EXAM 4- Follen
1/53
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the definition of menopause?
cessation of menses permanently
amenorrhea for 12 months
What are the 3 stages of menopause?
perimenopause
menopause
post menopause
What is the clinical presentation of menopause?
vasomotor symptoms: hot flashes, night sweats
sleep changes
mood/cognitive changes
vulvovaginal symptoms: itching, burning, dryness, etc.
What are long term concerns following menopause tx?
osteoporosis
CVD
dementia
body changes
skin changes
What are the goals of therapy for menopause tx?
relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, minimize ADRs
What are non-pharm options for menopause?
dress in layers
decrease room temperature
stress management
exercise
avoid caffeine, alcohol, spicy food
What pharm therapy is considered the backbone of menopausal hormone therapy (MHT)?
estrogen
When using MHT, when should progesterone be added to estrogen therapy?
when the female has an INTACT UTERUS
What is recommended for pts. with mild menopausal symptoms?
NONPHARM THERAPY
A patient with no contraindications to menopausal hormone therapy is experiencing moderate to severe vulvovaginal symptoms. Should local or systemic menopausal hormone therapy be recommended for this patient?
local
A patient with no contraindications to menopausal hormone therapy is experiencing moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms. Should local or systemic menopausal hormone therapy be recommended for this patient?
systemic
What MHT products are local?
cream
ring
tablet
inserts
What MHT products are systemic?
transdermal patch
transdermal spray
gel
oral
pellet
Femrings
Does the Femring provide local or systemic effect?
systemic
What are the benefits of non-oral routes of estrogen?
bypass GI tract
avoid 1st pass metabolism
in patches: continuous infusion rate
What are the disadvantages of non-oral routes of estrogen?
variable absorption
What are the C/I to MHT?
undiagnosed genital bleeding'
breast cancer
neoplasia (E or P dependent)
thromboembolic issues
liver dysfunction
If MHT is used it should be used at the __________________effective dose for the _____________ duration needed.
minimum; shortest
Is compounded bioidentical therapy a preferred 1st tx for menopause symptoms?
no
Which SERM is FDA-approved for use in moderate-severe vasomotor symptoms?
Bazedoxifene
Which SERM is indicated for the tx of moderate-severe dyspareunia from menopausal vulvar and vaginal atrophy?
Ospemifene
What tx options are available for patients that cannot take MHT?
SSRIs/ SNRIs
ex: Paroxetine, citalopram
Gabapentin
Oxybutynin'
Fezolinetant
What is dysmenorrhea? What’s the difference between primary and secondary?
dysmenorrhea- painful periods
primary- not due to pelvic disease
secondary- due to pelvic origin
What is amenorrhea? What’s the difference between primary and secondary?
amenorrhea- absence of menstruation
primary- no menstrual bleeding by the age of 16
secondary- absence of periods for at least 3 previous cycles or 6 months
What is the definition of oligomenorrhea?
irregular cycle (>35 days, long bleeding, or lots of blood etc.)
What is the definition of heavy menstrual bleeding/ menorrhagia?
regular menstrual bleeding w/ blood loss >80 ml per cycle or prolonged bleeding >7 days
What is the cause of primary dysmenorrhea?
factors affecting:
uterine hypercontractility
reduced uterine blood flow
increase peripheral nerve hypersensitivity
What are the risk factors for severe episodes of dysmenorrhea?
<12 yrs old
longer cycles
longer duration of bleeding
heavy flow
nulliparity
family history
smoking
What is the clinical presentation of dysmenorrhea?
cramps before starting period
backache
thigh pain
n/v
HA
What are non-pharm recommendations for dysmenorrhea?
heating pad
exercise
vegetarian diet
What are the pharm recommendations for dysmenorrhea?
NSAIDS
not APA
Hormonal Contraceptives
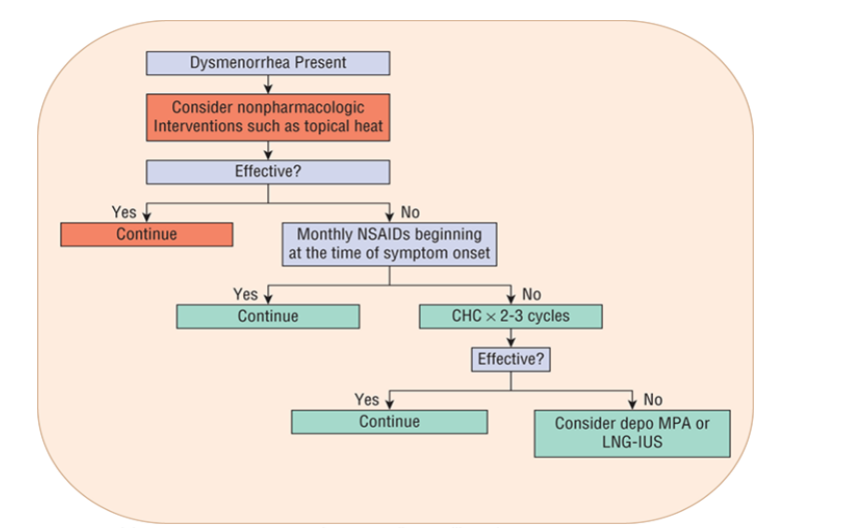
What are the goals of tx for oligomenorrhea and amenorrhea?
establish regular bleeding, resume ovulation
What are the pharm tx recommendations for amenorrhea and oligomenorrhea?
combined contraceptive (E+P)
Cyclic progestin
Bromocriptine and Cabergoline if cause is hyperprolactinemia
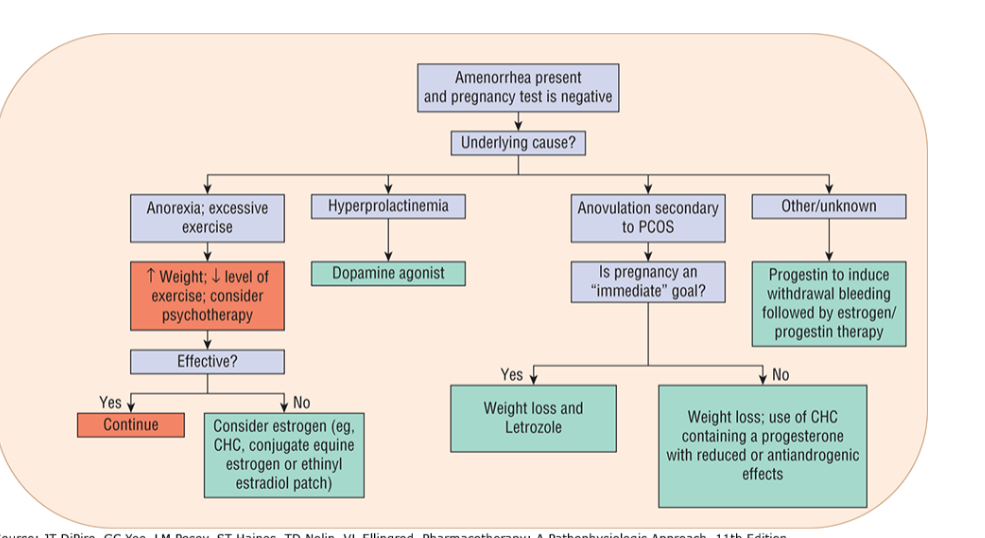
Which oligomenorrhea/amenorrhea tx option is preferred for a patient that does not want to become pregnant?
COMBINED CONTRACEPTIVE
(CYCLIC PROGESTIN DOES NOT PROVIDE CONTRACEPTION)
What are the goals of tx for heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)?
reduce monthly menstrual blood loss
correct iron-deficiency anemia
improve QOL
What are the tx options for heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)?
surgery
CHC’s
progestin only regimens
LNG- IUS
NSAIDs
GnRH antagonists
tranexamic acid
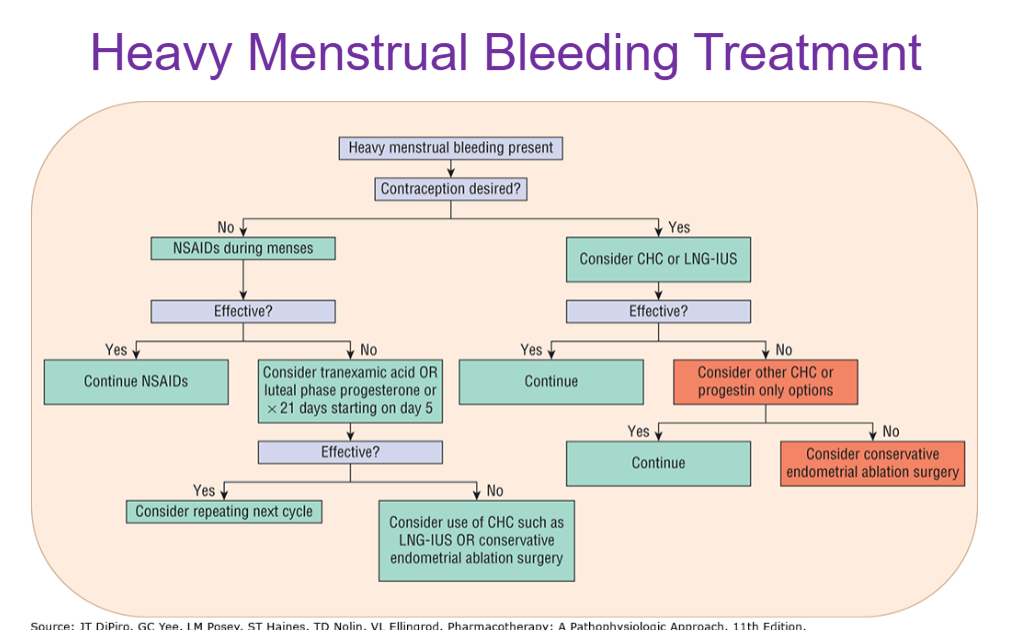
Which heavy menstrual bleeding tx options are preferred for a patient that does not want to become pregnant?
CHC’s
Depo Provera
IUD
What is the clinical presentation of endometriosis?
dysmenorrhea
pelvic pain
dyschezia (painful pooping)
dyspareunia (painful sex)
What are the non-pharm tx recommendations for endometriosis?
exercise
surgery
alternative therapies (ex: massage)
What are the pharm tx recommendations for endometriosis?
NSAIDS
CHC’s
progestins
GnRH agonists and antagonists
Danazol
What is the most common cause of tubal factor infertility?
PID (pelic inflammatory disease)
What are the nonpharm tx recommendations for infertility?
weight management
stress control
avoid smoking, caffeine marijuana
What is the MOA of clomiphene?
SERM—> inhibits negative feedback of estrogen
Does clomiphene stimulate the ovary directly?
no
Can clomiphene be used with other medications? If so, which meds?
yes, dexamethasone, hCG, low dose exogenous gonadotropins
Whats ADRs of clomiphene should patients be instructed to notify their physician?
visual disturbances
What is the MOA of aromatase inhibitors?
inhibit conversion of androgens to estrogens
What is the MOA of the gonadotropins?
Allow development of multiple follicles by exposure to an increased level of FSH
FSH—> follicular growth
LH—> ovulation
Do gonadotropins stimulate the ovaries directly?
yes
Why GnRH agonists and antagonists are used in the management of infertility?
Used to suppress spontaneous LH surge in ovulation induction procedures
Allows optimal duration of gonadotropin administration to maximize follicular maturation
What is the MOA of hCG?
stimulate natural LH surge
What medication is used in patients with PCOS? Why?
Metformin because it helps increase insulin sensitivity
Which medications are dopamine agonists? What are they used to treat?
meds- bromocriptine and cabergoline
tx for hyperprolactinemia
What are potential complications of infertility tx?
OHSS (ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome)
ovarian enlargement
multiple births
cancer risk