Chapter 22 Echinoderms
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
phylogenetic position of echinoderm
deuterostome (anus before mouth)
distinguishing features
- "Spiny Skin"
- Exclusively marine
- Endoskeleton of calcareous plates connected by ligaments of "mutable collagenous tissue under neural control"
- (Penta)radial symmetry in most adults, bilateral larva
- Water vascular system
- Complete digestive system (in most)
- Respiration by various structures depending on class (most are dermal branchiae/papulae)
- Nervous system with circumoral ring and radial nerves; no distinct brain or ganglia, but sensory organs are chemoreceptors, podia, terminal tentacles, photoreceptors, and statocysts
-NO EXCRETORY SYSTEM
- Regeneration and autotomy
- Hemal system is reduced, more so for movement
5 classes and examples
Asteroids (sea star)
Echinoids (Sand dollar + heart urchin (irregular) , sea urchin)
Ophiuroid (brittle star and basket star),
Holthuroid (sea cucumbers),
Crinoid (feather star, sea lily)
pedicellariae
different types, but are either spines or ‘jaw’ structures'
body protection, defense of papullae, and sometimes food capture
papullae
dermal brachiae (skin gills)
respiration, and excretion of ammonia
water flow through vasc system
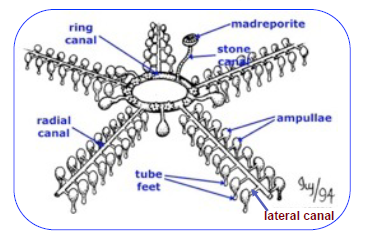
Madreporite, stone canal, ring canal, radial canal, lateral canal, ampullae, tube feet
purpose of the water vascular system
creates hydraulic system for
effective locomotion and food gathering / respiration / excretion
parts of water vascular system
madreporite: opening for water in the middle of the sea star, aboral side
stone canal: made of calcium, connects ring canal to madreporite
ring canal: distribute water around mid body and circulate around for beginning of legs
radial canal: extend straight down into legs
lateral canal: extend outward to sides of legs
ampullae: store water for tube feet
tube feet: locomotion, food gathering, etc.
sea star feeding behavior
complete digestive system
- Two part stomach: pyloric stomach (upper) & cardiac stomach (lower/muscular).
- When feeding, cardiac stomach is pushed out of mouth, ex. when eating a bivalve, podia will punch it until the shell cracks, then the water vascular system + catch collagen force cardiac stomach into crack and digest the insides
sea stars as a keystone species
Sea stars predate on mussels in eco systems. If the sea stars are removed, the mussels over indulge in their prey and expand their territory towards lower intertidal zones, reducing diversity and messing up ecological balance
Sea star development + reproduction
dioecious with external fertilization
2 types of bilateral larva (bipinnaria, brachiolaria), go through metamorphosis and end up as a pentaradial adult
autotomy and regeneration
self amputation in case of danger and regeneration occurs afterwards to 1. repair missing limb 2. asexually produce an organism
locomotion in brittle stars
use long legs to move instead of individual tube feet
locomotion in sea stars
use of tube feet instead of sectioned leg
sea star vs brittle star anatomy
Sea stars: Madreporite is located on aboral surface. Complete digestive system with both mouth & anus. Walk using tube feet, Central disc with rays, yes to external gills (papulae), yes to pedicellaria
Brittle stars: Madreporite is located on oral surface. Only has mouth & stomach. Tentacle feet instead of sucker feet, arms have articulated ossicles. 4 SHIELDS, internal gills (bursae), NO pedicellariae/papulae
what’s in the arm of a star fish?
(ambulacral groove surrounded by podia/tube feet + radial nerve at the end, gonads, and pyloric ceca (digestive fluid for extracellular digestion)
echinoid (general)
compact body, hard endoskeletal shell (TEST) with tight dermal ossicles and moveable spines
‘ball and socket’ spine
no arms, have ambularcral areas that have the pentaradial symmetry
omnivores
regular echinoid
sea urchin
Radial symmetry, hemispherical shape
Medium to long spines
Move with tube feet & spines
irregular echinoid
sand dollar, heart urchin
Secondary bilateral symmetry
Spines are usually very short
Move with spines
Aristotle Lantern
echinoid,
scrape algae off rocks & other surfaces, as well as biting & chewing prey.
Holothuroid
sea cucumber
elongated on oral-aboral axis
REDUCED OSSICLES= SOFT BODY
separated sexes, 1 gonad, external fertilization, larva = auricularia
respiratory tree: 2 long tubes that empties into cloaca, pumps sea water for respiration and excretion
repiration through skin + tube feet
Sea cucumber defense
Cuvierian tubules: attached to hind end. shoots them out when scared, sticky/slightly toxic. Clogs fish gills and bother predators so they'll leave.
Evisceration: expel guts (digestive & respiratory tree)
Crinoids
Oldest cousins of others
Feather stars and sea lillies
cirri for feather, stalk for lillies for support