endoparasites and blood worms
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Round worms
Adults reside in the small intestine and may cause vomiting when they swim to the stomach
Direct life cycle
Ascarids
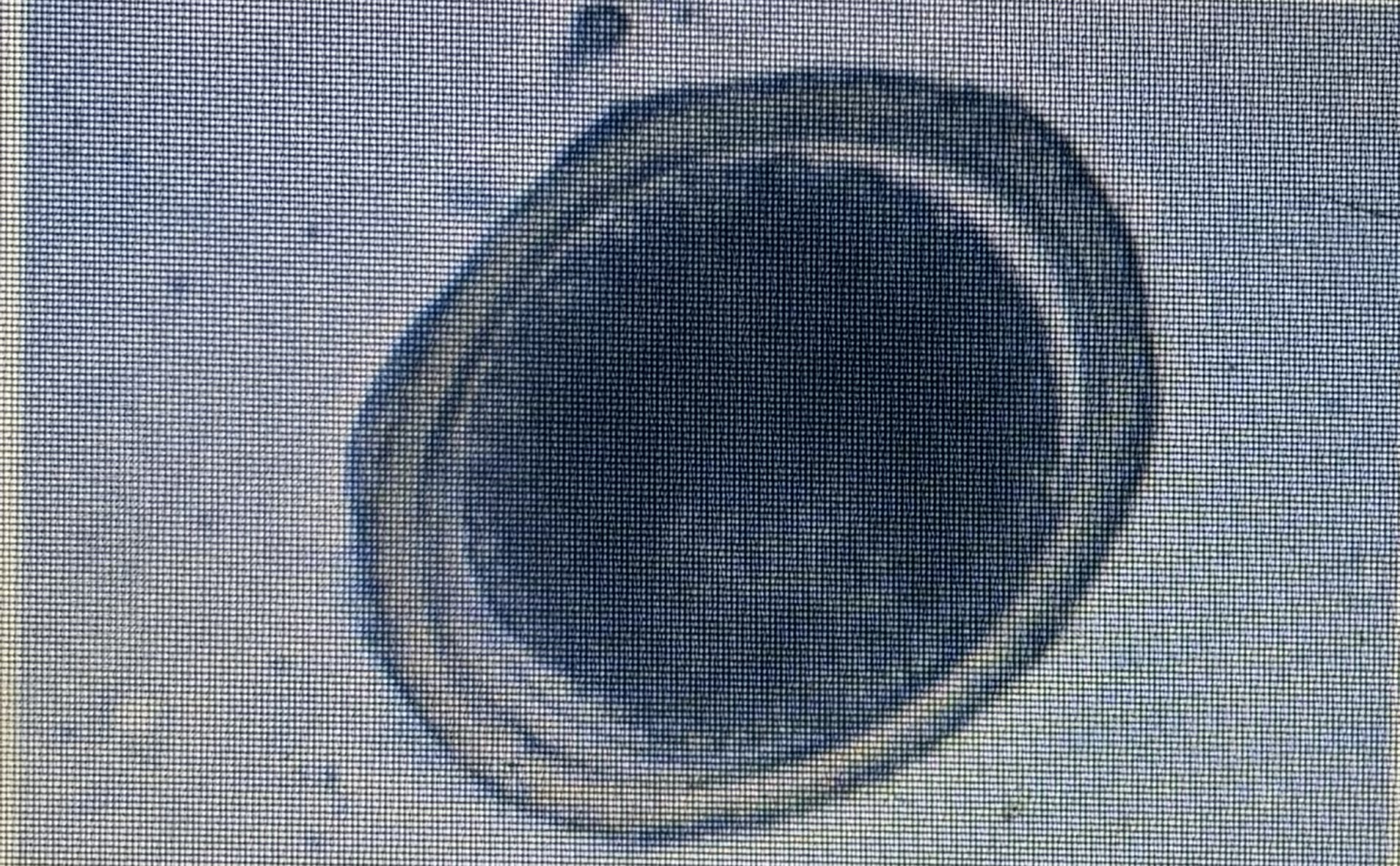
Ascarid
Host species: dog
Size: 75-90 um
Prepared period: 21-35 days
Transmission: ingestion Transplacental trans memory
Toxocara canis
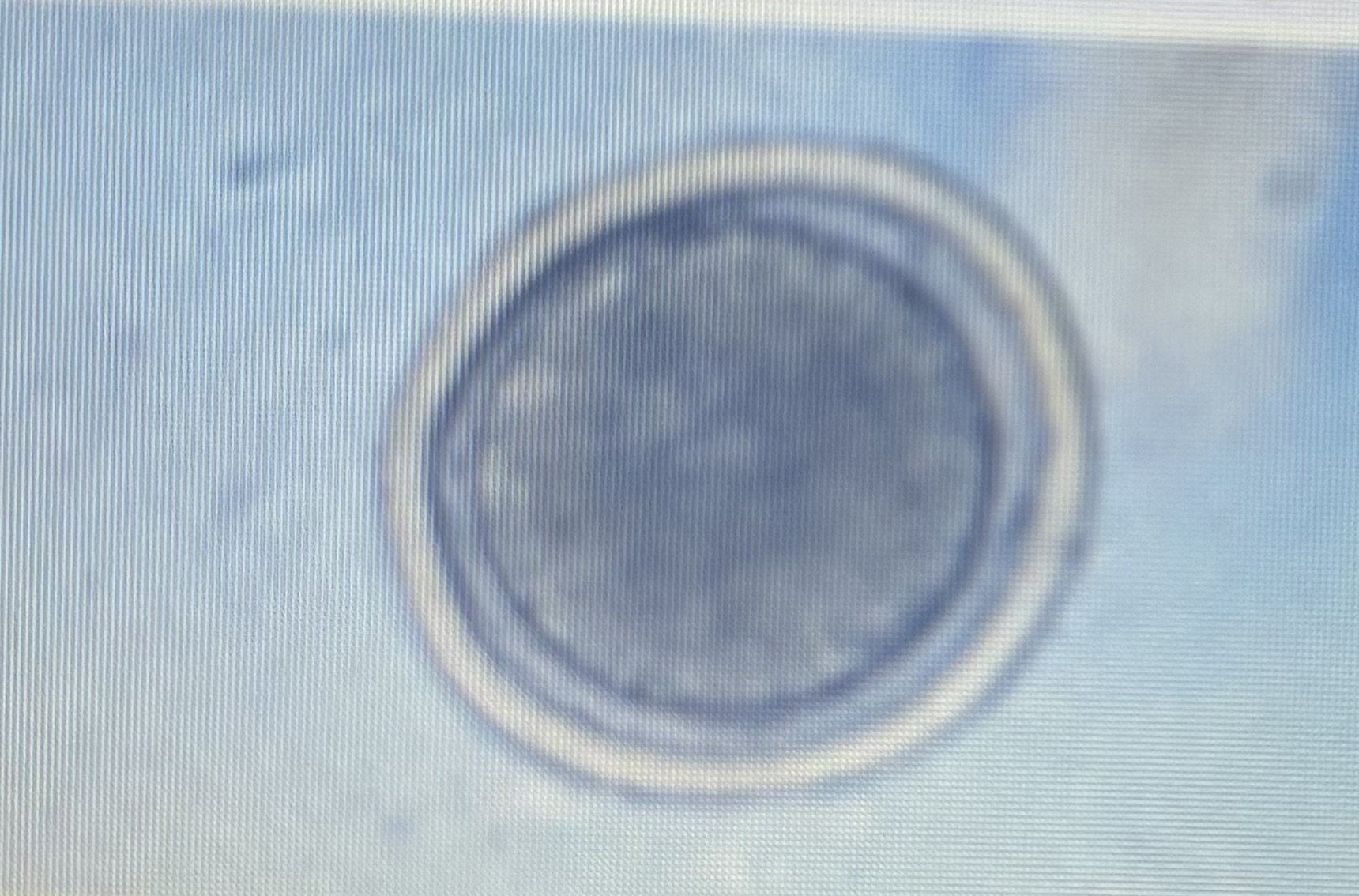
ascarid
Host species: cat
Size: 65-75 um
Prepatent period: 42-56 days
Transmission: ingestion trans mammary
Toxocara cati
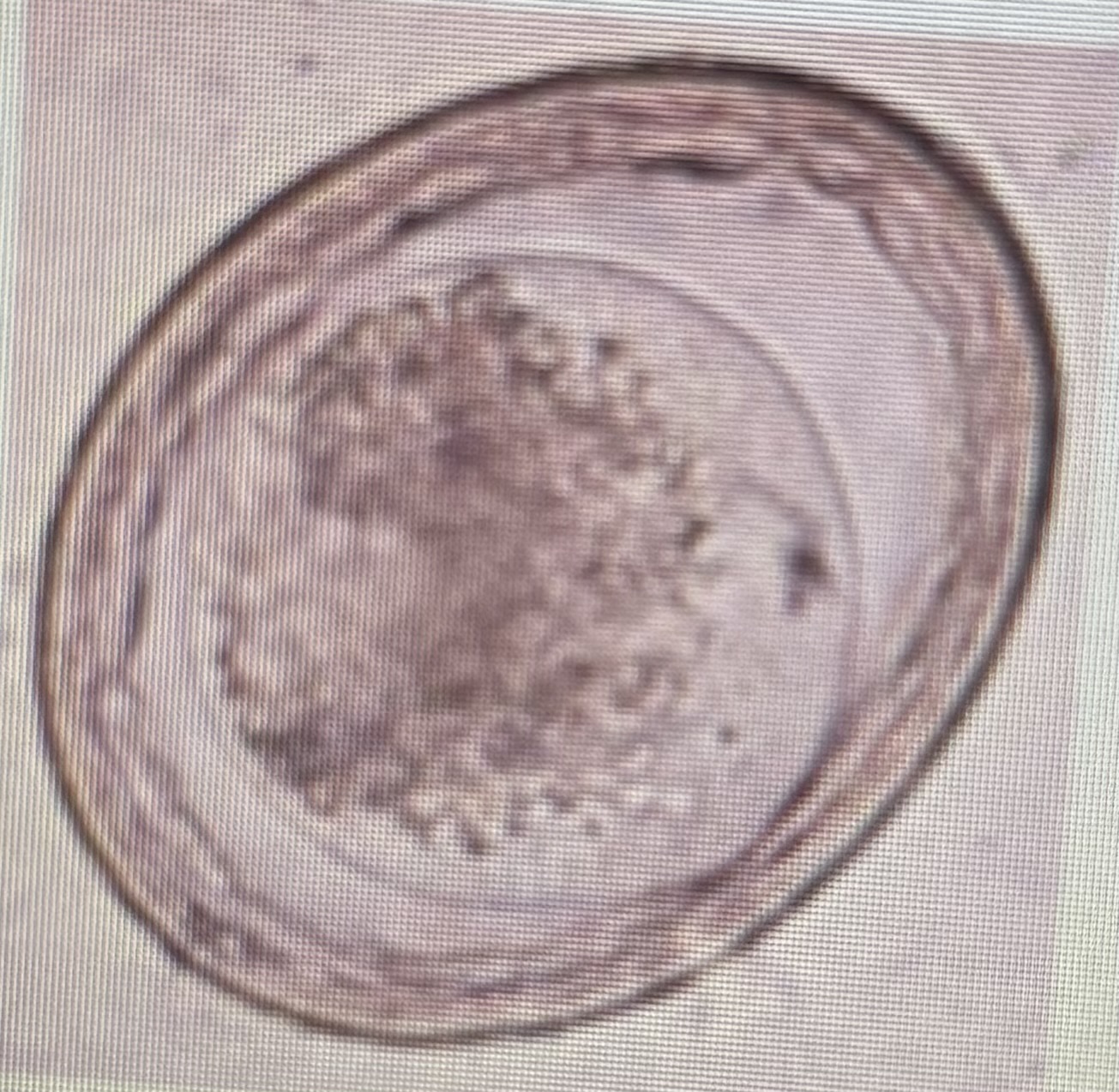
Ascarid
Host species: dog and cat
Size: 75-85 um
Prepatent period: 77 days
Transmission: ingestion trans placental
Does not have zoonotic potential
Toxascaris leonina
Ascarid
Host species: raccoon
Zoonotic parasite of significant concern
Larvae migrate to the CNS and produces a condition known as neurological larva migrans
Baylisascaris procyonis
Strongyloidea
Hookworm
Why must you remove feces immediately if you suspect hookworms
Eggs larvae rapidly and fresh feces is required to diagnose
how do hookworms cause damage
They attach to the intestinal lining and feed on blood. Black tarry stool may be evident
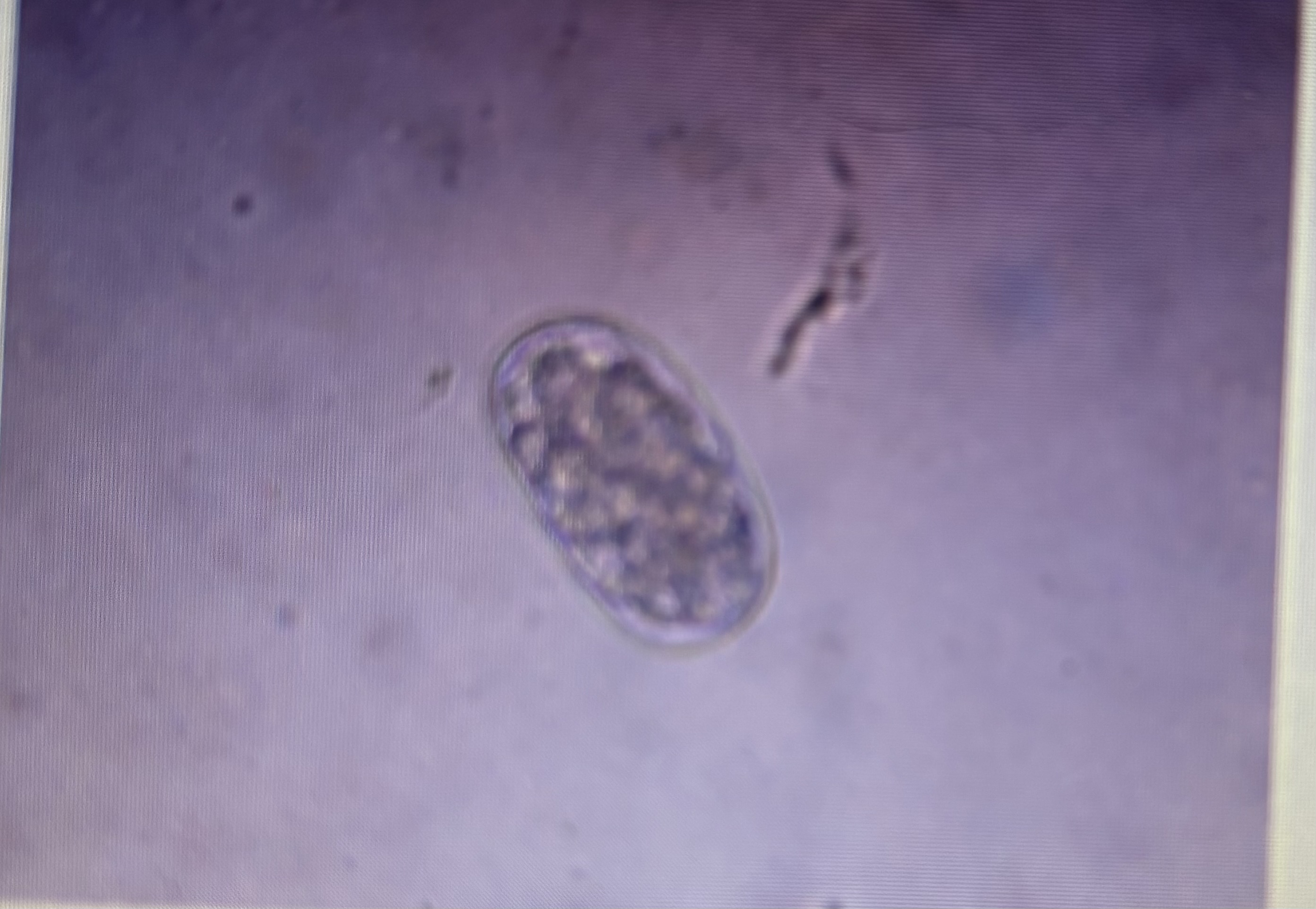
Strongyloidea
Southern canine hookworm
Host species: dog
Size: 55-75 um x 27-47 um
Prepatent period: 14-21 days
Transmission: ingestion trans placental percutaneous trans mammary
Anclyostoma caninum
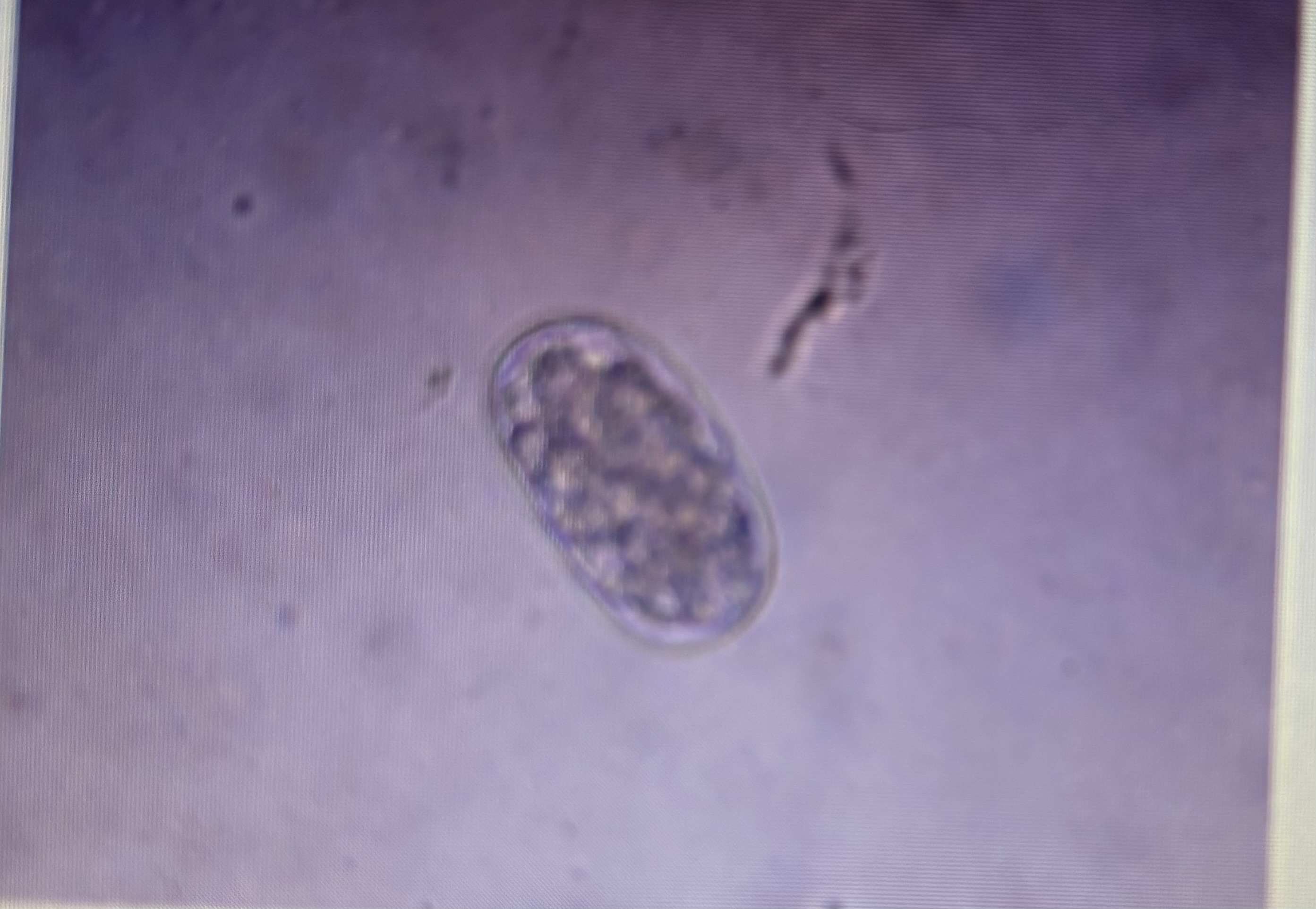
Strongyloidea
Northern canine hookworm
Host species: dog
Size: 63-93 um x 32-55 um
Prepatent period: 14 days
Transmission: ingestion percutaneous
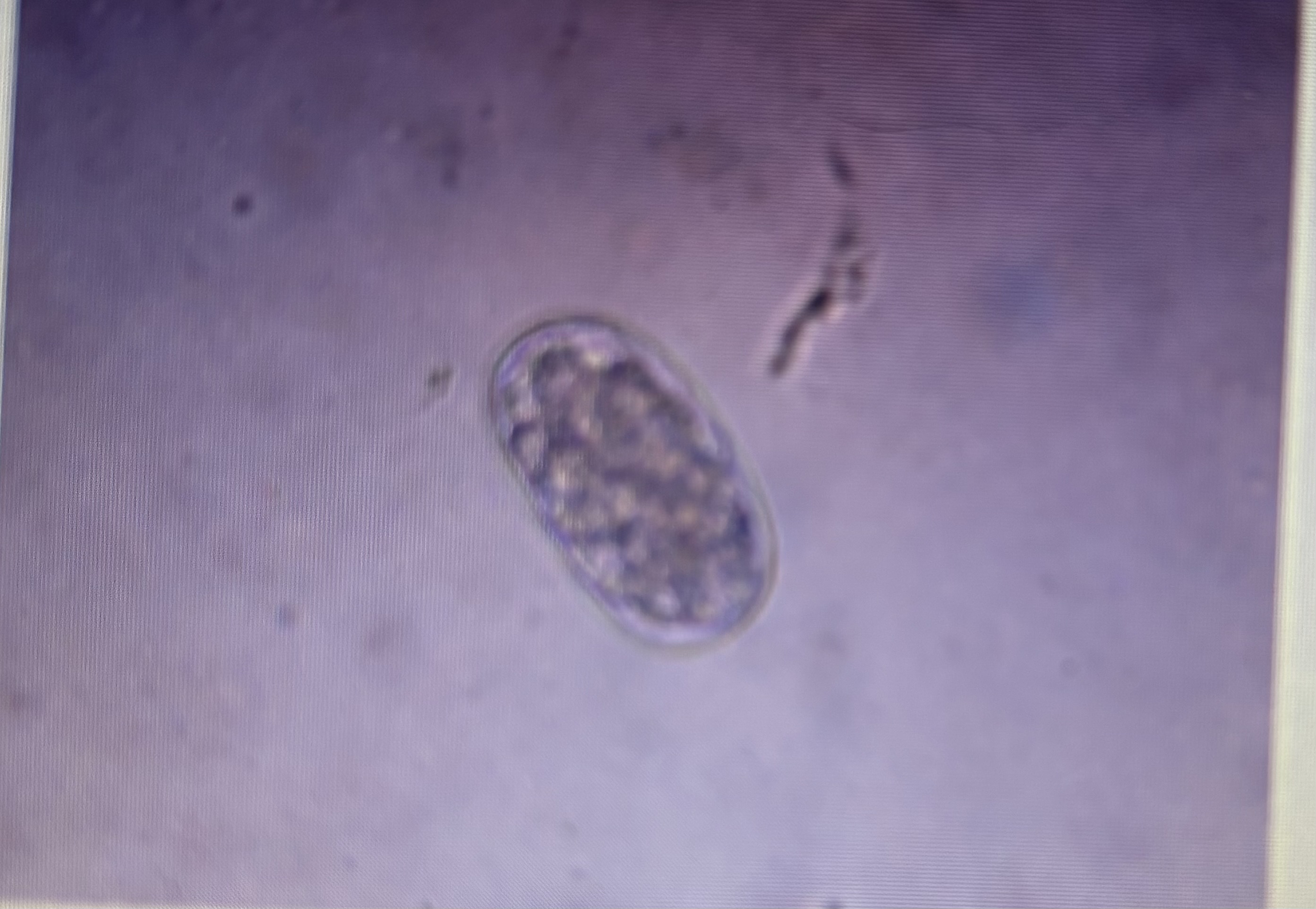
Strongyloidea
Feline hookworm
Host species: cat
Size : 55-75 um x 34.4-44.7 um
Prepatent period: 14-21 days
Transmission: ingestion percutaneous
Ancylostoma tubaeforme
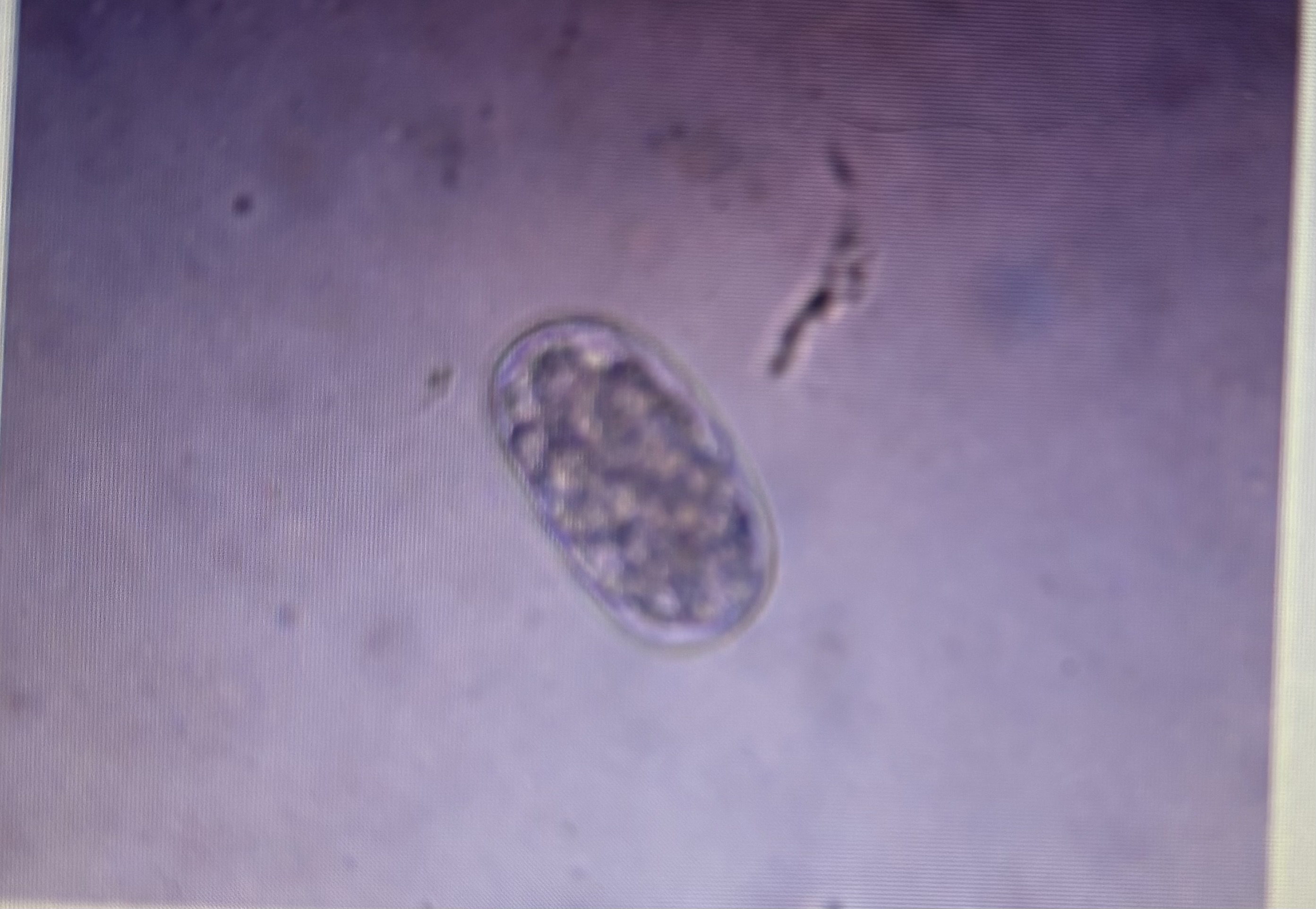
Strongyloidea
Canine and feline hookworm
Host species: dog and cat
Size: 75-95 um x 41-45 um
Prepatent period: 21 days
Transmission: ingestion percutaneous
Anclyostoma braziliense
trichuroidea
Whipworms
How do whipworms cause damage
They reside in the cecum and colog of respective host where they suck blood
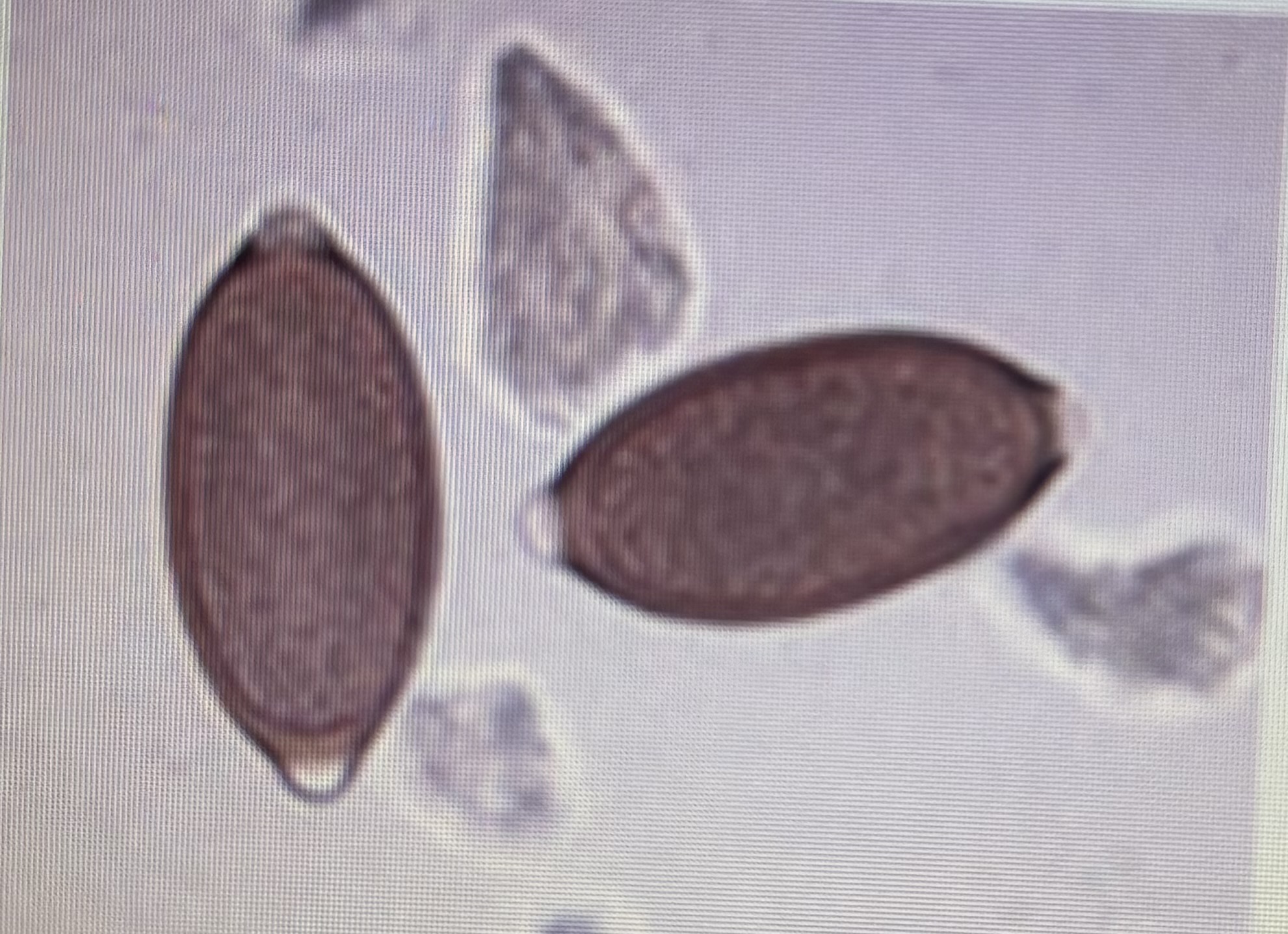
Trichurid
Host species: dog
Size: 72-90 um x 32-40 um
Prepatent period: 90 days
Transmission: ingestion
No zoonotic potential
Trichuris vulpis
Respiratory parasites within the trichuroidea family
E. Aerophilus
E. Boehmi
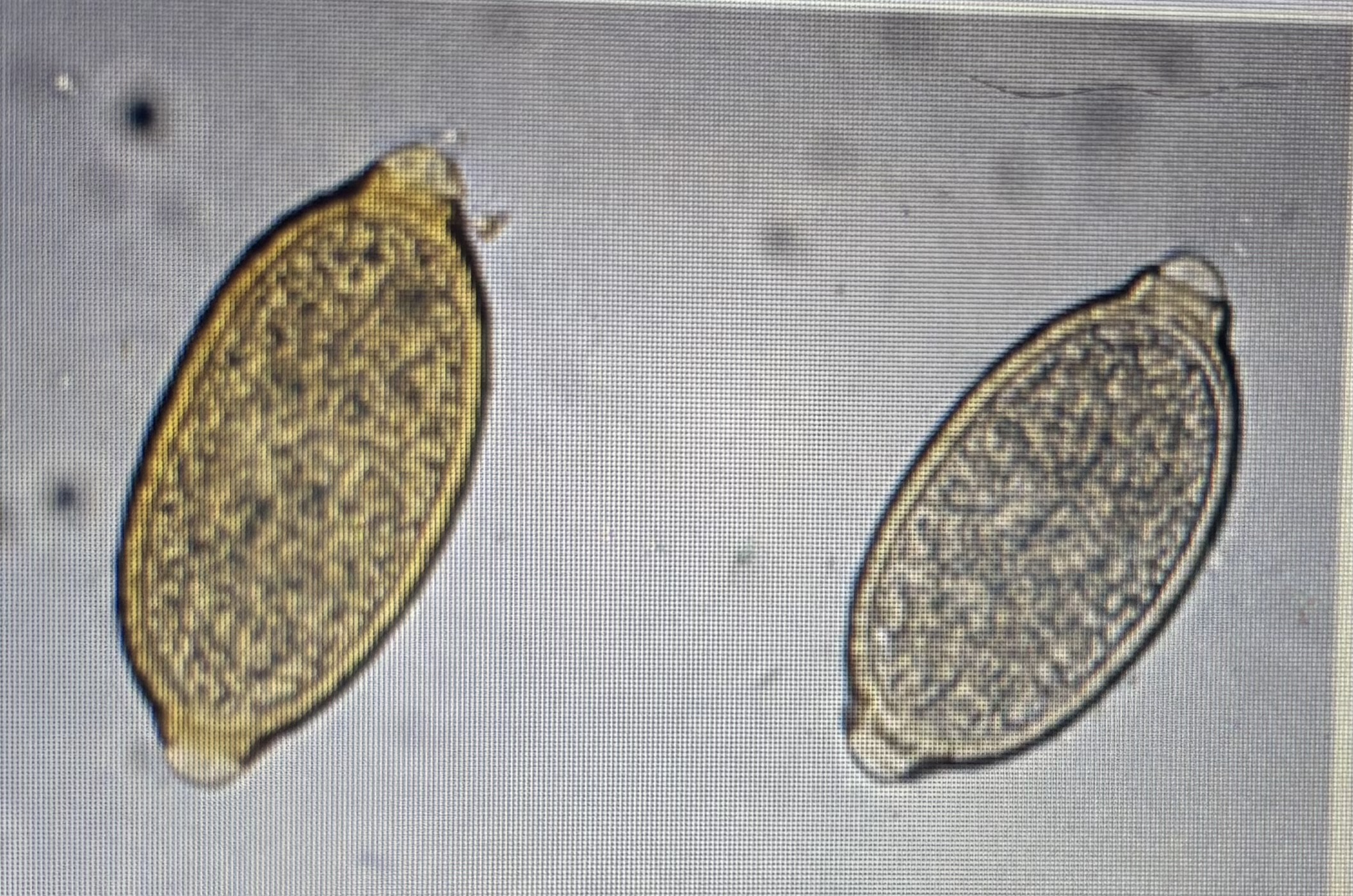
Trichurids - eucoleous
Host species: dog and cat
Size: 58-79 um x 29-40 um
Prepatent period: 42 days
Transmission: ingestion
asymetrical polar plugs
eucloeus aerophilus
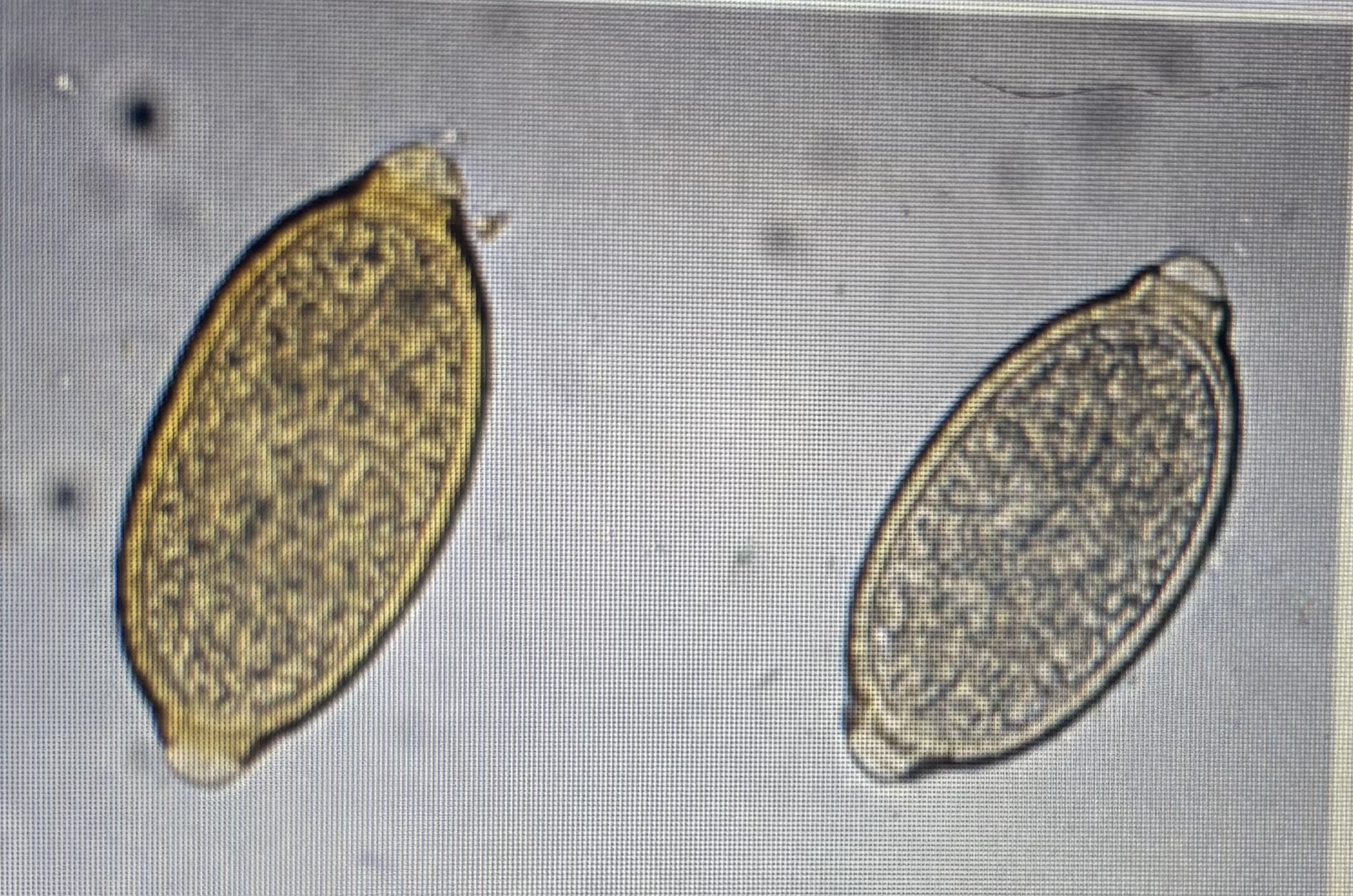
Trichurid - eucoleous
Host species: dogs
Size: 54-60 um x 30-35 um
Prepatent period: 42 days
Transmission: ingestion
symmetrical polar plugs
Eucoleus boehmi
Urinary parasites
Indirect life cycle
Pearsonema plica/feliscati
Respiratory parasite
Host species: cat Size
Adults live in respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts where they create egg nests. Larvae coughed up and passed in feces
Indirect lifecycle
Metastrongyloidea
Giant kidney worm
Host species: dog
Size: 71-84 um x 46-52 um
Prepatent period: 18 weeks
Transmission: ingestion
Phylum platyhelminthes
Flat worms
Two classes of flatworms
Cestoda and trematoda
Common name for cestoda
Tapeworm
Segments on tapeworms that are shed and contain a single egg of packets of eggs
proglottid
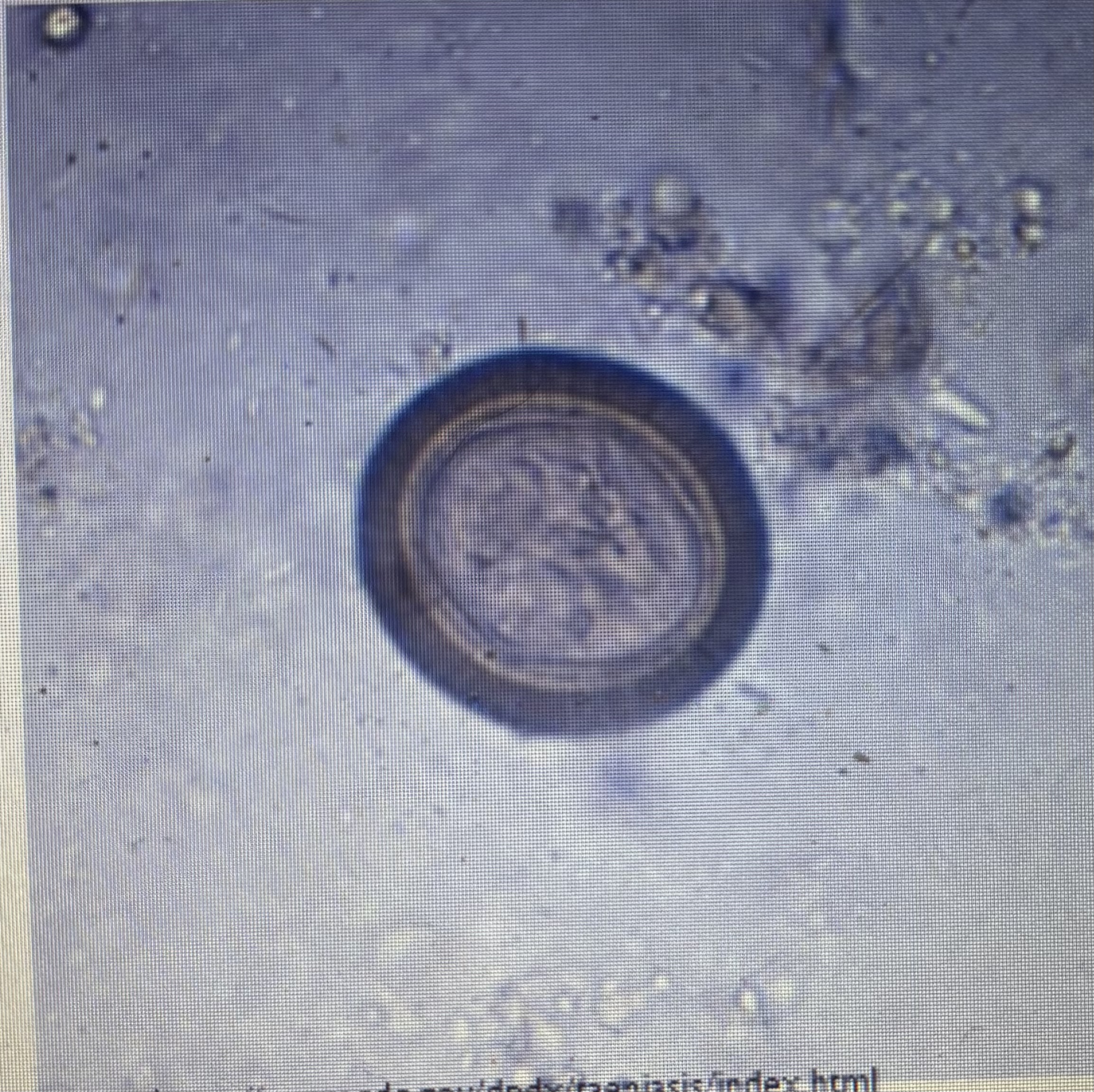
taenia spp
Rice grains - individual ova
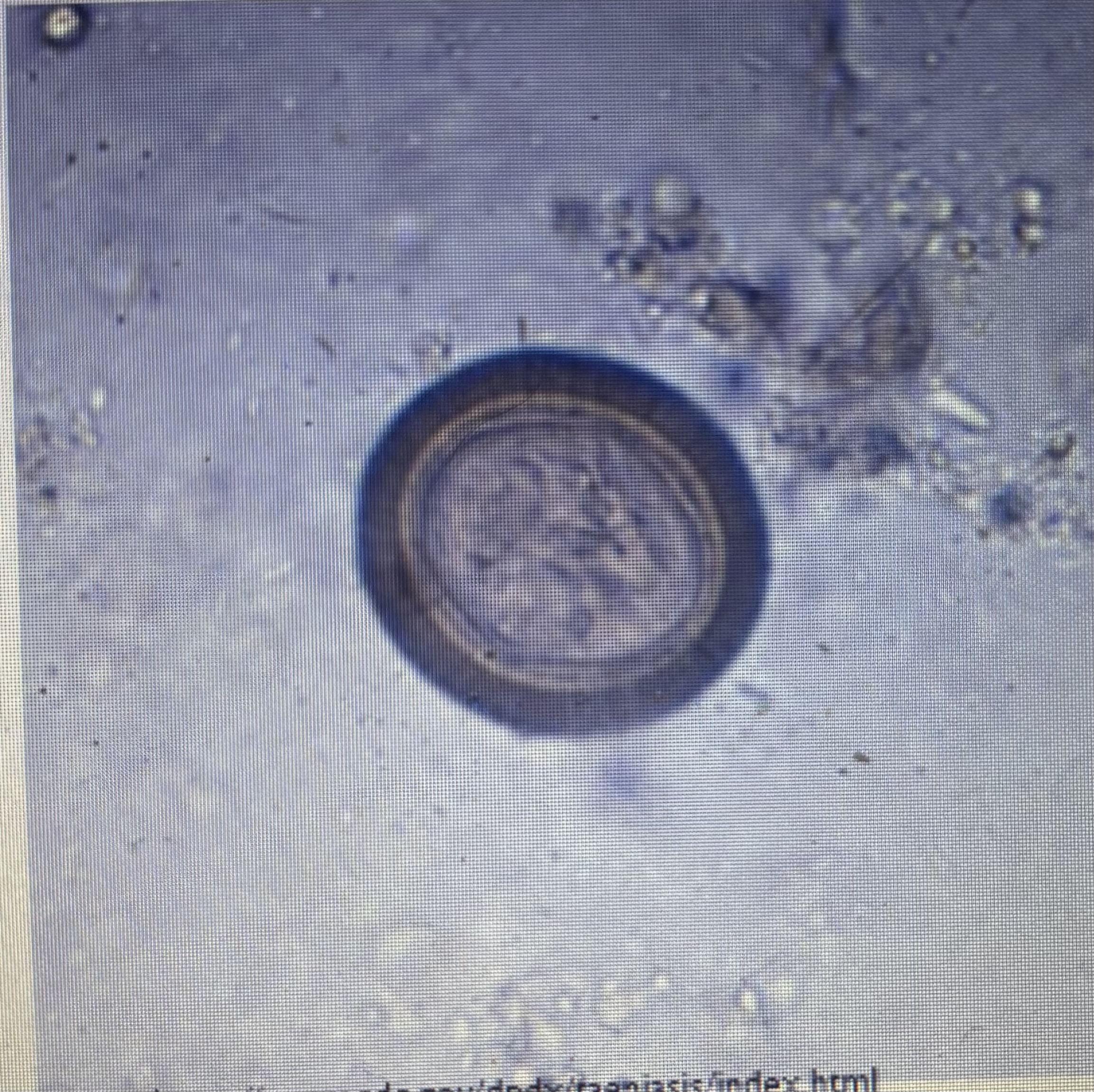
Size: 32 - 37 um
Prepatent period - 60 days
Transmission - ingestion
Taeniid tapeworm
Rabbit intermediate host
Host species - dog
Taenia pisiformis
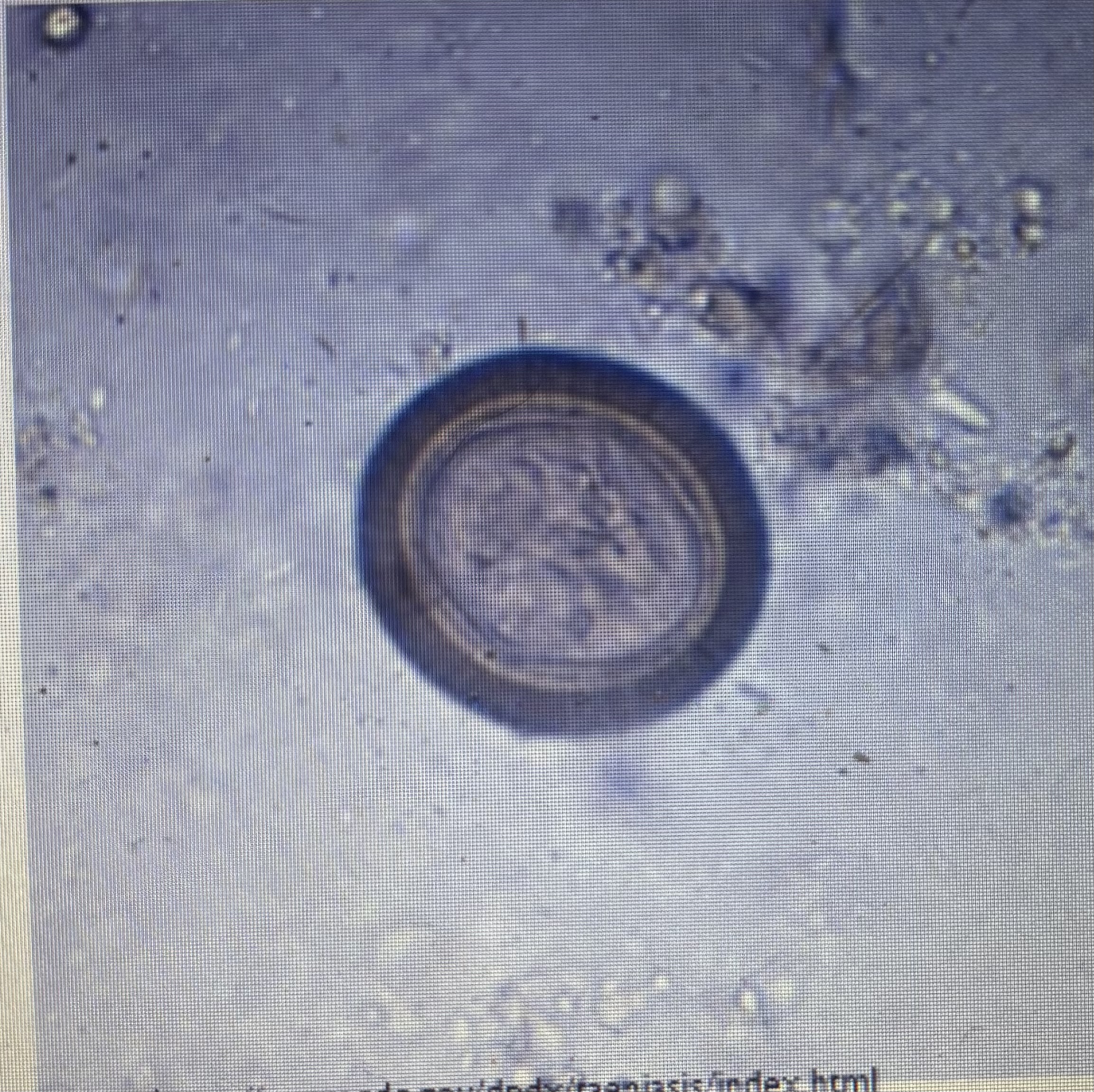
Small rodent intermediate host
Host species - cat
Taenia Taeniaformis
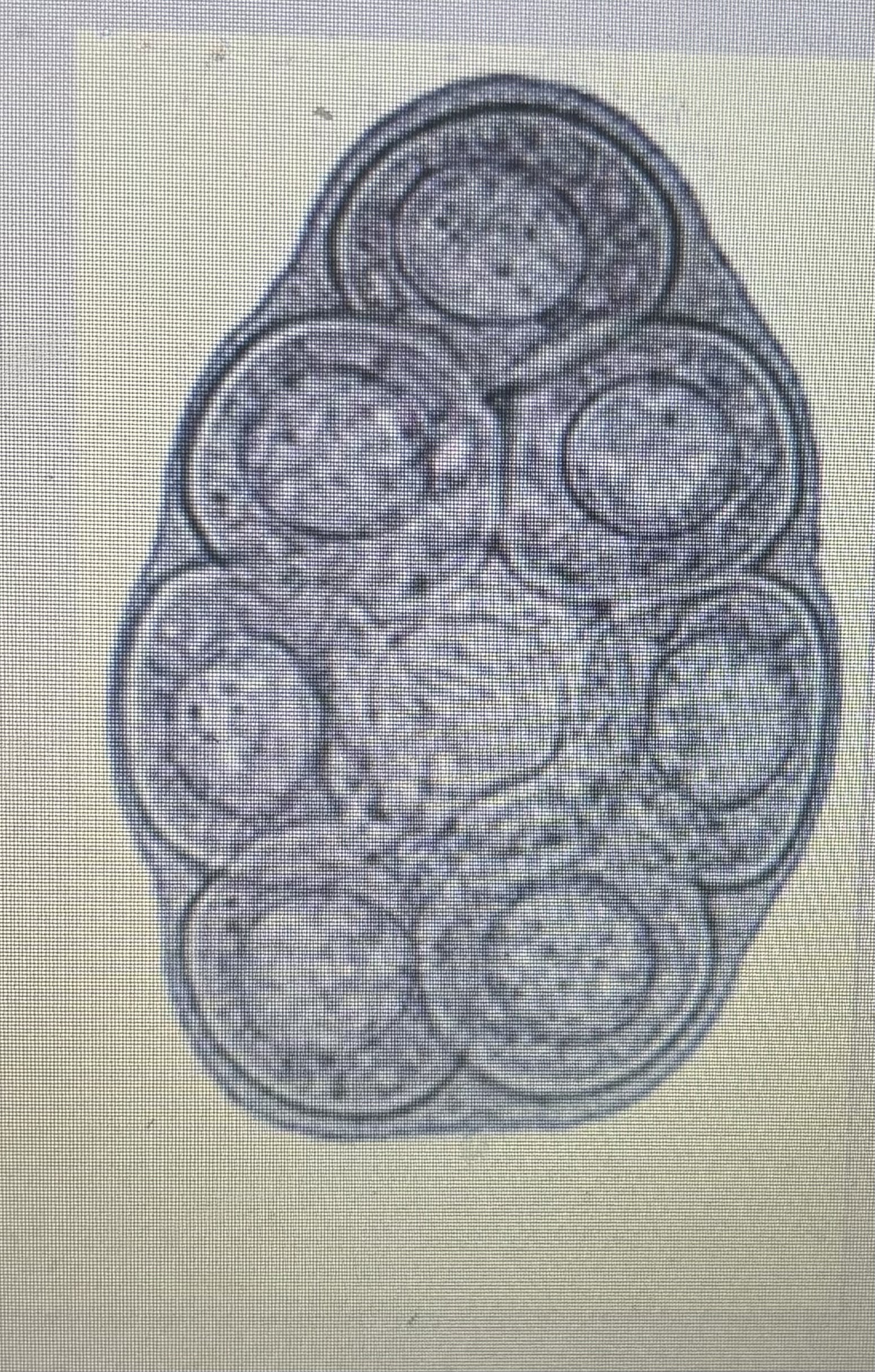
Intermediate host - flea
Host species - dog/cat
Size - 200um/50um - can vary
Prepatent period - 14-21 days
Transmission - ingestion
Dipylidium caninum
Intestinal fluke
Lizard poisoning - cat eats lizard or amphibian
Adult flukes inhabit liver, gallbladder, bile Ducts, and less commonly the small intestine
Platynosomum fastosum
Salmon poisoning fluke of dogs in the Pacific Northwest
Dogs eat infected fish
Adult fluke’s inhabits the small intestine and serves as vector for rickettsial agents
Nanophyetus salmincola
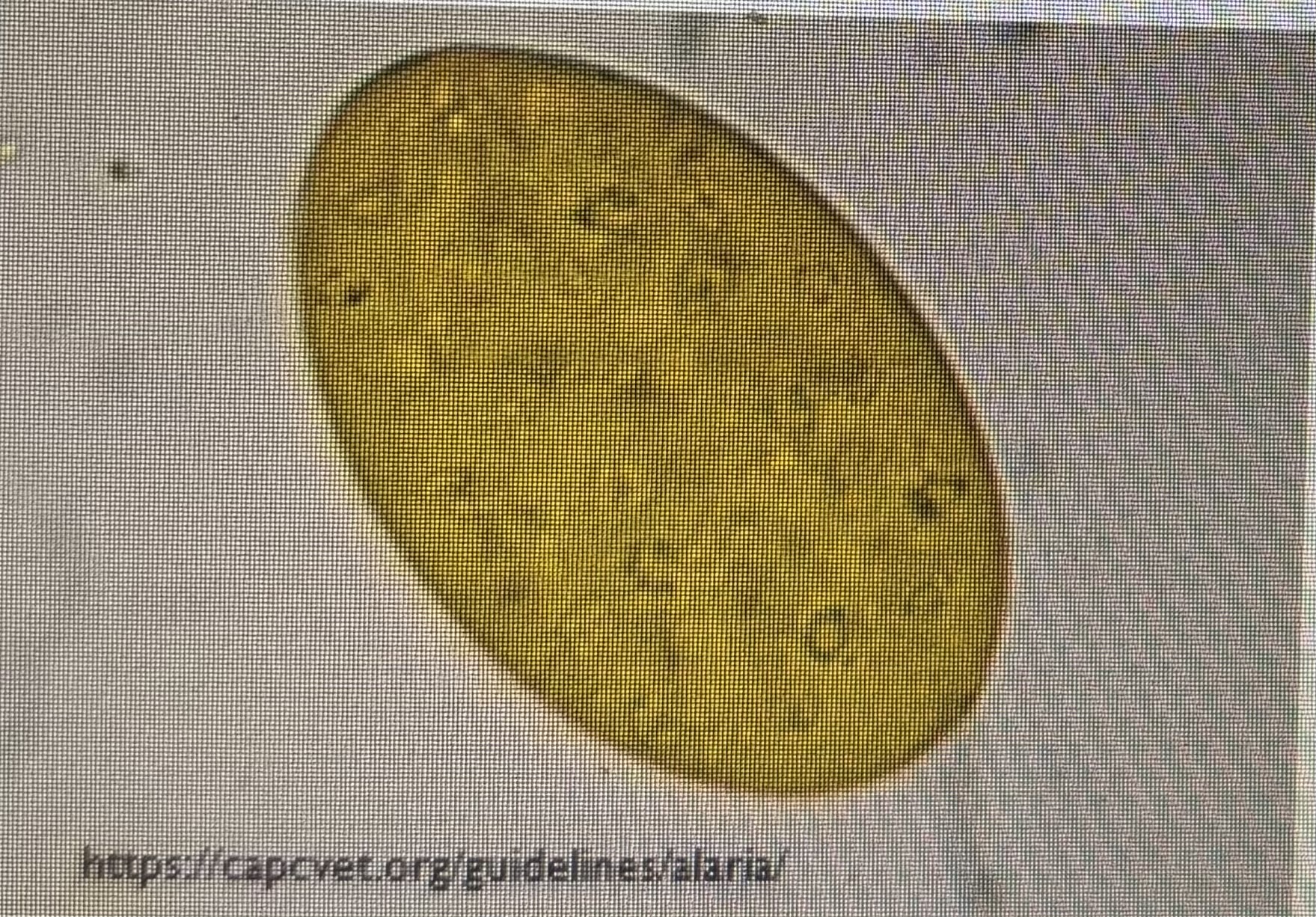
Intestinal flukes of dogs and cats
Found throughout North America
Dog or cat eats an infected frog snake or mouse
Ova are large, golden brown and operculated
Alaria spp
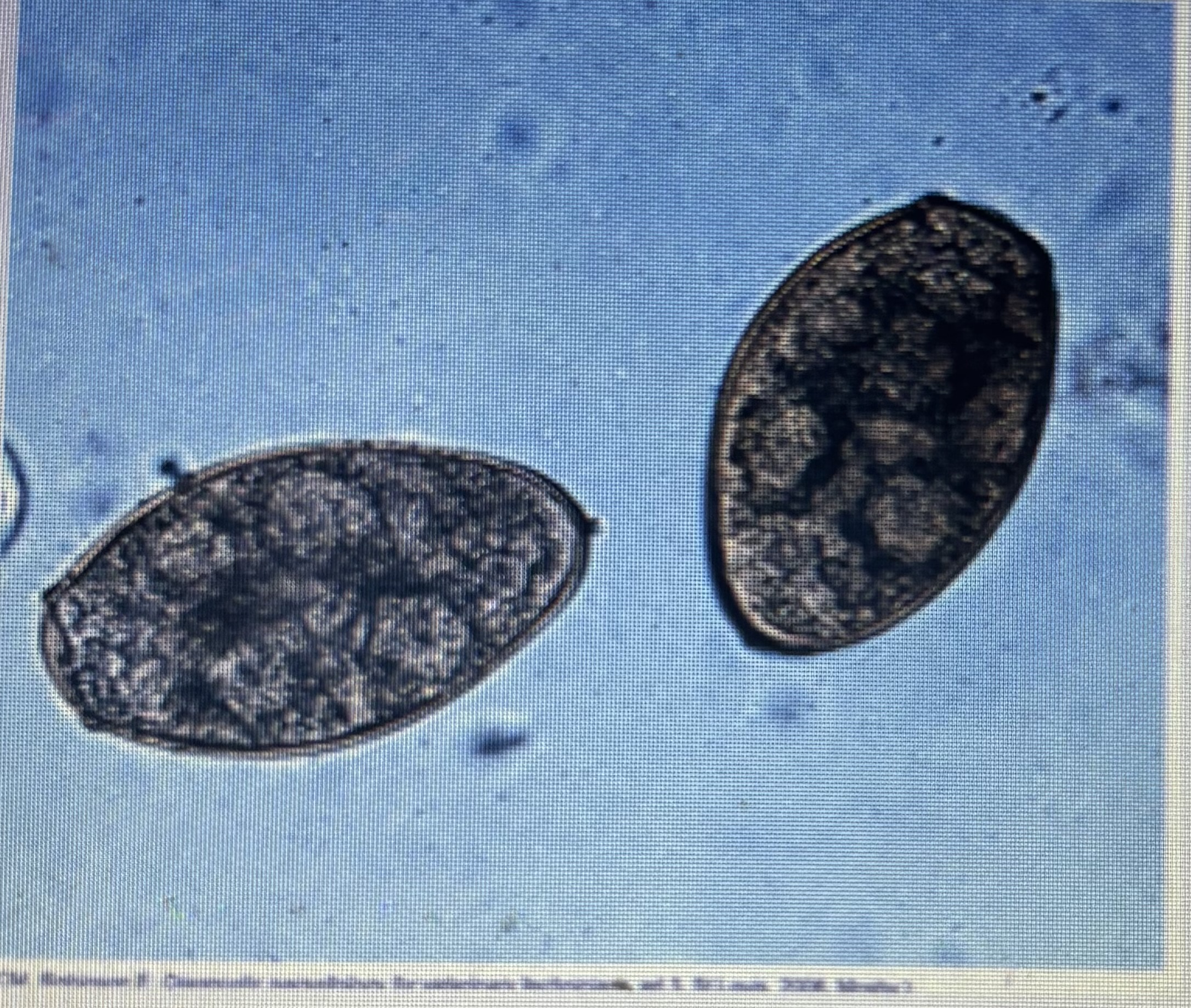
Lung fluke
Host species - dog/cats
Size - 75-118um x 42-67 um Prepatent
Prepatent period - 30-36 days
Transmission - ingestion of infected raw crayfish or crab
Paragonimus keliicotti
True or false
Paragonimus keliicotti can be observed on radiograph due to adult flukes occurring in cystic spaces connected to the terminal bronchioles within the lung parenchyma of dogs and cats
True
Why must certain flotation solutions of special techniques be used to observe Protozoa
Because of their size and fragility
Very small single celled parasites that are often transmitted to host via ingestion of a cyst
Protozoa
Techniques/solution commonly used to look for Protozoa
Direct smear + Legolas iodine
Acid fast staining
Antigen testing
Protozoa common in puppies and kittens
Characterized by diarrhea + lethargy and weight loss
Rarely clinically significant in adult animal
Coccidia - cystoisospora
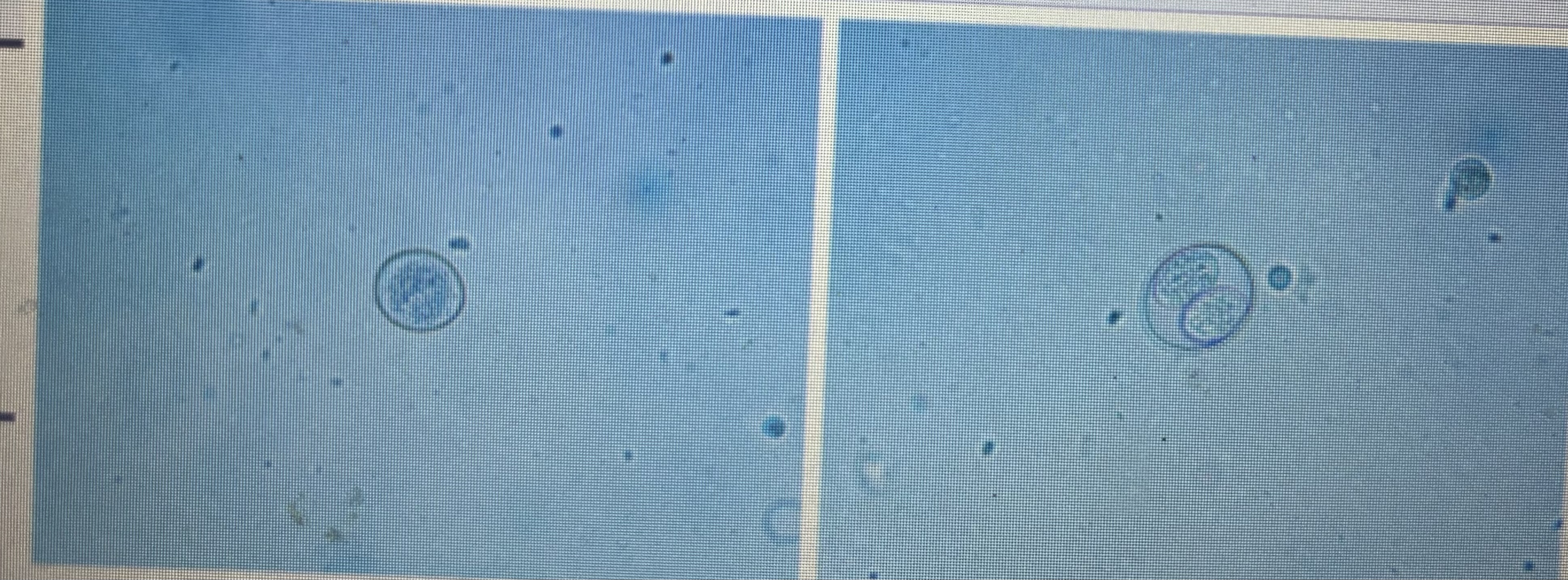
Direct life cycle with situated form
Prepatent period 7-14 days
Cystoisospora spp
Nematodes affecting horses
Strongyloidea, ascaroidea, rhabditoidea, oxyroidea
Strongyles affecting horses
Strongylus vulgaris, strongylus edentatus, strongylus equinus
Ascarid genus affecting horses
Parascaris equorum
Rhabditoidea genus affecting horses
Strongyloides westeri
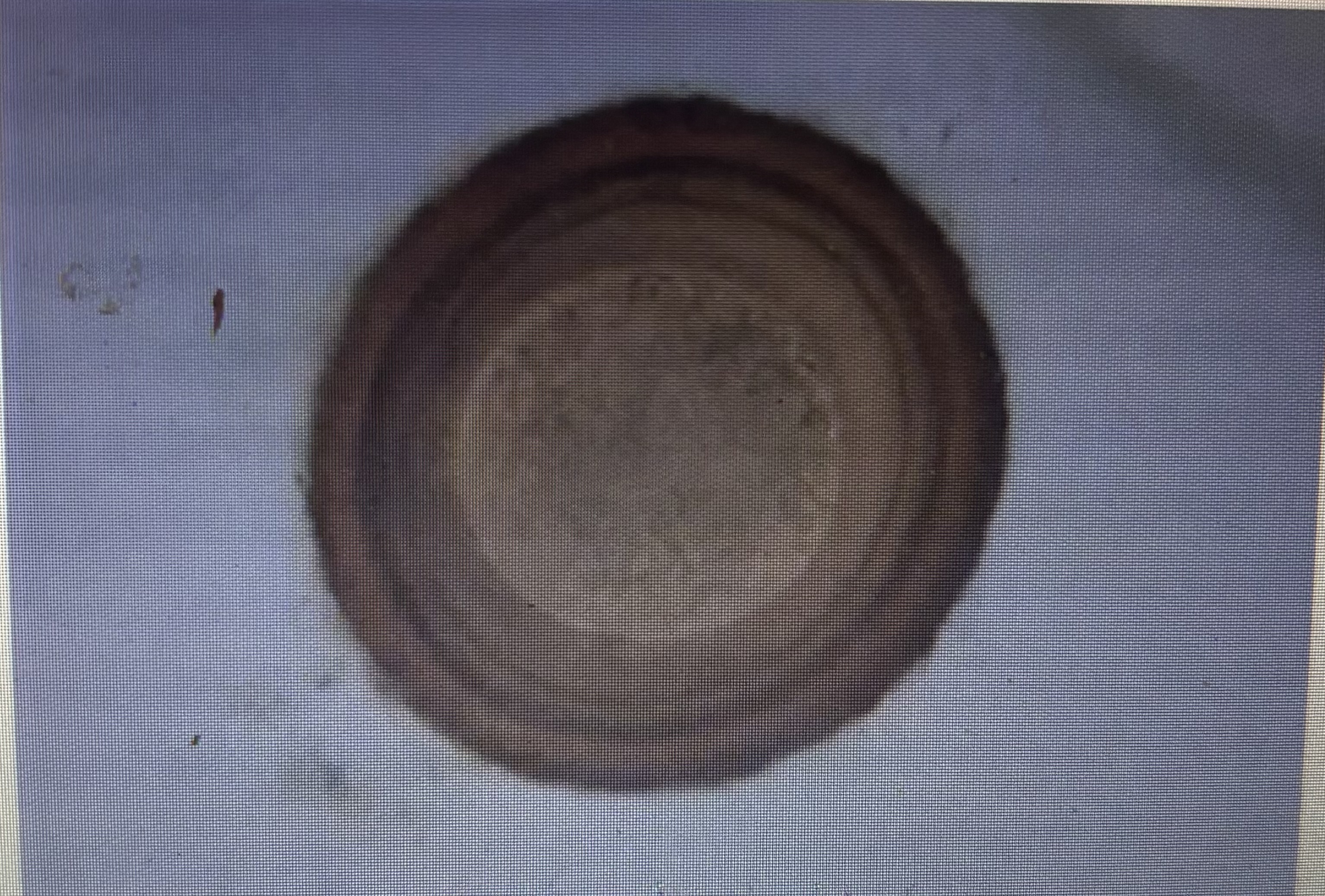

Host species horse
Prepatent period 70 days
Measurement 90-100 um
Found in the small intestine of horses - particularly in young foals
Ascarid
Parascaris equorum
Found in the large intestine
Referred to in Terms of “small type” or “large type”
Strongyles
Strongly referred to as the blood worm
Strongly vulgaris
Strongyles that cause liver damage
Edentatus and equinus
Strongyles size variation
70-90 um - 40-50 um
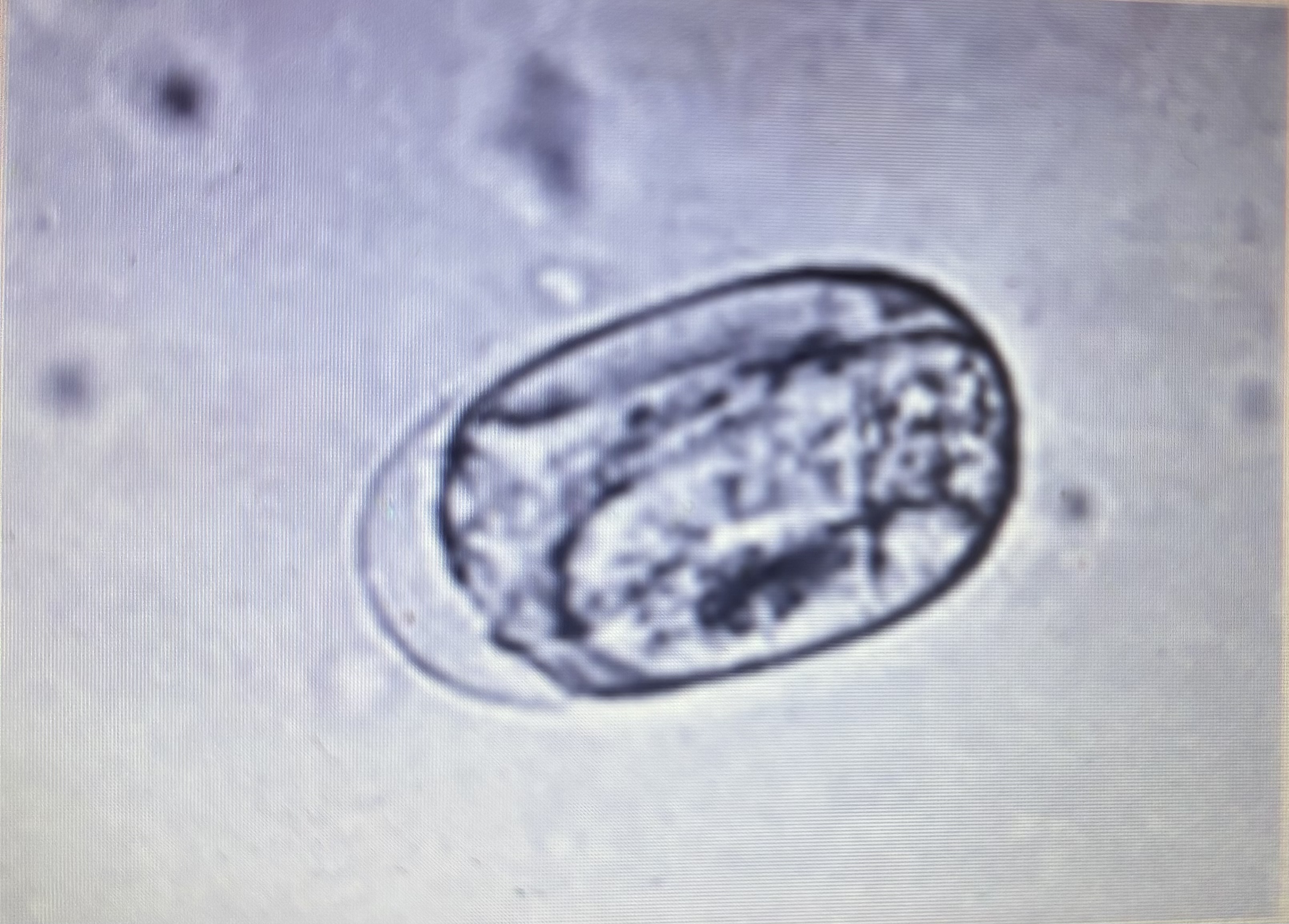
Parthenogenic female parasites - asexually reproducing female parasites affecting horses
Strongyloides westeri
True or false
Strongyloides westeri ova are larvated
True
Strongyloides westeri size and transmission
40-50 um x 32-40 um
Trans mammary and transcutaneous
equine pinworm
oxyuris equi
Where are adult picture equi worms found
cecum, colon, and rectum of horses - may protrude from the anus.
How can oxyuris equi eggs be recovered from the anus
By using cellophane tape or gentle scraping
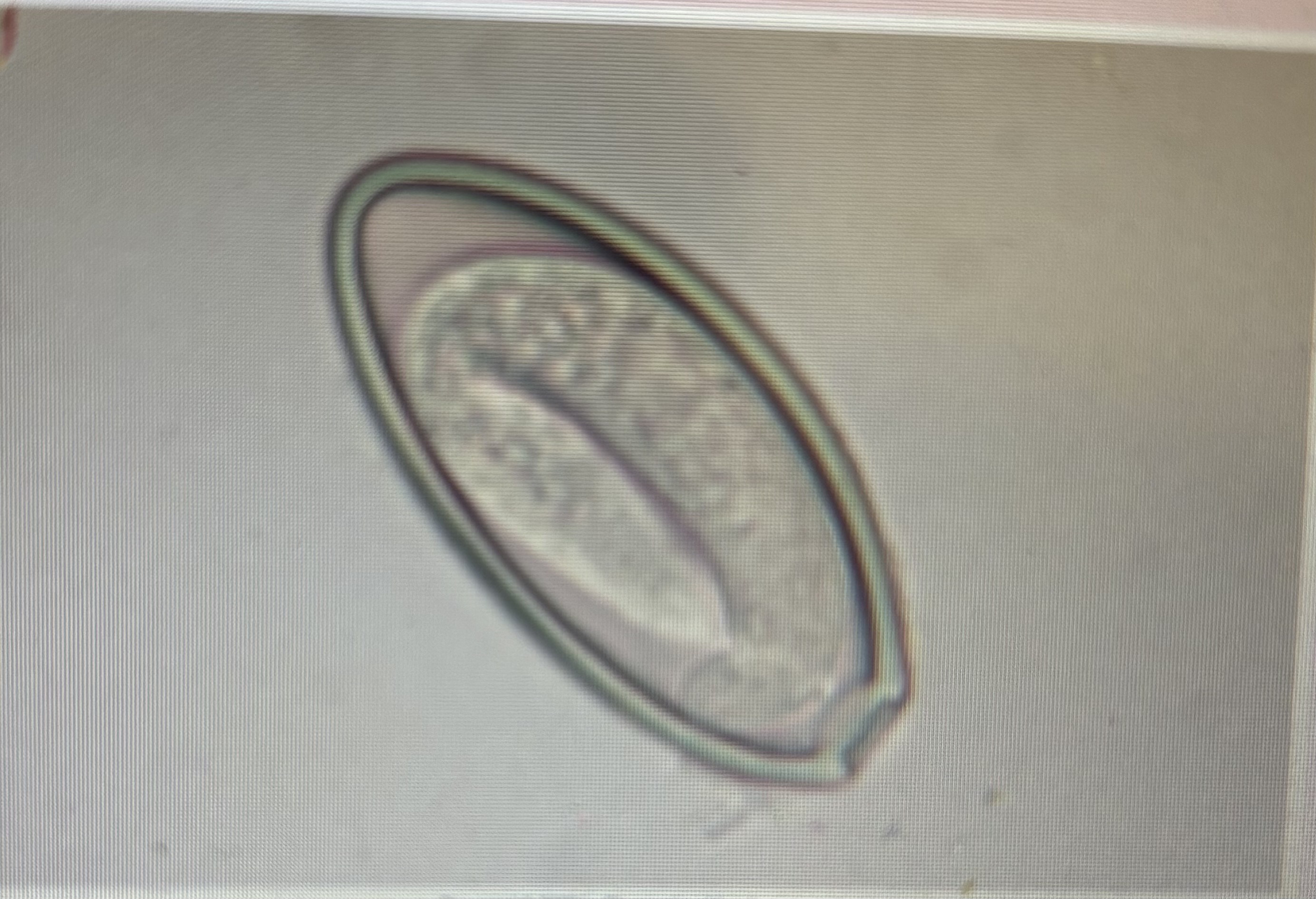
Host species horse
Size 90 × 40 um
Prepatent period 5 months
Eggs may be larvated
Oxyuris equi
Eucestode genus
Anaplocephala perfoliata, anaplocephala magna, anaplocephala mamillana
Anaplocephala common name
Equine tapeworm
What is the equine tapeworm intermediate host
Grain mite
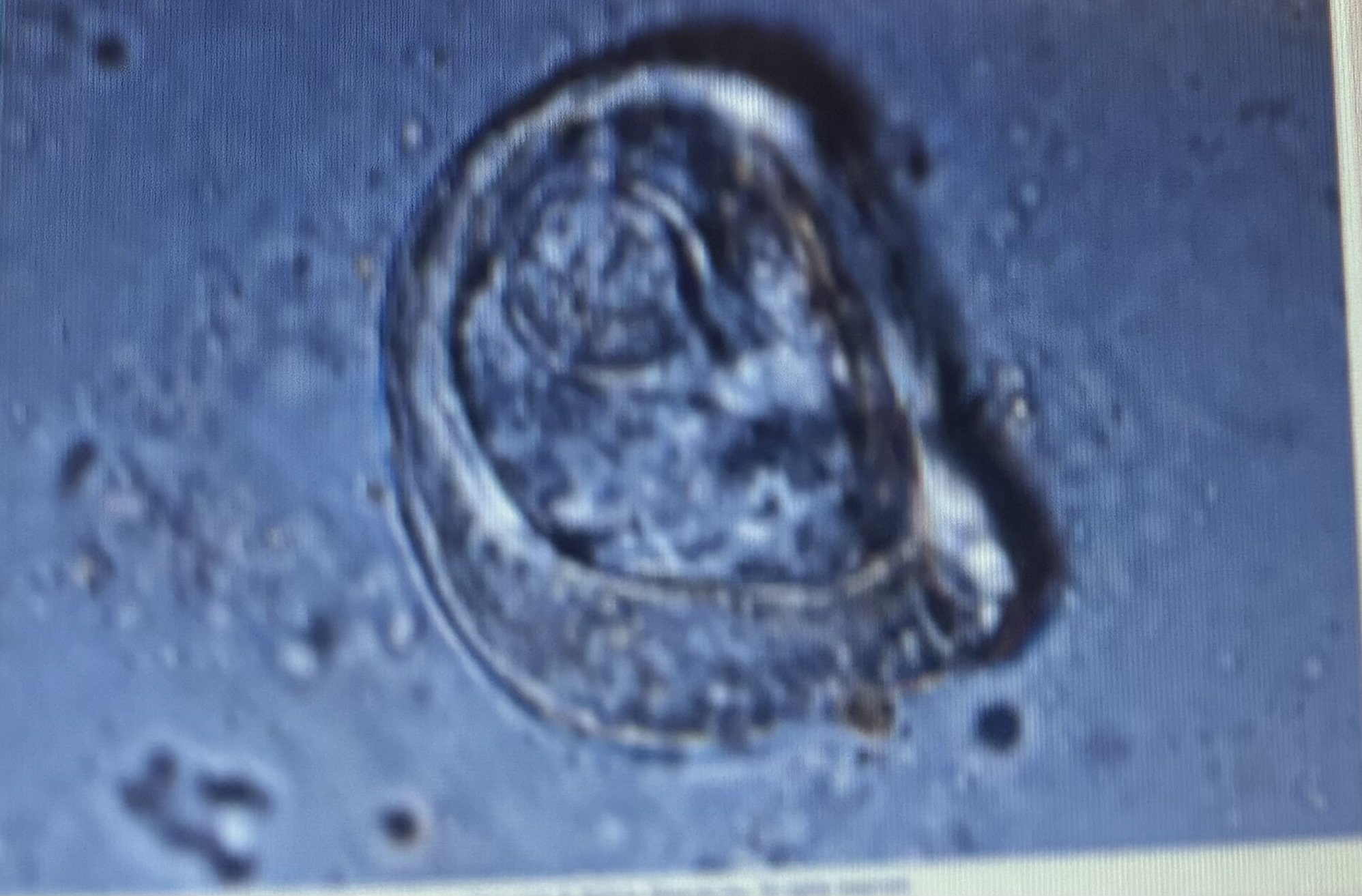
Host species horse
Size 65-80 um
A. Perfoliata
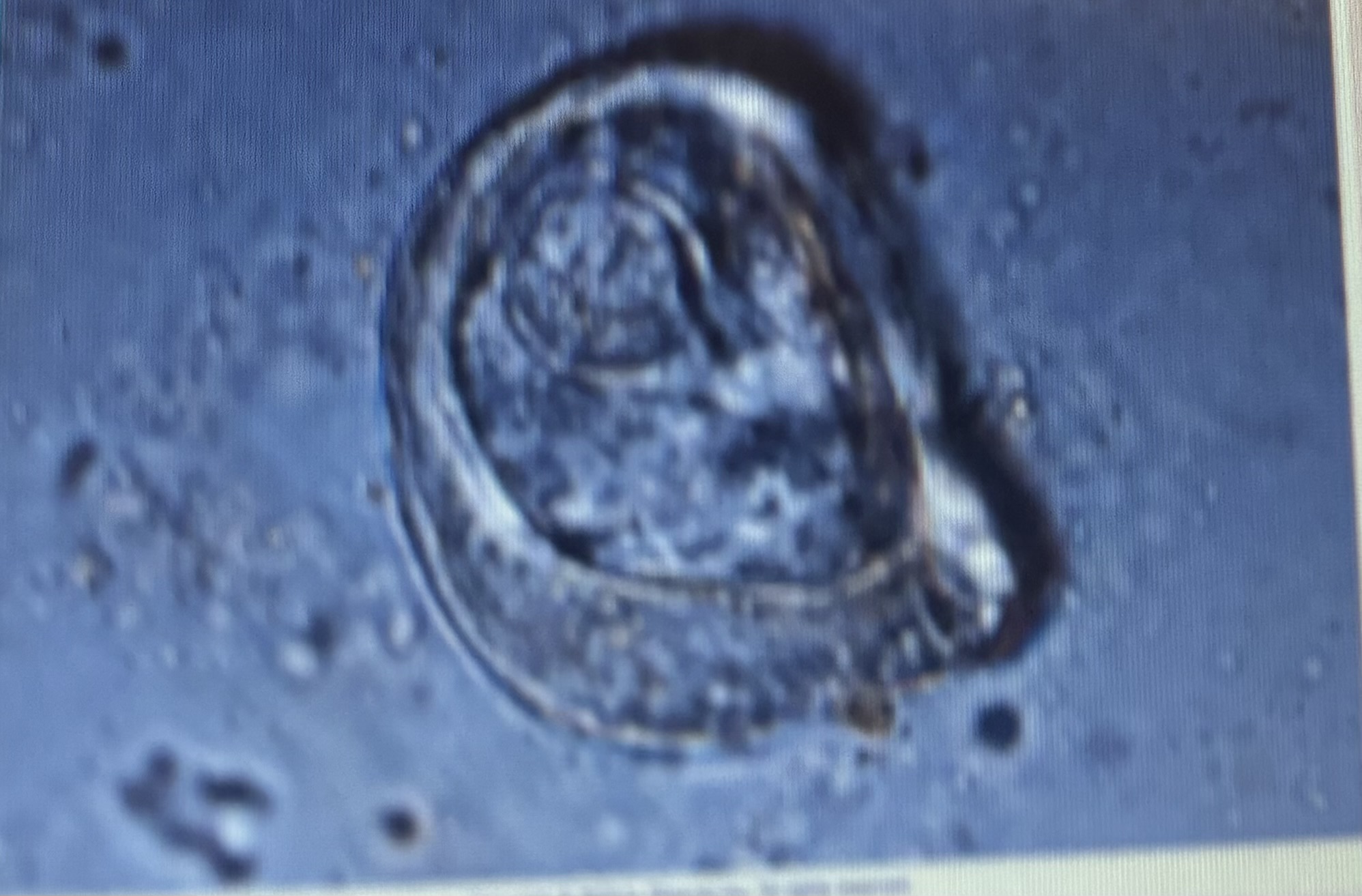
Host species horse
Size 50-60 um
A. Magna
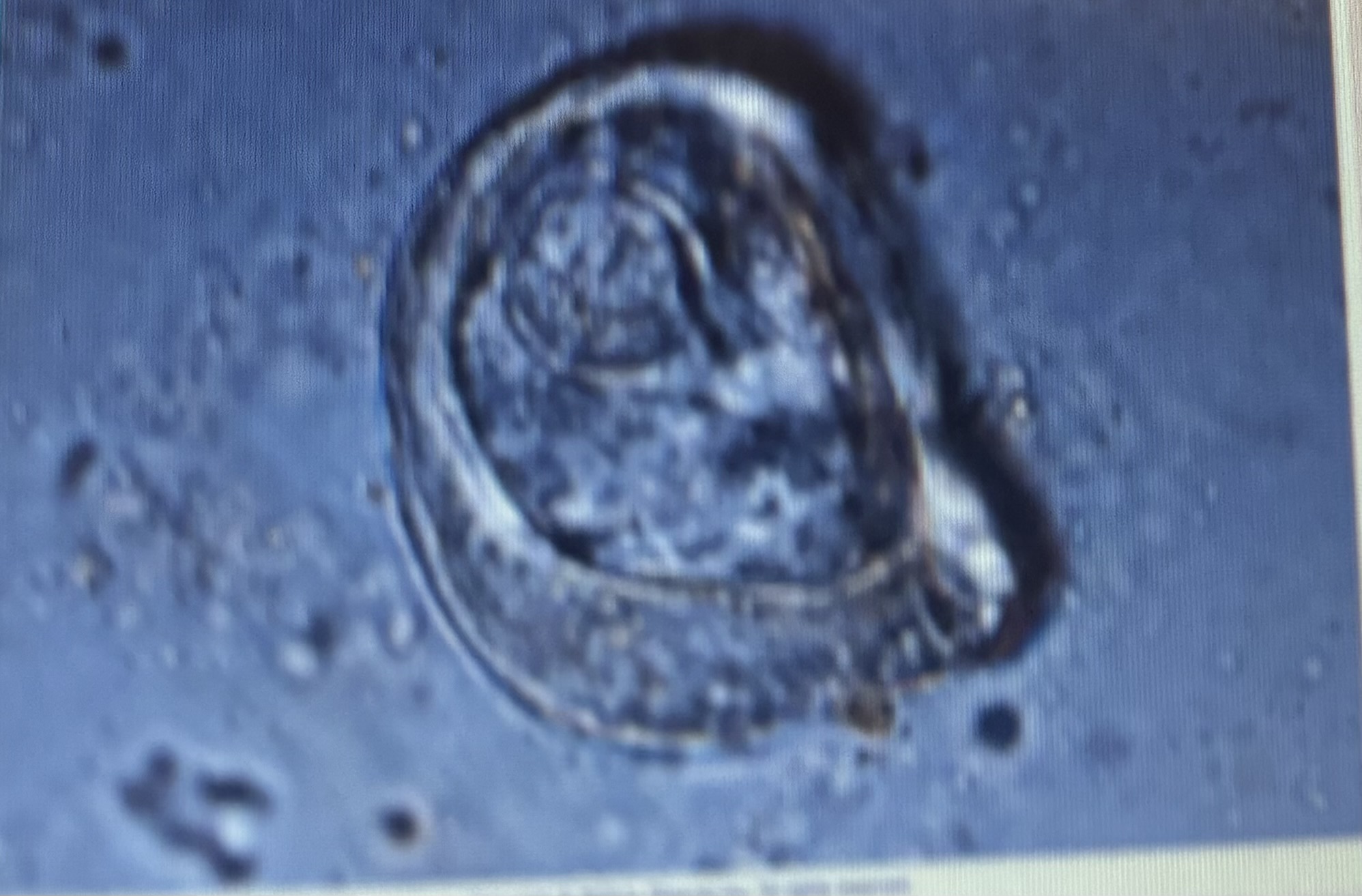
Host species horse
Size 37-51 um
P. Mamilliana
Apicomplexa common name and genus
Coccidia
Eimeria Leilani
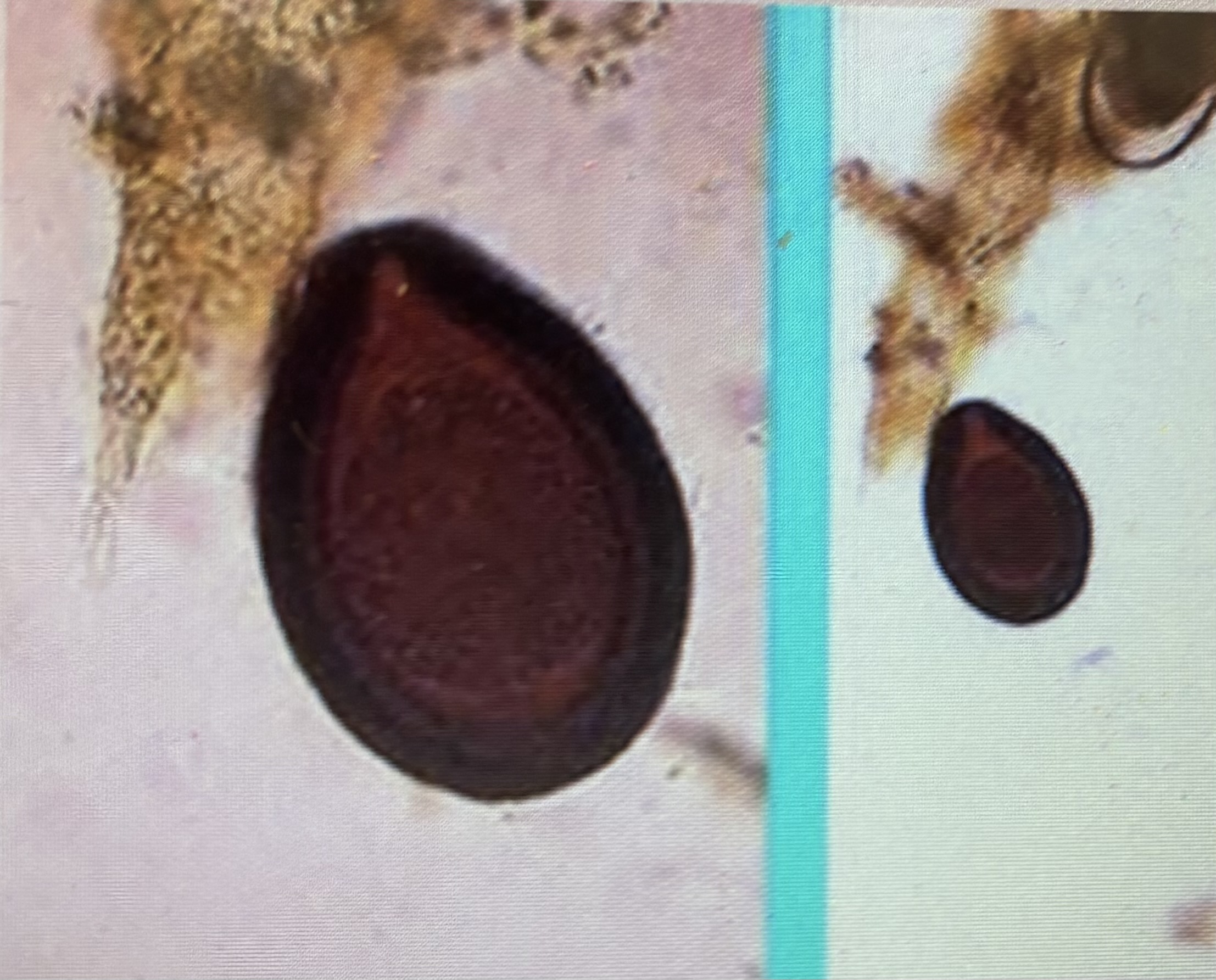
Host species horse
Size 70-90 um
Prepatent period 15-33 days Measurement
Usually found in young animals
Eimeria leuckarti
trichostrongyles genus
Trichostrongyles type
Nematodirus
Marshallagia
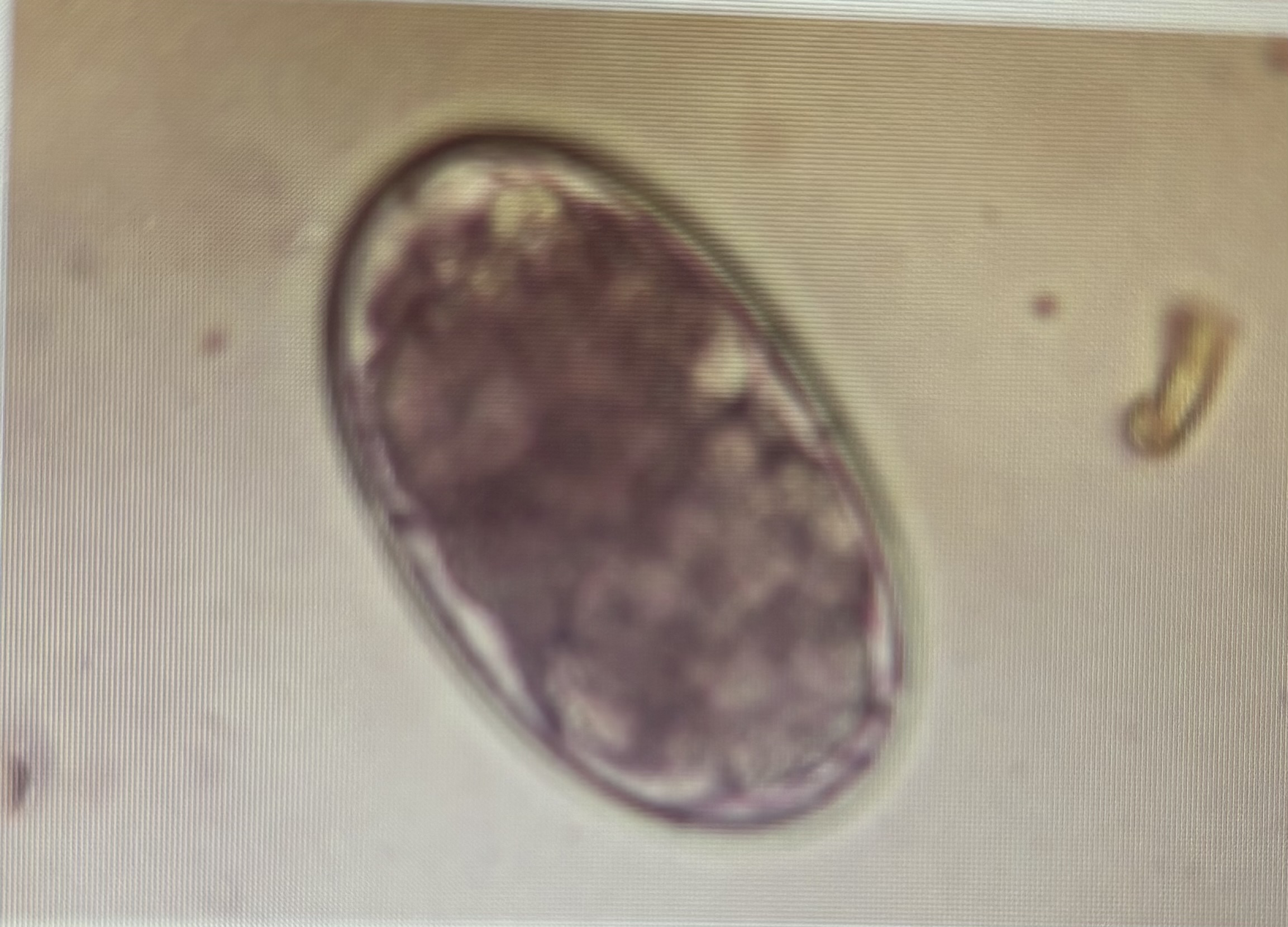
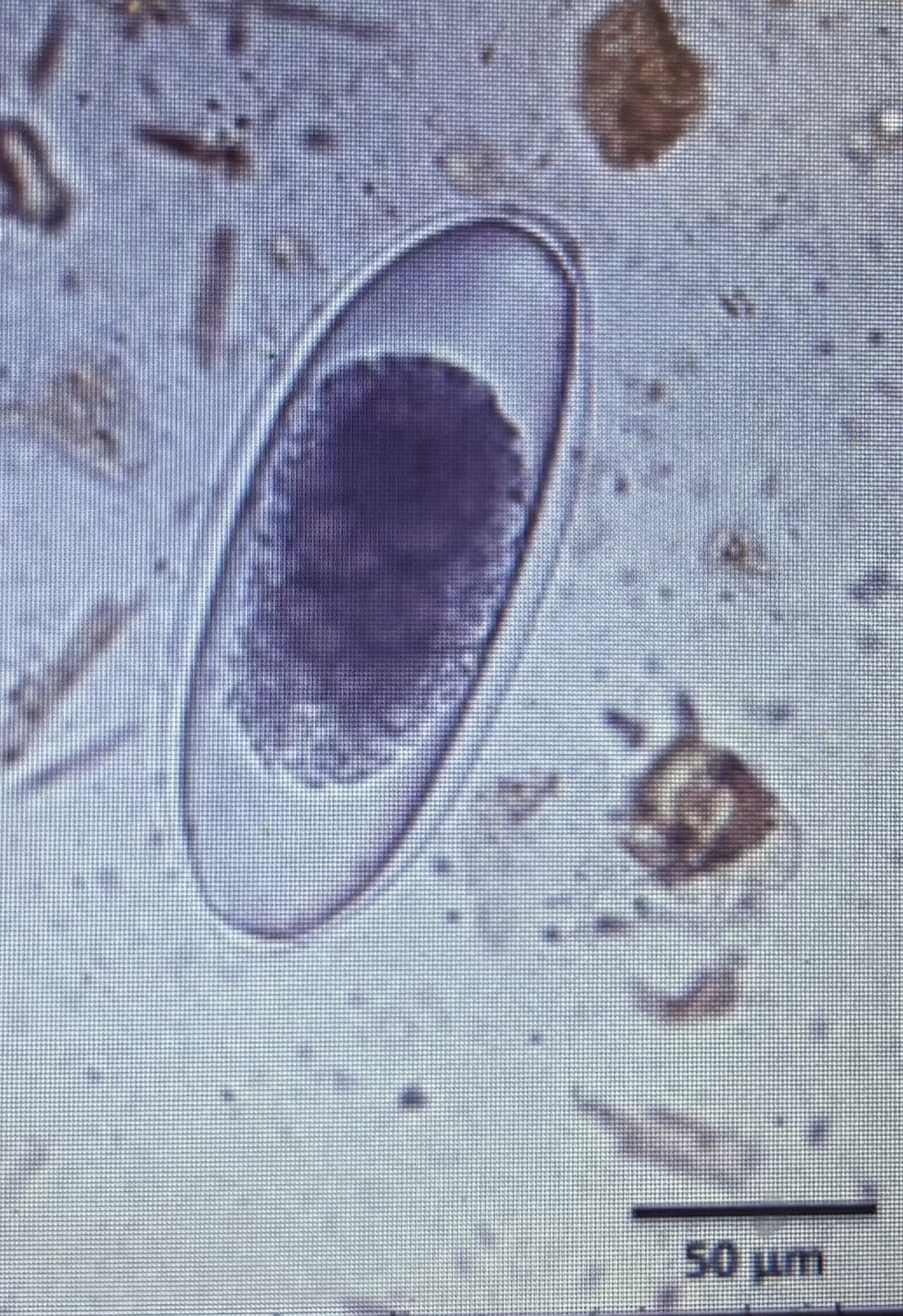
Host species ruminants
Regardless of size or species, ova are nearly identical
Trichostrongyles type
Host species ruminants
Size 150-230 um x 80-100 um
Nematodirus app
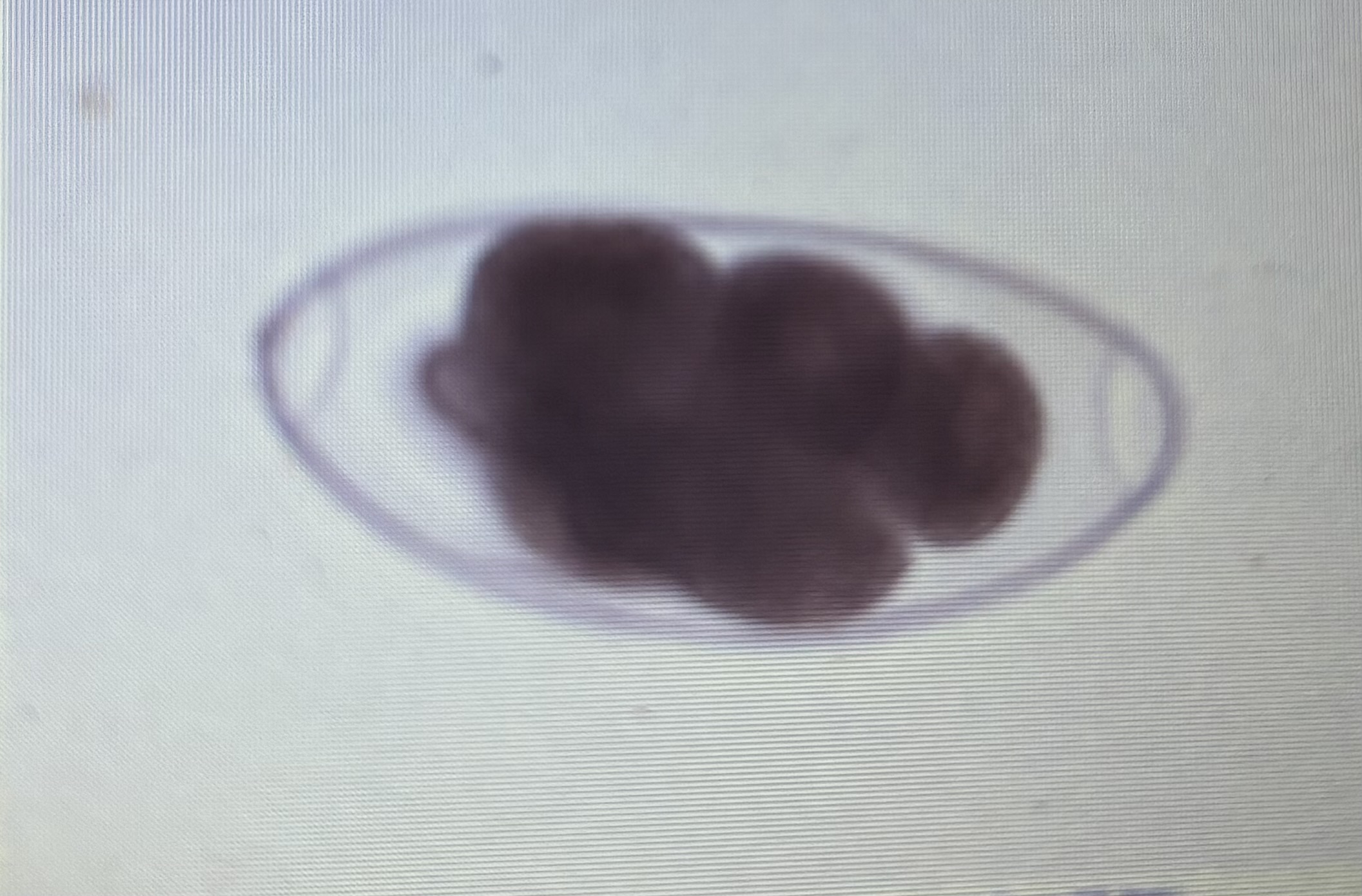
Host species ruminants
Size 160-200 um x 75-100 um
Marshallagia spp
Eucestode genus in ruminants
Maniezia benedeni
Maniezia expansa
Trematode genus in ruminants
Fasciola hepatica
Paramphistomum
Cotylophoron
Dicrocoellum dendriticum
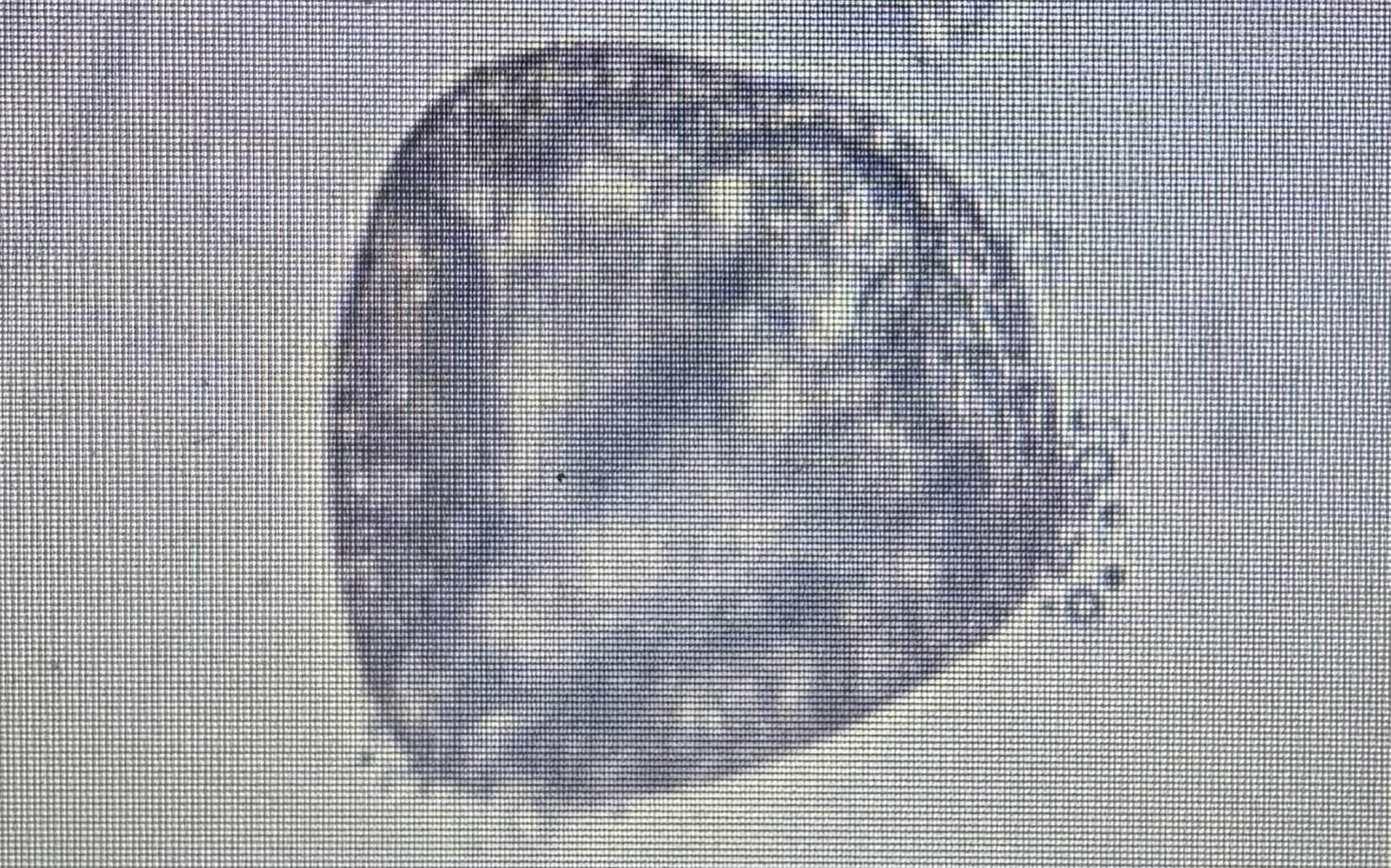
Host species cattle sheep and goats
Size 56-67 um
Cestode
Moniezia expansa
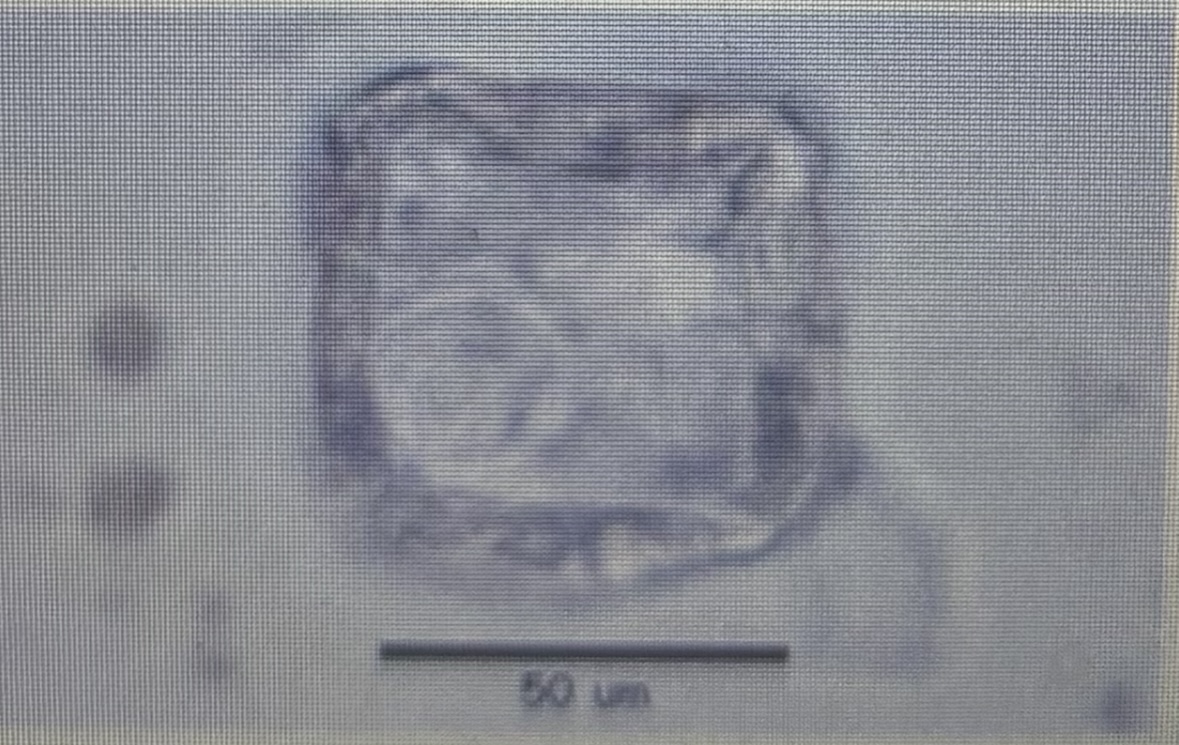
Host species cattle
Size 75 um
Cestode
Moniezia benedini
parasite that can leave cysticeri is cattle musculature of cattle and can cause beef measles in humans
Taenia saginata
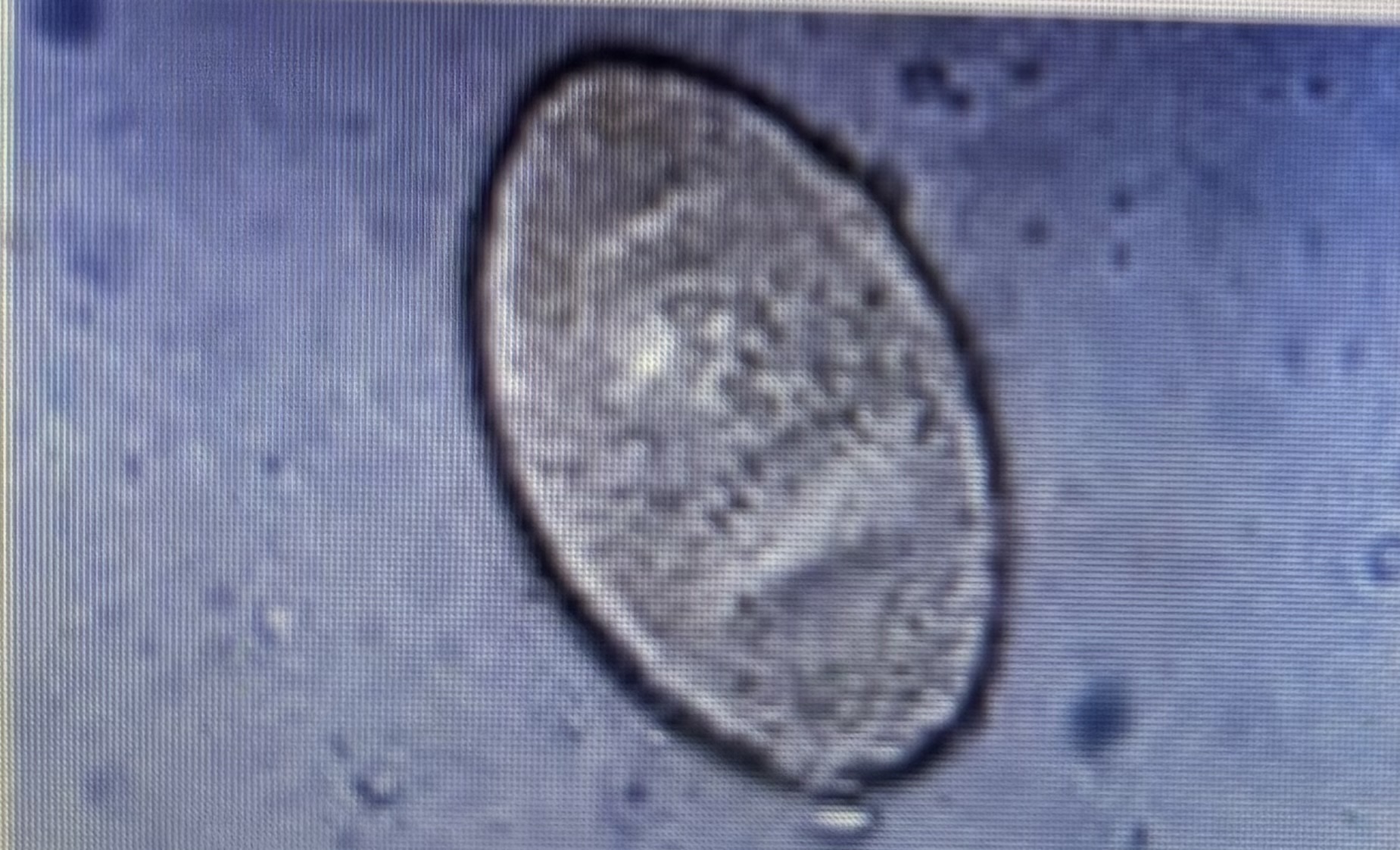
Host species ruminants
Size 130-150 um x 63-90 um
Liver fluke
Fasciola hepatica
Coccidia affecting ruminants
Eimeria spp
Eimeria bovis
Eimeria zuernii
Cryptosporidium
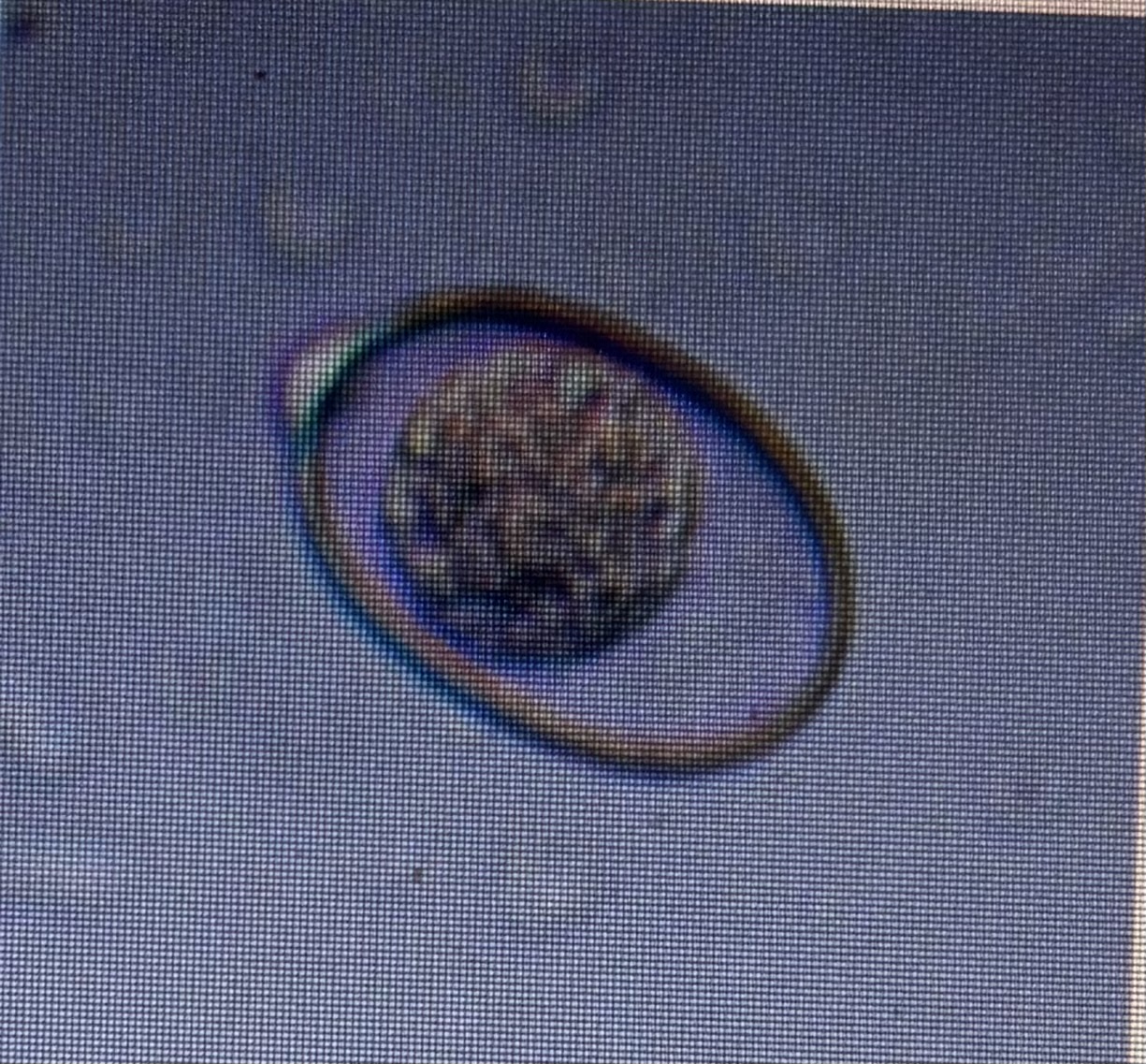
Host species cattle
Size 20 × 28 um
Eimeria bovis
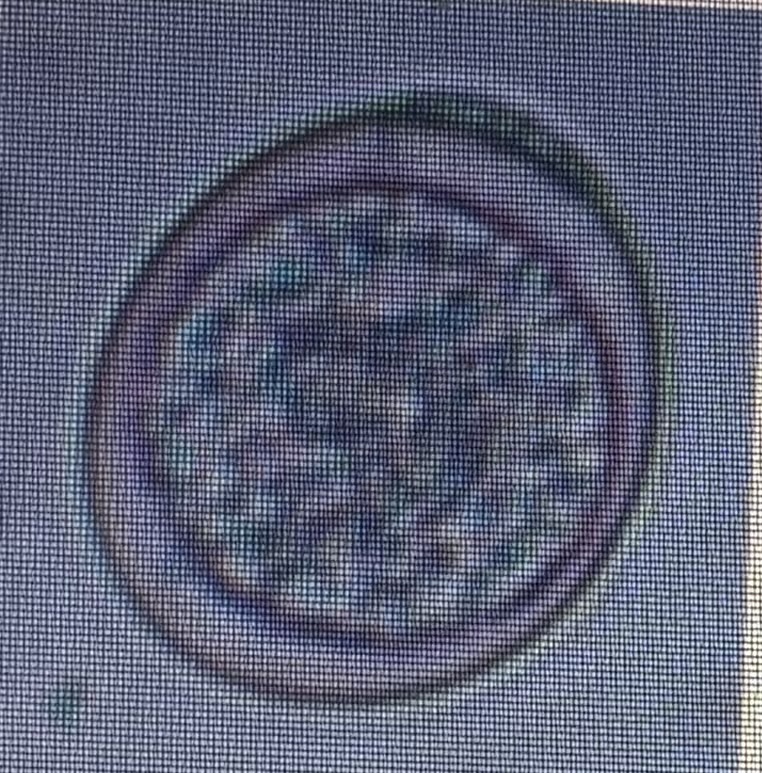
Host species cattle
Size 15-22 um x 13-18 um
Eimeria zuernii
Significant public health concern for humans
Causes frequent mucoid diarrhea
Size 4-6 um
Cryptosporidium
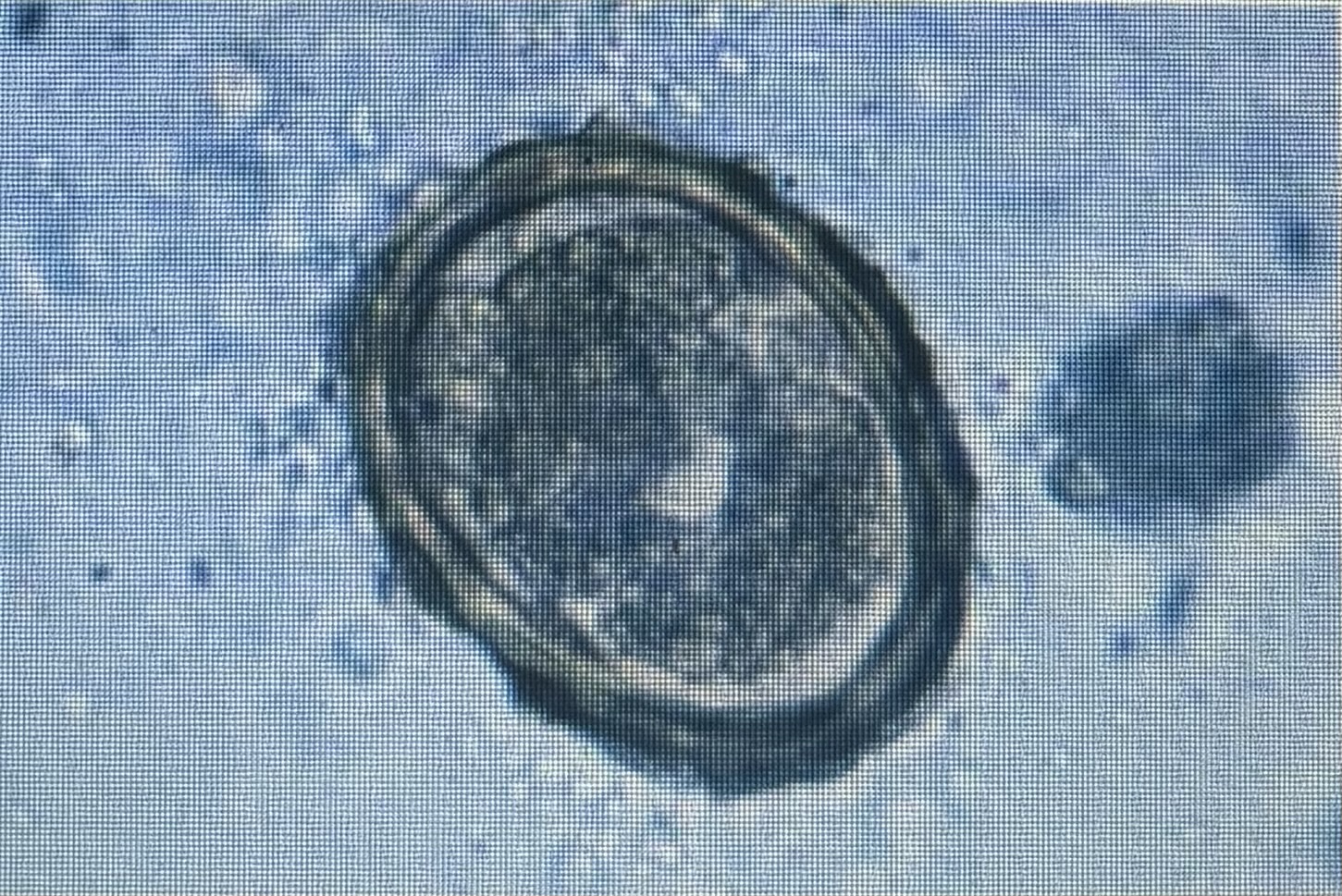
Host species swine
Size 50-80 um x 40-60 um
Damage to liver with larval migration
Ascaris suum
Host species swine
Size 40 um x 70 um
Ova are trichostrongyle type
Nodular worm of swine
Oesophagostomum debtatum
Parasite in which the intermediate host can be the same animal as the definitive host
Significant public health concern
Affects swine
Trichinella spirals
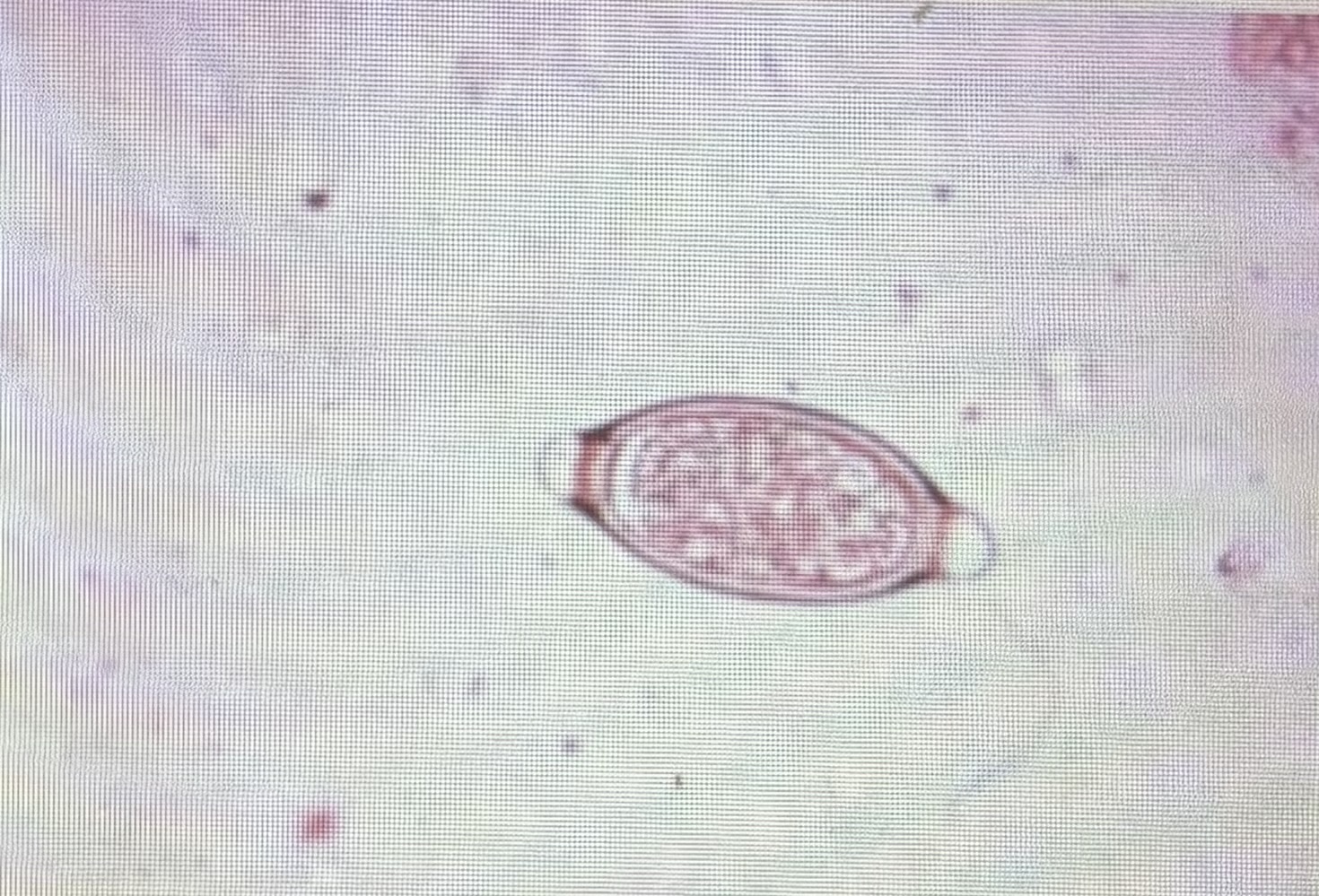
Swine whip worm
Size 50-56 um x 21-25 um
Trichuris suis
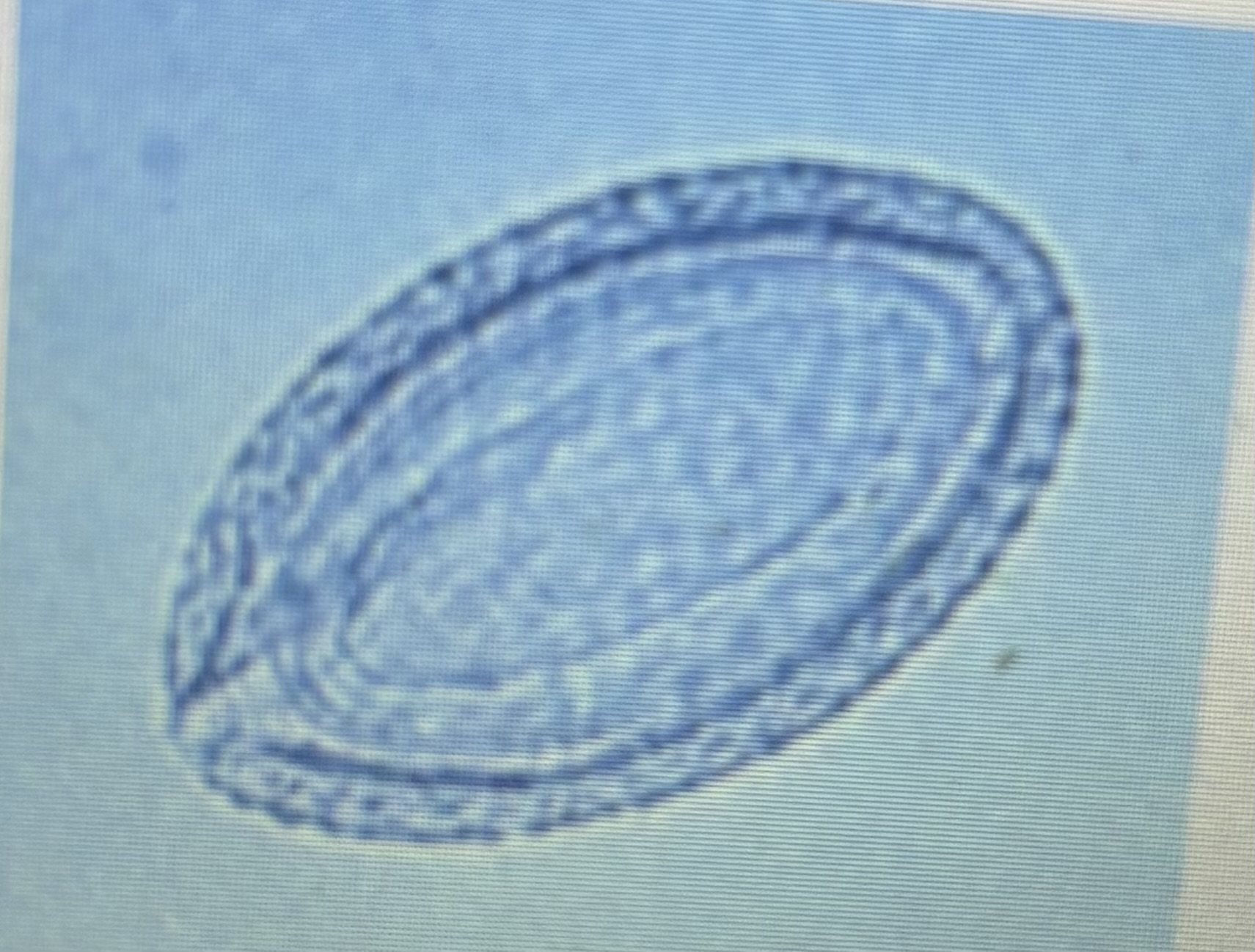
Thorny headed worm of swine
Typically found on necropsy
Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus
obligate intracellular gram negative bacteria
rickettsial parasites
genus of anaplasma that most commonly causes anaplasmosis in dogs
a. phagocytophilium
anaplasma genus that affects ruminants
a. marginale
cells affected by a. phagocytophilium
granulocytes - neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
vector of a. phagocytophilium
ixodes spp.
vector of a. marginale
multiple tick genus/speciess
ehrilichia genus that usually causes ehrilichiosis in dogs
e. canis
cells affected by e. canis
mononuclear leukocytes - monocytes and lymphocytes
what is the rickettsia genus that causes rocky mountain spotted fever
rickettsia sickettsii
cells affected by rickettsia rickettsii
endothelial cells lining vessels
vectors for rickettsia rickettsii
rhipicephalus sanguineus, dermacentor variabilis
protozoal blood parasites
babesia, cytauxoon felis, plasmodium
what phylum are the protozoal parasites in
apicomplexa
which protozoan blood parasite affects cats and has a high mortality rate if not treated
cytauzoonfelis
what is the natural host of cytauzoon felis
the bobcat
vector of cytauxoon felis
amblyomma americanum