Outcome 2 - Nutrition, metabolism and food models
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
1
New cards
What is the definition of food?
Refers to any editable material that supports growth, repair and maintenance, of the body. It also protects the body from infection and disease.
2
New cards
What is the definition of nutrition?
Refers to the process by which body utilizes food for growth, maintenance and healthy living.
3
New cards
What is the definition of nutrients?
Found in foods we eat, provides nourishment essential for maintenance of life and for growth. No food by itself has all the nutrients needed (except breast milk).
4
New cards
What are the six categories of nutrients?
* Carbohydrates (including fibre )
* Fats
* Protein
* Vitamins
* Minerals
* Water
* Fats
* Protein
* Vitamins
* Minerals
* Water
5
New cards
What are the five functions of water?
* To transport energy, waste , hormones and antibodies.
* To dilute waste products.
* To lubricate surfaces and membranes.
* To help regulate body temperature.
* To be involved in all chemical reactions in the body.
* To dilute waste products.
* To lubricate surfaces and membranes.
* To help regulate body temperature.
* To be involved in all chemical reactions in the body.
6
New cards
How much fluid should athletes consume prior to a event?
They should consume 200-600mls of fluid.
7
New cards
How much fluid should athletes consume during a event?
They should consume 500-1000mls of fluid per hour of the event.
8
New cards
How much fluid should athletes consume after a event?
Replace 150% of water loss.
1kg weight loss = 1 litre fluid loss.
1kg weight loss = 1 litre fluid loss.
9
New cards
What are macronutrients?
Are this that are needed in large quantities (tens or hundreds grams) everyday.
10
New cards
Examples of macronutrients include-
* Carbohydrates (including fibre)
* Proteins
* Fats
* Water
* Proteins
* Fats
* Water
11
New cards
What are micronutrients?
Are those that are need in minute/small quantities (micrograms or a best milligrams).
12
New cards
Examples of micronutrients, include -
* Vitamins
* Minerals
* Minerals
13
New cards
What are the functions of carbohydrates ?
* To provide fuel (glucose) for energy.
* Regulates the metabolism of fate and protein.
* The nervous system relies on them for energy in order to function.
* They are transported through the bloodstream.
* Regulates the metabolism of fate and protein.
* The nervous system relies on them for energy in order to function.
* They are transported through the bloodstream.
14
New cards
Examples of carbohydrates, include -
* Rice
* Pasta
* Cereals
* Fruits (bananas)
* Potatoes
* Pasta
* Cereals
* Fruits (bananas)
* Potatoes
15
New cards
What are the functions of protein?
* Muscles construction and repair.
* Promoting glycogen resynthesis (remaking).
* Playing an important role in immune function.
* Transmission of nerve impulses.
* Preventing sport anaemia (low iron).
* Protein can be used as a secondary source of energy to carbohydrates.
* Promoting glycogen resynthesis (remaking).
* Playing an important role in immune function.
* Transmission of nerve impulses.
* Preventing sport anaemia (low iron).
* Protein can be used as a secondary source of energy to carbohydrates.
16
New cards
Examples of animal protein, include -
* Red meat.
* Fish
* Eggs
* Dairy products
* Fish
* Eggs
* Dairy products
17
New cards
Examples of plant protein, include -
* Nuts
* Lentils
* Tofu
* Beans
* Spinach
* Lentils
* Tofu
* Beans
* Spinach
18
New cards
What are the functions of fats?
* Development and maintenance of cell membranes (e.g. - blood and soft tissue).
* Assists in the absorption, transport and storage of nutrients, gases and waste into and out of cells.
* Provides a layer of protection around major organs.
* Assists in keeping the body warm.
* Assists in the absorption, transport and storage of nutrients, gases and waste into and out of cells.
* Provides a layer of protection around major organs.
* Assists in keeping the body warm.
19
New cards
There are 4 types of fats, these include -
* Monounsaturated fats
* Polyunsaturated fats
* Saturated fats
* Trans fat
* Polyunsaturated fats
* Saturated fats
* Trans fat
20
New cards
Good fats, include -
* Monounsaturated fats
* Polyunsaturated fats
* Polyunsaturated fats
21
New cards
Bad fats, include -
* Saturated fats
* Trans fat
* Trans fat
22
New cards
Examples of good fats (monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats), include -
* Avocado
* Olive oil
* Nuts
* Peanut butter
* Omega-3
* Soy oils
* Olive oil
* Nuts
* Peanut butter
* Omega-3
* Soy oils
23
New cards
Examples of bad fats (saturated fats and trans fats), include -
* Full cream milk
* Cream
* Cheese
* Fried food
* Pastries
* Pies
* Cakes
* Margarine
* Cream
* Cheese
* Fried food
* Pastries
* Pies
* Cakes
* Margarine
24
New cards
What is the definition of GI? (Glycemic index)
Carbohydrate foods are ranked from 0-100 according to how quickly they effect the bloods glucose levels.
25
New cards
A low GI rating is between the numbers -
0-55
26
New cards
Foods that have a low GI rating (0-55)
* Spaghetti Bolognaise
* Porridge
* Apples
* Firm Bananas
* Porridge
* Apples
* Firm Bananas
27
New cards
A medium GI rating is between the numbers -
55-70
28
New cards
Foods that have a medium GI rating (55-70)
* Oranges
* Brown Rice
* Toast
* Carrots
* Oatmeal
* Brown Rice
* Toast
* Carrots
* Oatmeal
29
New cards
A high GI rating is between the numbers -
70-100
30
New cards
Foods that have a high GI rating (70-100)
* White bread and honey sandwich
* Very ripe banana
* Snakes
* Jelly beans
* Very ripe banana
* Snakes
* Jelly beans
31
New cards
What are vitamins?
They are elements of food that are vital for life. They cannot be made in the body and must therefore be taken with food.
32
New cards
What are the importance of vitamins?
* They protect the body against infections.
* Assist in regulating body functions.
* Assist in metabolism.
* Assist in regulating body functions.
* Assist in metabolism.
33
New cards
What are the functions of vitamin C?
Formation of protein, collagen and the absorption of iron.
34
New cards
In what foods is vitamin C found in?
* Fruits
* Vegetables
* Dark green leaves
* Vegetables
* Dark green leaves
35
New cards
What are the functions of vitamin A?
Maintains vision, skin health, reproductions and %%bone & teeth growth%%
36
New cards
In what food is vitamin A found in? (animal sources)
* Butter
* Eggs
* Milk
* Liver
* Eggs
* Milk
* Liver
37
New cards
In what food is vitamin A found in? (plant sources)
* Dark green leafy vegetables.
* Tomatoes
* Mangoes
* Tomatoes
* Mangoes
38
New cards
What are the functions of vitamin D?
Helps in the hardening of bone by enhancing absorption of calcium.
39
New cards
In what foods is vitamin D found in?
* Fish
* Liver
* Oils
* Eggs
* Cheese
* Butter
* Sunlight
* Liver
* Oils
* Eggs
* Cheese
* Butter
* Sunlight
40
New cards
Having a deficiency in vitamin D may lead to -
Osteoporosis
- Bone and joint pain.
- Bone and joint pain.
41
New cards
What are the functions of vitamin B₁₂?
Building proteins in the body by enhancing absorption of calcium.
42
New cards
In what foods is vitamin B₁₂ found in?
* Dairy products
* Shellfish
* Eggs
* Poultry
* Shellfish
* Eggs
* Poultry
43
New cards
Having a deficiency in vitamin B₁₂ may lead to -
Anemia
- When your blood produces a lower then normal amount of healthy red blood cells.
\
- When your blood produces a lower then normal amount of healthy red blood cells.
\
44
New cards
What are the functions of vitamin B₉?
Helps in the functions of DNA and new blood cells.
45
New cards
In what foods is vitamin B₉ found in?
* Asparagus
* Spinach
* Broccoli
* Oranges
* Bananas
* Strawberry’s
* Legumes
* Spinach
* Broccoli
* Oranges
* Bananas
* Strawberry’s
* Legumes
46
New cards
Having a deficiency in vitamin B₉ may lead to -
Neural tube defects
- Brain / Spinal cord doesn’t develop normally.
- Brain / Spinal cord doesn’t develop normally.
47
New cards
What are minerals?
Inorganic chemical elements which are resent throughout the body in varying amounts. Like vitamins, they cannot be made in the body and must be taken with food.
48
New cards
Why are minerals essential?
* Assist in metabolism.
* Forms part of the structure of body tissues such as bones, teeth, nails, blood, nerves and tissues.
* Assists in fighting infections.
* Forms part of the structure of body tissues such as bones, teeth, nails, blood, nerves and tissues.
* Assists in fighting infections.
49
New cards
What are the functions of Iron ?
Essential in the formation of blood, involved in the transports and storage of oxygen in the blood.
50
New cards
In what foods is Iron found in?
* Red meat
* Green leafy vegetables
* Nuts
* Whole grains
* Green leafy vegetables
* Nuts
* Whole grains
51
New cards
Having a deficiency in Iron may lead to -
Anemia
- When your blood produces a lower then normal amount of healthy red blood cells.
- When your blood produces a lower then normal amount of healthy red blood cells.
52
New cards
What are the functions of calcium?
Mineralization %%(hardening) of bones and teeth,%% regulator of many of the body’s biochemical process (blood clotting).
53
New cards
In what foods is calcium found in?
* Dairy products
* Nuts
* Fish
* Green leafy vegetables
* Nuts
* Fish
* Green leafy vegetables
54
New cards
Having a deficiency in calcium may lead to -
Osteoporosis
* Bone and joint pain.
* Bone and joint pain.
55
New cards
What are the functions of fluoride?
Involved in the formation of dental enamel and prevents dental cavities: Involved in the formation of teeth & skeleton and prevents osteoporosis in old age.
56
New cards
In what foods is fluoride found in?
* Fluoridized water
* Toothpaste
* Toothpaste
57
New cards
Having a deficiency in fluoride may lead to -
* Dental cavities
* Osteoporosis (bone and joint pain).
* Osteoporosis (bone and joint pain).
58
New cards
What are the functions of Iodine ?
Part of two thyroid hormones. Iodine regulates growth, physical and mental development.
59
New cards
In what foods is Iodine found in?
* Dairy products
* Seafood / Seaweed
* Eggs
* Bread
* Iodised salt
* Seafood / Seaweed
* Eggs
* Bread
* Iodised salt
60
New cards
Having a deficiency in Iodine may lead to -
* Hypothyroidism
* When the thyroid gland is underactive and fails to secrete enough hormones into the bloodstream.
* When the thyroid gland is underactive and fails to secrete enough hormones into the bloodstream.
61
New cards
What are the three commonly seen sports drinks
* Hypertonic
* Hypotonic
* Isotonic
* Hypotonic
* Isotonic
62
New cards
What are hypertonic drinks and what are they used for?
* Has a higher concentration of fluid, sugar and salts then the blood stream.
* Large doses of carbohydrates.
* Used as a recovery drink.
* Often contains add proteins.
* Large doses of carbohydrates.
* Used as a recovery drink.
* Often contains add proteins.
63
New cards
Disadvantages of hypertonic drinks?
The drinks can cause dehydration as the body has to move water from the bloodstream into the intestine.
64
New cards
What are hypotonic drinks and what are they used for?
* Has a ^^lower concentration of fluid, sugars and salt than blood.^^
* Rapid rehydration.
* Pre-hydration on shorter workouts, long rides or in hot weather, when you need a drink to rehydrate quicky and efficiently. ^^Absorbed fast^^ into the blood stream.
* Rapid rehydration.
* Pre-hydration on shorter workouts, long rides or in hot weather, when you need a drink to rehydrate quicky and efficiently. ^^Absorbed fast^^ into the blood stream.
65
New cards
Disadvantages of hypotonic drinks?
They focus on rehydration and therefore do no provide maximum carbohydrates (energy).
66
New cards
What are isotonic drinks and what are they used for?
* Has a @@similar concentration of fluid, sugars and salt to blood.@@
* Carbohydrates releases.
* Used in shorter duration or high intensity workouts, when you want carbohydrates during endurance events.
* Carbohydrates releases.
* Used in shorter duration or high intensity workouts, when you want carbohydrates during endurance events.
67
New cards
Disadvantages to isotonic drinks?
They have high levels of sugars, sweeteners and additives which can cause stomach cramps and bloating.
68
New cards
Similarities between hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic drinks are?
They are all ==sports drinks== and are used for ==hydration==
69
New cards
Similarities between hypertonic drinks and isotonic drinks are?
Both are a source of ^^carbohydrates^^.
70
New cards
What is metabolism?
* Metabolism involves a constant process of making energy, via chemical reactions, from the foods we eat.
* A process that begins conception and ends with death.
* It is a vital process for all life form, not just humans and is needed to do everything from moving to thinking, to growing.
* If metabolism stops we die.
\
* A process that begins conception and ends with death.
* It is a vital process for all life form, not just humans and is needed to do everything from moving to thinking, to growing.
* If metabolism stops we die.
\
71
New cards
How does the process of metabolism work in humans?
* When people and animals eat plants, they take in the energy from the plants (in the form of sugar), along with other vital cell-building chemicals.
* The body's next step is to break the sugar down so that the energy that is released can be distributed and used as fuel by the body's cells.
* @@When we take in food we take in energy in the form of sugar that is broken down so that energy can be released.@@
* @@Food → Digestion → Energy@@
* The body's next step is to break the sugar down so that the energy that is released can be distributed and used as fuel by the body's cells.
* @@When we take in food we take in energy in the form of sugar that is broken down so that energy can be released.@@
* @@Food → Digestion → Energy@@
72
New cards
What is BMR?
The rate at which a persons body “burns“ energy in the form of calories, while at rest.
73
New cards
What does BMR stand for?
Basal Metabolic Rate
74
New cards
Factors that may influence BMR -
* Genetics - BMR is inherited.
* Health problems - illness/injury where extended rest is needed.
* Exercise - Fitness/Muscle.
* Body composition - The amount of lean muscle and fat tissue will affect metabolism.
* Muscle goes up and so does your BMR
* Age
* Growth - During childhood and adolescence are high BMR periods.
* Body size - Bigger the body, higher the BMR.
* Health problems - illness/injury where extended rest is needed.
* Exercise - Fitness/Muscle.
* Body composition - The amount of lean muscle and fat tissue will affect metabolism.
* Muscle goes up and so does your BMR
* Age
* Growth - During childhood and adolescence are high BMR periods.
* Body size - Bigger the body, higher the BMR.
75
New cards
What is the difference between Metabolism and BMR
Metabolism is the constant process of ^^making^^ energy whereas BMR is the rate at which the body ^^burns^^ energy.
76
New cards
Foods that may alter metabolism
* Avoiding to much alcohol.
* Drinking water.
* Eating enough protein.
* Drinking water.
* Eating enough protein.
77
New cards
Eating enough protein
Studies show that after you eat a protein rich meal (chicken or fish) your metabolism may increase by 30%.
78
New cards
Avoiding to much alcohol
It can stimulate your appetite and lower your metabolism.
79
New cards
Drink water
* To burn energy your body needs water and a lot of it.
* At least 2 litres a day.
* At least 2 litres a day.
80
New cards
Who developed the Australian Guide to Healthy Eating (AGHE)?
Federal government initiative.
81
New cards
What is the aim of the Australian Guide to Healthy Eating (AGHE)?
To reduce the short and long term consequences associated with nutritional imbalance.
82
New cards
What are the 5 food groups of the Australian Guide to Healthy Eating (AGHE)?
* Vegetables, legumes and beans.
* Grain foods.
* Fruits.
* Meats.
* Milk/dairy products.
* Grain foods.
* Fruits.
* Meats.
* Milk/dairy products.
83
New cards
Foods in the vegetable, legume and beans group
* Pumpkin
* Onions
* Beans
* Kidney beans
* Lentils
* Chickpeas
* Broccoli
* Onions
* Beans
* Kidney beans
* Lentils
* Chickpeas
* Broccoli
84
New cards
Foods in the grains group
* Bread
* Rice
* Cereal
* Pasta
* Rice
* Cereal
* Pasta
85
New cards
Foods in the fruit group
* Bananas
* Apples
* Strawberries
* Blueberries
* Pears
* Apples
* Strawberries
* Blueberries
* Pears
86
New cards
Foods in the meat group
* Chicken
* Lamb
* Fish
* Beef
* Lamb
* Fish
* Beef
87
New cards
Foods in the milk/dairy products group
* Butter
* Milk
* Cream
* Ice cream
* Milk
* Cream
* Ice cream
88
New cards

Advice that is shown outside the AGHE poster
* Drink plenty of water
* Enjoy a wide variety of nutritious foods from all the five food groups each day.
* Use small amounts of oils, butters and margarines.
* Sometimes and in small amounts foods with lots of fat, sugars and salt.
* Enjoy a wide variety of nutritious foods from all the five food groups each day.
* Use small amounts of oils, butters and margarines.
* Sometimes and in small amounts foods with lots of fat, sugars and salt.
89
New cards
Two disadvantages of AGHE
* Doesn’t say the serving size.
* Doesn’t specify portion size.
* Doesn’t specify portion size.
90
New cards
How is AGHE promoted in youth?
* Colourful
* Visual images
* Pictures of different foods
* Clearly shows five different food groups
* Includes hydration - water
* Visual images
* Pictures of different foods
* Clearly shows five different food groups
* Includes hydration - water
91
New cards
Who developed the HSRS?
The federal government.
92
New cards
What is the aim of HSRS?
To promote healthy eating throughout the Australian community.
93
New cards
The four risk nutrients
* Saturated Fats
* Sodium (salt)
* Sugars
* Kilojoules (energy)
* Sodium (salt)
* Sugars
* Kilojoules (energy)
94
New cards
The four protective nutrients
* Dietary Fibres
* Protein
* Proportion of fruits and vegetables.
* Nuts and legume contents.
* Protein
* Proportion of fruits and vegetables.
* Nuts and legume contents.
95
New cards
Two advantages to the HSRS
* You can easily compare similar products to determine which is healthier.
* Easy to interrupt.
* Easy to interrupt.
96
New cards
Two disadvantages to the HSRS
* Not all foods have it so you can’t compare all foods.
* Has to be the same category of food that your comparing.
* Has to be the same category of food that your comparing.
97
New cards
How HSRS is promoted to youth
* Its simple
* Easy to see
* There’s an app you can use to scan the barcode and get the health star rating even when the package doesn’t have a rating on it.
* Easy to see
* There’s an app you can use to scan the barcode and get the health star rating even when the package doesn’t have a rating on it.
98
New cards
HSRS stands for
The health star rating system.
99
New cards
AGHE stand for
Australians guide to healthy eating
100
New cards
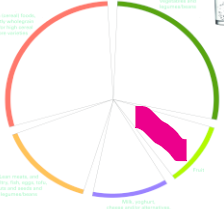
Which section of the AGHE is highlighted?
Fruits