Physics AQA Topic 3 (Internal energy and transfers)
1/12
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is internal energy of a substance
The energy stored by the particles - the sum of total kinetic and potential energies that make up the system
How does heating affect the energy of a substance
Heating transfers energy to the substance and increases the energy of the particles that make up the substance
What two things can heating a substance do
Raise its temperature and change the state of the substance
What three factors determine the temperature change of a system
Mass of a substance being heated, type of material (specific heat capacity) and the energy inputted into the system
State the equation used to calculate the temperature change when a substance is heated
∆E = mc∆θ (Change in energy = mass x specific heat capacity x change in temperature)
What are the units for the equation used to calculate the temperature change
Change in thermal energy = joules (J), mass = kilograms (kg), specific heat capacity = joules per kilogram degree Celsius (J/kg^C), temperature change = degrees Celsius (^C)
Define specific heat capacity
The amount of energy needed to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1^C
Describe how the internal energy and temperature of a substance changes when a change of state occurs
The internal energy of the substance will be increased or decreased - the temperature of the substance will remain constant
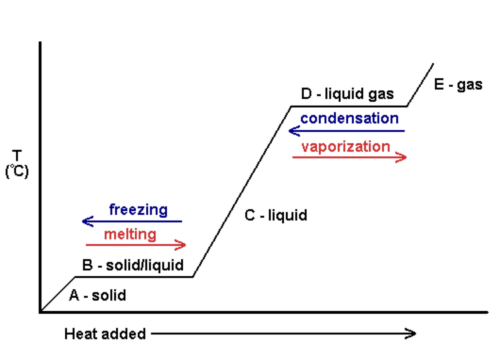
Define specific latent heat
The amount of energy needed to change the state of 1kg of a substance with no change in temperature
State the equation for the energy required to change state
E = mL (energy to change state = mass x specific latent heat)
Give the units for the equation for the energy required to change state
Energy = joules (J), mass = kilogram (kg), specific latent heat (J/kg)
What is the specific latent heat of fusion
The energy required to change 1kg of a substance from solid state to liquid state without a change in temperature
What is the specific latent heat of vaporisation
The energy required to change 1kg of a substance from liquid state to gas state without a change in temperature