Myers AP Psychology LEARNING
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:54 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
learning
a relatively permanent change in an organism's behavior due to experience
2
New cards
habituation
an organism's decreasing response to a stimulus with repeated exposure to it
3
New cards
associative learning
learning that certain events occur together.
4
New cards
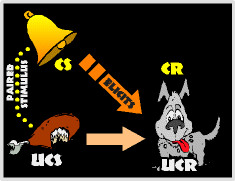
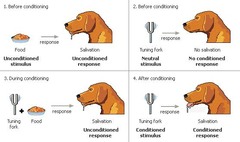
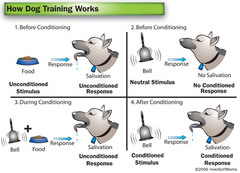
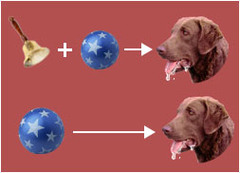
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
5
New cards
behaviorism
psychology: (1) should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes.

6
New cards
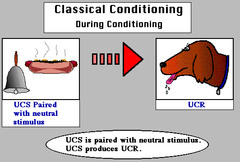
unconditioned response (UR)
the unlearned, naturally occurring reaction to US, such as salivation when food is in the mouth
7
New cards
unconditioned stimulus (US)
a stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a reaction (like food)
8
New cards
conditioned response (CR)
the learned reaction to a previously neutral (but now conditioned) stimulus (CS)

9
New cards
conditioned stimulus (CS)
an originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an US, comes to trigger a conditioned reaction
10
New cards
acquisition
the "learned" behavior or response

11
New cards
higher-order conditioning
a procedure in which the CS in one conditioning experience is paired with a new NS, creating a second (often weaker) CS.
12
New cards
extinction
the diminishing of a CR; when a response is no longer reinforced

13
New cards
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance, after a pause, of an extinguished CR

14
New cards
generalization
the tendency, once a response has been conditioned, for stimuli similar to the CS to elicit responses

15
New cards
discrimination
the learned ability to distinguish between a CS and stimuli that do not signal an US

16
New cards
learned helplessness
the hopelessness and passive resignation an animal or human learns when unable to avoid repeated aversive events

17
New cards
operant conditioning
a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished followed by a punisher
18
New cards
law of effect
Thorndike's principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, or where behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely

19
New cards
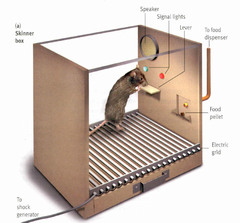
operant chamber
Skinner box containing a bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain food or water reinforce; attached devices record the animal's rate of bar pressing or key pecking

20
New cards
shaping
reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior

21
New cards
discriminative stimulus
a stimulus that elicits a response after association with reinforcement (in contrast to related stimuli not associated with reinforcement)

22
New cards
reinforcer
any event that strengthens the behavior it follows

23
New cards
positive reinforcement
increasing behaviors by presenting positive stimuli, such as food.

24
New cards
negative reinforcement
increasing behaviors by stopping or reducing negative stimuli, such as shock.

25
New cards
primary reinforce
an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need

26
New cards
continuous reinforcement
reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs

27
New cards
partial (intermittent) reinforcement
reinforcing a response only part of the time; results in slower acquisition of a response but much greater resistance to extinction than does continuous reinforcement

28
New cards
fixed-ratio schedule
a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses

29
New cards
variable-ratio schedule
a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses

30
New cards
fixed-interval schedule
a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed

31
New cards
variable-interval schedule
a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals

32
New cards
punishment
an event that decreases the behavior that it follows

33
New cards
cognitive map
a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. (For example, after exploring a maze, rats act as if they have learned a cognitive map of it)
34
New cards
latent learning
learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it LATER
35
New cards
insight
a sudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem

36
New cards
intrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior effectively for its own sake; INSIDE

37
New cards
extrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishment, OUTSIDE
38
New cards
modeling
the process of observing and imitating a specific behavior

39
New cards
mirror neurons
frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions or when observing another doing so. The brain's mirroring of another's actions may enable imitation and empath
40
New cards
prosocial behavior
positive, constructive, helpful behavior. The opposite of antisocial behavior

41
New cards
little albert
subject in John Watson's experiment, proved classical conditioning principles, especially the generalization of fear

42
New cards
Albert Bandura
researcher famous for work in observational or social learning including the famous Bobo doll experiment

43
New cards
John Garcia
Researched taste aversion. Showed that when rats ate a novel substance before being nauseated by a drug or radiation, they developed a conditioned taste aversion for the substance.

44
New cards
Ivan Pavlov
Russian physiologist who observed conditioned salivary responses in dogs (1849-1936)
45
New cards
B.F. Skinner
he is famous for use of his operant conditioning aparatus which he used to study schedules of reinforcement on pidgeons and rats.

46
New cards
John Watson
behaviorist; famous for Little Albert study in which a baby was taught to fear a white rat

47
New cards
biofeedback
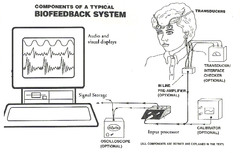
a technique that trains people to improve their health by controlling certain bodily processes that normally happen involuntarily, such as heart rate, blood pressure, muscle tension, and skin temperature.
48
New cards
aversion theory
an aversive (causing a strong feeling of dislike or disgust) stimulus is paired with an undesirable behavior in order to reduce or eliminate that behavior.

49
New cards
neutral stimulus (NS)
environmental factor that doesn't elicit a CR until it is repeatedly paired with the US (ex/ bell in Pavlov experiment)
50
New cards
token economy
object or point reward system used in jail, school, & at Chuck E Cheese
51
New cards
cognitive learning
the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language
52
New cards
Stimulus
a signal to which an organism responds
53
New cards
reinforcement
in operant conditioning, any event that strengthens the behavior it follows
54
New cards
conditioned reinforcer
a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer; also known as a secondary reinforcer
55
New cards
reinforcement schedule
the frequency and regularity with which rewards are offered; they can be based on a number of target behaviors (ratio) or on a time interval (interval); types include: fixed-ratio, variable-ratio, fixed-interval, and variable-interval
56
New cards
respondent behavior
behavior that occurs as an automatic response to some stimulus
57
New cards
Coping
alleviating stress using emotional, cognitive, or behavioral methods
58
New cards
learned helplessness
the hopelessness and passive resignation an animal or human learns when unable to avoid repeated aversive events
59
New cards
external locus of control
the perception that chance or outside forces beyond your personal control determine your fate.
60
New cards
internal locus of control
the perception that you control your own fate
61
New cards
self-control
the ability to control impulses and delay short-term gratification for greater long-term rewards
62
New cards
observational learning
learning by observing others; also called social learning