Astrophysics 02 - Optical Telescopes
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Explain how refracting telescopes work.
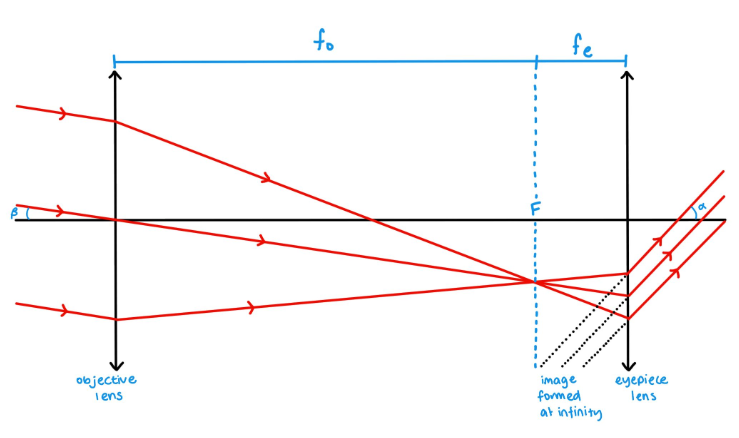
Refracting telescopes consist of two lenses. The objective lens converges light from the distant object, and focuses it onto a point in the focal plane, and the eyepiece lens is positioned so its focal plane lines up with that of the objective lens. It produces a magnified image at infinity.
Define magnifying power.
The magnifying power of an optical telescope is the ratio of the focal lengths of the objective and eyepiece lenses.
It is also the ratio of the angles subtending the image and the object.
Give the two equations for magnifying power of an optical telescope.
magnifying power = focal length of the objective lens / focal length of the eyepiece lens
m = fo / fe
magnifying power = angle subtending the image / angle subtending the object
m = α / β
Give the lens equation for a telescope.
For a very distance object:
(1/u → 0)
1/f = 1/v
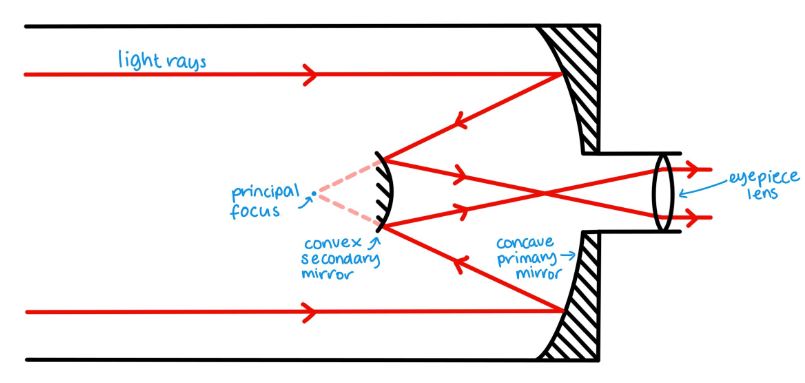
How do reflecting telescopes work?
Use mirrors (and lenses) to focus light.
Define Spherical Abberation.
When the curvature of a mirror is imperfect, so light is focused to different points.
How can spherical abberation be reduced?
Use a parabolic mirror.
Draw a diagram of a cassegrain arrangement reflecting telescope.
Explain Chromatic Abberation.
Light refracting by different amounts depending on its wavelength, causing different colours to focus in different points, causing blurring.
How can chromatic abberation be reduced?
Use a larger lens and an apperture, only allowing light to pass through the centre of the lens, or filter out all but one wavelength of light.
Explain how a CCD works.
Photons of light are incident on silicon in the CCD, causing electrons to be liberated.
These electrons are stored to be read back later.
Give some differences between the eye and a CCD.
The eye has a low quantum efficiency (percentage of incident photons detected), whereas CCDs have a high quantum efficiency.
CCDs can detect a much wider spectrum than just visible light like the eye.
CCDs have a spatial resolution of 10 μm whereas the eye has a spatial resolution of 100 μm.
CCDs require additional equipment to use and must be placed in the correct location.
CCDs produce digital images which can be stored and shared.