PHYS 100: Ch. 6
1/124
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
A favorite college prank involves simultaneously flushing several toilets while someone is in the shower. The cold water pressure to the shower drops and the shower becomes very hot. Why does the cold water pressure suddenly drop?
Flushing makes the water in the pipes flow faster, dropping the pressure and there is more water output
On hot days in the city, people sometimes open up fire hydrants and play in the water. Why does this activity reduce the water pressure in nearby hydrants?
The water in the pipes flows faster, dropping the pressure.
Why does a relatively modest narrowing of the coronary arteries, the blood vessels supplying the blood to the heart, cause a dramatic drop in the amount of blood flowing through them?
the blood flow is proportional to the diameter of the blood vessel to the fourth power
Why does hot maple syrup pour more easily than cold maple syrup?
it has a lower viscosity at a higher temperature
Why is "molasses in January" slower than "molasses in July," at least in the northern hemisphere?
its viscosity is higher at lower temperatures
Why is it so difficult to squeeze ketchup through a very small hole in its packet?
The rate at which ketchup flows is proportional to the diameter of the hole to the fourth power
A baker is decorating a cake by squeezing frosting out of a sealed paper cone with the tip cut off. If the baker makes the hole at the tip of the cone too small, it's extremely difficult to get any frosting to flow out of it. Why?
frosting has a high viscosity and squeezing it through the narrow pipe requires a large pressure difference across the pipe
Why is the wind stronger several meters above a flat field than it is just above the ground?
The air just above the ground is kept from moving by viscous forces.
Pedestrians on the surface of a wind-swept bridge don’t feel the full intensity of the wind because the air is moving relatively slowly near the bridge’s surface. Explain this effect in terms of a boundary layer.
The air just above the bridge is kept from moving by viscous forces, forming a boundary layer. Viscous forces act like friction of the air with itself.
An electric valve controls the water for the lawn sprinklers in your backyard. Why do the pipes in your home shake whenever this valve suddenly stops the water but not when the valve suddenly starts the water?
When the valve closes the water flow stops suddenly which causes water hammer, but when the valve opens the flow does not instantly reach full speed.
If you drop a full can of applesauce and it strikes a cement floor squarely with its flat bottom, what happens to the pressures at the top and bottom of the can?
The pressure at the top is lower than the pressure at the bottom
moving water experiences __ forces that oppose its motion relative to a hose
frictional
most water in a hose never actually touches the hose; forces have to occur __ the water, the water must exert frictional forces on ITSELF
within
what are the internal frictional forces that water experiences called?
viscous forces
viscous forces
forces that appear whenever one layer of a fluid tries to slide across another layer of that fluid
the measure of resistance to relative motion within a fluid is called…
viscosity
the hotter a fluid is, the __ viscosity it has.
less
hotter fluids have less viscosity because their molecules have more __ energy and as a result, bonds are broken more easily.
thermal
water flow rate is __ proportional to diameter
directly
water flow rate is __ proportional to length (and viscosity)
Inversely
if fluid has to travel a large length will it experience more or less friction?
more
Poiseuille’s Law
volume = pi x pressure difference x pipe diameter^4 / 128 x pipe length x fluid viscosity
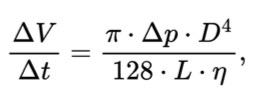
what law does the equation show?
poiseuille’s law
what does poiseuille’s law state?
flow rate is proportional to the radius to the fourth power
even in steady state flow, water can accelerate but for it to accelerate it must involve __
turning
acceleration toward the side (turning) requires:
obstacles, involves pressure imbalances, and changes in speed
bending the flow of water requires a __ imbalance
pressure
toward what pressure does water accelerate to?
low
on the outside of the bend, the pressure is __ while the speed is __
high; low
on the inside of the bend, the pressure is __ while the speed is __
low; high
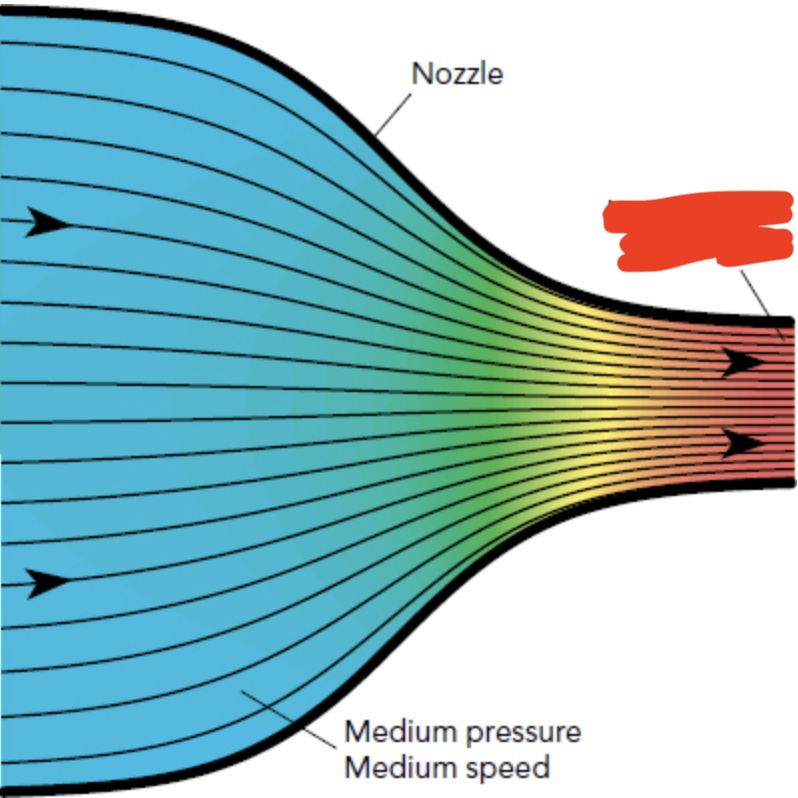
what is the pressure and speed like at the end of the nozzle (the red colored area)?
low pressure and high speed
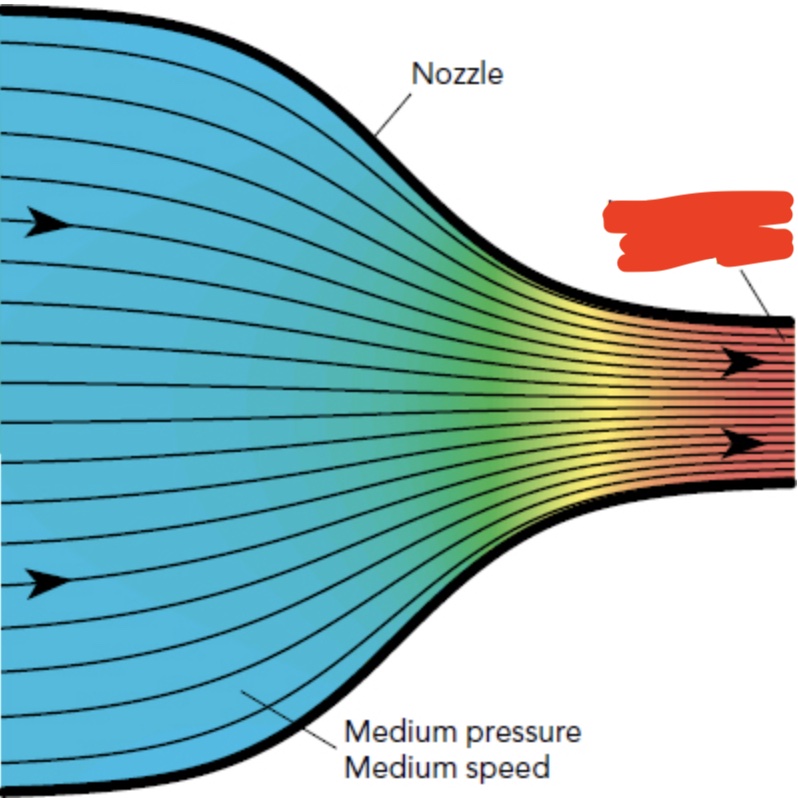
what would speed and pressure be if the color were purple/violet and the streamlines were extremely far apart? (in other words, what is the pressure and speed like at the start of the nozzle?)
low speed and high pressure
flow type (laminar or turbulent) depends on the __ number
reynolds
equation for reynolds number
density x obstacle length x speed / viscosity
the more viscous water is, the more difficult it is to __ through a hose
flow
a longer hose has __ viscous forces to slow water down
more
if you have a hose and let the water flow out without your thumb blocking it or without a nozzle, why does the water pour out gently?
the water will move quickly out and encounter large viscous forces which causes most of the waters ordered energy to be wasted as thermal energy. the water pours out gently.
why does water spray out if you block the hose’s opening with your thumb?
water travels slowly and encounters smaller viscous forces which helps it keep most of its ordered energy and be at high pressure when it meets your thumb. the high pressure water accelerates to great speed as it passes through the small opening and sprays out.
laminar flow
the smooth, silent flow that is characterized by simple streamlines; adjacent portions of fluid have same velocity
when viscosity dominates the fluids motion what is the flow like?
laminar
turbulent flow
noisy flow in which adjacent regions on fluid soon become separated from one another as they move independently in unpredictable directions
what is the flow when inertia dominates the fluids motion?
turbulent
viscous forces keep nearby regions of fluid moving together. Would high viscosity would favor laminar or turbulent flow?
laminar
why does honey follow more of a laminar flow than water?
honey has a higher viscosity than water
whether flow is laminar or turbulent depends on several characteristics of the fluid and its environment, name the 4.
the fluids viscosity, the fluids speed past a stationary obstacle, the size of the obstacle the fluid encounters, fluids density
2 nearby regions of a fluid can become separated and it becomes harder for viscous fluids to keep them together if the fluid moves (a) faster, or (b) slower?
(a) faster
the __ the obstacle a fluid encounters, the more likely it is to cause turbulence because viscous forces are unable to keep the fluid ordered over such a long distance.
larger
how does a fluid respond to viscous fluids if it is denser? its flow is more likely to turn laminar or turbulent?
it responds less to viscous fluids and it is likely to turn turbulent
as reynolds number increases, flow goes from __-dominated to __-dominated (laminar to turbulent)
viscous; inertia
turbulence usually appears when reynolds number exceeds…
2300
what is a vortex?
a common feature of turbulent flow, it is a swirling region of fluid that moves in a circle around the central cavity
when a spoon stirs coffee quickly, the spoon moves fast enough through the fluid to create turbulence forms, this is an example of…
vortex
turbulent flow exhibits chaotic behavior or…
chaos, you can’t predict exactly where any drop of water will go
water hammer
sound heard when the flow of water is suddenly stopped
forces exerted on a ball by the air because of their relative motion are called…
aerodynamic forces
2 types of aerodynamic forces
drag and lift
drag forces push the ball __
downwind
lift forces push the ball to the __
sides
airflow around a slow moving ball is laminar or turbulent?
laminar
air speed __ in the front and behind the ball but the pressure __
decreases; rises
in a slow ball, air speed __ at the sides of the ball and the pressure __
increases; decreases
an air trail behind a ball that is smooth with no turbulence is known as…
wake
because of the symmetrical arrangement of a slow moving ball, the only aerodynamic force acting on the ball is…
viscous drag
when air flowing around a ball is turbulent, the air pressure distribution is no longer symmetrical and the ball experiences what drag?
pressure drag
pressure drag
downstream force exerted by unbalanced pressures in the moving air
if air has a low reynolds number, airflow is laminar because __ dominated over its __
viscosity; inertia
air’s inertia dominated viscosity and air flow is turbulent if reynolds number is (a) high, or (b) low
(a) high
Air effected by ball’s surface is the…
boundary layer
the boundary layer is laminar or turbulent in a fast moving ball?
turbulent
Why do balls experience air resistance?
Balls interact with and transfer momentum to air
surface friction causes __ drag
viscous
turbulence causes __ drag
pressure
why do some balls have dimples?
to produce a turbulent boundary layer
in a fast ball, a small __ forms behind the ball
wake
in a fast ball, the ball experiences a small __ drag force
pressure
how does a turbulent boundary layer affect a ball?
there is more ordered energy and creates more forward momentum for the ball to travel farther
pressure __ in the front of a fast ball while it __ on the sides
rises; drops
why do spinning balls curve in flight?
they experience magnus force and wake deflection force
magnus force
Turning surface pushes/pulls on the air flow
when does wake deflection force appear?
when ball's fast rotation deforms the wake that is created behind it and a high reynolds number
airflow bends __ above a frisbee
inward
there is __ pressure but __ speed above a frisbee
low; high
airflow bends __ below frisbee
outward
there is __ pressure but __ speed below a frisbee
high; low
what causes a frisbee to lift?
pressure imbalance
Airplanes use the __ to support themselves
air
what do airplanes need to stay aloft?
airspeed
Airplanes seem to follow their __, up or down
nose
how does an airplane support itself in air?
it deflects air downward and the air pushes it upward
when a plane is in the air, there is an __ pressure force on the wing and the wing transfers downward __ to the air.
upward; momentum
How does the airplane “lift off” the runway?
The airplane sheds a vortex and is lifted upward.
Why does plane tilt up to rise; down to descend?
The wing’s angle of attack affects its lift
A wing’s lift depends on what 2 things?
the shape of its airfoil and its angle of attack
angle of attack
the angle at which a wing approaches the onrushing air
greater angle of attack causes greater __
lift
Why are there different wing shapes?
Airspeed and performance influence wing design
Asymmetric airfoils produce large lifts and are well-suited to __-speed flight
low
Symmetric airfoils produce small lifts and are well suited to __-speed flight
high
too great of an angle of attack causes
stalling and severe pressure drag appears
when the boundary layer stalls, it comes to a stop and thereby spoils __ __ flow
steady state