psyc 375 chapter 2
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
agenesis
failure of brain region to developproperly during embryonic development
ataxia
failure of motor coordination
what is the brain’s primary function
to produce behaviour, coordinated movements that are internally generated in response to external stimuli
sensory input
conduction of signals from sensory receptors to the CNS, usually function of PNS
integration
analysis and interpretation of the sensory signals and formulation of responses, within the CNS
motor output
send command (CNS) to effector cells (PNS) to carry out response
subjective reality
sensory organs convert info abt sensory stimuli into biology activity that constructs perceptions and experiences unique to each individual.
neuroplasticity
neural tissue has the capacity to change in response to the world by modifying its organization
what is the PNS comprised of
somatic nervous system, autonomic nervous system, enteric nervous system
somatic nervous system
transmits sensation, produces movement (Info in and out)
what is the somatic nervous system comprised of
cranial nerves and spinal nerves
what is the autonomic nervous system comprised of
sympathetic division and parasympatheic
sympathetic division
fight or flight, energizing
parasympathetic
rest and digest, calming
afferent
input
efferent
output
dorsal
top
ventral
bottom
anterior
front
posterior
back
medial
midline
lateral
side
components of meninges
dura mater, arachnoid membrane, pia mater
meningtis
inflammation of meninges due to infection
encephalitis
infection of the brain
nuclei
a group of similar neurons forming a cluster, in CNS
ganglia
a group of similar neurons forming a cluster, in PNS
tracts
large collection of axons coursing together in the CNS
nerves
large collection of axons coursing together, outside CNS
grey matter
cell bodies, dendrites, capillaries
white matter
nerve fatty covering (myelin sheath) and nerve fibers
components of cerebral cortex
neocortex and allocortex
components of allocortex
hippocampus, amygdala
neocortex
6 layers, constructs our reality, perception planning, emotions, memory
allocortex
3 layers, role in emotional and motivational states, certain forms of learning and memory
basal ganglia
coordination of voluntary movements, movement force,
hippocampus
memory consolidation, spatial navigation, early and most affected structure in neuropsychiatric disorders
memory consolidation
short term memory into long term memory
movement force
keeping movement fluid
components of basal ganglia
caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
components of brainstem
diencephalon, midbrain, hindbrain, cerebellum
brainstem
receives afferent signals from body’s senses, sends efferent signals out to spinal cord to control most of body’s movements, life-sustaining behaviour
frontal lobe responsibility
executive functions, language
temporal lobe responsibility
audition, language, learning & memory
occipital lobe responsiblity
vision
parietal lobe responsbility
somatosenstion, TTP
gyri
bumps in brain’s folded surface
sulci
cracks in brain’s folded surface
amygdala responsiblity
affect, mostly fear and anxiety
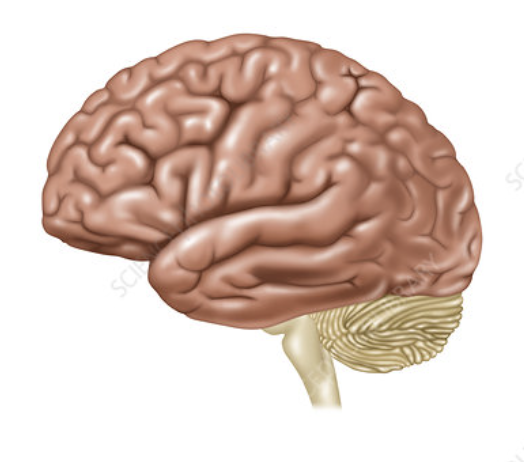
what view is this
lateral view
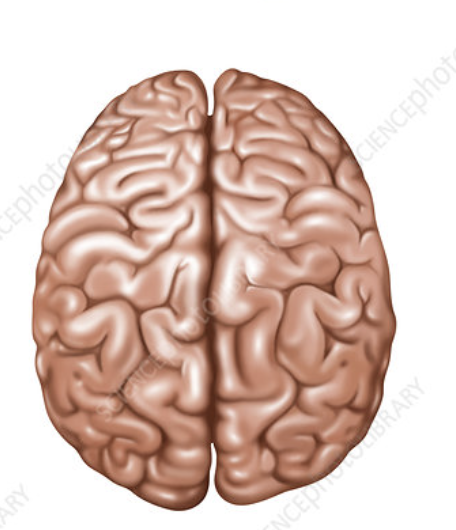
what view is this
dorsal view
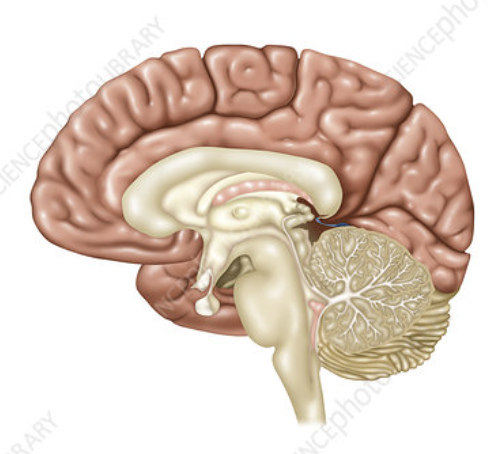
what view is this
medial view
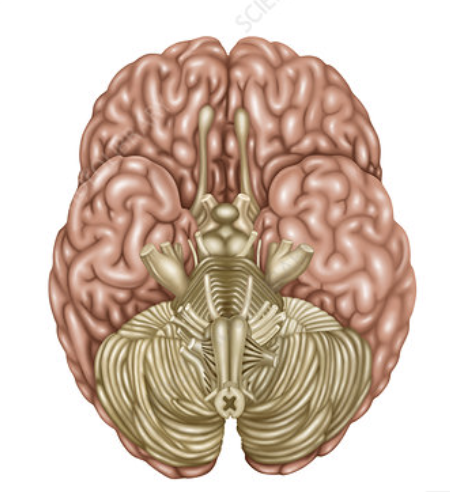
what view is this
ventral view
striatum
caudate nucleus and putamen
components of cerebrum
cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, olfactory bulbs