Fructose, Galactose, Sorbitol, and Ethanol Metabolism
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What enzyme phosphorylates fructose?
Fructokinase
What does fructokinase produce?
Fructose-1-phosphate (F-1-P)
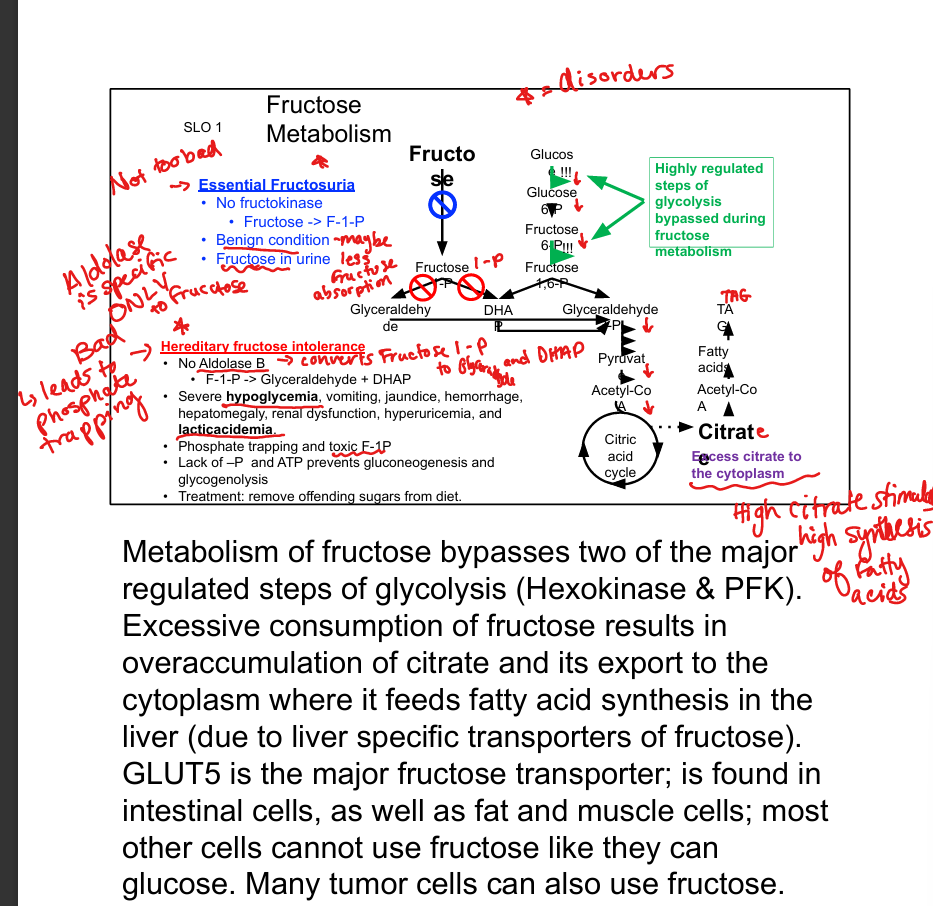

What enzyme cleaves F-1-P?
Aldolase B
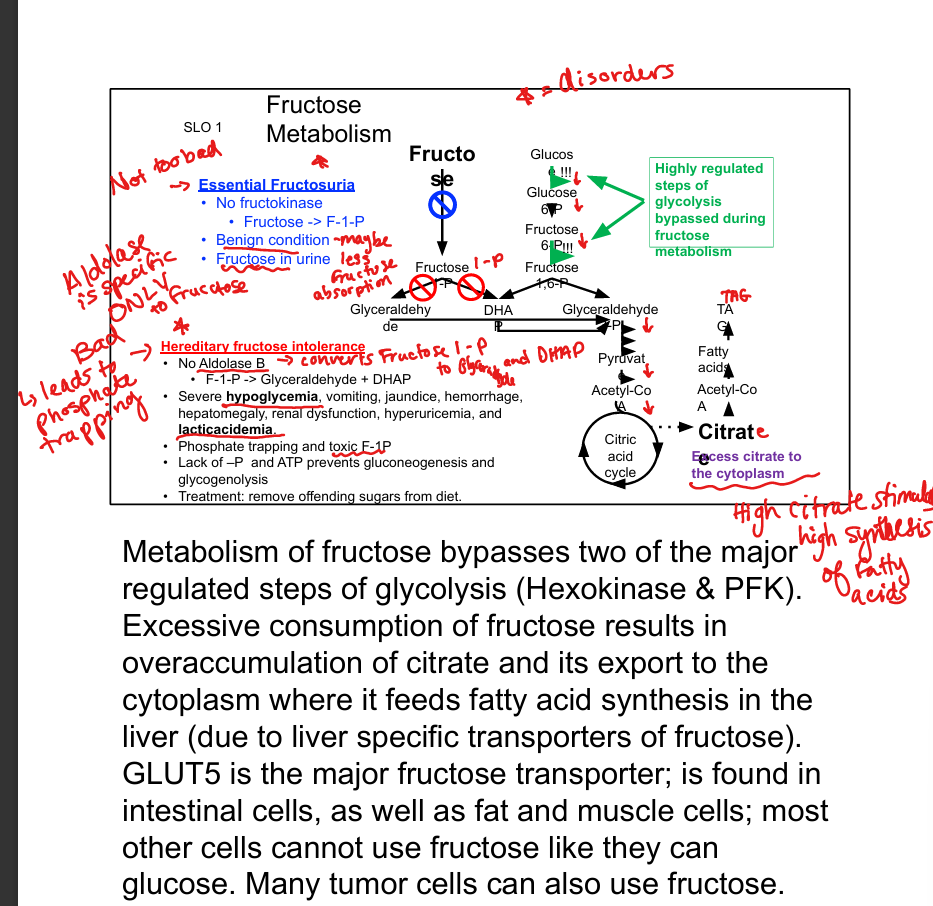

What are the products of F-1-P cleavage?
DHAP and glyceraldehyde
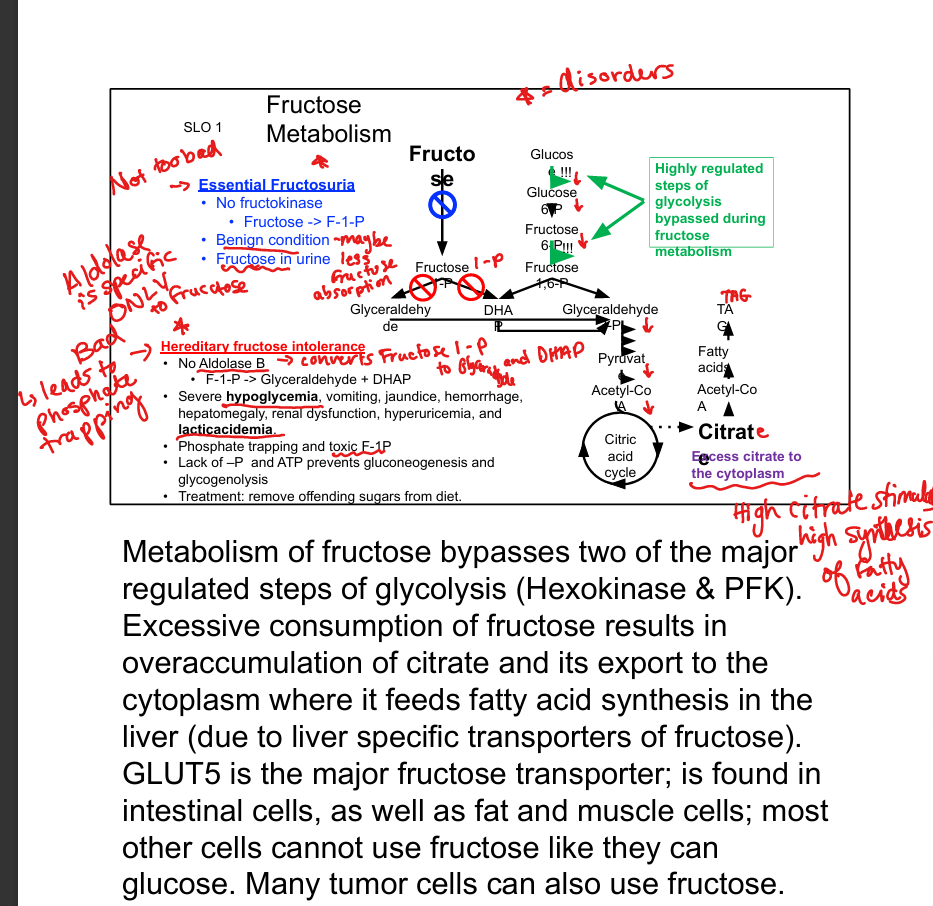

Which glycolytic steps are bypassed by fructose metabolism?
Hexokinase and PFK-1
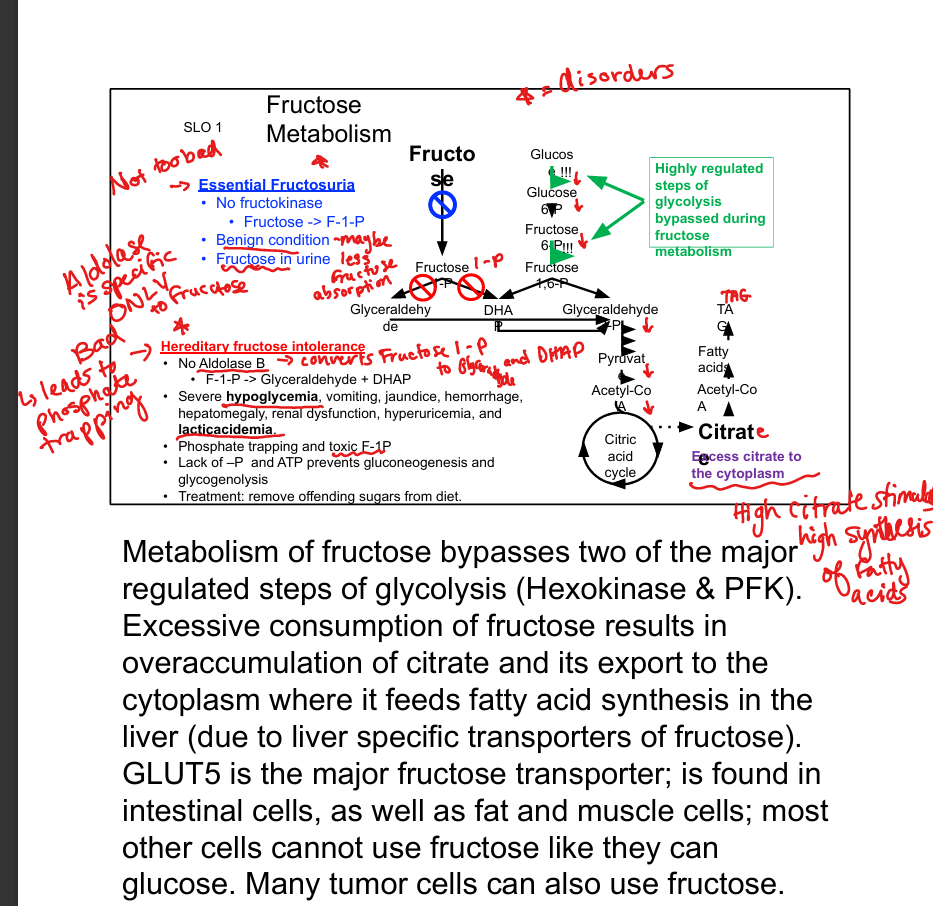

What transporter brings fructose into cells?
GLUT5
What is essential fructosuria?
Fructokinase deficiency; benign condition with fructose in urine
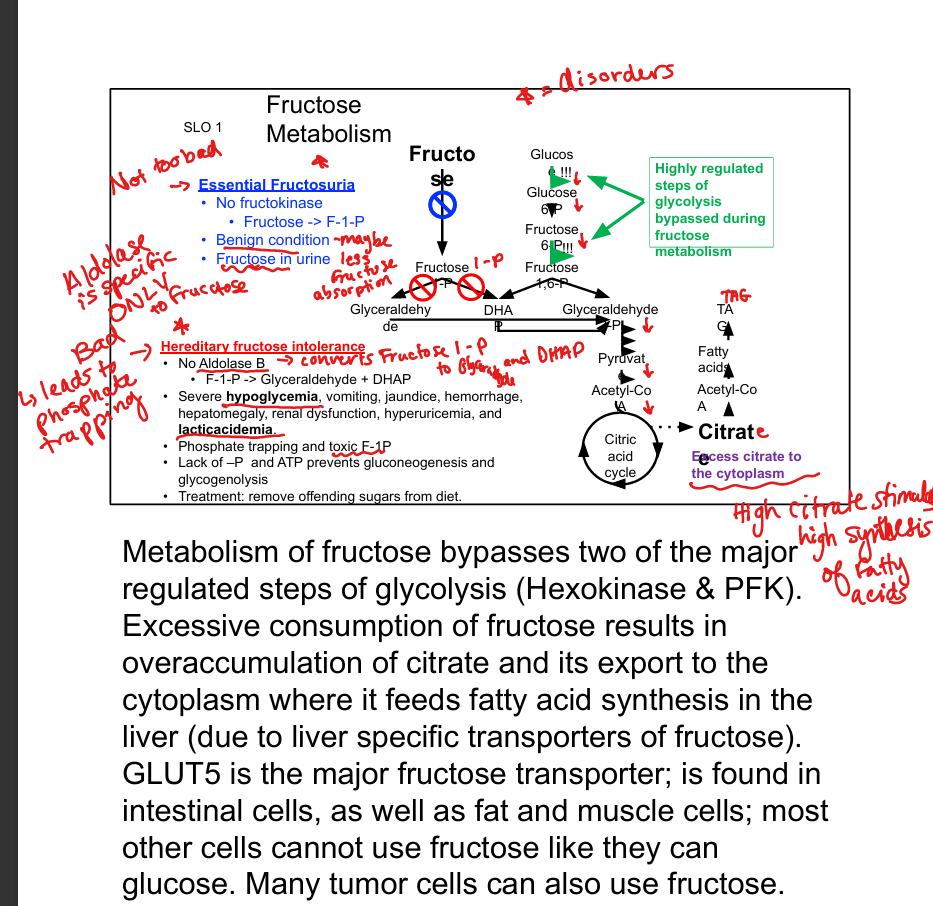

What is hereditary fructose intolerance?
Aldolase B deficiency; causes phosphate trapping and severe hypoglycemia
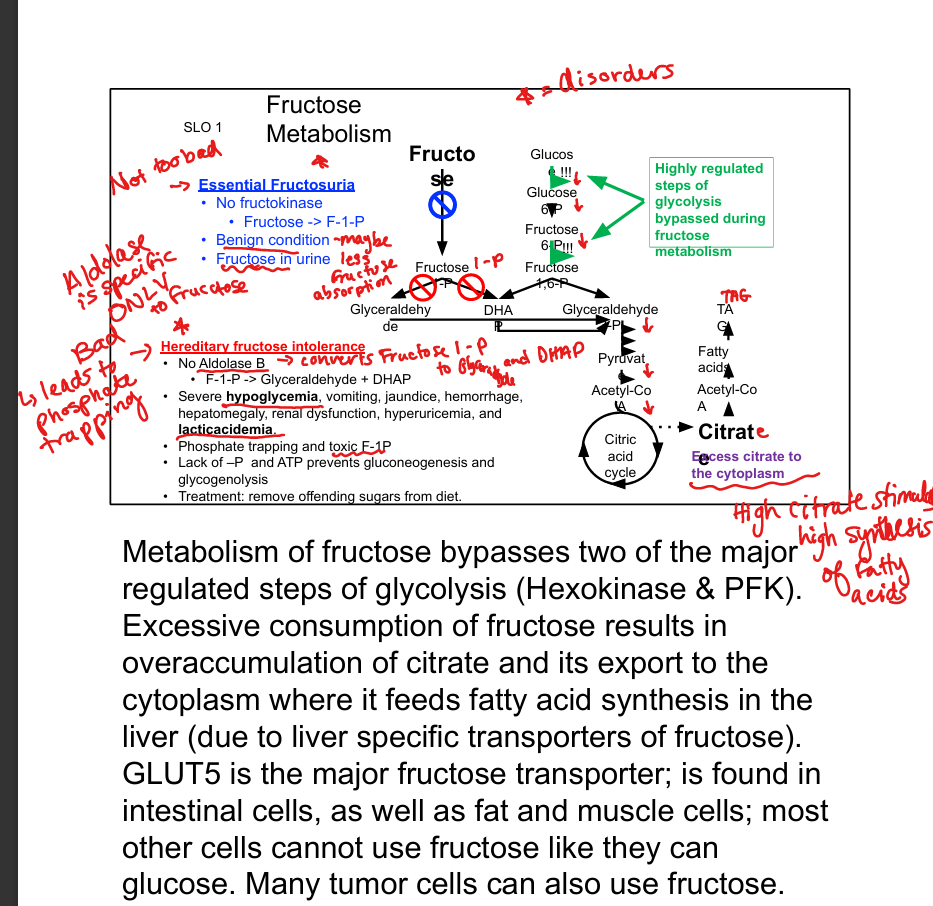

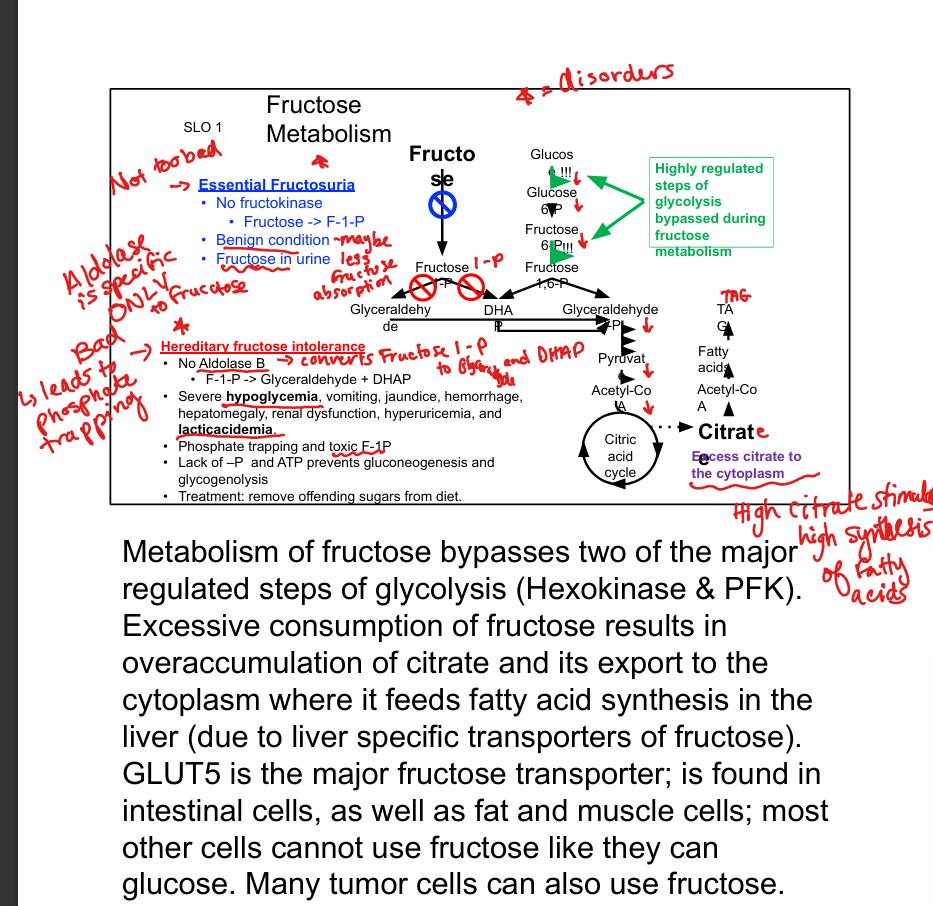
What is the consequence of excess fructose intake?
Citrate accumulation → fatty acid synthesis → hyperlipidemia

What enzyme converts glucose to sorbitol?
Aldose reductase
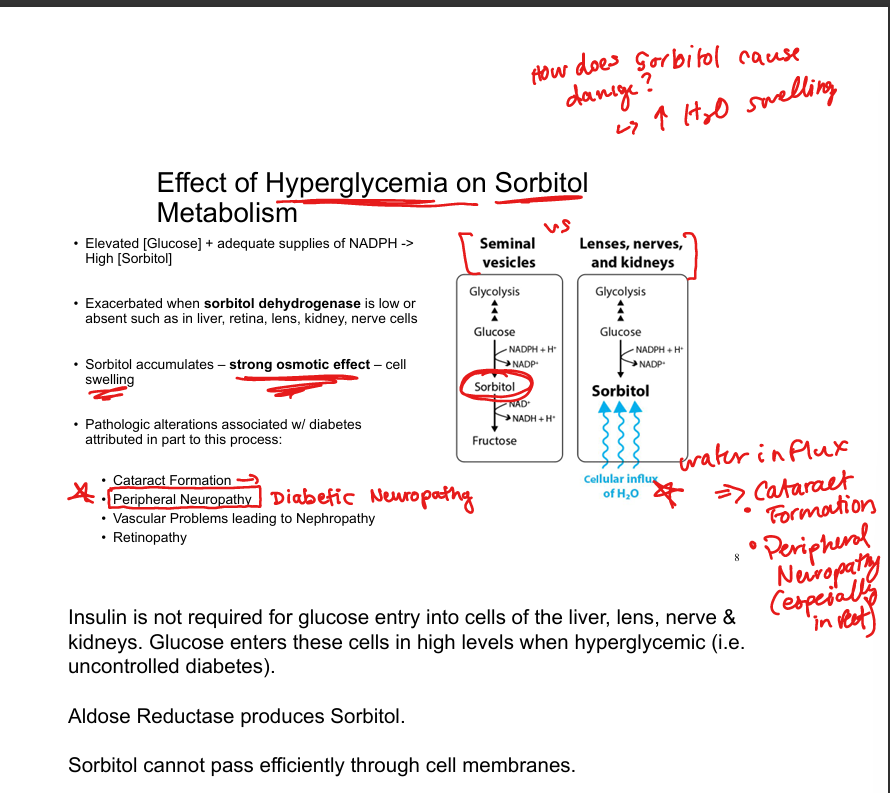

What enzyme converts sorbitol to fructose?
Sorbitol dehydrogenase
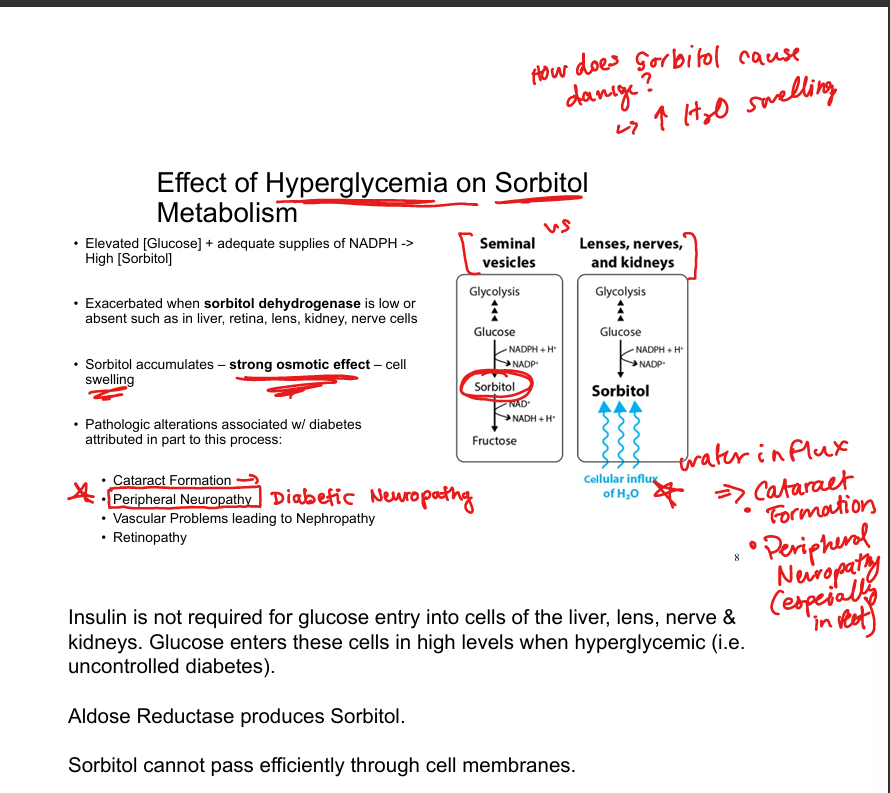

Where is sorbitol dehydrogenase low or absent?
Lens, retina, kidney, nerve cells
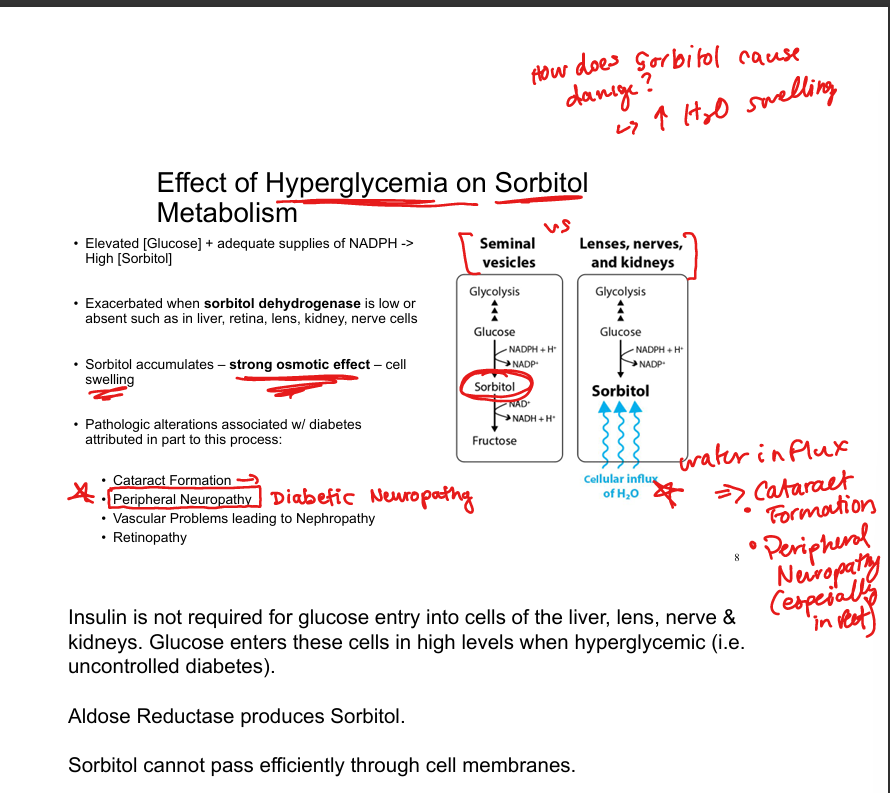

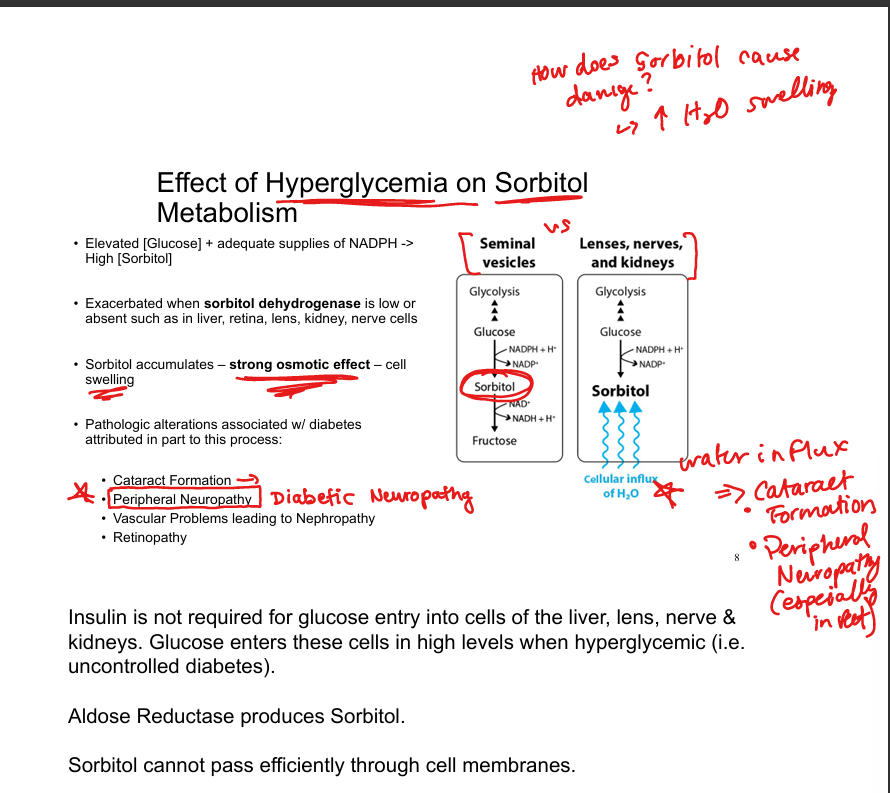
Why is sorbitol accumulation harmful?
Strong osmotic effect → cell swelling
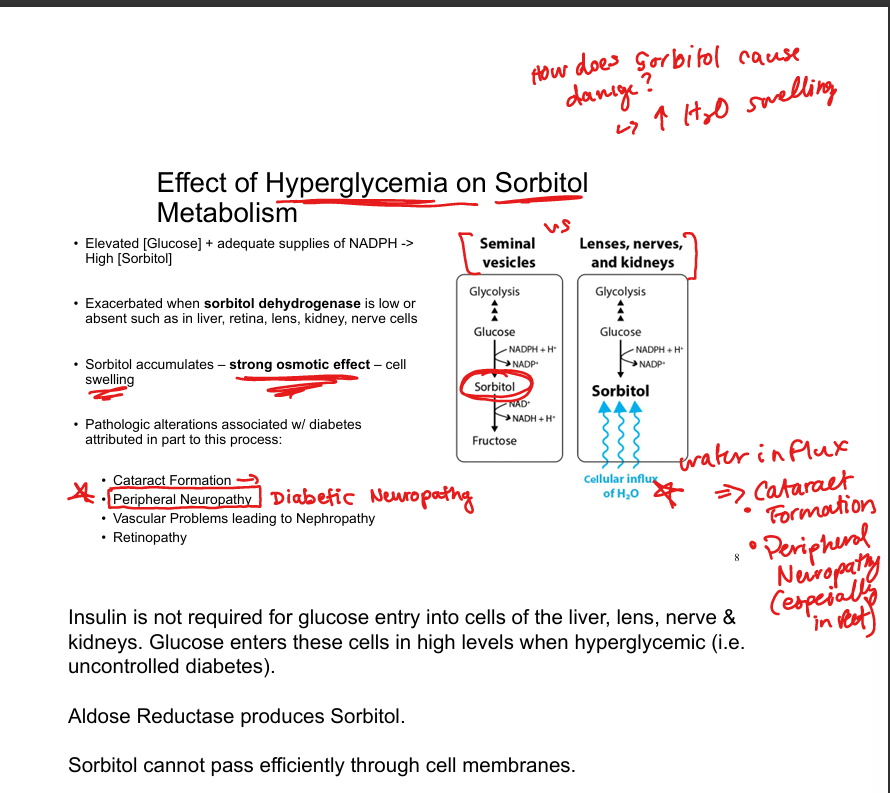

What conditions are associated with sorbitol accumulation?
Cataracts, peripheral neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy
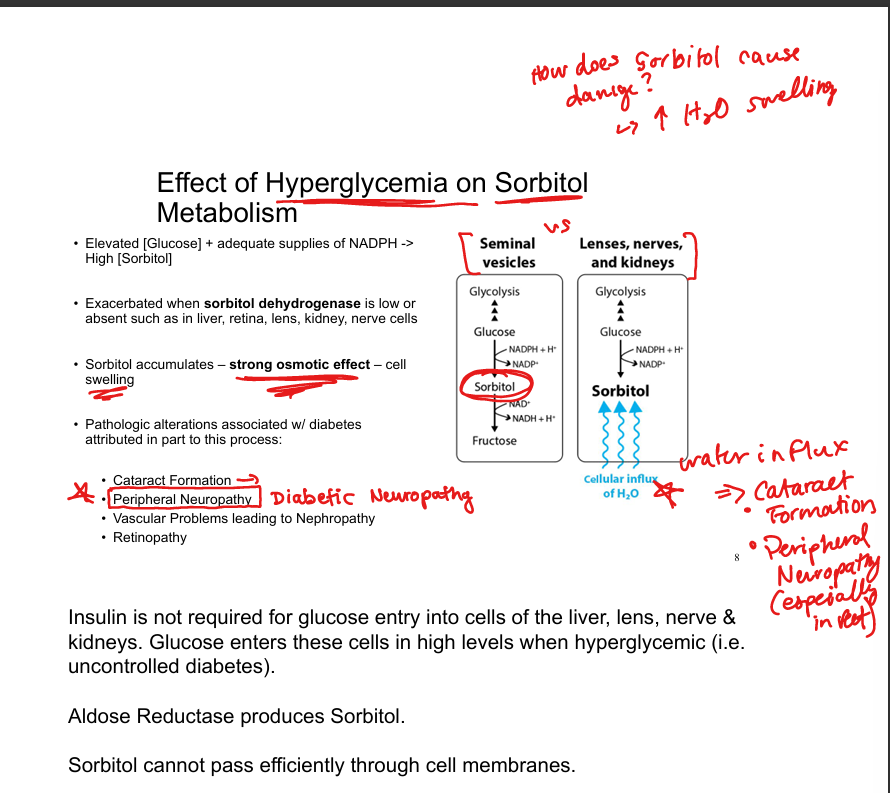

Why does sorbitol accumulate in diabetes?
High intracellular glucose enters insulin-independent tissues and is converted to sorbitol

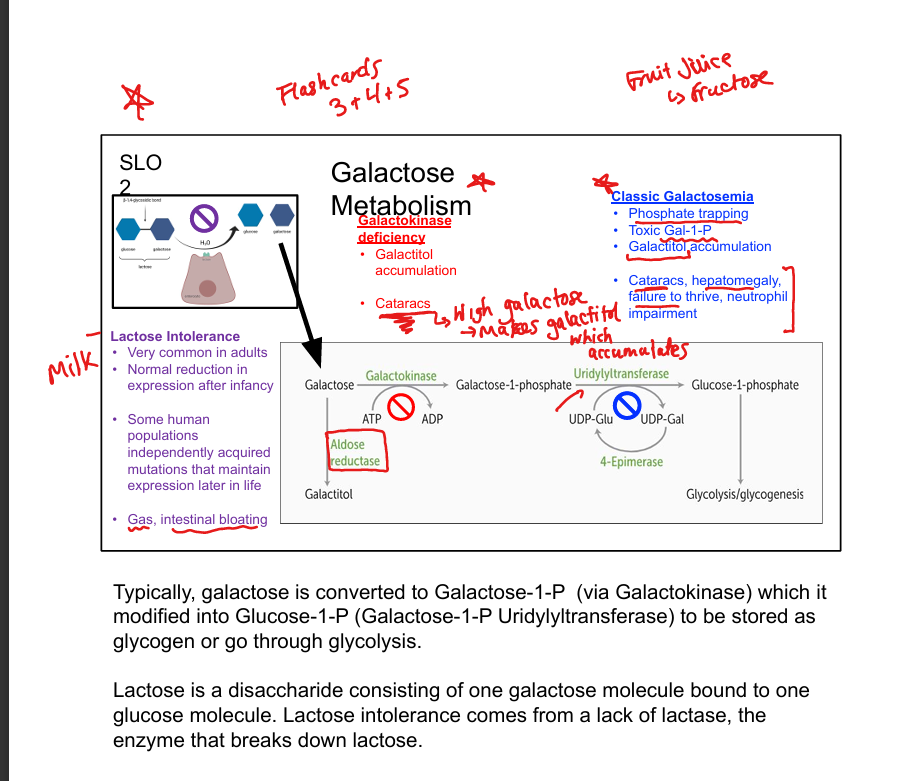
What enzyme phosphorylates galactose?
Galactokinase
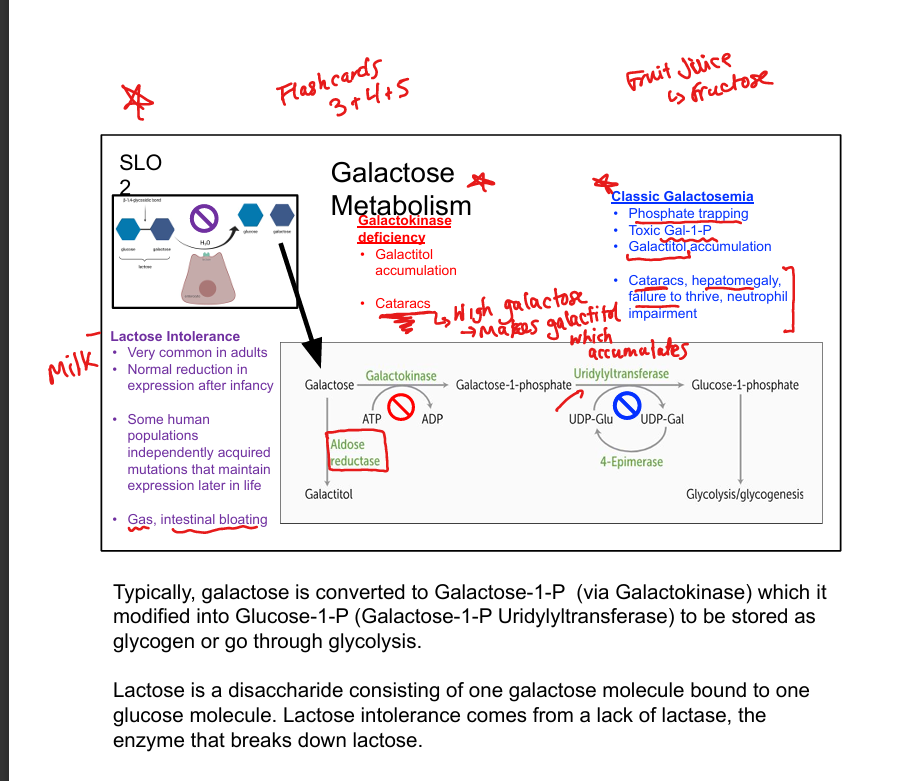

What does galactokinase produce?
Galactose-1-phosphate (Gal-1-P)
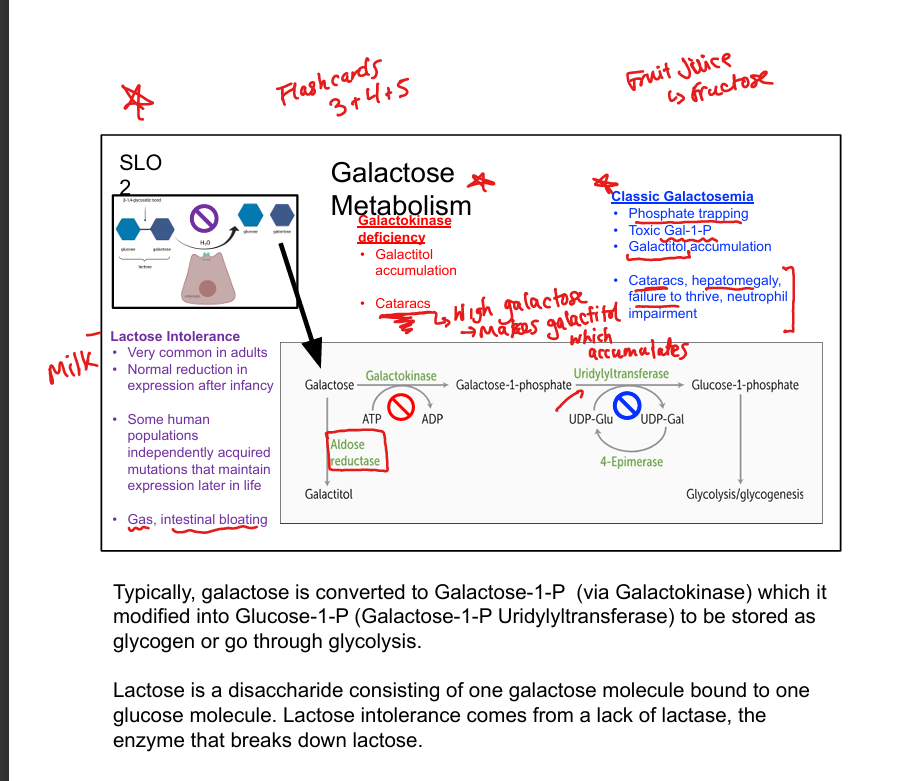

What enzyme converts Gal-1-P to glucose-1-phosphate?
Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase
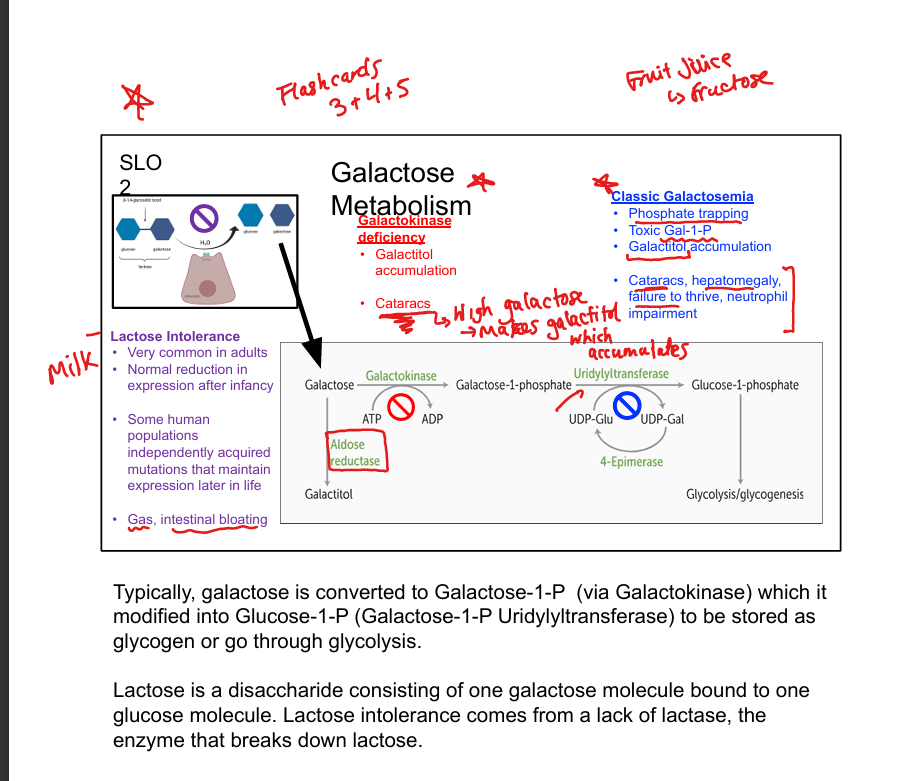

What is classic galactosemia?
Uridyltransferase deficiency; causes Gal-1-P and galactitol accumulation
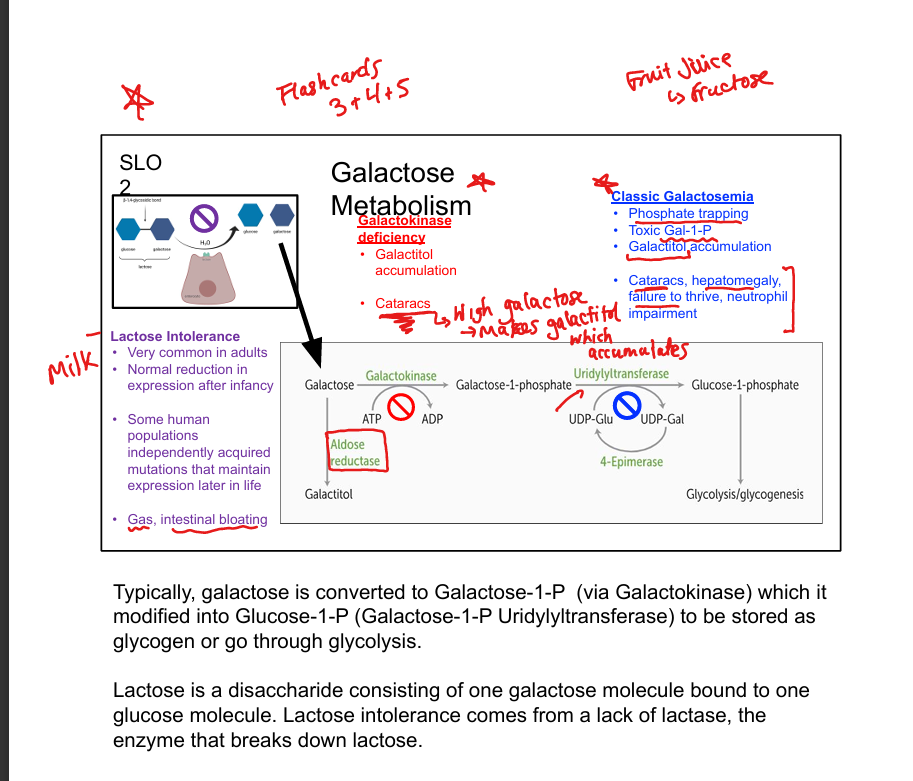

What are symptoms of classic galactosemia?
Cataracts, hepatomegaly, failure to thrive, neutrophil dysfunction
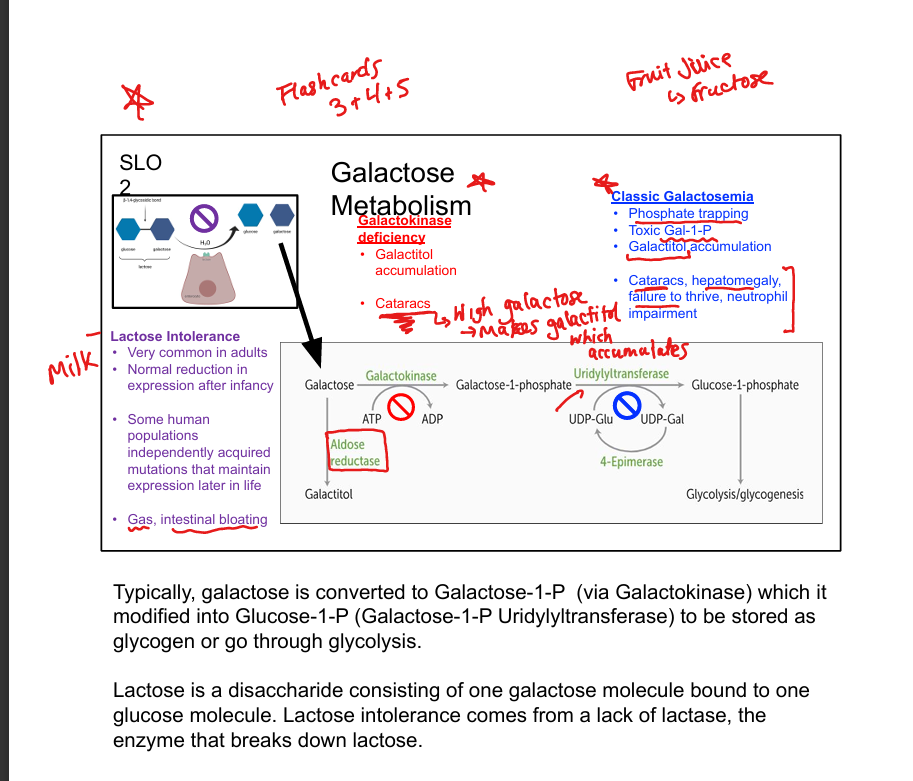

What is galactokinase deficiency?
Benign condition; causes galactitol accumulation and cataracts
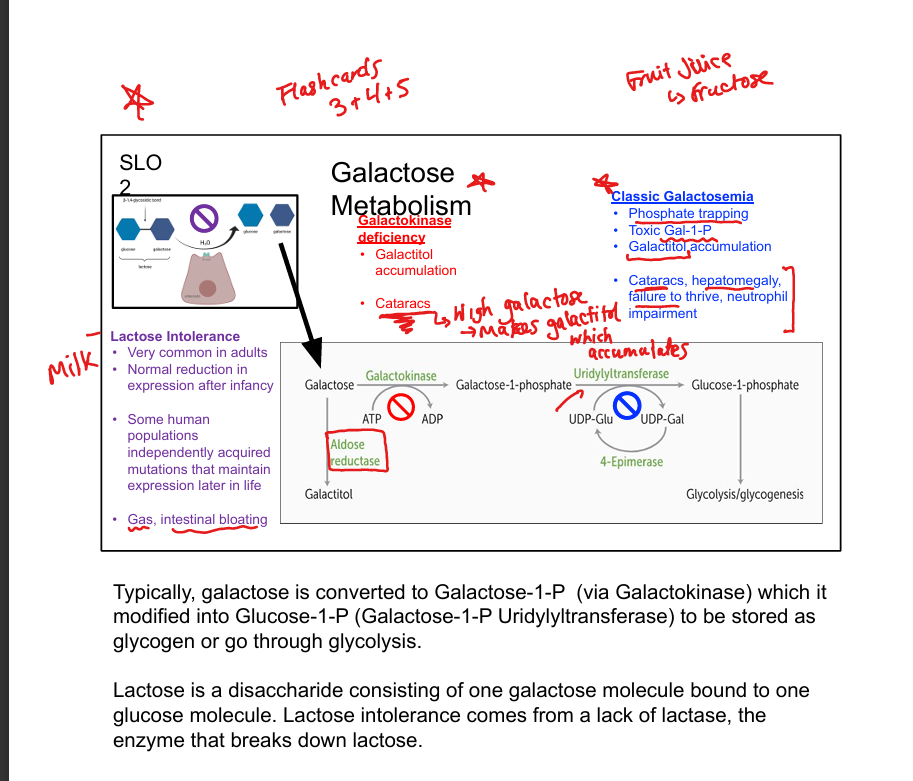

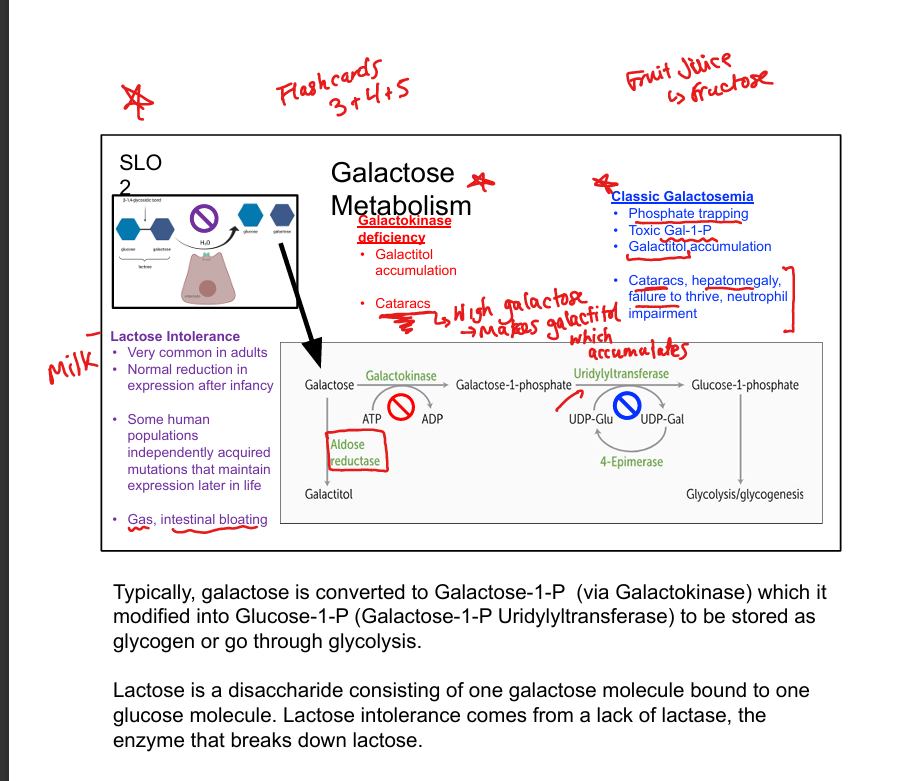
What is lactose intolerance?
Deficiency of lactase; causes bloating, gas, diarrhea

What is the fate of galactose in metabolism?
Converted to glucose-1-phosphate → glycolysis or glycogenesis

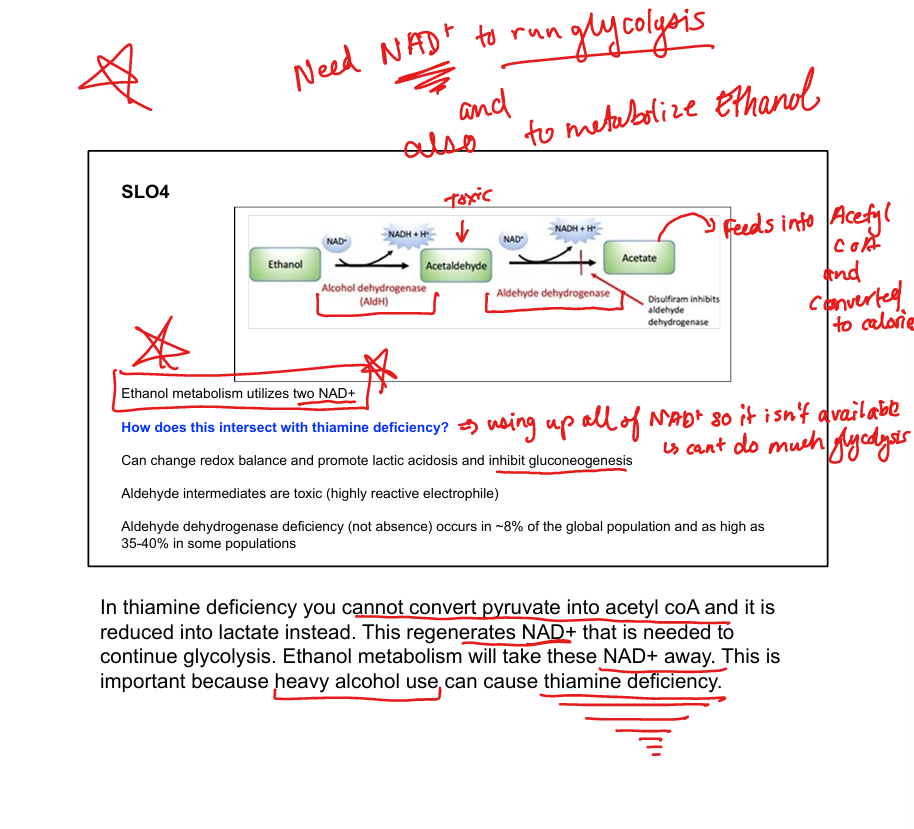
What enzyme converts ethanol to acetaldehyde?
Alcohol dehydrogenase
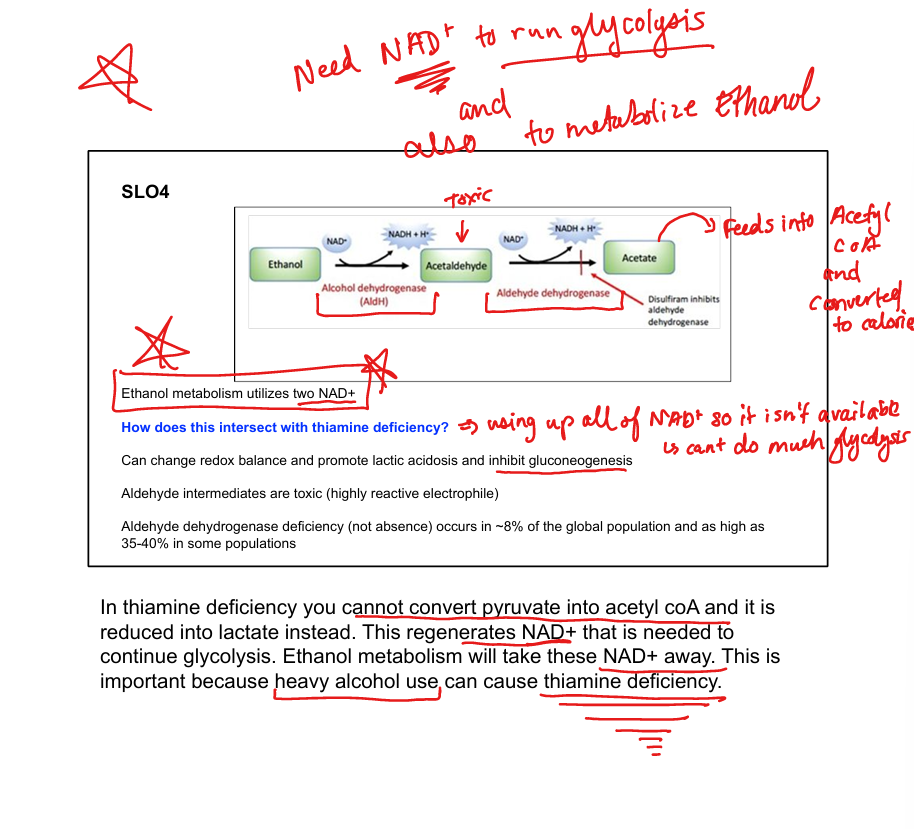

What enzyme converts acetaldehyde to acetate?
Aldehyde dehydrogenase
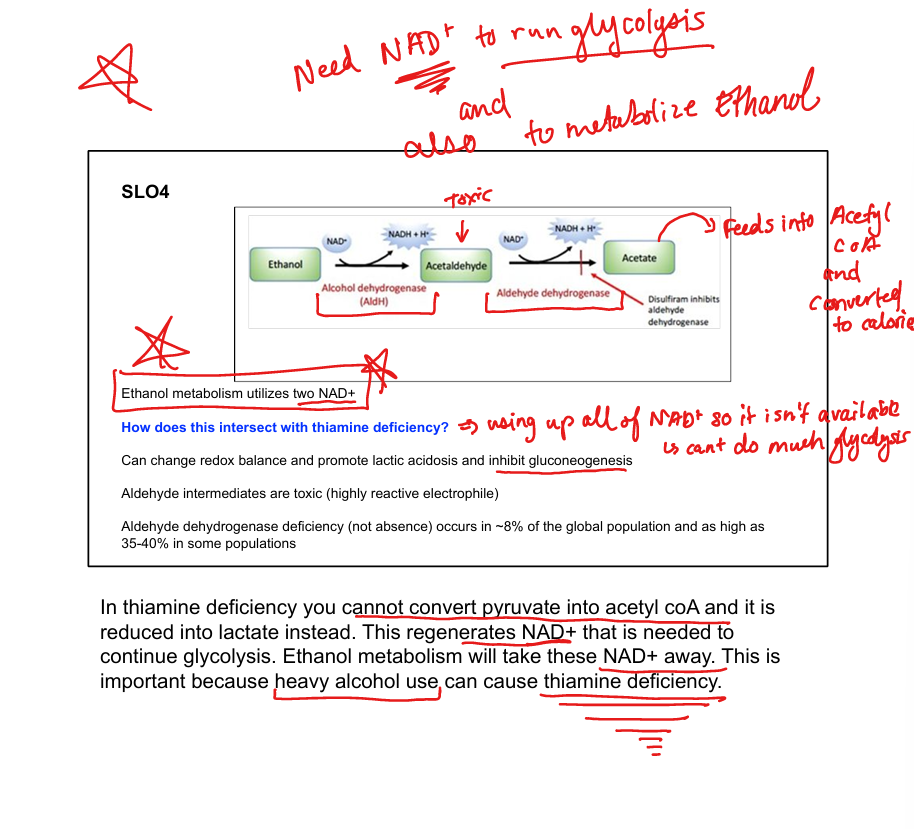

What cofactors are used in ethanol metabolism?
2 NAD⁺ per ethanol molecule
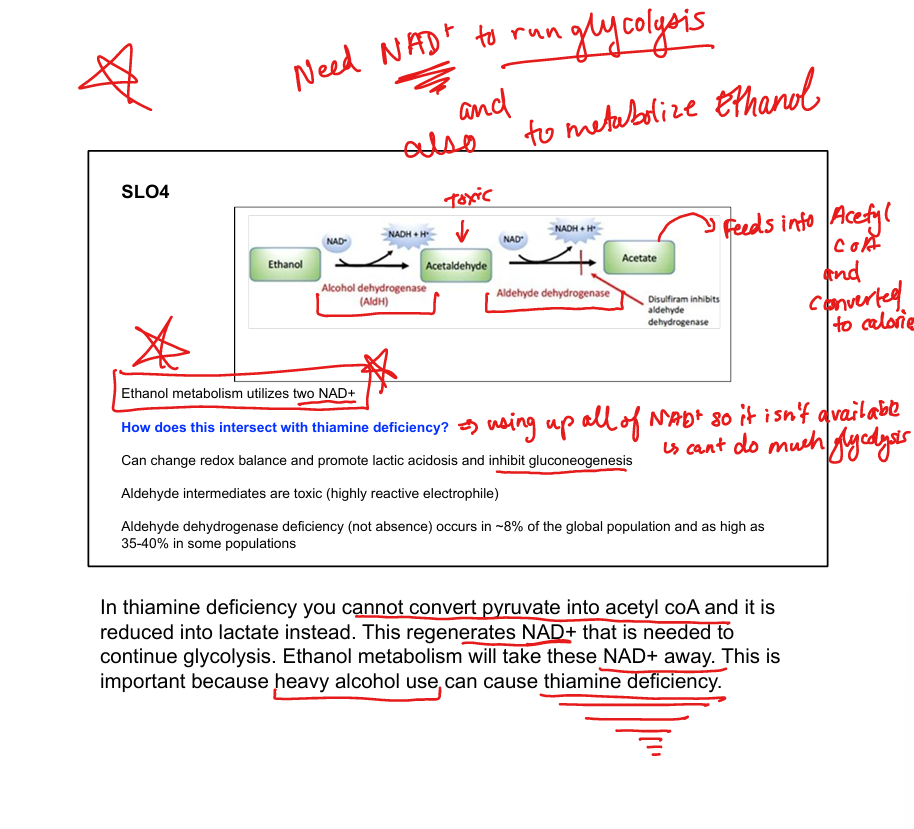

What toxic intermediate is produced from ethanol?
Acetaldehyde
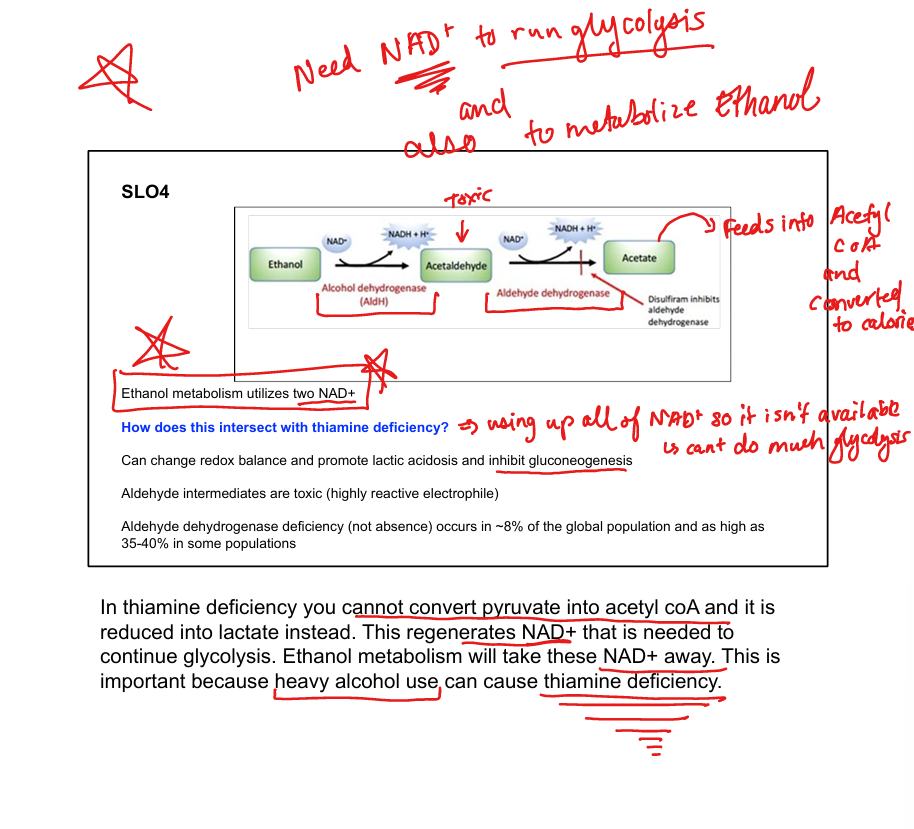

What is disulfiram’s mechanism?
Inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase → acetaldehyde buildup
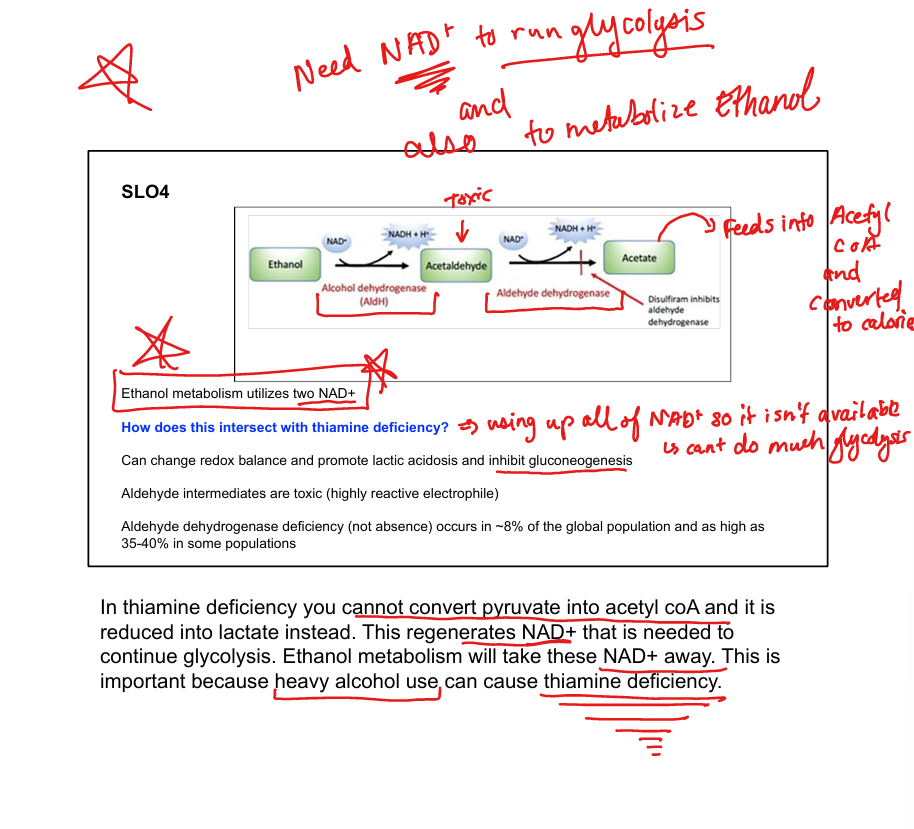

How does ethanol affect gluconeogenesis?
Consumes NAD⁺ → inhibits gluconeogenesis → lactic acidosis
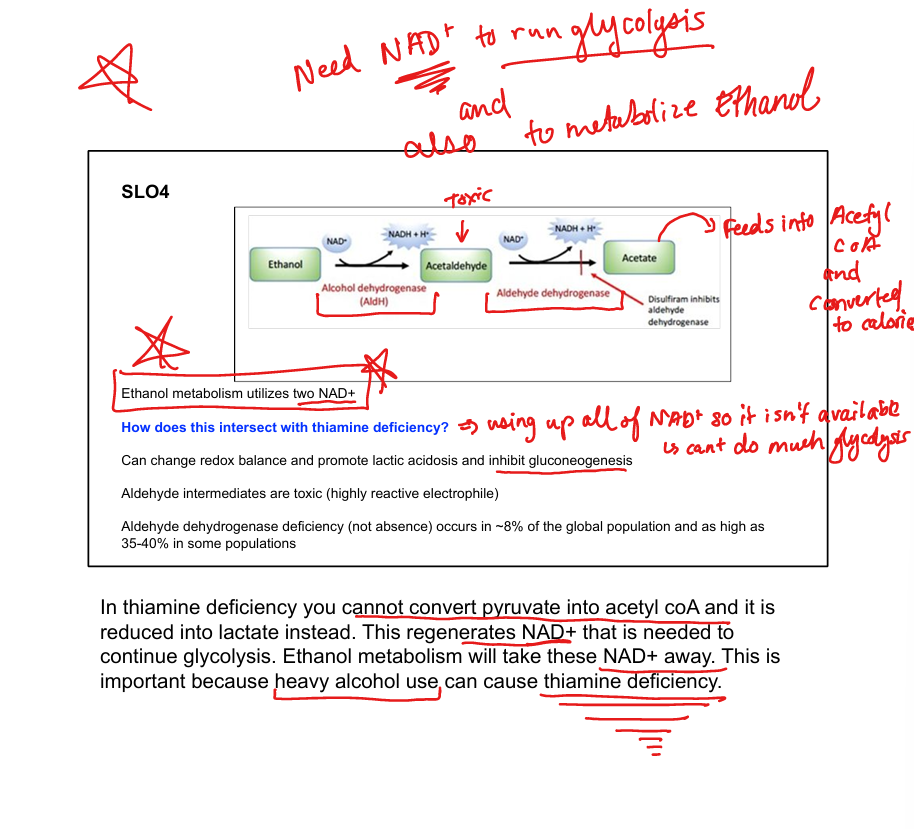

How does ethanol intersect with thiamine deficiency?
Thiamine is needed for pyruvate → acetyl-CoA; deficiency worsens lactic acidosis

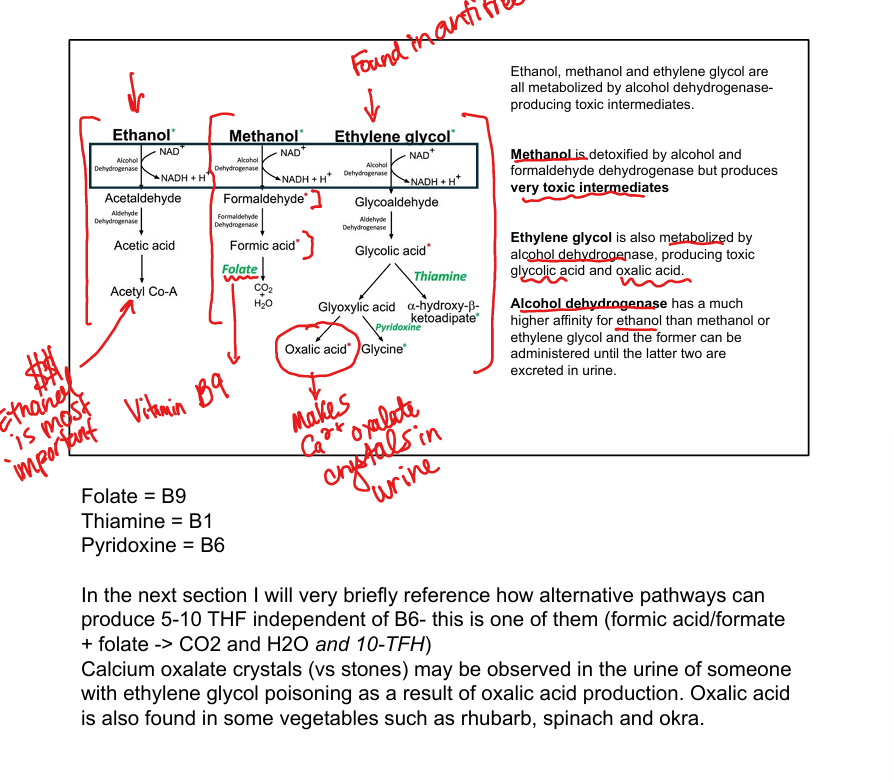
What toxic metabolites are produced from methanol and ethylene glycol? (less important than ethanol)
Formic acid and oxalic acid
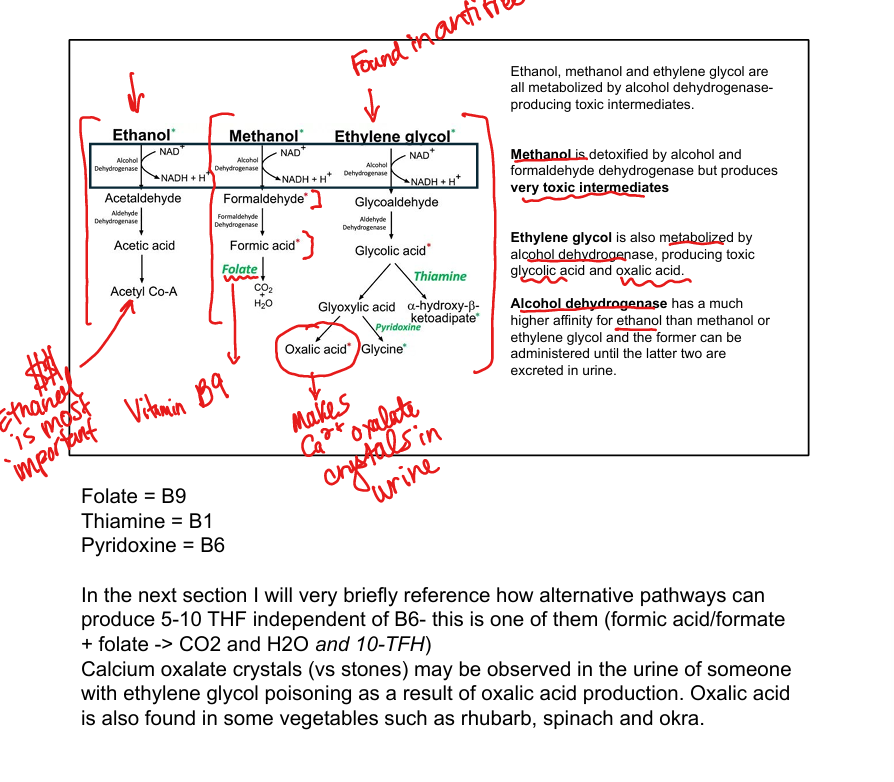

Why is ethanol used as an antidote for methanol or ethylene glycol poisoning?
Alcohol dehydrogenase has higher affinity for ethanol