Botany Vocab (Biology 2)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/29
Last updated 11:51 PM on 11/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
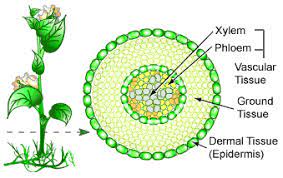
Vascular tissue
tissue that conducts water and allows for the movement of fluids against gravity
2
New cards
Xylem
the type of tissue in vascular plants that provides support and conducts both water and nutrients from the roots
3
New cards
Phloem
tissue that carries organic and inorganic nutrients in any direction depending on the plant's needs
4
New cards
Seed
embryo of a plant
5
New cards
Pollen grain
the structure that contains the male gametophyte of seed plants
6
New cards
Pollination
the transfer of pollen from male reproductive structures (the anthem) to the tip of the female reproductive structure (the pistil) of a flower in angiosperms or to ovule in gymnosperms.
7
New cards
Seed coat
the protective, outer covering of a seed
8
New cards
Pollen tube
a tubular structure that grows from a pollen grain, enters the embryo sac, and allows the male reproductive cells to move to the ovule
9
New cards
Ovule
a structure that's in the ovary of a seed plant that contains an embryo sac and that develops into a seed after fertilization
10
New cards
Ovary
the lower parts of a pistil that produces eggs in ovules/ base of carpel, contains eggs
11
New cards
Fruit
ripened ovary containing angiosperm, a mature plant ovary; the organ in which the seeds are enclosed
12
New cards
Cotyledon
embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants
13
New cards
Apical meristem
the growing region at the tips of stems and roots in plants
14
New cards
Root hair
an extension of the epidermis of a root that increases the root's surface area for absorption
15
New cards
Root cap
the protective layer of cells that covers the tip of a root
16
New cards
Mesophyll
in leaves, the tissue between epidermal layers where photosynthesis occurs
17
New cards
Stoma
one of many openings in a leaf or stem of a plant that enables gas exchange to occur
18
New cards
Transpiration
the process by which plants release water vapor into the air through stomata
19
New cards
Guard Cell
one of a pair of specialized cells that border a stoma and regulate gas exchange
20
New cards
adhesion
the attractive force of one substance to another. Water is sticky and clumps together into drops because of its cohesive properties.
21
New cards
Capillary action
the process of liquid flowing in a narrow space in opposition to gravity through adhesion and cohesion
22
New cards
Dormancy
a state in which seeds, spores, bulbs, and other reproductive organs stop growth and development and reduce their development
23
New cards
Germination
growth that begins from an embryo into a mature plant
24
New cards
Hormone
a chemical substance that controls plant growth and development
25
New cards
Receptor
a specialized sensory nerve that reacts to certain stimuli and work as detectors
26
New cards
Auxin
a plant hormone that is produced in the apical meristem and transported downward to stimulate elongation
27
New cards
Cytokinin
a class of hormones that stimulate cell division, growth of lateral buds, and cause dormant seeds to sprout
28
New cards
Gibberellin
a plant hormone that produces a dramatic increase in size of stems and flowers, and the overall plant size
29
New cards
Abscisic acid
a hormone that helps regulate the growth of buds and the germination of seeds
30
New cards
Cortex
the primary tissue located in the epidermis