved in an inert solvent (eg. CCl4 or CH2X2)
Conditions: dark, room temp
Electrophilic addition of halogens in H2O
Reagents: X2 in water
Conditions: dark, room temp

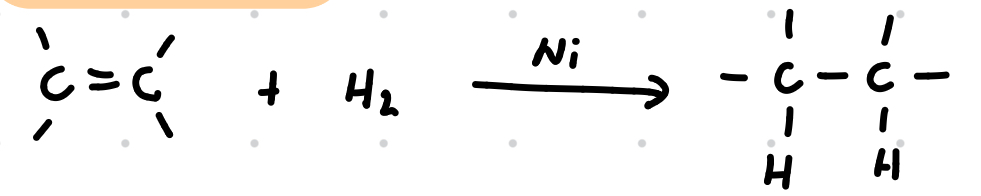
Reduction of alkenes
Reagent: H2
Conditions: Ni/Pt/Pd catalyst
Combustion of alkenes
CnH2n + (3n /2) O2(g) → nCO2(g) + nH2O(l)
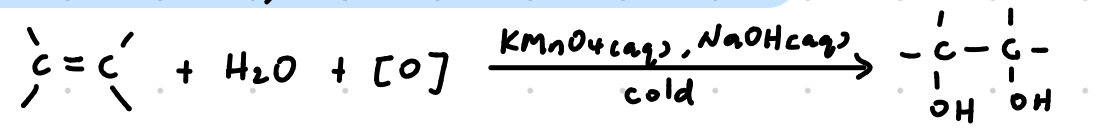
Oxidation with cold, alkaline KMnO4
Mild oxidation
Reagents: KMnO4 (aq), NaOH (aq)
Conditions: Cold
Observations:
Purple KMnO4 decolourised
Brown-black ppt of MnO2 observed
Oxidation with cold, acidified KMnO4
Mild oxidation
Reagents: KMnO4 (aq), H2SO4 (aq)
Conditions: Cold
Observations: Purple KMnO4 decolourised
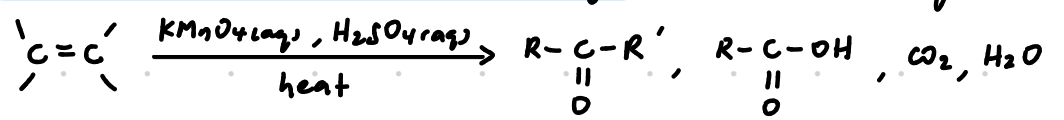
Oxidation with hot, acidified KMnO4
Strong oxidation
Reagents: KMnO4(aq), H2SO4(aq)
Conditions: Heat/ heat under reflux
Observations:
Purple KMnO4 decolourised
For terminal alkenes, a colourless gas (CO2) which forms a white ppt with limewater is evolved
Oxidation with hot, alkaline KMnO4
Strong oxidation
Reagents: KMnO4 (aq), NaOH (aq)
Condition: Heat/ heat under reflux
Observations:
Purple KMnO4 decolourised
Brown-black ppt of MnO2 observed