Abdominal Disorders in Critically Ill Patients
1/214
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
215 Terms
Liver Disorders
Conditions affecting liver function and structure.
Cirrhosis
Chronic liver inflammation leading to structural changes.
Pancreatic Disorders
Conditions impacting pancreatic function.
Pancreatitis
Inflammation of the pancreas, causing abdominal pain.
HHS
Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State, severe diabetes complication.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Conditions affecting the GI tract.
Right Upper Quadrant
Abdominal area where the liver is located.
Lobules
Functional units of the liver containing hepatocytes.
Hepatocytes
Liver cells responsible for metabolic functions.
Portal Triad
Structure including portal vein, hepatic artery, bile duct.
Kupffer Cells
Liver macrophages that phagocytize debris and bacteria.
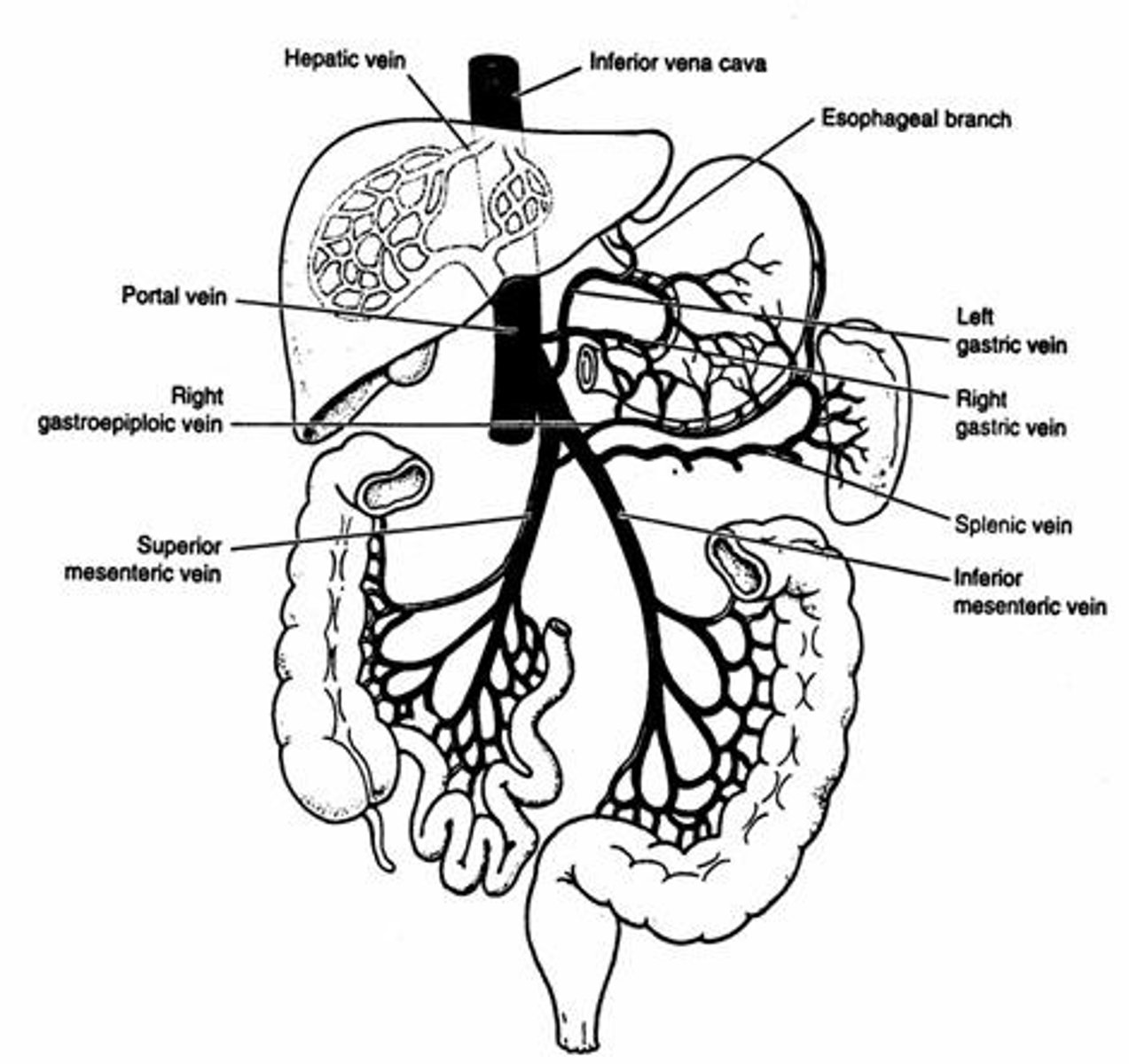
Portal Vein
Carries venous blood from GI tract to liver.
Common Hepatic Artery
Supplies arterial blood to the liver.
Hepatic Vein
Drains blood from the liver to the vena cava.
Albumin
Plasma protein maintaining oncotic pressure.
Glycogenesis
Conversion of glucose to glycogen in liver.
Glycogenolysis
Breakdown of glycogen to glucose in liver.
Bilirubin
Byproduct of RBC degradation, elevated in liver dysfunction.
Ammonia
Toxin from protein metabolism, detoxified by liver.
Fat Metabolism
Liver processes fats, synthesizes cholesterol and phospholipids.
Fibrous Tissue
Irreversible scarring in cirrhosis affecting liver function.
Chronic Alcohol Abuse
Primary cause of cirrhosis and liver damage.
Liver Failure
Severe dysfunction leading to loss of liver function.
Portal Hypertension
Increased pressure in the portal venous system.
Intrahepatic Vascular Resistance
Resistance within liver vessels causing blood flow obstruction.
Fatty Deposits
Lipids obstructing veins, causing portal hypertension.
Venous Congestion
Back pressure leading to varicose veins formation.
Varices
Dilated veins in esophagus, stomach, or rectum.
Nutrient Shunting
Redirection of blood away from the liver.
Poor Metabolism
Inefficient processing of nutrients, drugs, toxins.
AST & ALT
Liver enzymes indicating liver dysfunction when elevated.
Unconjugated Bilirubin
Bilirubin not processed by the liver, causing jaundice.
Increased Ammonia
Result of poor protein breakdown, indicating liver failure.
Decreased Albumin
Low protein levels affecting osmotic pressure.
Increased PT/PTT
Prolonged clotting times indicating bleeding risk.
Edema
Swelling due to decreased colloid osmotic pressure.
Jaundice
Yellowing of skin due to high bilirubin levels.
Cognitive Changes
Altered mental state due to liver dysfunction.
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Neurological decline from toxin accumulation.
Asterixis
Hand flapping indicating early hepatic encephalopathy.
Fluid Overload Monitoring
Assessing for weight gain and hemodynamic stability.
Daily Weights
Tracking weight changes to monitor fluid retention.
Abdominal Girth Measurement
Assessing ascites by measuring waist circumference.
Fall Precautions
Safety measures to prevent patient falls.
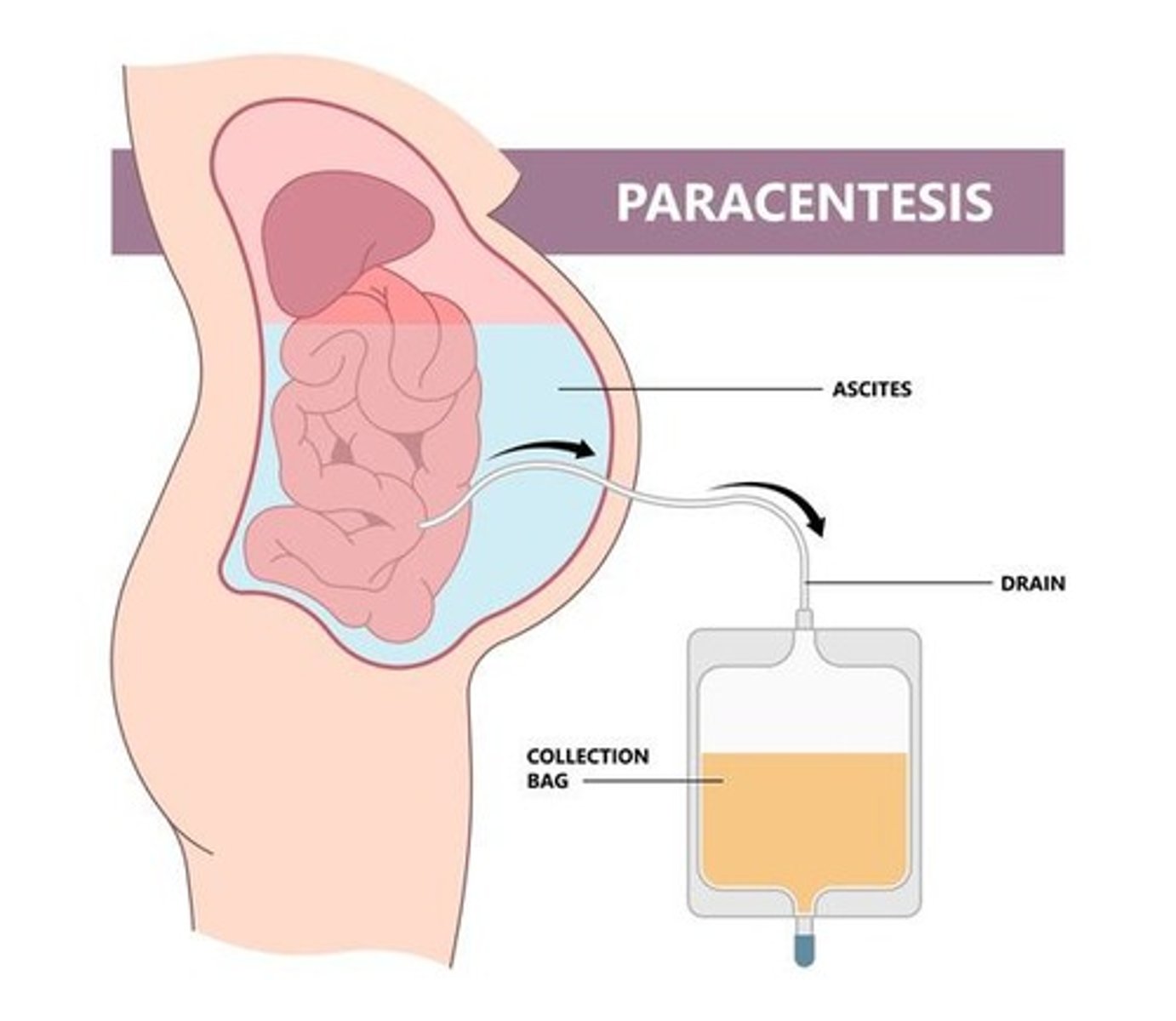
Ascites
Fluid accumulation in the peritoneum causing abdominal swelling.
Colloid Osmotic Pressure
Pressure exerted by plasma proteins preventing fluid leakage.
Lactulose
Osmotic agent that clears ammonia from the gut.
Neomycin
Antibiotic used to reduce gut bacterial action.
Xifaxan
Antibiotic that targets gut bacteria, reducing ammonia.
Aldosterone
Hormone that promotes sodium and water retention.
ADH
Hormone that regulates water balance in the body.
Diuretics
Medications that promote fluid excretion from the body.
Spironolactone
Aldosterone antagonist used to treat ascites.
Furosemide
Loop diuretic often combined with spironolactone.
Paracentesis
Procedure to remove fluid from the peritoneal cavity.
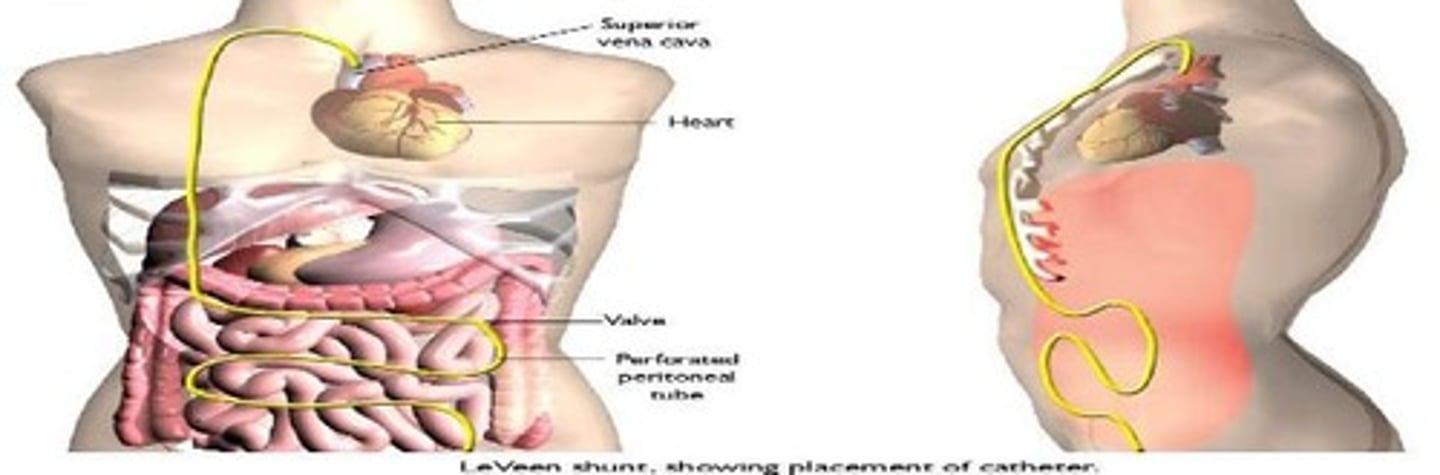
LeVeen Shunt
Device to drain fluid from the peritoneal cavity.
TIPS
Procedure to decompress portal venous system.
Caput Medusae
Venous pattern indicating severe portal hypertension.
Fluid Wave
Physical exam sign indicating fluid presence in abdomen.
Electrolyte Loss
Depletion of essential minerals during diuretic therapy.
Sepsis
Systemic infection that can arise from paracentesis.
Peritonitis
Infection of the peritoneum, potential complication of paracentesis.
Esophagogastric Varices
Distended veins in esophagus due to portal hypertension.
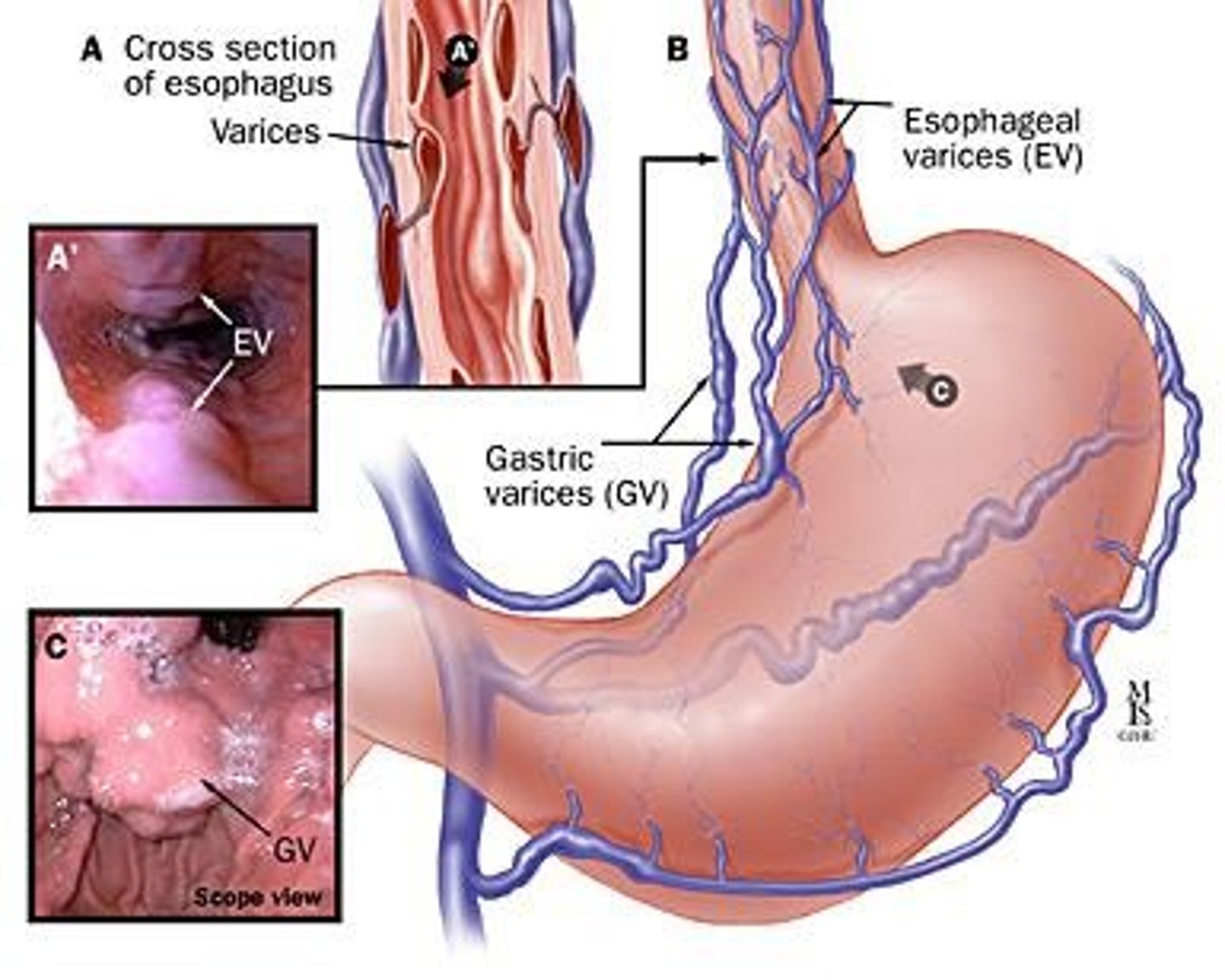
Acute GI Hemorrhage
Life-threatening bleeding from ruptured varices.
Supportive Management
Primary care approach focusing on symptom relief.
Ethical Issues
Concerns about candidate selection in medical treatment.
Abstinence
Seeking help for self-induced alcoholism.
Liver Damage Severity
Assessment of liver health and function.
Medical Therapy Response
Stability of patient for treatment effectiveness.
Social Support Importance
Essential for successful recovery in patients.
Acute GI Bleeding
Potentially lethal medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Breakdown of gastro-mucosal lining causing bleeding.
Glycoprotein Mucus Barrier
Protective layer in gastric mucosa against damage.
Mucosal Blood Supply
Blood flow necessary for gastric mucosal health.
Tight Junctions
Connections between gastric cells preventing leakage.
H. Pylori Role
Bacteria that disrupts gastric mucosal protection.
NSAID Risks
Can erode stomach lining, leading to ulcers.
Stress-Related Erosive Syndrome
Increased gastric acid due to stress or trauma.
ICU Patient Risk
75-100% may develop stress ulcers within 24 hours.
Postural Hypotension
Drop in blood pressure upon standing.
Decreased H & H
Indicates potential blood loss; requires monitoring.
Tachycardia Signs
Increased heart rate indicating possible hypovolemic shock.
Coffee Ground Emesis
Vomiting resembling coffee grounds from gastric bleeding.
Hematochezia
Bright red blood per rectum indicating lower GI bleed.
Melena
Tarry stool indicating upper GI bleeding.
Physical Examination Signs
Assess for poor tissue perfusion and abdominal issues.
NG Tube Assessment
Evaluate bleeding extent; caution with esophageal varices.
H2 antagonists
Block acid secretion; used for stress ulcers.
Famotidine
An H2 antagonist; brand name Pepcid.
Ranitidine
An H2 antagonist; brand name Zantac.
Cimetidine
An H2 antagonist; brand name Tagamet.
Proton pump inhibitors
Block final stage of gastric acid production.
Omeprazole
A PPI; brand name Prilosec.
Lansoprazole
A PPI; brand name Prevacid.
Pantoprazole
A PPI; brand name Protonix.
Esomeprazole
A PPI; brand name Nexium.
Antacids
Neutralize stomach acid; bind phosphates.
Sucralfate
Forms protective covering over ulcer sites.
Hemodynamic stabilization
Replacement of blood products for GI bleeding.
Endoscopy
Procedure to visualize and repair GI structures.