Anatomy Chapter 1
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
Anatomy
the structure
Physiology
The function
Complementarity
How the structure and function complement each other
Levels of organization
Chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Integumentary System
System including hair, nails, and skin. Protects deeper tissues and synthesizes Vitamin D and houses pain/pressure receptors and sweat/oil glands
Skeletal system
System including the joints and bones. Protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement. Blood cells are formed within bones and bones store minerals
Muscular system
System allowing manipulation of environment, motion, and facial expression. Maintains posture and produces heat.
Nervous system
System including brain, nerves, and spinal cord. Fast-acting control system of the body. Responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands
Endocrine system
System including the pineal and pituitary glands, thyroid gland, thymus, adrenal gland, pancreas, testes, and ovaries. Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes including growth, reproduction, and nutrient use by body cells.
Cardiovascular system
System including heart and blood vessels. Blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, etc. Heart pumps blood.
Lymphatic system/Immunity
System including red bone marrow, the thymus, lymphatic vessels, thoractic duct, spleen, and lymph nodes. Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood. Disposes of debris in the lymphatic system and houses white blood cells involved in immunity.
Respiratory system
System including nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lung, and bronchus. Keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. Gaseous exchanges occur through walls of air sacs of the lungs.
Digestive system
System including oral cavity, esophagus, liver, stomach, small/large intestine, rectum, and anus. Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells. Indigestible food are eliminated as feces
Urinary system
System including kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra. Elimates nitrogenous waste from the body. Regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-based balance of the blood.
Male reproductive system
System including prostate gland, penis, testis, ductus deferens, scrotum. Overall function is production of offspring. Testes produce sperm and male sex hormone, and male ducts and glands aid in delivery of sperm to the female reproductive tract.
Female reproductive system
System including mammary glands, ovary, uterine tube, uterus, vagina. Ovaries produce eggs and female sex hormones. The remaining female structures serve as sites for fertilization and development of the fetus. Mammary glands of female breasts produce milk to nourish the newborn.
Homeostasis
Maintains internal stability when there is external change.
Homeostatic imbalance
Things that take body out of norm (ex. diseases)
Negative feedback mechanism
Output shuts off stimulus. Reduces to steady state.
Pancreas
Releases insulin if there is high blood glucose, and releases glucagon if there is low blood sugar (negative feedback)
Positive feedback mechanism
Output turns on stimulus. Takes further and further from steady state and will suddenly end. (childbirth, breast feeding, blood clotting)
Anatomical position
Body erect, palms forward
Superior/cephalad
Toward the top of head
Inferior/caudal
Toward the feet
Anterior/ventral
Front
Posterior/dorsal
Back
Medial
toward midline
Lateral
Away from midline
Intermediate
in between
Proximal
closer to center of body or the origin
Distal
further from center of body or the origin
Superficial/external
toward or at body surface
Deep/internal
away from body surface; internal
Frontal/coronal
Anterior to posterior plane. Vertically cuts through torso
Sagittal/midsagittal
Left to right plane
Transverse
through torso, horizontally cut plane
Dorsal cavity
Cavity containing cranial cavity (brain) and vertebral cavity (spinal cord)
Thoracic cavity
Cavity containing superior mediastinum (includes thorax), plural cavity (includes lungs), and pericardial cavity with mediastinum (includes heart)
Diaphram
Separates thoracic from abdominal cavity
Ventral body cavity
Cavity including the thoracic cavity and abdomino-pelvic cavity.
Abdomino-pelvic cavity
Cavity including abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
Abdominal cavity
Cavity containing digestive viscera
Pelvic cavity
Cavity containing urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
Other body cavities
Orbital cavity (eye socket), nasal cavity (nose), oral cavity (mouth), tongue cavity (tongue), middle ear cavity (middle ear)
Synovial cavity
Cavity in joint between neck vertebrate
Serosa
Tissue layer that lines body cavities and organs. Dual layer membrane
Peritoneum
Serosa that lines abdominal cavity
Pericardium
Serosa that lines heart
Pleura
Serosa that lines lungs and chest cavity
Parietal serosa
Layer that lines body cavity
Visceral serosa
Layer that lines body organ
Serous fluid
Fluid in between parietal and visceral layers to reduce friction
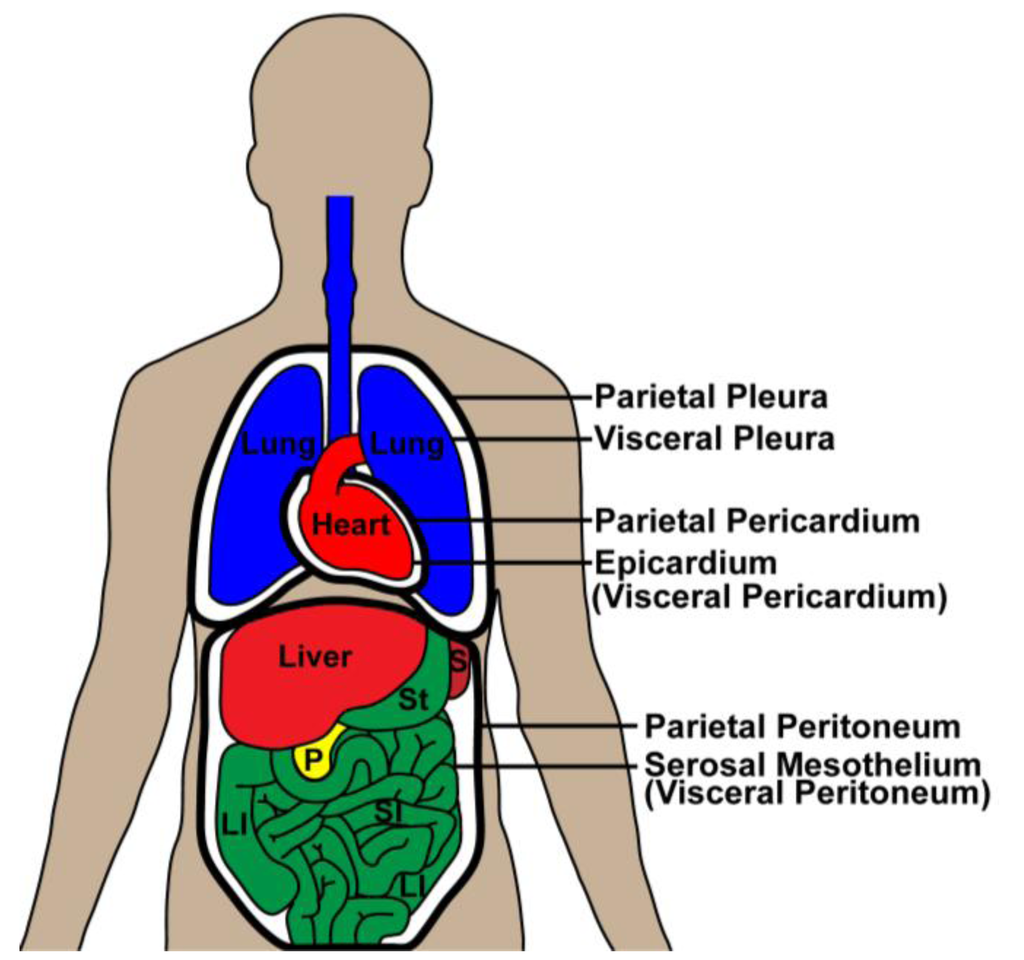
Parietal peritoneum
Front part of serosa that lines abdominal cavity
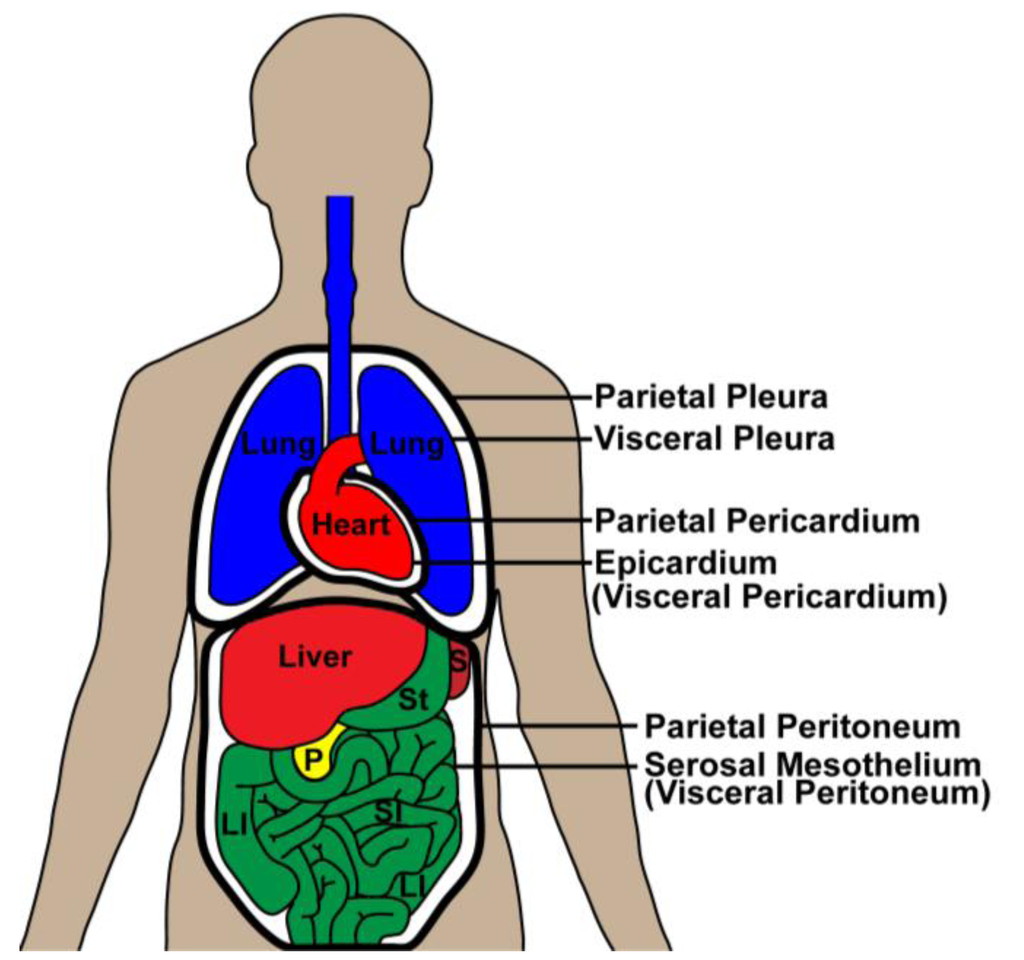
Visceral peritoneum
Back part of serosa that lines abdominal organs
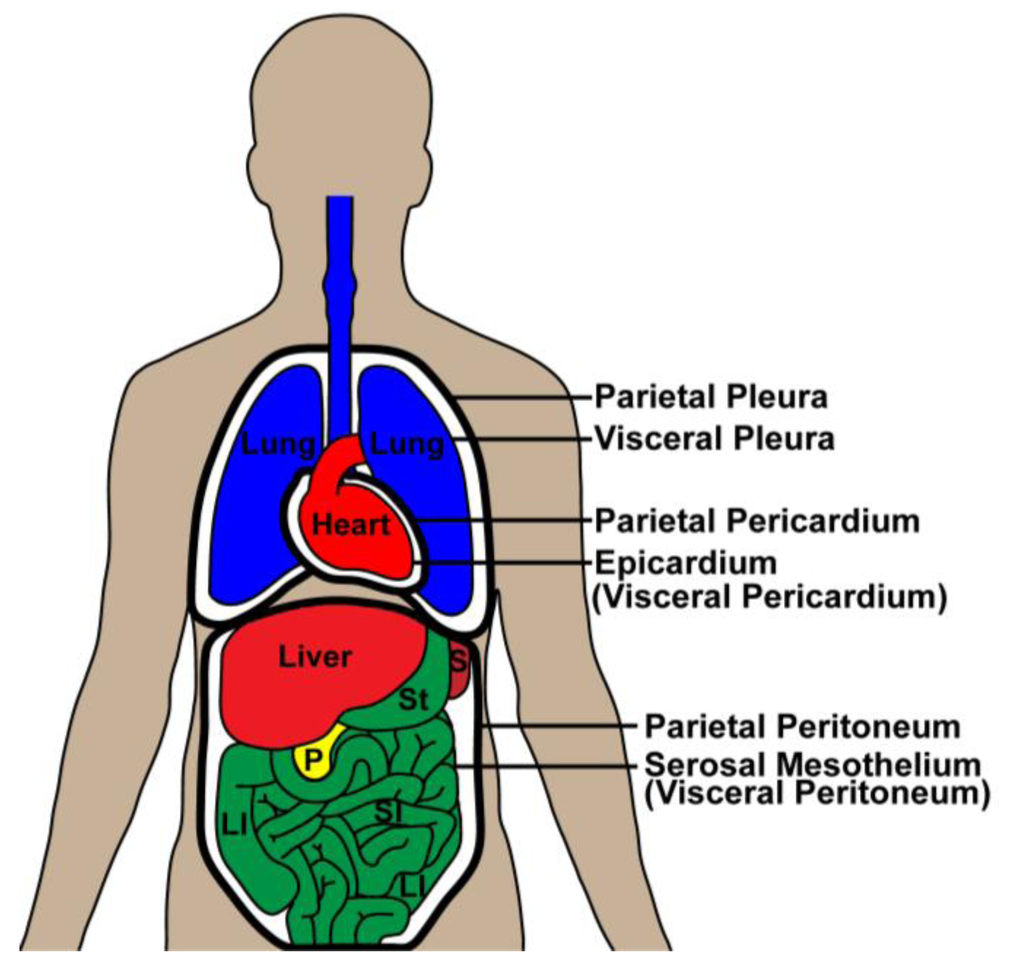
Parietal pericardium
Front part of serosa that lines heart cavity
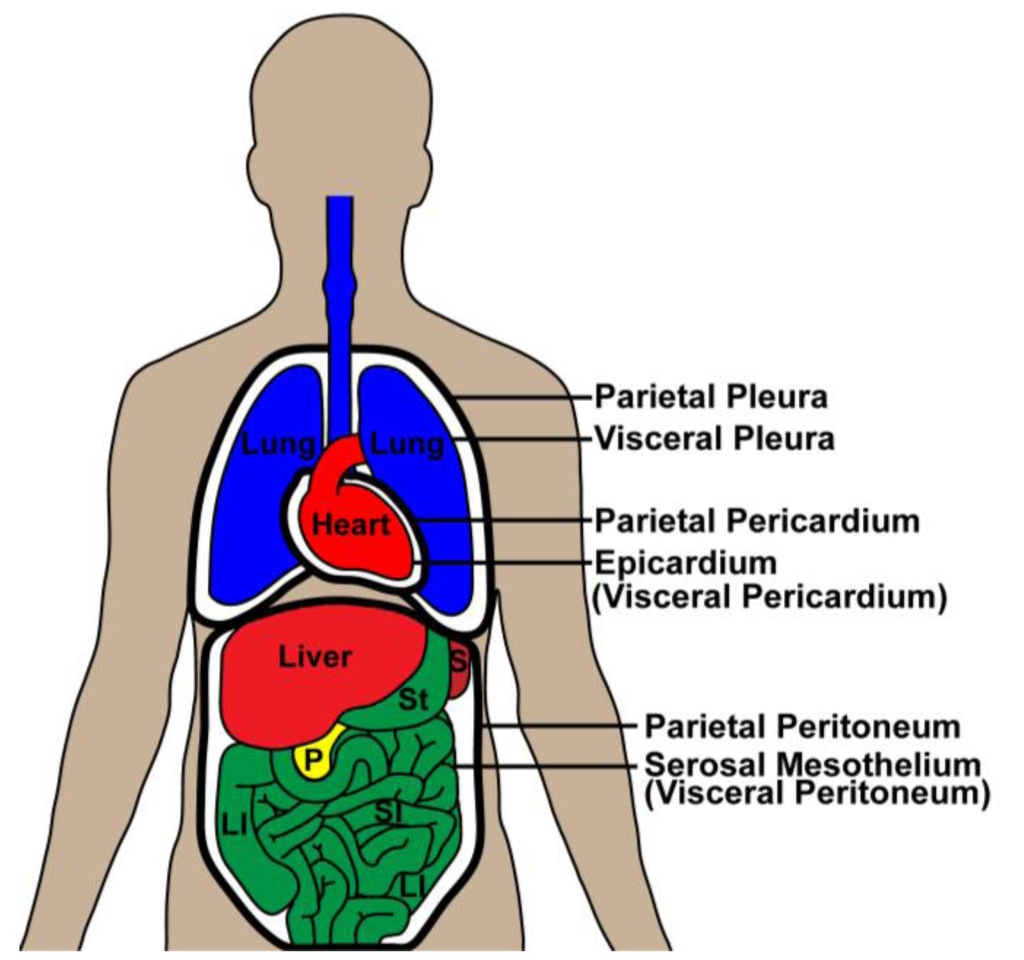
Viceral pericardium
Back part of serosa that lines actual heart organ
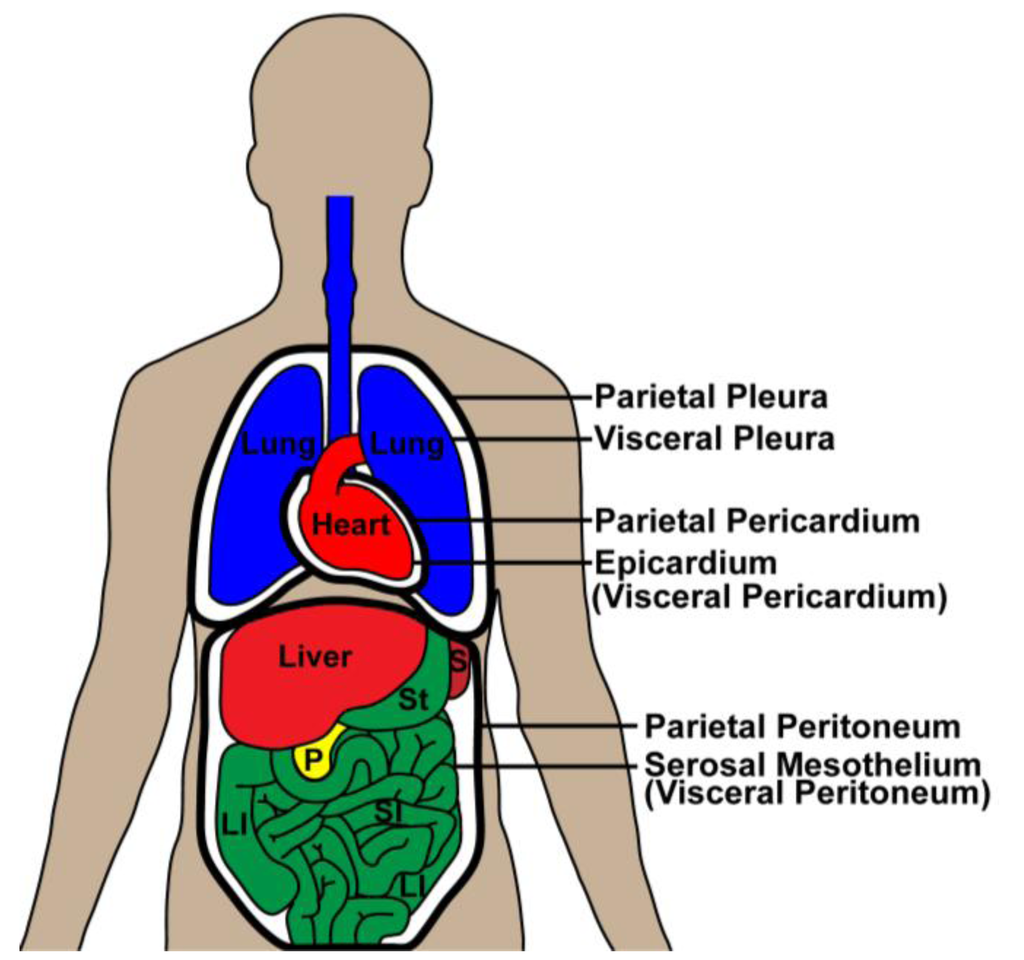
Parietal pleura
Front part of serosa that lines lung and chest cavity
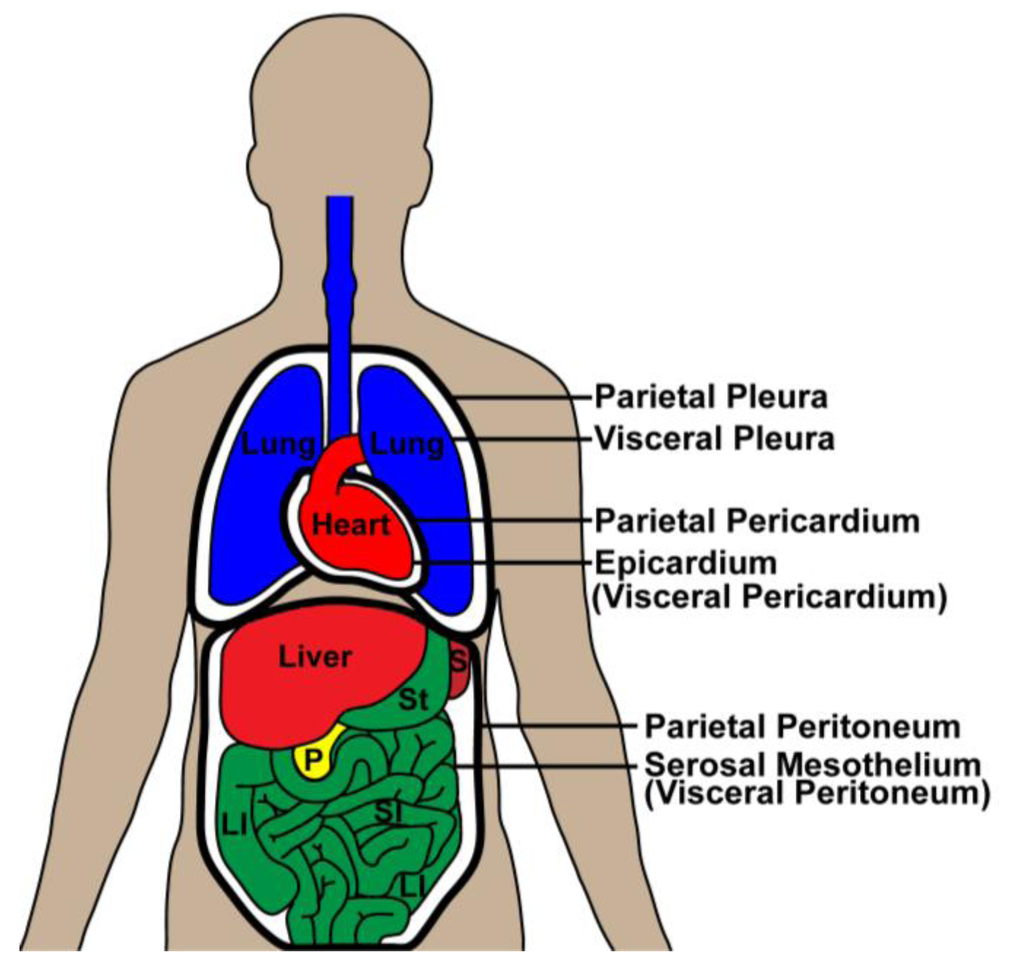
Visceral pleura
Back part of serosa that lines actual lungs
Quadrants of abdominal cavity
Right upper quadrant (RUQ), left upper quadrant (LUQ), right lower quadrant (RLQ), left lower quadrant (LLQ)
Right hypochondriac region
Top right region of abdomen (liver, gallblader)
Epigastric region
Top middle region of abdomen (stomach)
Left hypochondriac
Top left region of abdomen (diaphragm, spleen)
Right lumbar region
Middle right region of abdomen (ascending colon of large intestine)
Umbilical region
Middle middle region of abdomen (small intestine, transverse colon of large intenstine)
Left lumbar region
Middle left region of abdomen (descending colon of large intestine)
Right iliac (inguinal) region
Bottom right region of abdomen (cecum, appendix)
Hypogastric (pubic region)
Bottom middle region of abdomen (urinary bladder)
Left iliac (inguinal) region
Bottom left region of abdomen (initial part of sigmoid colon)
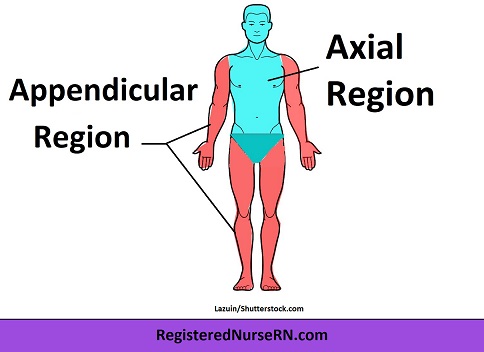
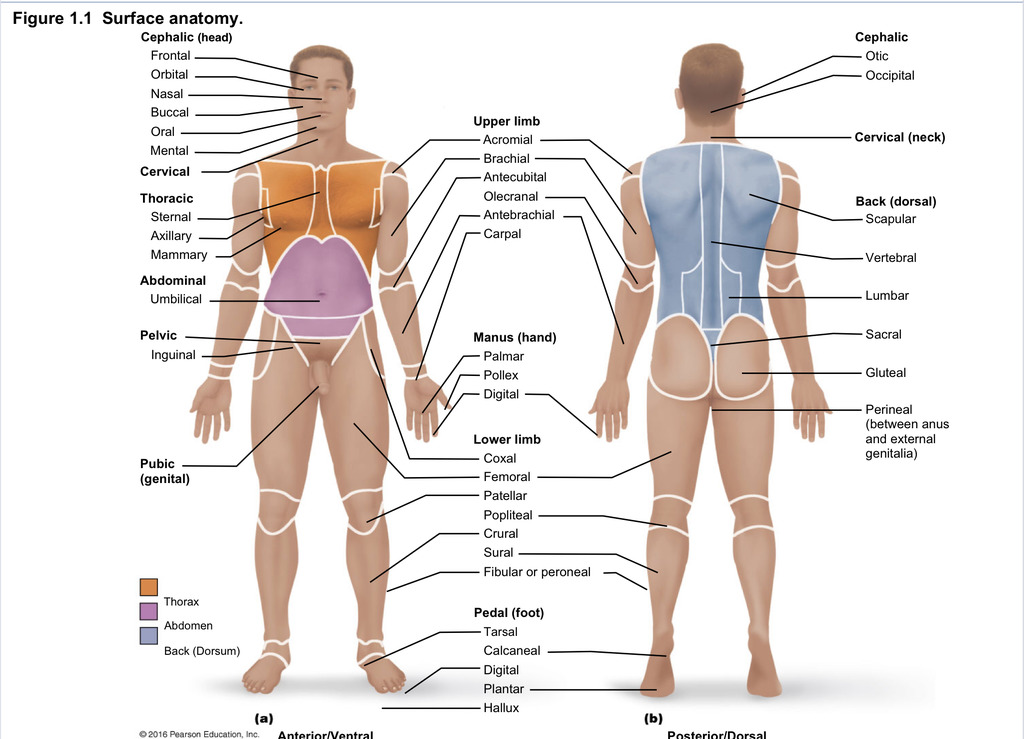
Axial region
Region of body describing the head, neck, and trunk
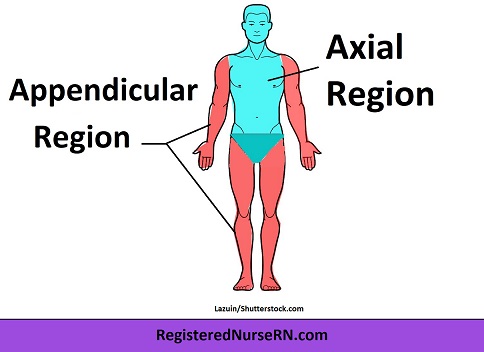
Appendicular region
Region of body describing limbs
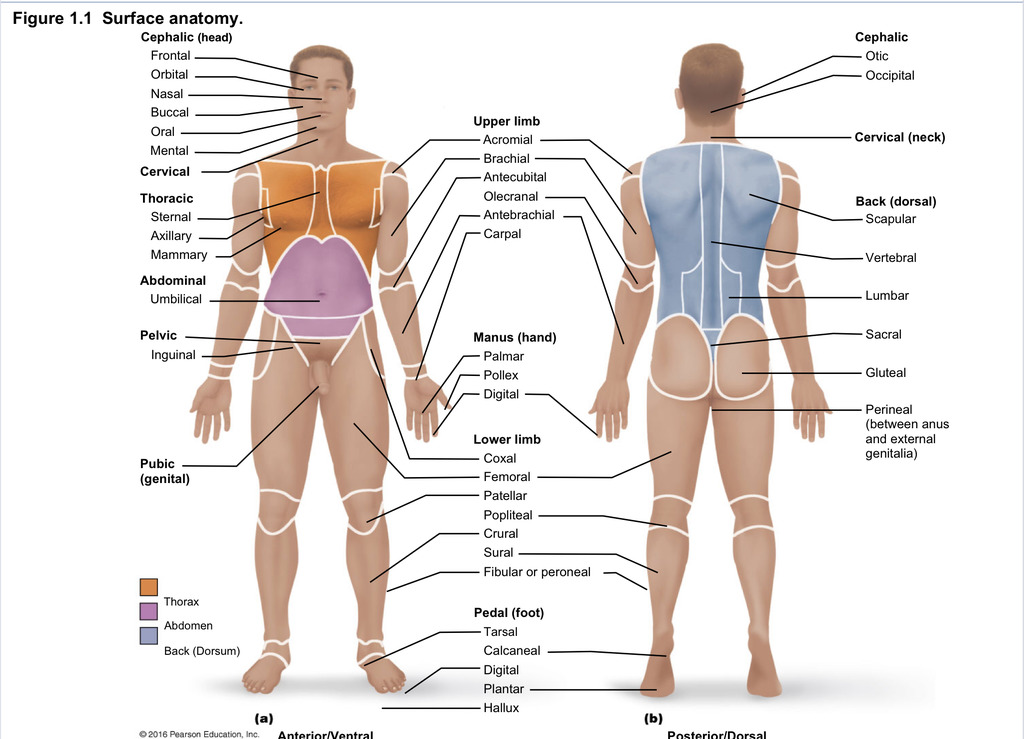
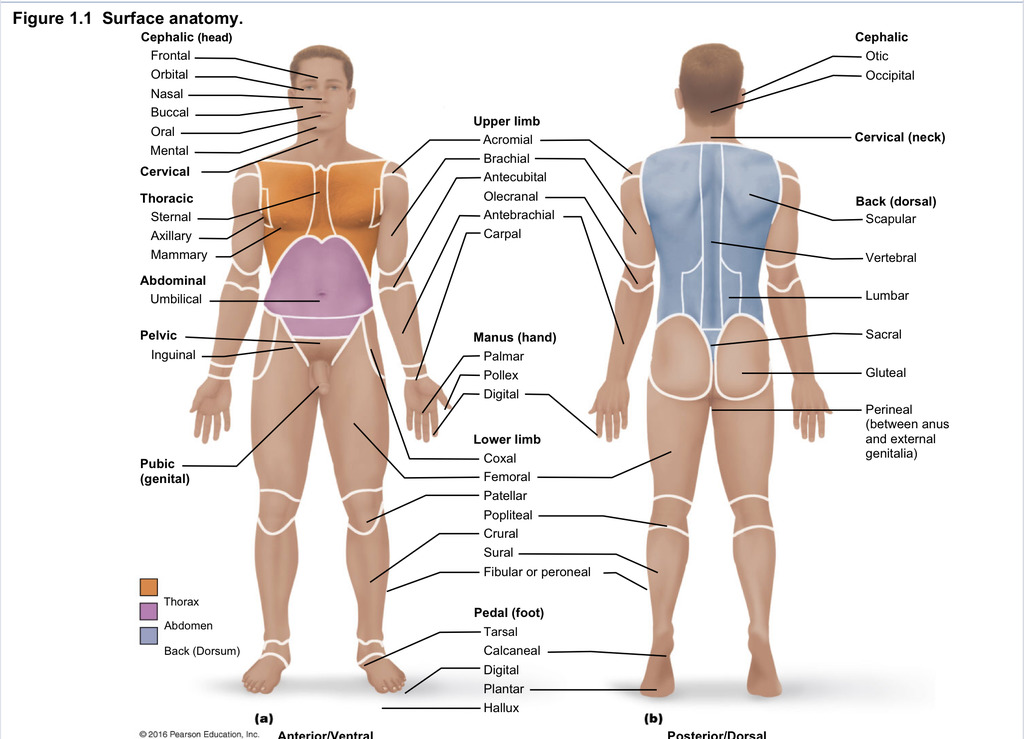
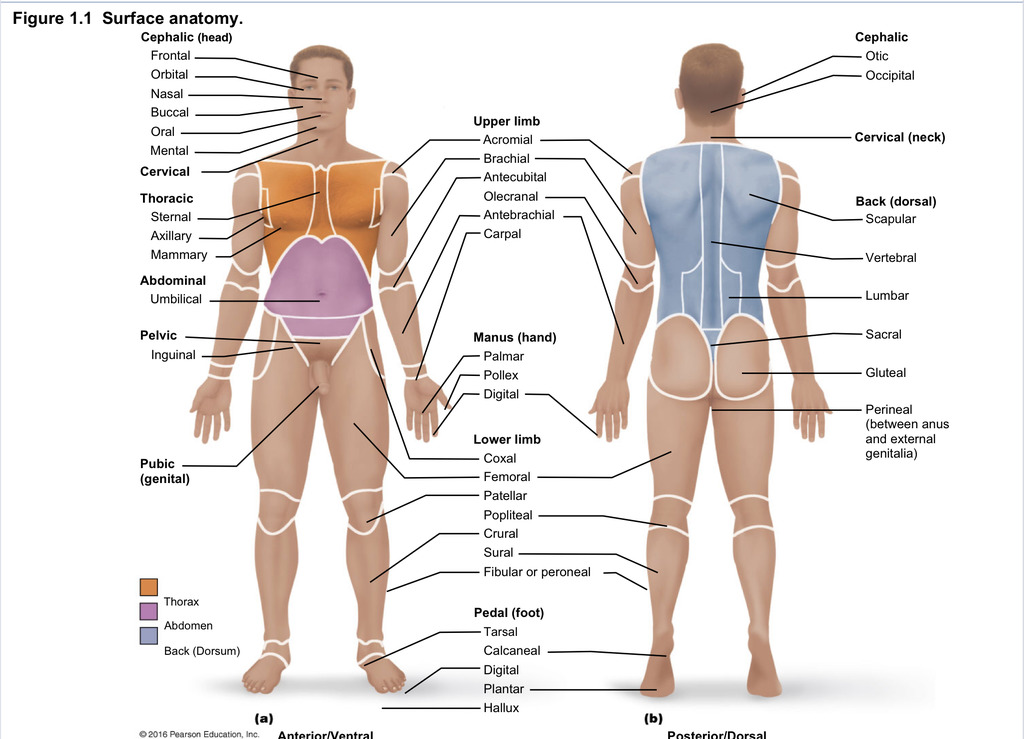
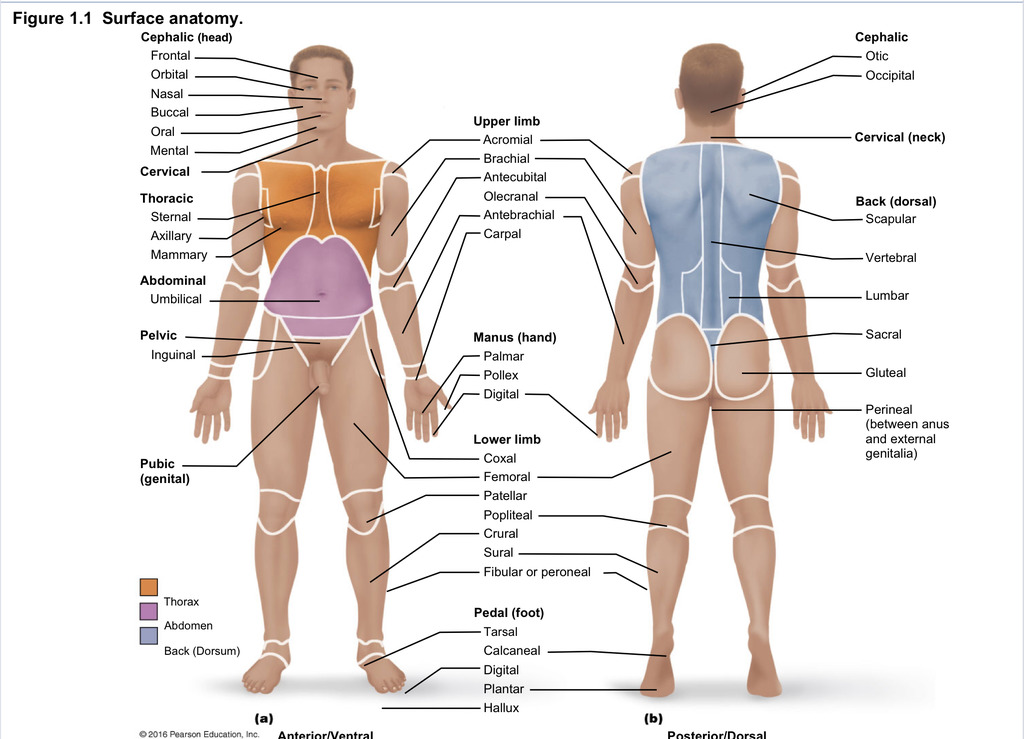
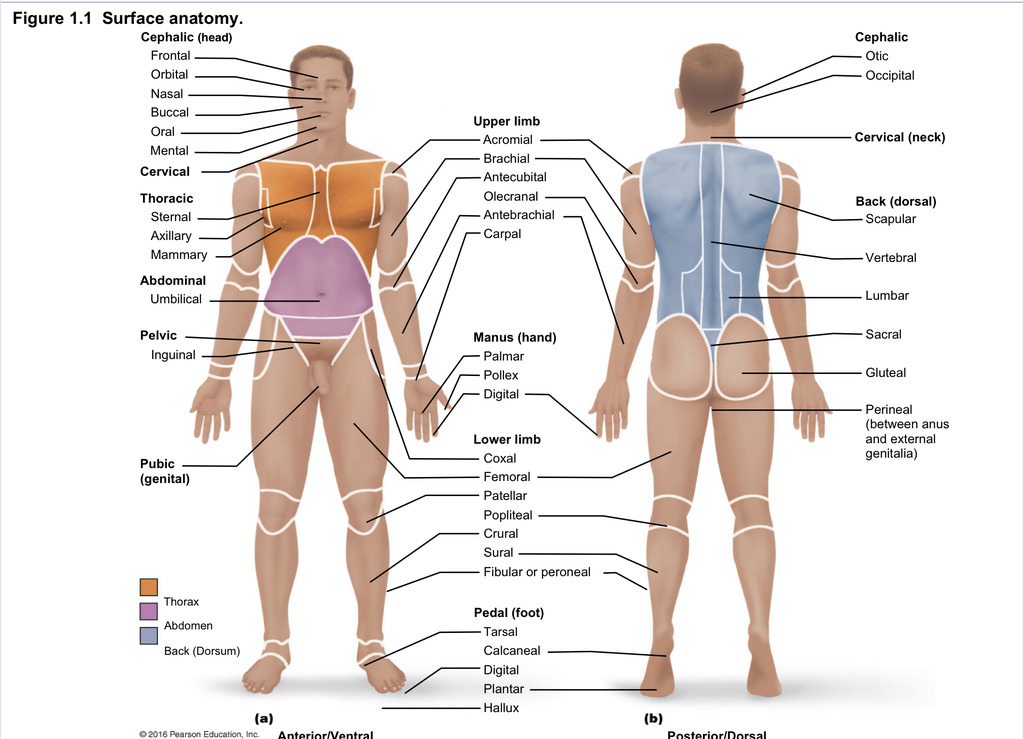
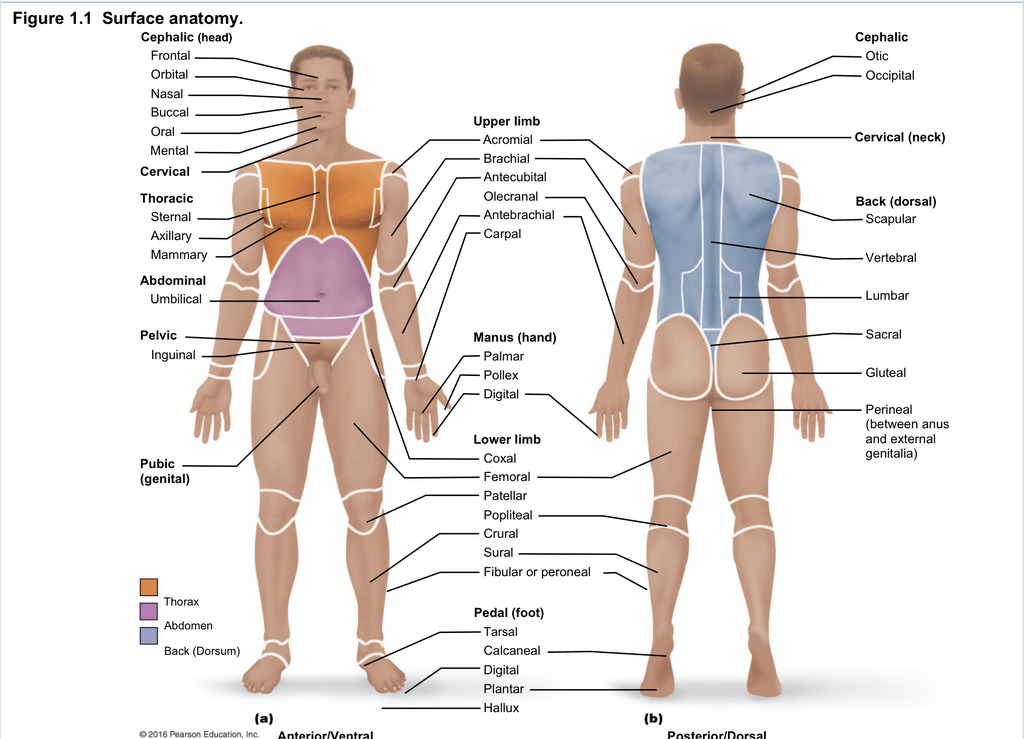
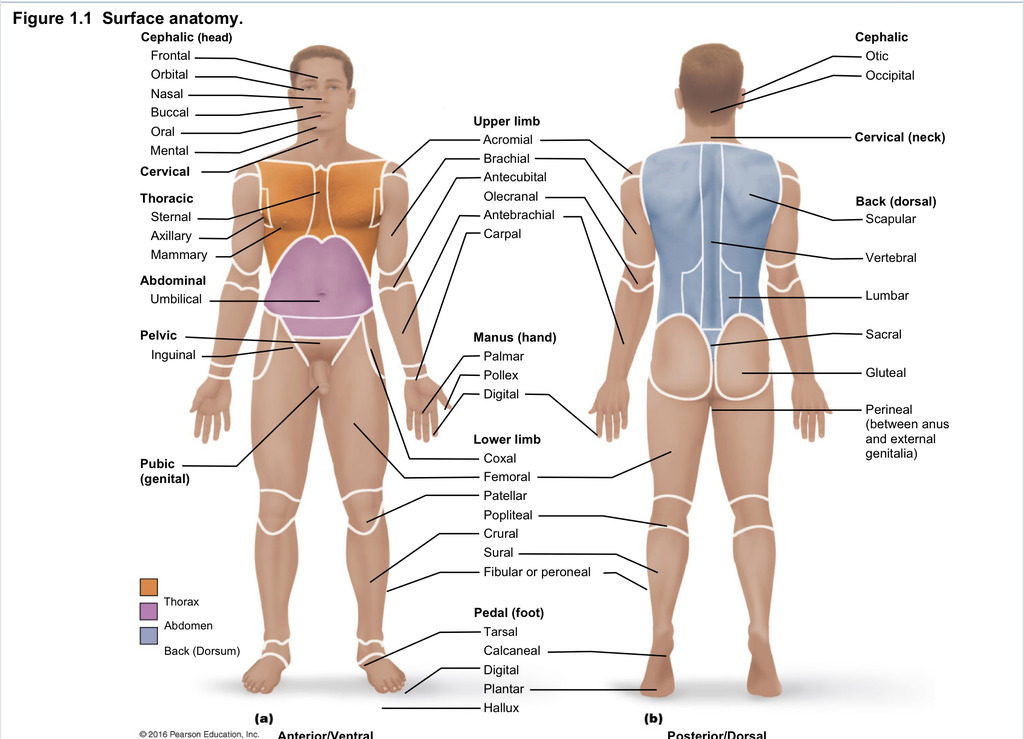
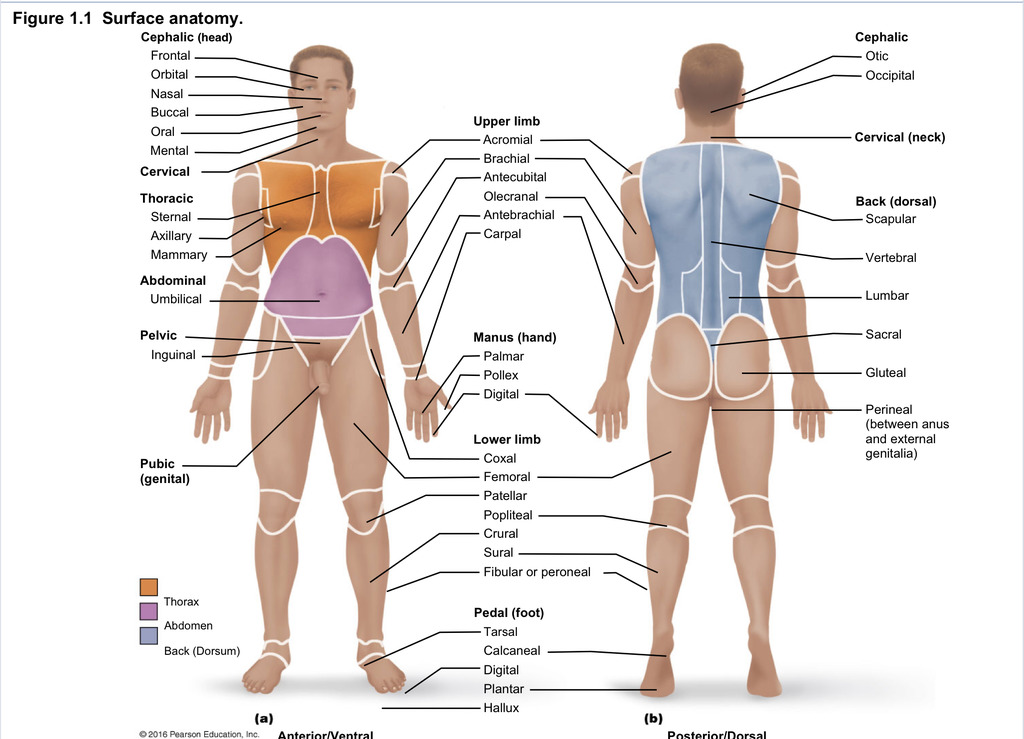
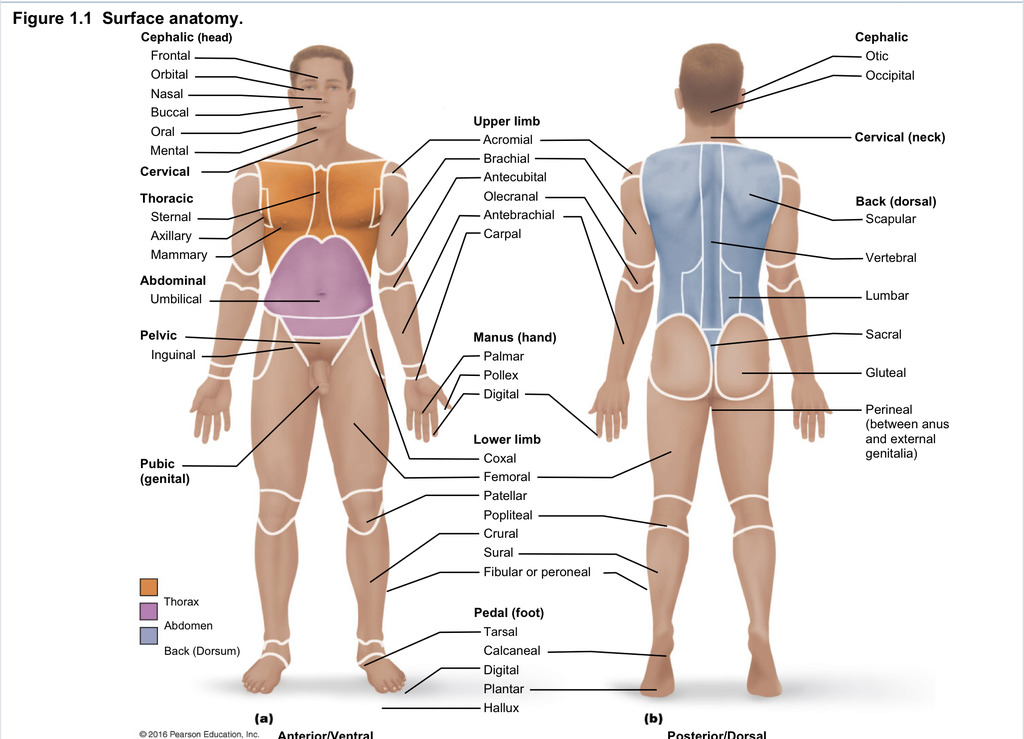
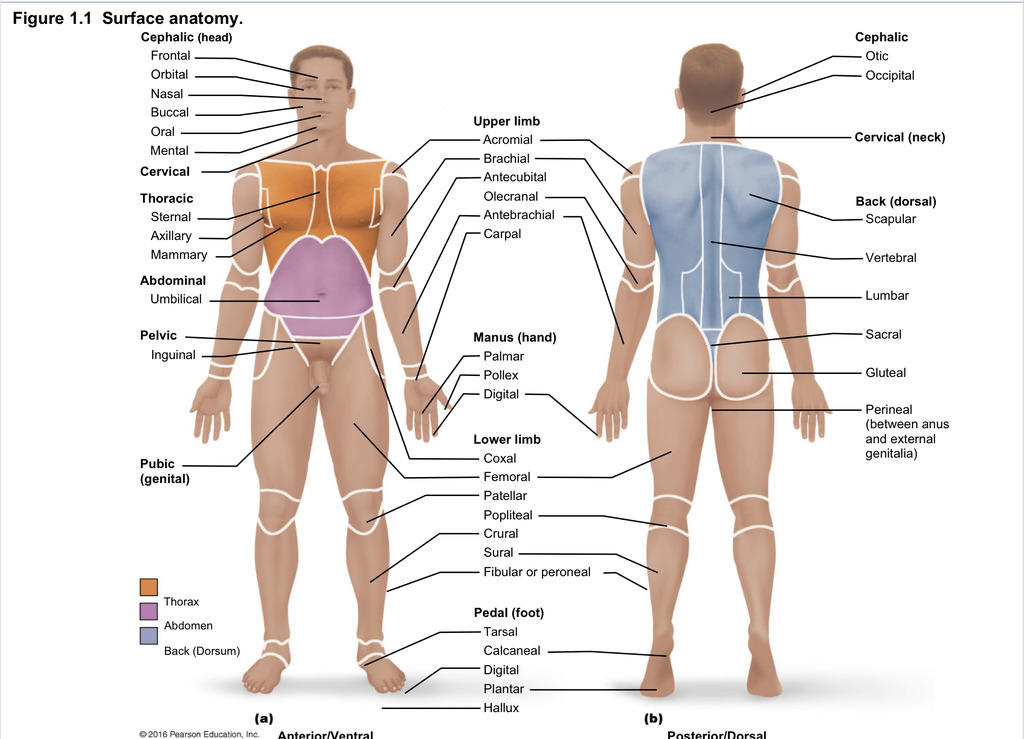
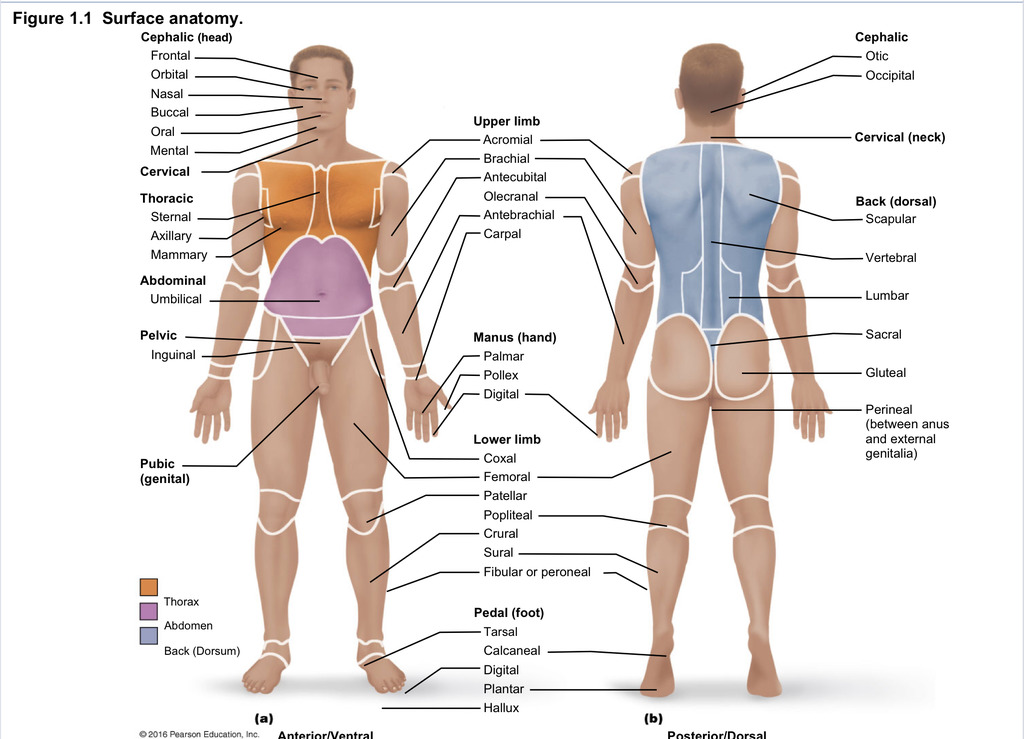
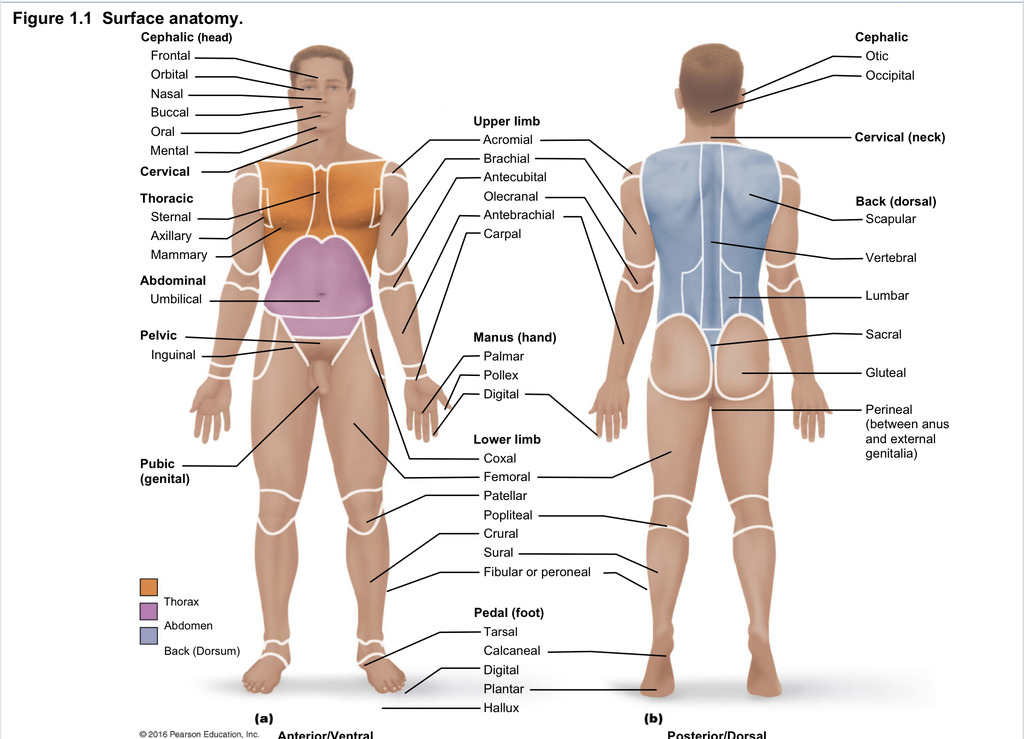
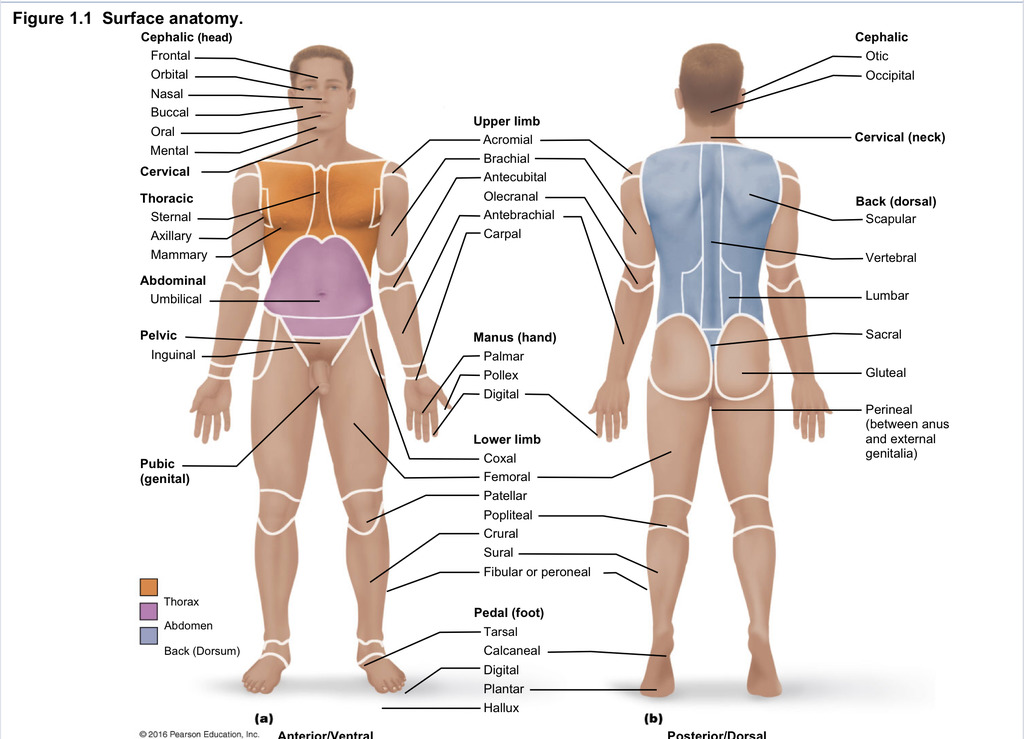
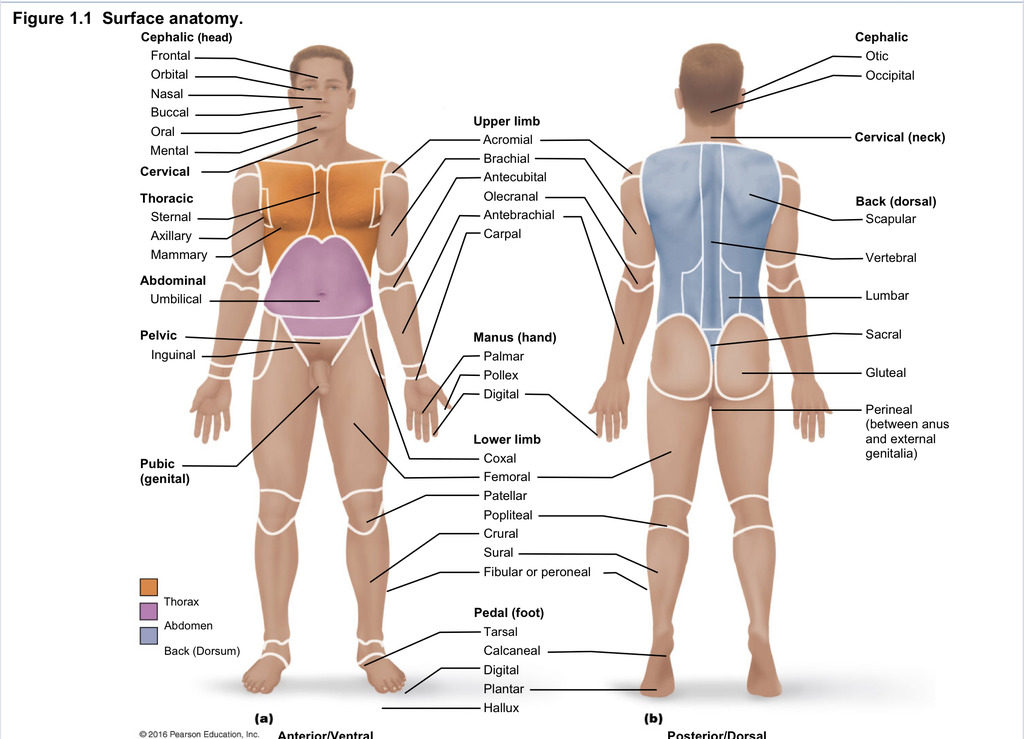
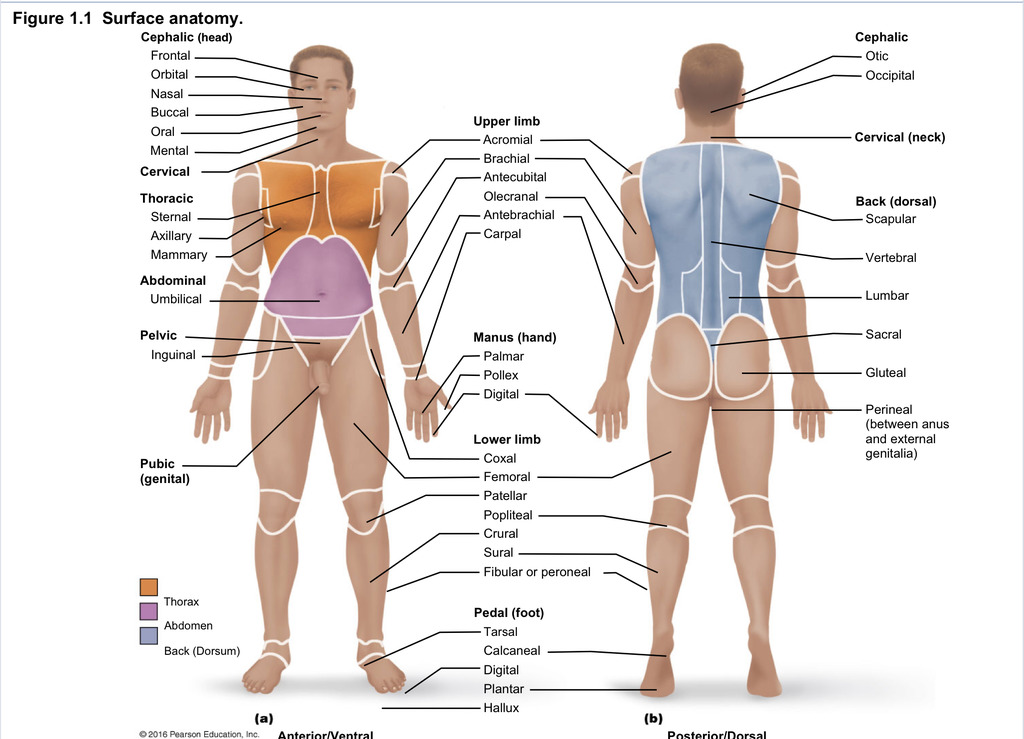
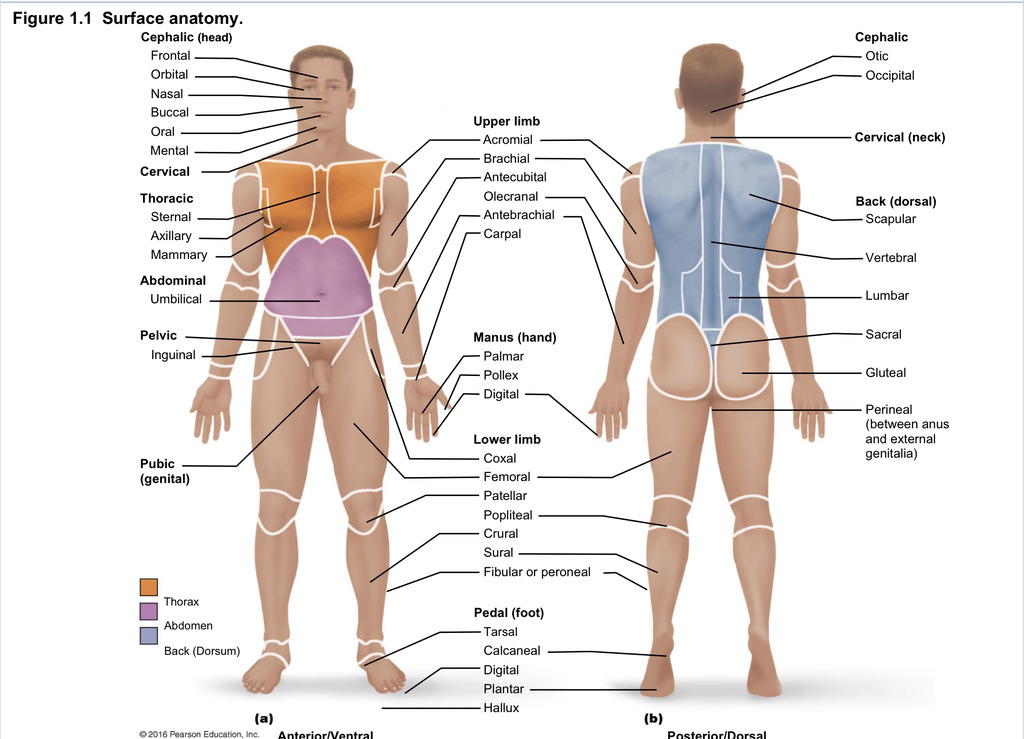
Back (dorsal)
Part of axial region describing back (including scapular, vertebral, lumber, sacral, gluteal, perineal)
Cephalic
Part of axial region describing head (including frontal, orbital, nasal, oral, mental, otic, occupital)
Cervical
Part of axial region including neck
Thoracic
Part of axial region including sternal, axillary, mammary
Abdominal
Part of axial region including the umbilical
Pelvic
Part of axial region including genital area
Upper limb
Part of appendicular region describing upper part of arm (includes acromial, brachial, antecubital, olecranal, antebrachial, carpal)
Manus
Part of appendicular region describing hand (pollex, metacarpal, palmar, digits)
Lower limb
Part of appendicular region describing lower limb (coxal (hip), femoral (thigh), patellar (kneecap), popliteal (behind kene), crucal (leg), sural (calf), fibular or peroneal (side of leg)
Pedal
Part of appendicular region describing foot (including tarsal (ankle), calcaneal (heel), metatarsal (foot front), digital (toes), plantar (sole), hallux (big toe))
Abdominal
Located below the ribs and above the hips
Acromial
Point of the shoulder
Antebrachial
Forearm
Antecubital
Anterior surface of the elbow
Axillary
Armpit
Brachial
arm (upper portion of upper limb)
Buccal
Cheek
Calcaneal
heel of foot
Carpal
wrist
Cephalic
Head
Cervical
Neck
coxal
hip
Crural
leg
digital
fingers or toes
Femoral
thigh
fibular (peroneal)
side of leg
Frontal
forehead
gluteal
buttox
hallux
great toe
Inguinal
groin