Civil War
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1IfNZZgFnwQIOpLBVUK4w7AYJERoriWQFilKEm1npq9E/edit?usp=sharing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Sectional Issues that Divided the Country
National Bank
Tariffs
Transportation
Immigration
Admission of new western states to union
Slavery
Sectional Issues: National Bank
North
supported
business men placed large investments in Bank
large measure of control over Bank and subsequently government
South
opposed
did not want National Bank
felt State Banks could provide cheaper laons
believed North (Northeast) had too much control over Bank and government
Sectional Issues: Tariffs
North
supported
wanted high tax on imports
forced people to buy American goods instead of European goods
South
opposed
against tax on imports
forced to buy goods manufactured in northeast
south exported cotton to foreign markets → imports from foreign markets decrease and those foreign countries have less money to spend on importing cotton → south sells less cotton → cotton price drops → north can buy cotton at a reduced price
Sectional Issues: Transportation
North
more unified
Allowed workers to migrate into industrial Northern cities
stimulate economic growth and population growth → states with growing populations could gain more seats in House of Representatives
centralized: could easily travel from one state to another via railroad
larger and more developed
South
less centralized
railroads had different-sized bearings across states
had to unload and reload goods when crossing state lines
wanted more railroads
Sectional Issues: Immigration
North
supported
encourage immigration → had no anti-immigration laws
provided cheap labor in factories
more job opportunities → attracted more immigrants
esp. due to the Great Famine
South
opposed
immigrants had to compete with uncompensated slave labor
attracted fewer immigrants
immigrants usually came for economic reasons and could not afford to buy large plots of land
Sectional Issues: Admission of new western states to union
North
admission of free states
South
admission of slave states
Sectional Issues: Slavery
North
opposed
thought it was morally incorrect
South
supported
basis of economy
viewed it as a way of life
Slavery: effects of cotton gin
more plantations pop up → more slaves needed
Eli Whitney
Legislation re: slavery
Missouri Compromise
Missouri entered as a slave state, while Maine entered as a free state
No slavery north of 36°30’ (Mason-Dixon Line)
Compromise of 1850
Popular sovereignty and fugitive slave law put in place
slave trade was prohibited in Washington D.C.
Kansas-Nebraska Act
proposed to establish territorial government in northern part of Louisiana Purchase
Creation of Kansas & Nebraska territories
question of slavery was to be settled based on popular sovereignty
less to Bleeding Kansas
warm-up to Civil War
Dred Scott
Scott traveled from slave state to free state
Wanted to sue for freedom
Justice Taney ruled against Scott
Black people were not citizens
Property is property wherever you take it
Technically made Mason-Dixon Line unconstitutional and slavery legal everywhere
Misconceptions about Slavery
All Black people came to the USA as slaves
False
some came as indentured servants
went through indentured servitude system → servitude period ends → given land
there were successful Black plantation owners
Not all Southerners owned slaves
True
Most Southerners did not own slaves (75% in 1860)
those that owned slaves owned 2-4 slaves
South Carolina and Mississippi were made up of more than 50% slaveholders
Only cotton was grown in deep South
False
rice, sugar, and tobacco were also grown -
enslaved people were horribly dehumanized and forced to work in hot + humid conditions with lots of mosquitos
Plantation owners were legislators that did not oversee their plantations
True
overseer oversaw plantations
gained from production efficiency
overseer were instructed to not kill enslaved people when they tried to escape → maimed them, they still could work
many plantation owners worked as legislators, trying to pass pro-slavery legislation (yikes!)
Enslaved people were completely isolated and not allowed near children
False
female slaves were nurses to white children
white children were closer to slave than own mother
Enslaved people were forced to work all day, every day
False
Laborer usual work times: Start at 6AM → 1 hour break at 9AM for breakfast → Assigned tasks finished from 2PM to 3PM
Laborer summer work times: Sleep in middle of day → Spend night chatting, merry-making, preaching, + psalm-singing
Christmas time: week-long holiday with celebration + no work
The Election of 1860: Candidates
Stephen Douglass
Democratic Party
advocated for popular sovereignty
Abraham Lincoln
Republican Party
wanted union to stay together
slavery can exist where it does but cannot spread
The Election of 1860: Outcome
Lincoln won
The Election of 1860: Effect
Southern secession (starting with South South Carolina) → formation of confederacy
Confederacy elects Jefferson Davis as president
Map of Civil War Battles
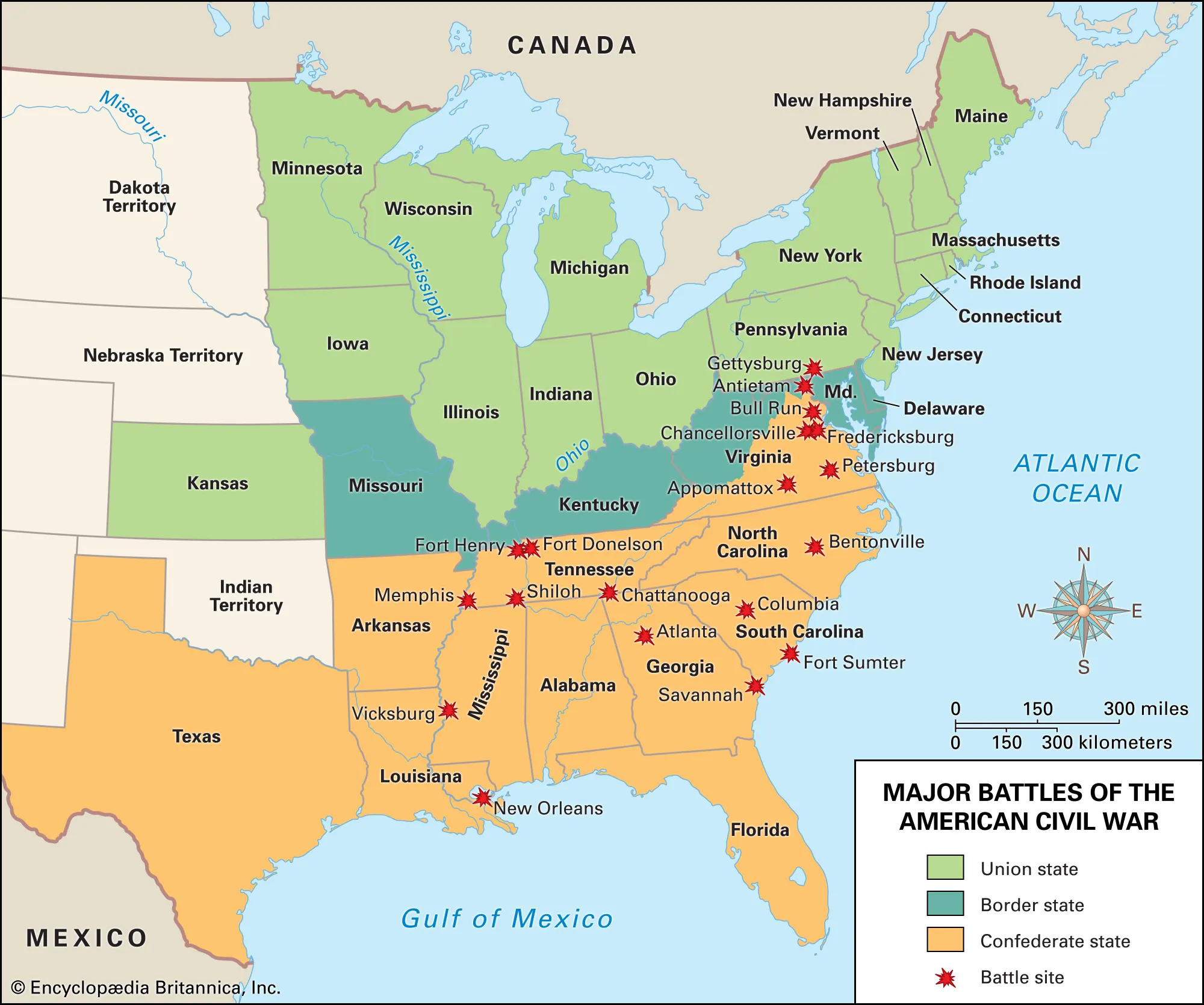
The Civil War: Northern Strategy
Take Mississippi River (split Confederacy)
March from Mississippi River to shoreline of Savannah, Georgia (split Confederacy)
Capture Richmond, Virginia
Anaconda Plan: blockade southern ports
The Civil War: Southern Strategy
Defend ports, capital, forts and outlast North (war of attrition)
Attack Washington D.C.
Fort Sumter
located at harbor of Charleston, South Carolina
after Southern secession, forts, ports, and offices that belonged to the north were still operating in the south
Major Robert Anderson was running low and supplies → people from Charleston did not help them
Lincoln sent supply ship + aid to Fort Sumter
City guns drove Union supply ships off
General Beauregard demanded surrender → Anderson refused
Confederates open fire → Union surrenders
start of Civil War
The Civil War: Eastern Campaign
First Battle of Bull Run
Peninsula Campaign and Second Battle of Bull Run
Antietam
Chancellorsville
Gettysburg
Sherman’s March to the Sea
Grant Captures Petersburg
The Civil War: Western Campaign
Fort Henry
Fort Donelson
Shiloh
New Orleans
Vicksburg
Chattanooga
Civil War Timeline
Fort Sumter (coast of South Carolina)
First Battle of Bull Run (Manassas Junction in VA)
Fort Henry (Tennessee, near Cumberland and Tennessee River)
Fort Donelson (Tennessee, near Cumberland and Tennessee River)
Peninsula Campaign (Virginia Peninsula )
Shiloh (Tennessee-Mississippi border)
New Orleans (mouth of Mississippi, Louisiana)
Second Battle of Bull Run (Manassas Junction )
Antietam (Antietam Creek, Maryland)
Chancellorsville (North-ish of VA)
Gettysburg (south of Pennsylvania)
Vicksburg (Mississippi River, near Mississippi-Arkansas border)
Chattanooga (southern Tennessee, borders Georgia)
Sherman’s March to the Sea (Atlanta → Savannah, Georgia southeast)
Petersburg (towards east of Virginia)
The Civil War: First Battle of Bull Run
Location: Manassas Junction in Virginia
Date: July 21, 1861
Generals
North: McDowell
South: Johnston, Beauregard
Objective: Union wanted to take Richmond, VA
Outcome: Union lost and gets humiliated
Union was confident in victory; some brought their families
Stopped 30 mi. from Washington D.C. near Manassas Junction
Confederacy knew they were coming and had trenches + weapons ready
Confederate army stood firm “as a wall” under Stonewall Jackson
North was shocked; retreated to Washington D.C.
McDowell replaced by Meade then by McClellan
Moved their focus to Mississippi River (led by Grant) - Fort Henry
Would split Confederacy in half (stops goods transportation along & across)
The Civil War: Peninsula Campaign and 2nd Battle of Bull Run
Location: Virginia Peninsula
Date: March-July, 1862
Generals
North: McClellan, Pope
South: Johnston, Smith, Lee, Magruder, Jackson
Objective: Union wanted to capture Richmond, VA
Outcome: Confederate victory; Union soldiers withdrew from Virginia Peninsula
The Civil War: Antietam
Location: Antietam Creek, Maryland
Date: September 17, 1862
Generals
North: McClellan
South: Lee
Objective: Lee wanted to take D.C. and split Union in half
Lee tries to use element of surprise → invade D.C. from behind (go way up north and attack from behind)
Outcome: Union stops Confederates in Maryland
Deadliest one-day battle in American military history → 22,717 estimated casualties
Lincoln uses this military success to issue his preliminary Emancipation Proclamation (September 22nd)
prevented Lee’s invasion of north and set stage for Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation
Grant found battle plan in cigar
discovered Confederacy’s plan for Antietam
The Civil War: Chancellorsville
Location: Spotsylvania County, Virginia
Date: April 30 – May 6, 1863
Generals
North: Hooker
South: Lee
Objective: Union wants to take Richmond, VA
Outcome: Confederate victory
Stonewall Jackson dies
South stops North from advancing south
The Civil War: Gettysburg
Location: Gettysburg, Pennsylvania
Date: July 1–3, 1863
Generals
North: Meade
South: Lee,
Pickett
Objective: Lee wanted to invade North
Outcome: Union victory
Turning point of Civil War
After Chancellorsville, Lee led troops to Shenandoah Valley to begin invasion of north
Confederacy stopped for shoes (their shoes were breaking) → shoe factory
Union intercepted Confederacy at Gettysburg → 3-day battle
The South suffered a massive loss and had to retreat all the way back to Virgini
Bloodiest Civil War battle
The Civil War: Sherman’s March to the Sea
Location: Georgia (Atlanta → Savannah)
Date: November 15 – December 21, 1864
Generals
North: Sherman
South: Hardee,
Wheeler
Objective: Union wanted to take important transportation routes, divide South in half, and decrease morale
Outcome: Union victory
Soldiers in Savannah had fled by the time Sherman arrived
Southern morale was low, extreme loss of supplies
frightened Georgia’s civilians
stole food, burned down houses of those who rebelled, raided farms
pillaging
The Civil War: Grant Captures Petersburg
Location: Petersburg, Virginia
Date: June 9, 1864 – March 25, 1865
Generals
North: Grant, Meade,
Butler
South: Lee,
Beauregard
Objective: Union wanted to surround Petersburg + cut off Lee’s supply lines
Outcome: Union victory
9-month siege to hold off Union from capturing Petersburg
Evacuation of Petersburg → Eventually loss of the Confederate capital at Richmond, VA and loss of South
Lee retreats from the city and surrenders
April 9, 1865 - Grant surrounds Lee's forces at Appomattox Courthouse
The Civil War: Fort Henry
Location: Tennessee River
Date: February 6, 1862
Generals
North: Grant, Foote
South: Tilghman
Objective: Union wanted to take fort and advance south
Outcome: Union successfully takes fort + opens Tennessee River and Cumberland River
The Civil War: Fort Donelson
Location: Cumberland River, Tennessee
Date February 11–16, 1862
Generals
North: Grant, Foote
South: Floyd, Pillow, Buckner
Objective: Union wanted to take fort and advance south
Outcome: Union successfully takes fort, become in control of Kentucky & Tennessee
The Civil War: Shiloh
Location: Southwest Tennessee (Hardin County, Tennessee)
Date: April 6–7, 1862
Generals
North: Grant, Buell
South: Johnston, Beauregard
Objective: Union wanted to control a vital rail center at Tennessee-Mississippi border; South wanted to keep North out of Mississippi
Outcome: Union victory
Union was running low on supplies
south initially winning
eventually supplies came → Grant decided to attack at dawn
narrow victory for union → many union casualties
The Civil War: New Orleans
Location: New Orleans, Louisiana
Date: April 25 - May 1, 1862
Generals
North: Farragut, Butler
South: Lovell
Objective: Union wanted to capture New Orleans port and secure lower part of Mississippi River
Outcome: Union victory
Farragut was an admiral
attacked at twilight (when your vision is most impaired)
decorated ships with green to camouflage with green and leafy river
told men not to engage with southerners when they were fired at
Union gained control of Mississippi River’s mouth and cut off the southern port→ captured New Orleans
met Grant at Vicksburg
The Civil War: Siege of Vicksburg
Location: Vicksburg, Mississippi
Date: May 18 – July 4, 1863
Generals
North: Grant
South: Pemberton
Objective: Union wanted to capture last Confederate stronghold on Mississippi River (Anaconda Plan)
Outcome: Union victory
Vicksburg was an affluent city on a hill
lots of trading bc it was an in-land harbor
many hotels, wealthy merchants, restaurants, entertainment
part of Grant’s plan to take Mississippi
lay siege on city → prevented people from leaving → people starved and could not get supplies
wanted to place explosives under city → dug tunnels → eventually dug zig-zag tunnels to confuse southerners
Confederate surrender
war in west is over
split Confederacy into two
Texas, Arkansas, & Louisiana cut off from other states
The Civil War: Chattanooga
Location: Chattanooga Tennessee
(Southern part)
Date: September 21 – November 25, 1863
Generals
North: Grant, Sherman, Rosecrans,
Hooker, Thomas
South: Bragg, Longstreet,
Breckinridge,
Hardee
Objective: Union wanted to take control of vital rail lines
Outcome: Union victory
Chattanooga transformed into a based for Sherman’s March to the Sea
opened door for invasion of deep south
Ulysses S. Grant
alcohol made him more effective
opposite of McClellan
liked by Linocoln
found battle plan in cigar
discovered Confederacy’s plan for Antietam
The Civil War: Surrender
Grant accepted Lee’s surrender at Appomattox Courthouse, Virginia